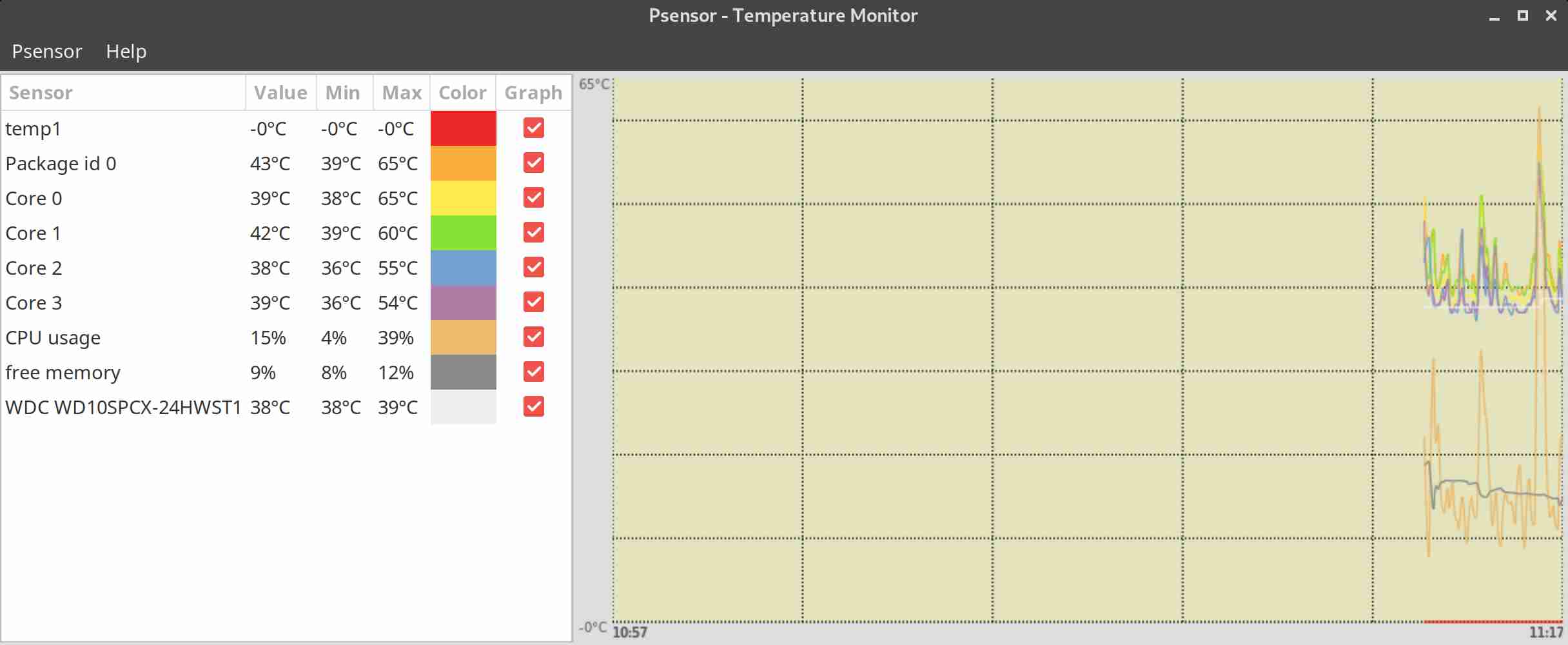
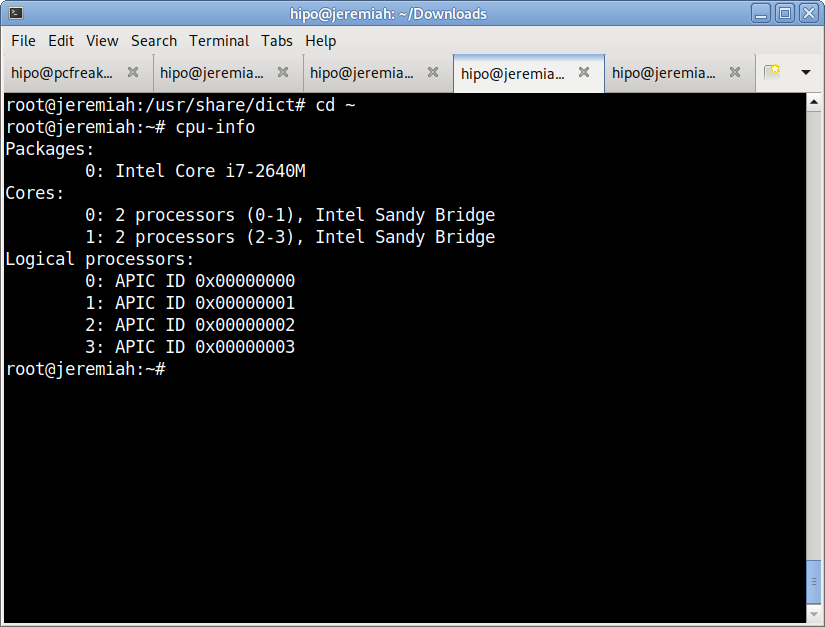
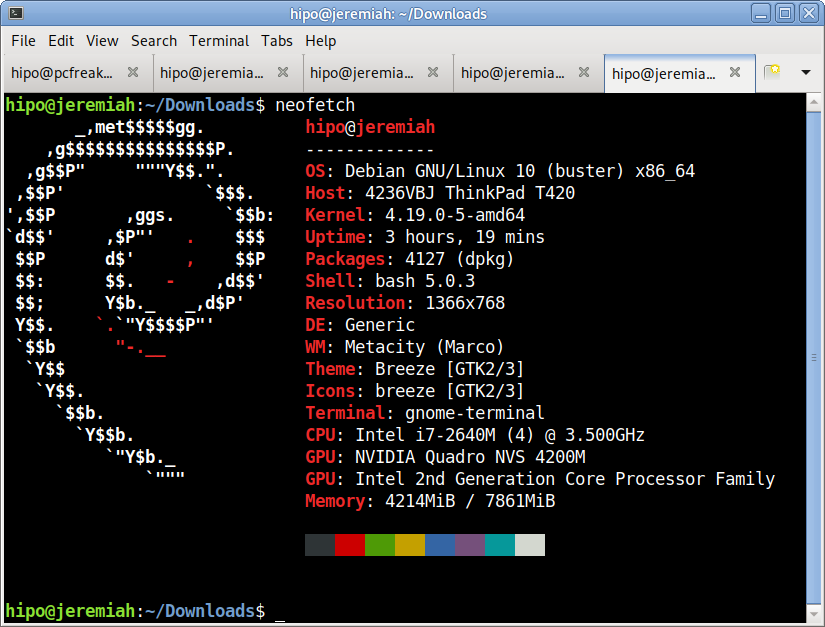
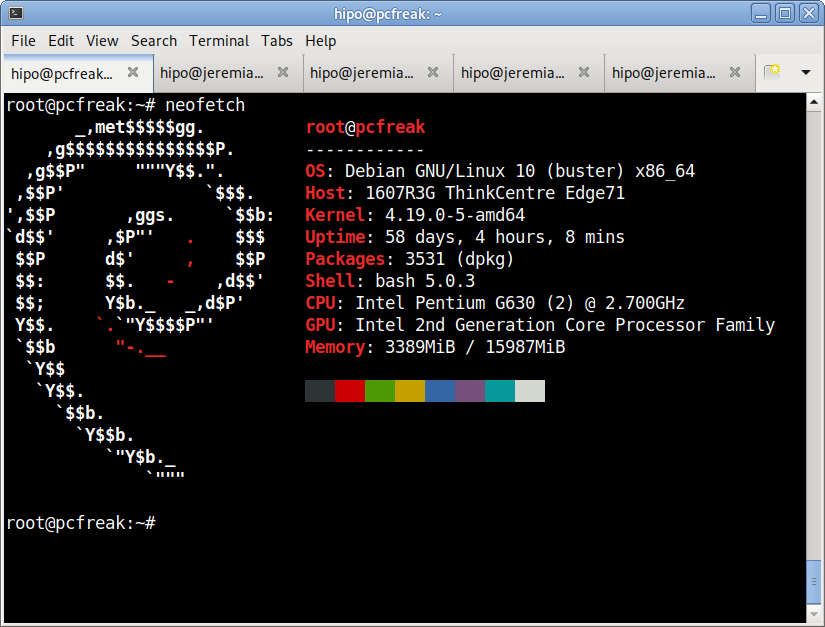
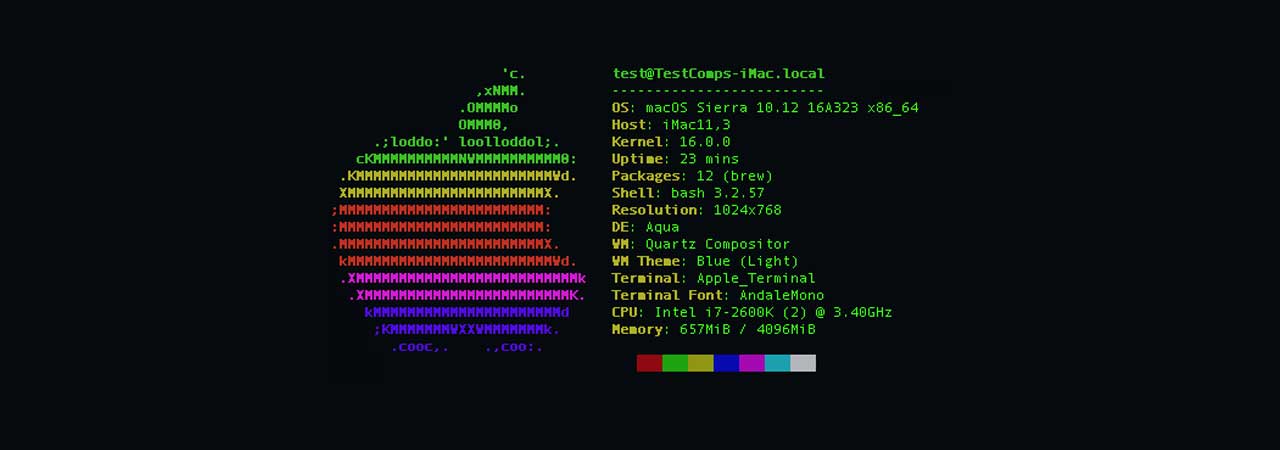
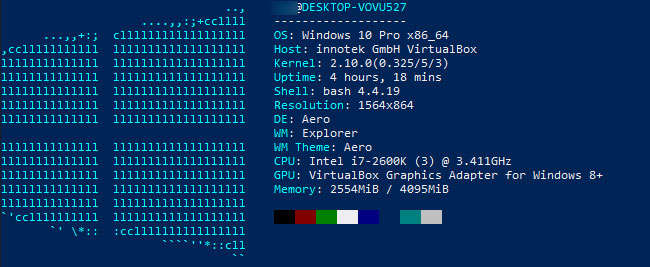
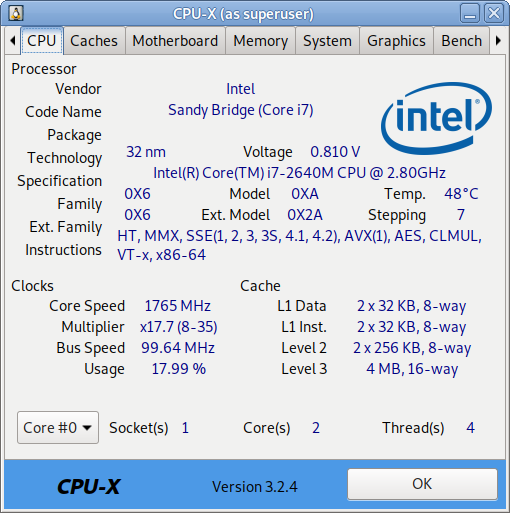
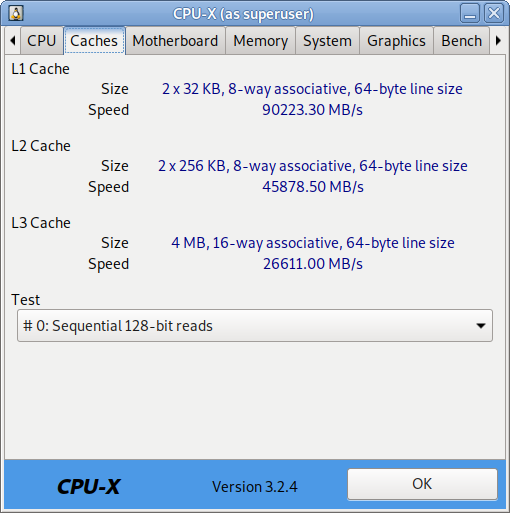
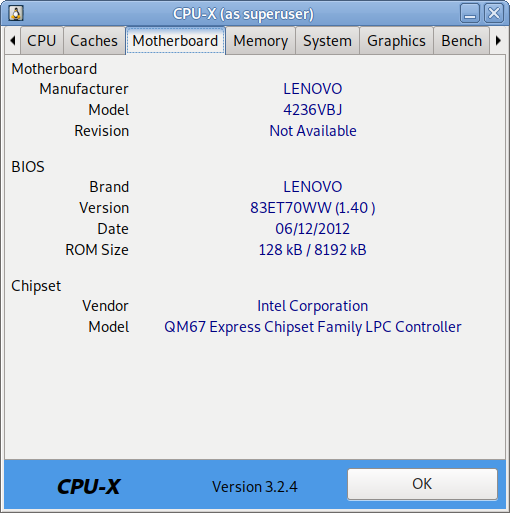
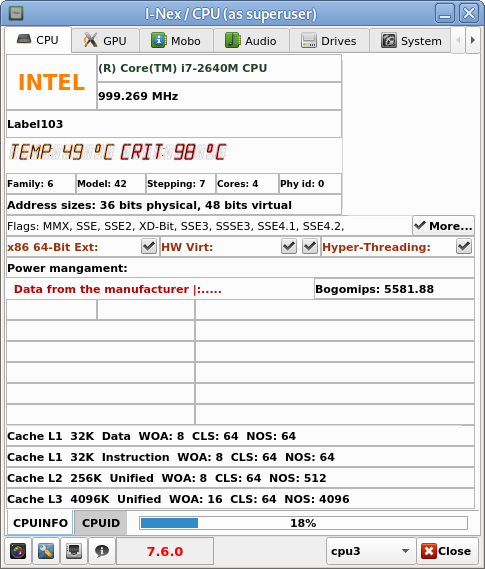
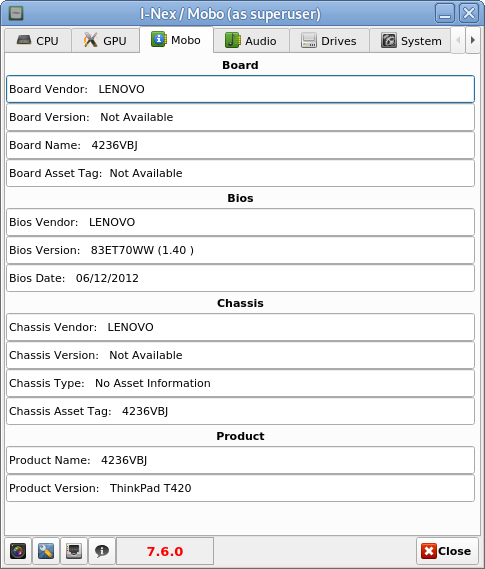
I have not blogged for a long time due to being on a few weeks vacation and being in home with a small cute baby. However as a hardcore and a bit of dumb System administrator, I have spend some of my vacation and worked on bringing up the the www.pc-freak.net and the other Websites hosted as a high availvailability ones living on a 2 Webservers running on a Master to Master MySQL Replication backend database, this is oll hosted on servers, set to run as a round robin DNS hosts on 2 servers one old Lenove ThinkCentre Edge71 as well as a brand new real Lenovo server Lenovo ThinkServer SD350 with 24 CPUs and a 32 GB of RAM.
To assure Internet Connectivity is having a good degree of connectivity and ensure websites hosted on both machines is not going to die if one of the 2 pair configured Fiber Optics Internet Providers Bergon.NET has some Issues, I've rented another Internet Provider Line is set bought from the VIVACOM Mobile Fiber Internet provider – that is a 1 Gigabit Fiber Optics Line.
Next to that to guarantee there is no Database, Webserver, MailServer, Memcached and other running services did not hit downtimes due to Electricity power outage, two Powerful Uninterruptable Power Supplies (UPS) FPS Fortron devices are connected to the servers each of which that could keep the machine and the connected switches and Servers for up to 1 Hour.
The machines are configured to use dhcpd to distributed IP addresses and the Main Node is set to distribute IPs, however as there is a local LAN network with more of a personal Work PCs, Wireless Devices and Testing Computers and few Virtual machines in the Network and the IPs are being distributed in a consequential manner via a ISC DHCP server.
As always to make everything work properly hence, I had again some a bit weird non-standard requirement to make some of the computers within the Network with Static IP addresses and the others to have their IPs received via the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and add some filter for some of the Machine MAC Addresses which are configured to have a static IP addresses to prevent the DHCP (daemon) server to automatically reassign IPs to this machines.
After a bit of googling and pondering I've done it and some of the machines, therefore to save others the efforts to look around How to set Certain Computers / Servers Network Card MAC (Interfaces) MAC Addresses configured on the LAN network to use Static IPs and instruct the DHCP server to ingnore any broadcast IP addresses leases – if they're to be destined to a set of IGNORED MAcs, I came up with this small article.
Here is the DHCP server /etc/dhcpd/dhcpd.conf from my Debian GNU / Linux (Buster) 10.4
option domain-name "pcfreak.lan";
option domain-name-servers 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4, 208.67.222.222, 208.67.220.220;
max-lease-time 891200;
authoritative;
class "black-hole" {
match substring (hardware, 1, 6);
ignore booting;
}
subclass "black-hole" 18:45:91:c3:d9:00;
subclass "black-hole" 70:e2:81:13:44:11;
subclass "black-hole" 70:e2:81:13:44:12;
subclass "black-hole" 00:16:3f:53:5d:11;
subclass "black-hole" 18:45:9b:c6:d9:00;
subclass "black-hole" 16:45:93:c3:d9:09;
subclass "black-hole" 16:45:94:c3:d9:0d;/etc/dhcpd/dhcpd.conf
subclass "black-hole" 60:67:21:3c:20:ec;
subclass "black-hole" 60:67:20:5c:20:ed;
subclass "black-hole" 00:16:3e:0f:48:04;
subclass "black-hole" 00:16:3e:3a:f4:fc;
subclass "black-hole" 50:d4:f5:13:e8:ba;
subclass "black-hole" 50:d4:f5:13:e8:bb;
subnet 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers 192.168.0.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
}
host think-server {
hardware ethernet 70:e2:85:13:44:12;
fixed-address 192.168.0.200;
}
default-lease-time 691200;
max-lease-time 891200;
log-facility local7;
To spend you copy paste efforts a file with Deny DHCP Address by Mac Linux configuration is here
/home/hipo/info
Of course I have dumped the MAC Addresses to omit a data leaking but I guess the idea behind the MAC ADDR ignore is quite clear
The main configuration doing the trick to ignore a certain MAC ALenovo ThinkServer SD350ddresses that are reachable on the Connected hardware switch on the device is like so:
class "black-hole" {
match substring (hardware, 1, 6);
ignore booting;
}
subclass "black-hole" 18:45:91:c3:d9:00;
…
The Deny DHCP Address by MAC is described on isc.org distribution lists here but it seems the documentation on the topic on how to Deny / IGNORE DHCP Addresses by MAC Address on Linux has been quite obscure and limited online.
As you can see in above config the time via which an IP is freed up and a new IP lease is done from the server is severely maximized as often DHCP servers do use a max-lease-time like 1 hour (3600) seconds:, the reason for increasing the lease time to be to like 10 days time is that the IPs in my network change very rarely so it is a waste of CPU cycles to do a frequent lease.
default-lease-time 691200;
max-lease-time 891200;
As you see to Guarantee resolving works always as expected I have configured – Google Public DNS and OpenDNS IPs
option domain-name-servers 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4, 208.67.222.222, 208.67.220.220;
One hint to make is, after setting up all my desired config in the standard config location /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf it is always good idea to test configuration before reloading the running dhcpd process.
root@pcfreak: ~# /usr/sbin/dhcpd -t
Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Server 4.4.1
Copyright 2004-2018 Internet Systems Consortium.
All rights reserved.
For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/
Config file: /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
Database file: /va/home/hipo/infor/lib/dhcp/dhcpd.leases
PID file: /var/run/dhcpd.pid
That's all folks with this sample config the IPs under subclass "black-hole", which are a local LAN Static IP Addresses will never be offered leasess anymore from the ISC DHCP.
Hope this stuff helps someone, enjoy and in case if you need a colocation of a server or a website hosting for a really cheap price on this new set High Availlability up described machines open an inquiry on https://web.www.pc-freak.net.