Part of migration project for a customer I'm working on is migration of a couple of KVM based Guest virtual machine servers. The old machines has a backup solution stratetegy using IBM's TSM and the new Machines should use the Cheaper solution adopted by the Customer company using the CommVault backup solution (an enterprise software thath is used for data backup and recovery not only to local Tape Library / Data blobs on central backup servers infra but also in Cloud infrastructure.
To install the CommVault software on the Redhat Linux-es, the official install documentation (prepared by the team who prepared the CommVault) infrastructure for the customer recommends to have a separate partition for the CommVault backups under /opt directory (/opt/commvault) and the partition should be as a minumum at least 10 Gigabytes of size.
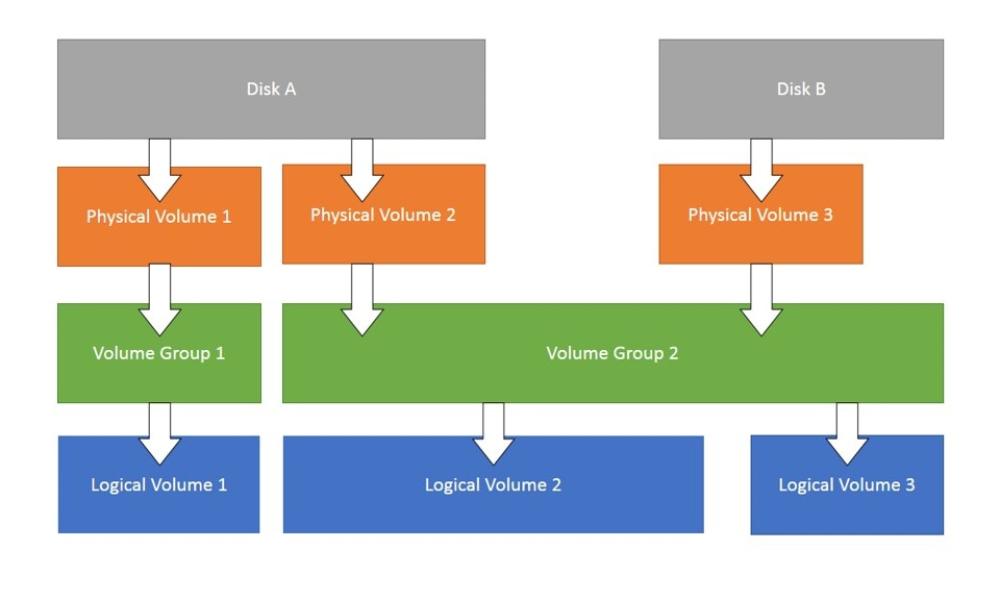
Unfortunately on our new prepared KVM VM guest machines, it was forgotten to have the separate /opt of 10GB prepared in advanced. And we ended up with Virtual Machines that has a / (root directory) of 68GB size and a separate /var and /home LVM parititons. Thus to correct the issues it was required to find a way to add another separate LVM partition inside the KVM VirtualMachine.img (QCOW Image file).
This seemed to be an easy task at first as that might be possible with simple .img partition mount with losetup command kpartx and simple lvreduce command in some way such as
# mount /dev/loop0 /mnt/test/
# kpartx -a /dev/loop0
# kpartx -l /dev/loop0
# ls -al /dev/mapper/*
…
# lvreduce
etc. however unfortunately kpartx though not returning error did not provided the new /dev/mapper devices to be used with LVM tools and this approach seems to not be possible on RHEL 8.8 as the kpartx couldn't list.
A colleague of mine Mr. Paskalev suggested that we can perhaps try to mount the partition with default KVM tool to mount .img partitions which is guestmount but unfortunately
with a command like:
# guestmount -a /kvm/VM.img -i –rw /mnt/test/
But unfortunately this mounted the filesystem in fuse filesystem and the LVM /dev/mapper of the VM can't be seen so we decided to abondon this method.
After some pondering with Dimitar Paskalev and Dimitar Hristov, thanks to joint efforts we found the way to do it, below are the steps we followed to succeed in creating new LVM ext4 partition required.
One would wonder how many system
1. Check enough space is available on the HV machine
The VMs are held under /kvm so in this case:
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# df -h|grep -i /kvm
/dev/mapper/vg00-vmprivate 206G 27G 169G 14% /kvm
2. Shutdown the running VM and make sure it is stopped
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# virsh shutdown vm-host
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# virsh list –all
Id Name State
————————–
4 lpdkv01f running
5 vm-host shut off
3. Check current Space status of VM
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# qemu-img info /kvm/vm-host.img
image: /kvm/vm-host.img
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 100 GiB (107374182400 bytes)
disk size: 8.62 GiB
cluster_size: 65536
Format specific information:
compat: 1.1
compression type: zlib
lazy refcounts: true
refcount bits: 16
corrupt: false
extended l2: false
4. Resize (extend VM) with whatever size you want
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# qemu-img resize /kvm/vm-host.img +10G
…
5. Start VM
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# virsh start vm-host
…
7. Check the LVM and block devices on HVs (not necessery but good for an overview)
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# pvs
PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
/dev/sda2 vg00 lvm2 a– 277.87g 19.87g
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# vgs
VG #PV #LV #SN Attr VSize VFree
vg00 1 11 0 wz–n- 277.87g 19.87g
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 278.9G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 277.9G 0 part
├─vg00-root 253:0 0 15G 0 lvm /
├─vg00-swap 253:1 0 1G 0 lvm [SWAP]
├─vg00-var 253:2 0 5G 0 lvm /var
├─vg00-spool 253:3 0 2G 0 lvm /var/spool
├─vg00-audit 253:4 0 3G 0 lvm /var/log/audit
├─vg00-opt 253:5 0 2G 0 lvm /opt
├─vg00-home 253:6 0 5G 0 lvm /home
├─vg00-tmp 253:7 0 5G 0 lvm /tmp
├─vg00-log 253:8 0 5G 0 lvm /var/log
├─vg00-cache 253:9 0 5G 0 lvm /var/cache
└─vg00-vmprivate 253:10 0 210G 0 lvm /vmprivate
8 . Check logical volumes on Hypervisor host
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# lvdisplay
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/swap
LV Name swap
VG Name vg00
LV UUID 3tNa0n-HDVw-dLvl-EC06-c1Ex-9jlf-XAObKm
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:45 +0200
LV Status available
# open 2
LV Size 1.00 GiB
Current LE 256
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:1
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/var
LV Name var
VG Name vg00
LV UUID JBerim-fxVv-jU10-nDmd-figw-4jVA-8IYdxU
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:45 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 5.00 GiB
Current LE 1280
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:2
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/spool
LV Name spool
VG Name vg00
LV UUID nFlmp2-iXg1-tFxc-FKaI-o1dA-PO70-5Ve0M9
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:45 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 2.00 GiB
Current LE 512
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:3
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/audit
LV Name audit
VG Name vg00
LV UUID e6H2OC-vjKS-mPlp-JOmY-VqDZ-ITte-0M3npX
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:46 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 3.00 GiB
Current LE 768
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:4
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/opt
LV Name opt
VG Name vg00
LV UUID oqUR0e-MtT1-hwWd-MhhP-M2Y4-AbRo-Kx7yEG
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:46 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 2.00 GiB
Current LE 512
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:5
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/home
LV Name home
VG Name vg00
LV UUID ehdsH7-okS3-gPGk-H1Mb-AlI7-JOEt-DmuKnN
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:47 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 5.00 GiB
Current LE 1280
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:6
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/tmp
LV Name tmp
VG Name vg00
LV UUID brntSX-IZcm-RKz2-CP5C-Pp00-1fA6-WlA7lD
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:47 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 5.00 GiB
Current LE 1280
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:7
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/log
LV Name log
VG Name vg00
LV UUID ZerDyL-birP-Pwck-yvFj-yEpn-XKsn-sxpvWY
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:47 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 5.00 GiB
Current LE 1280
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:8
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/cache
LV Name cache
VG Name vg00
LV UUID bPPfzQ-s4fH-4kdT-LPyp-5N20-JQTB-Y2PrAG
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:48 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 5.00 GiB
Current LE 1280
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:9
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/root
LV Name root
VG Name vg00
LV UUID mZr3p3-52R3-JSr5-HgGh-oQX1-B8f5-cRmaIL
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-08-07 13:47:48 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 15.00 GiB
Current LE 3840
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:0
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/vmprivate
LV Name vmprivate
VG Name vg00
LV UUID LxNRWV-le3h-KIng-pUFD-hc7M-39Gm-jhF2Aj
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time hypervisor-host, 2023-09-18 11:54:19 +0200
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 210.00 GiB
Current LE 53760
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:10
9. Check Hypervisor existing partitions and space
[root@hypervisor-host ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 278.9 GiB, 299439751168 bytes, 584843264 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0581e6e2
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 2097152 1G 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 584843263 582744064 277.9G 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-root: 15 GiB, 16106127360 bytes, 31457280 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-swap: 1 GiB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-var: 5 GiB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-spool: 2 GiB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-audit: 3 GiB, 3221225472 bytes, 6291456 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-opt: 2 GiB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-home: 5 GiB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-tmp: 5 GiB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-log: 5 GiB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-cache: 5 GiB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vg00-vmprivate: 210 GiB, 225485783040 bytes, 440401920 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
10. List block devices on VM
[root@vm-host ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 100G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
├─vda2 252:2 0 88G 0 part
│ ├─vg00-root 253:0 0 68G 0 lvm /
│ ├─vg00-home 253:2 0 10G 0 lvm /home
│ └─vg00-var 253:3 0 10G 0 lvm /var
├─vda3 252:3 0 1G 0 part [SWAP]
└─vda4 252:4 0 10G 0 part
11. Create new LVM partition with fdisk or cfdisk
If there is no cfdisk new resized space with qemu-img could be setup with a fdisk, though I personally always prefer to use cfdisk
[root@vm-host ~]# fdisk /dev/vda
# > p (print)
# > m (manfile)
# > n
# … follow on screen instructions to select start and end blocks
# > t (change partition type)
# > select and set to 8e
# > w (write changes)
[root@vm-host ~]# cfdisk /dev/vda
Setup new partition from Free space as [ primary ] partition and Choose to be of type LVM
12. List partitions to make sure new LVM partition is present
[root@vm-host ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/vda: 100 GiB, 107374182400 bytes, 209715200 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xe7b2d9fd
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/vda1 * 2048 2099199 2097152 1G 83 Linux
/dev/vda2 2099200 186646527 184547328 88G 8e Linux LVM
/dev/vda3 186646528 188743679 2097152 1G 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/vda4 188743680 209715199 20971520 10G 8e Linux LVM
The extra added 10 Giga is seen under /dev/vda4.
— Physical volume —
PV Name /dev/vda4
VG Name vg01
PV Size 10.00 GiB / not usable 4.00 MiB
Allocatable yes (but full)
PE Size 4.00 MiB
Total PE 2559
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 2559
PV UUID yvMX8a-sEka-NLA7-53Zj-fFdZ-Jd2K-r0Db1z
— Physical volume —
PV Name /dev/vda2
VG Name vg00
PV Size <88.00 GiB / not usable 3.00 MiB
Allocatable yes (but full)
PE Size 4.00 MiB
Total PE 22527
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 22527
PV UUID i4UpGr-h9Cd-iKBu-KqEI-15vK-CGc1-DwRPj8
[root@vm-host ~]#
13. List LVM Physical Volumes
[root@vm-host ~]# pvdisplay
— Physical volume —
PV Name /dev/vda2
VG Name vg00
PV Size <88.00 GiB / not usable 3.00 MiB
Allocatable yes (but full)
PE Size 4.00 MiB
Total PE 22527
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 22527
PV UUID i4UpGr-h9Cd-iKBu-KqEI-15vK-CGc1-DwRPj8
Notice the /dev/vda4 is not seen in pvdisplay (Physical Volume display command) because not created yet, so lets create it.
14. Initialize new Physical Volume to be available for use by LVM
[root@vm-host ~]# pvcreate /dev/vda4
15. Inform the OS for partition table changes
If partprobe is not available as command on the host, below obscure command should do the trick.
[root@vm-host ~]# echo "- – -" | tee /sys/class/scsi_host/host*/scan
However usually, better to use partprobe to inform the Operating System of partition table changes
[root@vm-host ~]# partprobe
16. Use lsblk again to see the new /dev/vda4 LVM is listed into "vda" root block device
[root@vm-host ~]#
[root@vm-host ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 100G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
├─vda2 252:2 0 88G 0 part
│ ├─vg00-root 253:0 0 68G 0 lvm /
│ ├─vg00-home 253:1 0 10G 0 lvm /home
│ └─vg00-var 253:2 0 10G 0 lvm /var
├─vda3 252:3 0 1G 0 part [SWAP]
└─vda4 252:4 0 10G 0 part
[root@vm-host ~]#
17. Create new Volume Group (VG) on /dev/vda4 block device
Before creating a new VG, list what kind of VG is on the machine to be sure the new created one will not be already present.
[root@vm-host ~]# vgdisplay
— Volume group —
VG Name vg00
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 1
Metadata Sequence No 4
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 3
Open LV 3
Max PV 0
Cur PV 1
Act PV 1
VG Size <88.00 GiB
PE Size 4.00 MiB
Total PE 22527
Alloc PE / Size 22527 / <88.00 GiB
Free PE / Size 0 / 0
VG UUID oyo1oY-saSm-0IKk-gZnf-Knwz-utO7-Aw8c60
vg00 is existing only, so we can use vg01 as a Volume Group name for the new volume group where the fresh 10GB LVM partition will lay
[root@vm-host ~]# vgcreate vg01 /dev/vda4
Volume group "vg01" successfully created
18. Create new Logical Volume (LV) and extend it to occupy the full space available on Volume Group vg01
[root@vm-host ~]# lvcreate -n commvault -l 100%FREE vg01
Logical volume "commvault" created.
An alternative way to create the same LV is by running:
# lvcreate -n commvault -L 10G vg01
19. Relist block devices with lsblk to make sure the new created Logical Volume commvault is really present and seen, in case of it missing re-run again partprobe cmd
[root@vm-host ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 100G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
├─vda2 252:2 0 88G 0 part
│ ├─vg00-root 253:0 0 68G 0 lvm /
│ ├─vg00-home 253:1 0 10G 0 lvm /home
│ └─vg00-var 253:2 0 10G 0 lvm /var
├─vda3 252:3 0 1G 0 part [SWAP]
└─vda4 252:4 0 10G 0 part
└─vg01-commvault 253:3 0 10G 0 lvm
As it is not mounted yet, the VG will be not seen in df free space but will be seen as a volume group with vgdispaly
[root@vm-host ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 2.8G 0 2.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs 2.8G 33M 2.8G 2% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2.8G 17M 2.8G 1% /run
tmpfs 2.8G 0 2.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/vg00-root 67G 2.4G 61G 4% /
/dev/mapper/vg00-var 9.8G 1021M 8.3G 11% /var
/dev/mapper/vg00-home 9.8G 24K 9.3G 1% /home
/dev/vda1 974M 242M 665M 27% /boot
tmpfs 569M 0 569M 0% /run/user/0
[root@vm-host ~]# vgdisplay
— Volume group —
VG Name vg01
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 1
Metadata Sequence No 2
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 1
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 1
Act PV 1
VG Size <10.00 GiB
PE Size 4.00 MiB
Total PE 2559
Alloc PE / Size 2559 / <10.00 GiB
Free PE / Size 0 / 0
VG UUID nYP0tv-IbFw-fBVT-slBB-H1hF-jD0h-pE3V0S
— Volume group —
VG Name vg00
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 1
Metadata Sequence No 4
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 3
Open LV 3
Max PV 0
Cur PV 1
Act PV 1
VG Size <88.00 GiB
PE Size 4.00 MiB
Total PE 22527
Alloc PE / Size 22527 / <88.00 GiB
Free PE / Size 0 / 0
VG UUID oyo1oY-saSm-0IKk-gZnf-Snwz-utO7-Aw8c60
20. Create new ext4 filesystem on the just created vg01-commvault
[root@vm-host ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg01-commvault
[root@vm-host ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg01-commvault
mke2fs 1.45.6 (20-Mar-2020)
Discarding device blocks: done
Creating filesystem with 2620416 4k blocks and 655360 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 1491d8b1-2497-40fe-bc40-5faa6a2b2644
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (16384 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
21. Mount vg01-commvault into /opt directory
[root@vm-host ~]# mkdir -p /opt/
[root@vm-host ~]# mount /dev/mapper/vg01-commvault /opt/
22. Check mount is present on VM guest OS
[root@vm-host ~]# mount|grep -i /opt
/dev/mapper/vg01-commvault on /opt type ext4 (rw,relatime)
[root@vm-host ~]#
[root@vm-host ~]# df -h|grep -i opt
/dev/mapper/vg01-commvault 9.8G 24K 9.3G 1% /opt
[root@vm-host ~]#
23. Add vg01-commvault to be auto mounted via /etc/fstab on next Virtual Machine reboot
[root@vm-host ~]# echo '/dev/mapper/vg01-commvault /opt ext4 defaults 1 2' >> /etc/fstab
[root@vm-host ~]# rpm -ivh commvault-fs.Instance001-11.0.0-80.240.0.3589820.240.4083067.el8.x86_64.rpm
…
[root@vm-host ~]# systemctl status commvault
● commvault.Instance001.service – commvault Service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/commvault.Instance001.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2023-11-10 15:13:59 CET; 27s ago
Process: 9972 ExecStart=/opt/commvault/Base/Galaxy start direct -focus Instance001 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 54
Memory: 155.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/commvault.Instance001.service
├─10132 /opt/commvault/Base/cvlaunchd
├─10133 /opt/commvault/Base/cvd
├─10135 /opt/commvault/Base/cvfwd
└─10137 /opt/commvault/Base/ClMgrS
Nov 10 15:13:57 vm-host.ffm.de.int.atosorigin.com systemd[1]: Starting commvault Service…
Nov 10 15:13:58 vm-host.ffm.de.int.atosorigin.com Galaxy[9972]: Cleaning up /opt/commvault/Base/Temp …
Nov 10 15:13:58 vm-host.ffm.de.int.atosorigin.com Galaxy[9972]: Starting Commvault services for Instance001 …
Nov 10 15:13:59 vm-host.ffm.de.int.atosorigin.com Galaxy[9972]: [22B blob data]
Nov 10 15:13:59 vm-host.ffm.de.int.atosorigin.com systemd[1]: Started commvault Service.
[root@vm-host ~]#
24. Install Commvault backup client RPM in new mounted LVM under /opt
[root@vm-host ~]# rpm -ivh commvault.rpm
…








No Comments »