
1. Testing the memory with motherboard integrated tools
Memory testing has been integral part of Computers for the last 50 years. In the dawn of computers those older perhaps remember memory testing was part of the computer initialization boot. And this memory testing was delaying the boot with some seconds and the user could see the memory numbers being counted up to the amount of memory. With the increased memory modern computers started to have and the annoyance to wait for a memory check program to check the computer hardware memory on modern computers this check has been mitigated or completely removed on some hardware.
Thus under some circumstances sysadmins or advanced computer users might need to check the memory, especially if there is some suspicion for memory damages or if for example a home PC starts crashing with Blue screens of Death on Windows without reason or simply the PC or some old arcane Linux / UNIX servers gets restarted every now and then for now apparent reason. When such circumstances occur it is an idea to start debugging the hardware issue with a simple memory check.
There are multiple ways to test installed memory banks on a server laptop or local home PC both integrated and using external programs.
On servers that is usually easily done from ILO or IPMI or IDRAC access (usually web) interface of the vendor, on laptops and home usage from BIOS or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) acces interface on system boot that is possible as well.
HP BIOS Setup
An old but gold TIP, more younger people might not know is the
Prolonged SHIFT key press which once held with the user instructs the machine to initiate a memory test before the computer starts reading what is written in the boot loader.
So before anything else from below article it might be a good idea to just try HOLD SHIFT for 15-20 seconds after a complete Shut and ON from the POWER button.
If this test does not triggered or it is triggered and you end up with some corrupted memory but you're not sure which exact Memory bank is really crashing and want to know more on what memory Bank and segments are breaking up you might want to do a more thorough testing. In below article I'll try to explain shortly how this can be done.
2. Test the memory using a boot USB Flash Drive / DVD / CD
Say hello to memtest86+. It is a Linux GRUB boot loader bootable utility that tests physical memory by writing various patterns to it and reading them back. Since memtest86+ runs directly off the hardware it does not require any operating system support for execution. Perhaps it is important to mention that memtest86 (is PassMark memtest86)and memtest86+ (An Advanced Memory diagnostic tool) are different tools, the first is freeware and second one is FOSS software.
To use it all you'll need is some version of Linux. If you don't already have some burned in somewhere at your closet, you might want to burn one.
For Linux / Mac users this is as downloading a Linux distribution ISO file and burning it with
# dd if=/path/to/iso of=/dev/sdbX bs=80M status=progress
Windows users can burn a Live USB with whatever Linux distro or download and burn the latest versionof memtest86+ from https://www.memtest.org/ on Windows Desktop with some proggie like lets say UnetBootIn.
2.1. Run memtest86+ on Ubuntu
Many Linux distributions such as Ubuntu 20.0 comes together with memtest86+, which can be easily invoked from GRUB / GRUB2 Kernel boot loader.
Ubuntu has a separate menu pointer for a Memtest.
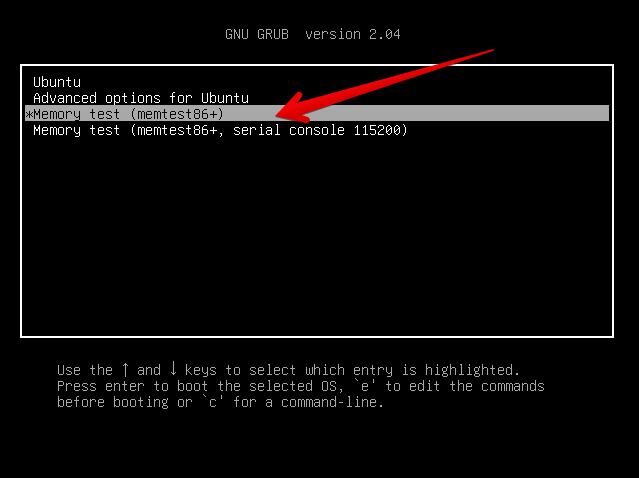
Other distributions RPM based distributions such as CentOS, Fedora Linux, Redhat things differ.
2.2. memtest86+ on Fedora
Fedora used to have the memtest86+ menu at the GRUB boot selection prompt, but for some reason removed it and in newest Fedora releases as of time such as Fedora 35 memtest86+ is preinstalled and available but not visible, to start on already and to start a memtest memory test tool:
- Boot a Fedora installation or Rescue CD / USB. At the prompt, type "memtest86".
boot: memtest86
2.3 memtest86+ on RHEL Linux
The memtest86+tool is available as an RPM package from Red Hat Network (RHN) as well as a boot option from the Red Hat Enterprise Linux rescue disk.
And nowadays Red Hat Enterprise Linux ships by default with the tool.
Prior redhat (now legacy) releases such as on RHEL 5.0 it has to be installed and configure it with below 3 commands.
[root@rhel ~]# yum install memtest86+
[root@rhel ~]# memtest-setup
[root@rhel ~]# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Again as with CentOS to boot memtest86+ from the rescue disk, you will need to boot your system from CD 1 of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation media, and type the following at the boot prompt (before the Linux kernel is started):
boot: memtest86
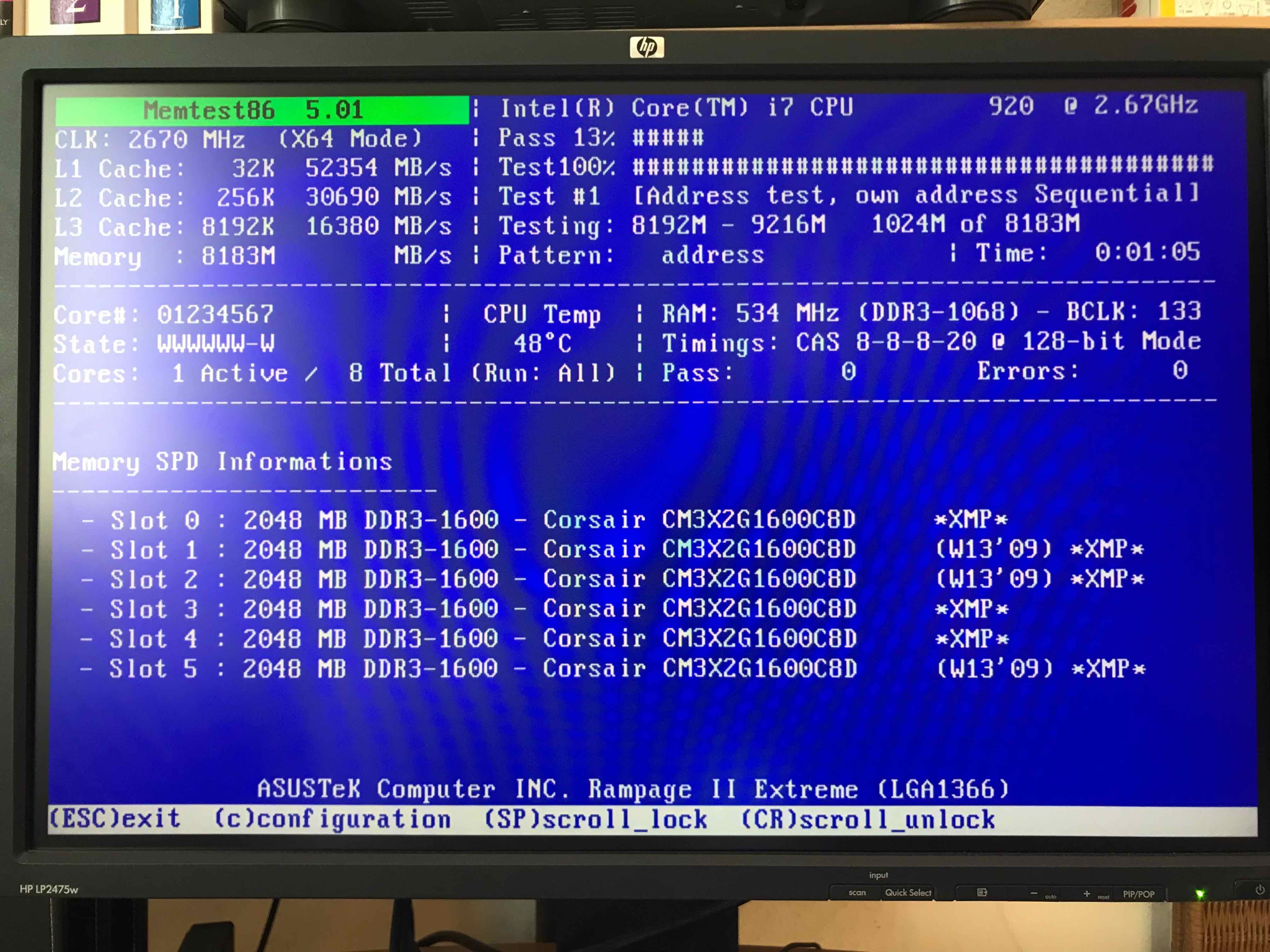
memtest86+ testing 5 memory slots
As you see all on above screenshot the Memory banks are listed as Slots. There are a number of Tests to be completed until
it can be said for sure memory does not have any faulty cells.
The
Pass: 0
Errors: 0
Indicates no errors, so in the end if memtest86 does not find anything this values should stay at zero.
memtest86+ is also usable to detecting issues with temperature of CPU. Just recently I've tested a PC thinking that some memory has defects but it turned out the issue on the Computer was at the CPU's temperature which was topping up at 80 – 82 Celsius.
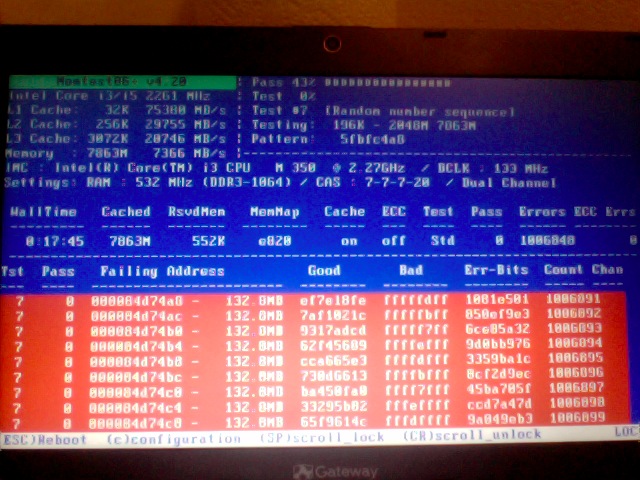
If you're unfortunate and happen to get some corrupted memory segments you will get some red fields with the memory addresses found to have corrupted on Read / Write test operations:
2.4. Install and use memtest and memtest86+ on Debian / Mint Linux
You can install either memtest86+ or just for the fun put both of them and play around with both of them as they have a .deb package provided out of debian non-free /etc/apt/sources.list repositories.
root@jeremiah:/home/hipo# apt-cache show memtest86 memtest86+
Package: memtest86
Version: 4.3.7-3
Installed-Size: 302
Maintainer: Yann Dirson <dirson@debian.org>
Architecture: amd64
Depends: debconf (>= 0.5) | debconf-2.0
Recommends: memtest86+
Suggests: hwtools, memtester, kernel-patch-badram, grub2 (>= 1.96+20090523-1) | grub (>= 0.95+cvs20040624), mtools
Description-en: thorough real-mode memory tester
Memtest86 scans your RAM for errors.
.
This tester runs independently of any OS – it is run at computer
boot-up, so that it can test *all* of your memory. You may want to
look at `memtester', which allows testing your memory within Linux,
but this one won't be able to test your whole RAM.
.
It can output a list of bad RAM regions usable by the BadRAM kernel
patch, so that you can still use you old RAM with one or two bad bits.
.
This is the last DFSG-compliant version of this software, upstream
has opted for a proprietary development model starting with 5.0. You
may want to consider using memtest86+, which has been forked from an
earlier version of memtest86, and provides a different set of
features. It is available in the memtest86+ package.
.
A convenience script is also provided to make a grub-legacy-based
floppy or image.
Description-md5: 0ad381a54d59a7d7f012972f613d7759
Homepage: http://www.memtest86.com/
Section: misc
Priority: optional
Filename: pool/main/m/memtest86/memtest86_4.3.7-3_amd64.deb
Size: 45470
MD5sum: 8dd2a4c52910498d711fbf6b5753bca9
SHA256: 09178eca21f8fd562806ccaa759d0261a2d3bb23190aaebc8cd99071d431aeb6
Package: memtest86+
Version: 5.01-3
Installed-Size: 2391
Maintainer: Yann Dirson <dirson@debian.org>
Architecture: amd64
Depends: debconf (>= 0.5) | debconf-2.0
Suggests: hwtools, memtester, kernel-patch-badram, memtest86, grub-pc | grub-legacy, mtools
Description-en: thorough real-mode memory tester
Memtest86+ scans your RAM for errors.
.
This tester runs independently of any OS – it is run at computer
boot-up, so that it can test *all* of your memory. You may want to
look at `memtester', which allows to test your memory within Linux,
but this one won't be able to test your whole RAM.
.
It can output a list of bad RAM regions usable by the BadRAM kernel
patch, so that you can still use your old RAM with one or two bad bits.
.
Memtest86+ is based on memtest86 3.0, and adds support for recent
hardware, as well as a number of general-purpose improvements,
including many patches to memtest86 available from various sources.
.
Both memtest86 and memtest86+ are being worked on in parallel.
Description-md5: aa685f84801773ef97fdaba8eb26436a
Homepage: http://www.memtest.org/
Tag: admin::benchmarking, admin::boot, hardware::storage:floppy,
interface::text-mode, role::program, scope::utility, use::checking
Section: misc
Priority: optional
Filename: pool/main/m/memtest86+/memtest86+_5.01-3_amd64.deb
Size: 75142
MD5sum: 4f06523532ddfca0222ba6c55a80c433
SHA256: ad42816e0b17e882713cc6f699b988e73e580e38876cebe975891f5904828005
root@jeremiah:/home/hipo# apt-get install –yes memtest86+
…
root@jeremiah:/home/hipo# apt-get install –yes memtest86
Reading package lists… Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information… Done
Suggested packages:
hwtools kernel-patch-badram grub2 | grub
The following NEW packages will be installed:
memtest86
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 21 not upgraded.
Need to get 45.5 kB of archives.
After this operation, 309 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://ftp.de.debian.org/debian buster/main amd64 memtest86 amd64 4.3.7-3 [45.5 kB]
Fetched 45.5 kB in 0s (181 kB/s)
Preconfiguring packages …
Selecting previously unselected package memtest86.
(Reading database … 519985 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack …/memtest86_4.3.7-3_amd64.deb …
Unpacking memtest86 (4.3.7-3) …
Setting up memtest86 (4.3.7-3) …
Generating grub configuration file …
Found background image: saint-John-of-Rila-grub.jpg
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.19.0-18-amd64
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.19.0-18-amd64
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.19.0-17-amd64
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.19.0-17-amd64
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.19.0-8-amd64
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.19.0-8-amd64
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.19.0-6-amd64
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.19.0-6-amd64
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.19.0-5-amd64
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.19.0-5-amd64
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.9.0-8-amd64
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.9.0-8-amd64
Found memtest86 image: /boot/memtest86.bin
Found memtest86+ image: /boot/memtest86+.bin
Found memtest86+ multiboot image: /boot/memtest86+_multiboot.bin
File descriptor 3 (pipe:[66049]) leaked on lvs invocation. Parent PID 22581: /bin/sh
done
Processing triggers for man-db (2.8.5-2) …
After this both memory testers memtest86+ and memtest86 will appear next to the option of booting a different version kernels and the Advanced recovery kernels, that you usually get in the GRUB boot prompt.
2.5. Use memtest embedded tool on any Linux by adding a kernel variable
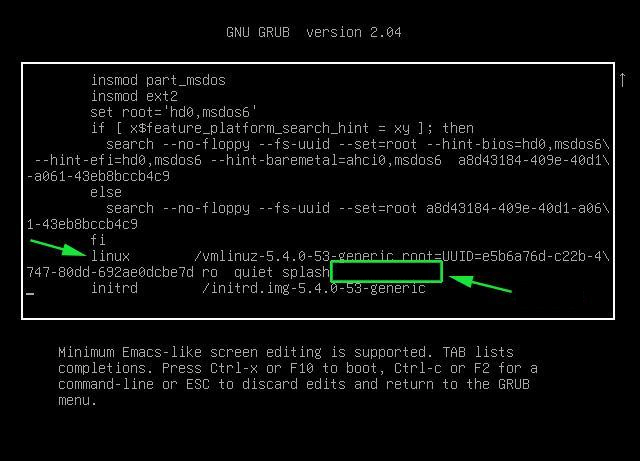
2.4.1. Reboot your computer
# reboot
2.4.2. At the GRUB boot screen (with UEFI, press Esc).
2.4.3 For 4 passes add temporarily the memtest=4 kernel parameter.
memtest= [KNL,X86,ARM,PPC,RISCV] Enable memtest
Format: <integer>
default : 0 <disable>
Specifies the number of memtest passes to be
performed. Each pass selects another test
pattern from a given set of patterns. Memtest
fills the memory with this pattern, validates
memory contents and reserves bad memory
regions that are detected.
3. Install and use memtester Linux tool
At some condition, memory is the one of the suspcious part, or you just want have a quick test. memtester is an effective userspace tester for stress-testing the memory subsystem. It is very effective at finding intermittent and non-deterministic faults.
The advantage of memtester "live system check tool is", you can check your system for errors while it's still running. No need for a restart, just run that application, the downside is that some segments of memory cannot be thoroughfully tested as you already have much preloaded data in it to have the Operating Sytstem running, thus always when possible try to stick to rule to test the memory using memtest86+ from OS Boot Loader, after a clean Machine restart in order to clean up whole memory heap.
Anyhow for a general memory test on a Critical Legacy Server (if you lets say don't have access to Remote Console Board, or don't trust the ILO / IPMI Hardware reported integrity statistics), running memtester from already booted is still a good idea.
3.1. Install memtester on any Linux distribution from source
# wget http://pyropus.ca/software/memtester/old-versions/memtester-4.2.2.tar.gz
# tar zxvf memtester-4.2.2.tar.gz
# cd memtester-4.2.2
# make && make install
3.2 Install on RPM based distros
On Fedora memtester is available from repositories however on many other RPM based distros it is not so you have to install it from source.
[root@fedora ]# yum install -y memtester
3.3. Install memtester on Deb based Linux distributions from source
To install it on Debian / Ubuntu / Mint etc. , open a terminal and type:
root@linux:/ # apt install –yes memtester
The general run syntax is:
memtester [-p PHYSADDR] [ITERATIONS]
You can hence use it like so:
hipo@linux:/ $ sudo memtester 1024 5
This should allocate 1024MB of memory, and repeat the test 5 times. The more repeats you run the better, but as a memtester run places a great overall load on the system you either don't increment the runs too much or at least run it with lowered process importance e.g. by nicing the PID:
hipo@linux:/ $ nice -n 15 sudo memtester 1024 5
- If you have more RAM like 4GB or 8GB, it is upto you how much memory you want to allocate for testing.
- As your operating system, current running process might take some amount of RAM, Please check available Free RAM and assign that too memtester.
- If you are using a 32 Bit System, you cant test more than 4 GB even though you have more RAM( 32 bit systems doesnt support more than 3.5 GB RAM as you all know).
- If your system is very busy and you still assigned higher than available amount of RAM, then the test might get your system into a deadlock, leads to system to halt, be aware of this.
- Run the memtester as root user, so that memtester process can malloc the memory, once its gets hold on that memory it will try to apply lock. if specified memory is not available, it will try to reduce required RAM automatically and try to lock it with mlock.
- if you run it as a regular user, it cant auto reduce the required amount of RAM, so it cant lock it, so it tries to get hold on that specified memory and starts exhausting all system resources.
If you have 8 Gigas of RAM plugged into the PC motherboard you have to multiple 1024*8 this is easily done with bc (An arbitrary precision calculator language) tool:
root@linux:/ # bc -l
bc 1.07.1
Copyright 1991-1994, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2004, 2006, 2008, 2012-2017 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
For details type `warranty'.
8*1024
8192
for example you should run:
root@linux:/ # memtester 8192 5
memtester version 4.3.0 (64-bit)
Copyright (C) 2001-2012 Charles Cazabon.
Licensed under the GNU General Public License version 2 (only).
pagesize is 4096
pagesizemask is 0xfffffffffffff000
want 8192MB (2083520512 bytes)
got 8192MB (2083520512 bytes), trying mlock …Loop 1/1:
Stuck Address : ok
Random Value : ok
Compare XOR : ok
Compare SUB : ok
Compare MUL : ok
Compare DIV : ok
Compare OR : ok
Compare AND : ok
Sequential Increment: ok
Solid Bits : ok
Block Sequential : ok
Checkerboard : ok
Bit Spread : ok
Bit Flip : ok
Walking Ones : ok
Walking Zeroes : ok
8-bit Writes : ok
16-bit Writes : ok
Done.
4. Shell Script to test server memory for corruptions
If for some reason the machine you want to run a memory test doesn't have connection to the external network such as the internet and therefore you cannot configure a package repository server and install memtester, the other approach is to use a simple memory test script such as memtestlinux.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Downloaded from https://www.srv24x7.com/memtest-linux/
echo "ByteOnSite Memory Test"
cpus=`cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor | wc -l`
if [ $cpus -lt 6 ]; then
threads=2
else
threads=$(($cpus / 2))
fi
echo "Detected $cpus CPUs, using $threads threads.."
memory=`free | grep 'Mem:' | awk {'print $2'}`
memoryper=$(($memory / $threads))
echo "Detected ${memory}K of RAM ($memoryper per thread).."
freespace=`df -B1024 . | tail -n1 | awk {'print $4'}`
if [ $freespace -le $memory ]; then
echo You do not have enough free space on the current partition. Minimum: $memory bytes
exit 1
fi
echo "Clearing RAM Cache.."
sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_cachesfile
echo > dump.memtest.img
echo "Writing to dump file (dump.memtest.img).."
for i in `seq 1 $threads`;
do
# 1044 is used in place of 1024 to ensure full RAM usage (2% over allocation)
dd if=/dev/urandom bs=$memoryper count=1044 >> dump.memtest.img 2>/dev/null &
pids[$i]=$!
echo $i
done
for pid in "${pids[@]}"
do
wait $pid
done
echo "Reading and analyzing dump file…"
echo "Pass 1.."
md51=`md5sum dump.memtest.img | awk {'print $1'}`
echo "Pass 2.."
md52=`md5sum dump.memtest.img | awk {'print $1'}`
echo "Pass 3.."
md53=`md5sum dump.memtest.img | awk {'print $1'}`
if [ “$md51” != “$md52” ]; then
fail=1
elif [ “$md51” != “$md53” ]; then
fail=1
elif [ “$md52” != “$md53” ]; then
fail=1
else
fail=0
fi
if [ $fail -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Memory test PASSED."
else
echo "Memory test FAILED. Bad memory detected."
fi
rm -f dump.memtest.img
exit $fail
Nota Bene !: Again consider the restults might not always be 100% trustable if possible restart the server and test with memtest86+
Consider also its important to make sure prior to script run, you''ll have enough disk space to produce the dump.memtest.img file – file is created as a test bed for the memory tests and if not scaled properly you might end up with a full ( / ) root directory!
4.1 Other memory test script with dd and md5sum checksum
I found this solution on the well known sysadmin site nixCraft cyberciti.biz, I think it makes sense and quicker.
First find out memory site using free command.
# free
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 32867436 32574160 293276 0 16652 31194340
-/+ buffers/cache: 1363168 31504268
Swap: 0 0 0
It shows that this server has 32GB memory,
# dd if=/dev/urandom bs=32867436 count=1050 of=/home/memtest
free reports by k and use 1050 is to make sure file memtest is bigger than physical memory. To get better performance, use proper bs size, for example 2048 or 4096, depends on your local disk i/o, the rule is to make bs * count > 32 GB.
run
# md5sum /home/memtest; md5sum /home/memtest; md5sum /home/memtest
If you see md5sum mismatch in different run, you have faulty memory guaranteed.
The theory is simple, the file /home/memtest will cache data in memory by filling up all available memory during read operation. Using md5sum command you are reading same data from memory.
5. Other ways to test memory / do a machine stress test
Other good tools you might want to check for memory testing is mprime – ftp://mersenne.org/gimps/
(https://www.mersenne.org/ftp_root/gimps/)
- (mprime can also be used to stress test your CPU)
Alternatively, use the package stress-ng to run all kind of stress tests (including memory test) on your machine.
Perhaps there are other interesting tools for a diagnosis of memory if you know other ones I miss, let me know in the comment section.

















Report haproxy node switch script useful for Zabbix or other monitoring
Tuesday, June 9th, 2020For those who administer corosync clustered haproxy and needs to build monitoring in case if the main configured Haproxy node in the cluster is changed, I've developed a small script to be integrated with zabbix-agent installed to report to a central zabbix server via a zabbix proxy.
The script is very simple it assumed DC1 variable is the default used haproxy node and DC2 and DC3 are 2 backup nodes. The script is made to use crm_mon which is not installed by default on each server by default so if you'll be using it you'll have to install it first, but anyways the script can easily be adapted to use pcs cmd instead.
Below is the bash shell script:
To configure it with zabbix monitoring it can be configured via UserParameterScript.
The way I configured it in Zabbix is as so:
1. Create the userpameter_active_node.conf
Below script is 3 nodes Haproxy cluster
Once pasted to save the file press CTRL + D
The version of the script with 2 nodes slightly improved is like so:
The haproxy_active_DC_zabbix.sh script with a bit of more comments as explanations is available here
2. Configure access for /usr/sbin/crm_mon for zabbix user in sudoers
3. Configure in Zabbix for active.dc key Trigger and Item
Tags: access, ALL, and, Anyways, are, available, awk, bash shell, bash shell script, Below, bit, case, cat, Central, check, Cluster, cmd, Comments, conf, configure
Posted in Linux, Monitoring, Zabbix | No Comments »