Haproxy logging is a very big topic, worthy of many articles, but unfortunately not enough is written on the topic, perhaps for the reason haproxy is free software and most people who use it doesn't follow the philosophy of free software sharing but want to keep, the acquired knowledge on the topic for their own and if possible in the capitalist world most of us live to use it for a Load Balancer haproxy consultancy, consultancy fee or in their daily job as system administrators (web and middleware) or cloud specialist etc. 🙂
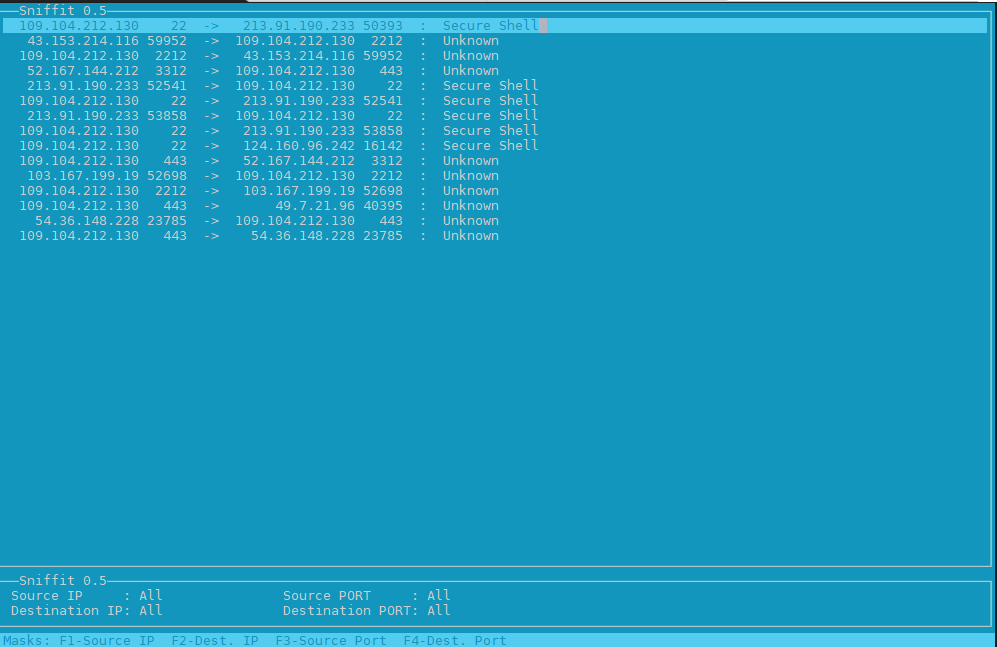
Having a good haproxy logging is very important as you need to debug issues with backend machines or some other devices throwing traffic to the HA Proxy.
Thus it is important to build a haproxy logging in a way that it provides most important information and the information is as simple as possible, so everyone can understand what is in without much effort and same time it contains enough debug information, to help you if you want to use the output logs with Graylog filters or process data with some monitoring advanced tool as Prometheus etc.
In our effort to optimize the way haproxy logs via a configured handler that sends the haproxy output to logging handler configured to log through rsyslog, we have done some experiments with logging arguments and came up with few variants, that we liked. In that article the idea is I share this set of logging parameters with hope to help some other guy that starts with haproxy to build a good logging readable and easy to process with scripts log output from haproxy.
The criterias for a decent haproxy logging used are:
1. Log should be simple but not dumb
2. Should be concrete (and not too much complicated)
3. Should be easy to read for the novice and advanced sysadmin
Before starting, have to say that building the logging format seems tedious task but to make it fit your preference could take a lot of time, especially as logging parameters naming is hard to remember, thus the haproxy logging documentation log-format description table comes really handy:
Haproxy log-format paremeters ASCII table
Please refer to the table for log-format defined variables :
+---+------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+
| R | var | field name (8.2.2 and 8.2.3 for description) | type |
+---+------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+
| | %o | special variable, apply flags on all next var | |
+---+------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+
| | %B | bytes_read (from server to client) | numeric |
| H | %CC | captured_request_cookie | string |
| H | %CS | captured_response_cookie | string |
| | %H | hostname | string |
| H | %HM | HTTP method (ex: POST) | string |
| H | %HP | HTTP request URI without query string (path) | string |
| H | %HQ | HTTP request URI query string (ex: ?bar=baz) | string |
| H | %HU | HTTP request URI (ex: /foo?bar=baz) | string |
| H | %HV | HTTP version (ex: HTTP/1.0) | string |
| | %ID | unique-id | string |
| | %ST | status_code | numeric |
| | %T | gmt_date_time | date |
| | %Ta | Active time of the request (from TR to end) | numeric |
| | %Tc | Tc | numeric |
| | %Td | Td = Tt - (Tq + Tw + Tc + Tr) | numeric |
| | %Tl | local_date_time | date |
| | %Th | connection handshake time (SSL, PROXY proto) | numeric |
| H | %Ti | idle time before the HTTP request | numeric |
| H | %Tq | Th + Ti + TR | numeric |
| H | %TR | time to receive the full request from 1st byte| numeric |
| H | %Tr | Tr (response time) | numeric |
| | %Ts | timestamp | numeric |
| | %Tt | Tt | numeric |
| | %Tw | Tw | numeric |
| | %U | bytes_uploaded (from client to server) | numeric |
| | %ac | actconn | numeric |
| | %b | backend_name | string |
| | %bc | beconn (backend concurrent connections) | numeric |
| | %bi | backend_source_ip (connecting address) | IP |
| | %bp | backend_source_port (connecting address) | numeric |
| | %bq | backend_queue | numeric |
| | %ci | client_ip (accepted address) | IP |
| | %cp | client_port (accepted address) | numeric |
| | %f | frontend_name | string |
| | %fc | feconn (frontend concurrent connections) | numeric |
| | %fi | frontend_ip (accepting address) | IP |
| | %fp | frontend_port (accepting address) | numeric |
| | %ft | frontend_name_transport ('~' suffix for SSL) | string |
| | %lc | frontend_log_counter | numeric |
| | %hr | captured_request_headers default style | string |
| | %hrl | captured_request_headers CLF style | string list |
| | %hs | captured_response_headers default style | string |
| | %hsl | captured_response_headers CLF style | string list |
| | %ms | accept date milliseconds (left-padded with 0) | numeric |
| | %pid | PID | numeric |
| H | %r | http_request | string |
| | %rc | retries | numeric |
| | %rt | request_counter (HTTP req or TCP session) | numeric |
| | %s | server_name | string |
| | %sc | srv_conn (server concurrent connections) | numeric |
| | %si | server_IP (target address) | IP |
| | %sp | server_port (target address) | numeric |
| | %sq | srv_queue | numeric |
| S | %sslc| ssl_ciphers (ex: AES-SHA) | string |
| S | %sslv| ssl_version (ex: TLSv1) | string |
| | %t | date_time (with millisecond resolution) | date |
| H | %tr | date_time of HTTP request | date |
| H | %trg | gmt_date_time of start of HTTP request | date |
| H | %trl | local_date_time of start of HTTP request | date |
| | %ts | termination_state | string |
| H | %tsc | termination_state with cookie status | string |
+---+------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+
R = Restrictions : H = mode http only ; S = SSL only
Our custom log-format built in order to fulfill our needs is as this:
log-format %ci:%cp\ %H\ [%t]\ [%f\ %fi:%fp]\ [%b/%s\ %si:%sp]\ %Tw/%Tc/%Tt\ %B\ %ts\ %ac/%fc/%bc/%sc/%sq/%bq
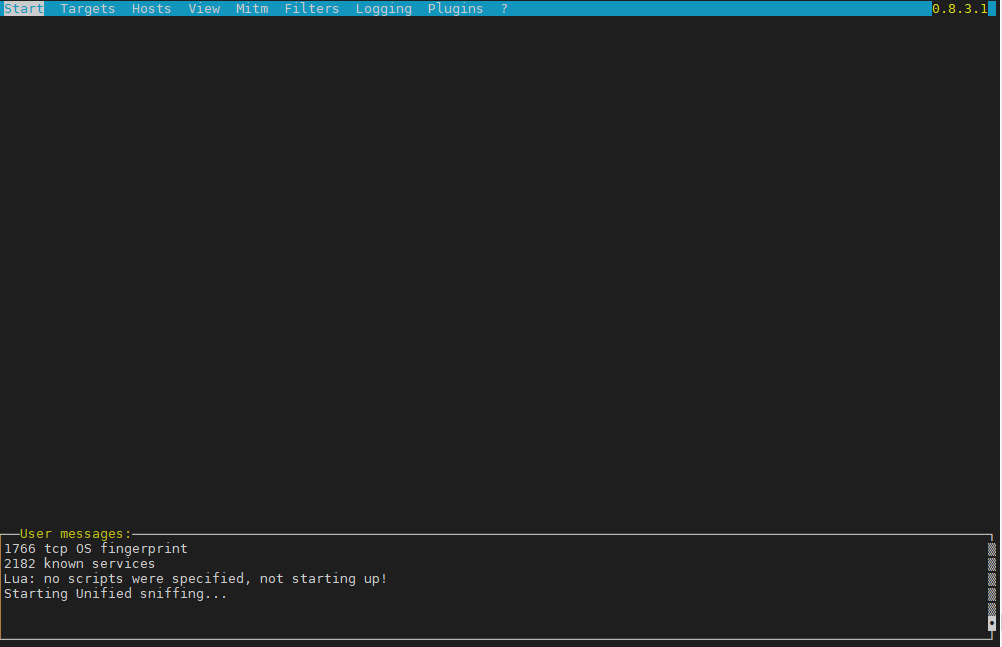
Once you place the log-format as a default for all haproxy frontend / backends or for a custom defined ones, the output you will get when tailing the log is:
# tail -f /var/log/haproxy.log
Apr 5 21:47:19 10.42.73.83:23262 haproxy-fqdn-hostname.com [05/Apr/2024:21:46:23.879] [ft_FRONTEND_NAME 10.46.108.6:61310] [bk_BACKEND_NAME/bk_appserv3 10.75.226.88:61310] 1/0/55250 55 sD 4/2/1/0/0/0
Apr 5 21:48:14 10.42.73.83:57506 haproxy-fqdn-hostname.com [05/Apr/2024:21:47:18.925] [ft_FRONTEND_NAME 10.46.108.6:61310] [bk_BACKEND_NAME//bk_appserv1 10.35.242.134:61310] 1/0/55236 55 sD 4/2/1/0/0/0
Apr 5 21:49:09 10.42.73.83:46520 haproxy-fqdn-hostname.com [05/Apr/2024:21:48:13.956] [ft_FRONTEND_NAME 10.46.108.6:61310] [bk_BACKEND_NAME//bk_appserv2 10.75.226.89:61310] 1/0/55209 55 sD 4/2/1/0/0/0
If you don't care about extra space and logs being filled with more naming, another variant of above log-format, that makes it even more readable even for most novice sys admin or programmer would look like this:
log-format [%t]\ %H\ [IN_IP]\ %ci:%cp\ [FT_NAME]\ %f:%fp\ [FT_IP]\ %fi:%fp\ [BK_NAME]\ [%b/%s:%sp]\ [BK_IP]\ %si:%sp\ [TIME_WAIT]\ {%Tw/%Tc/%Tt}\ [CONN_STATE]\ {%B\ %ts}\ [STATUS]\ [%ac/%fc/%bc/%sc/%sq/%bq]
Once you apply the config test the haproxy.cfg to make sure no syntax errors during copy / paste from this page
haproxy-serv:~# haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Configuration file is valid
Next restart graceously haproxy
haproxy-serv:~# /usr/sbin/haproxy -D -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg -p /var/run/haproxy.pid -sf $(cat /var/run/haproxy.pid)
Once you reload haproxy graceously without loosing the established connections in stead of restarting it completely via systemd sysctl restart haproxy:
2024-04-05T21:46:03+02:00 localhost haproxy[1897731]: 193.200.198.195:50714 haproxy-fqdn-hostname.com [05/Apr/2024:21:46:03.012] [FrotnendProd 10.55.0.20:27800] [BackendProd/<NOSRV> -:-] -1/-1/0 0 — 4/1/0/0/0/0
2024-04-05T21:46:03+02:00 localhost haproxy[1897731]: 193.100.193.189:54290 haproxy-fqdn-hostname.com [05/Apr/2024:21:46:03.056] [FrotnendProd 10.55.0.20:27900] [BackendProd/<NOSRV> -:-] -1/-1/0 0 — 4/4/3/0/0/0
2024-04-05T21:46:03+02:00 localhost haproxy[1897731]: 193.100.193.190:26778 haproxy-fqdn-hostname.com [05/Apr/2024:21:46:03.134] [FrotnendProd 10.55.0.20:27900] [BackendProd/tsefas02s 10.35.242.134:27900] 1/-1/0 0 CC 4/4/3/0/0/0
Note that in that log localhost haproxy[pid] is written by rsyslog, you can filter it out by modifying rsyslogd configurations
The only problem with this log-format is not everyone wants to have to much repeating information pointer on which field is what, but I personally liked this one as well because using it even though occuping much more space, makes the log much easier to process with perl or python scripting for data visualize and very for programs that does data or even "big data" analysis.






























 Saint Gabriel of Lesnovo, Saint Joachim of Osogovo and Saint Prohor Pchinski mosaic saint Alexander Nevski Cathedral Church, Sofia, Bulgaria
Saint Gabriel of Lesnovo, Saint Joachim of Osogovo and Saint Prohor Pchinski mosaic saint Alexander Nevski Cathedral Church, Sofia, Bulgaria 



