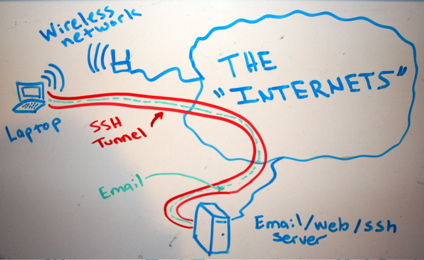
In my earlier articles I've explained about Creating SSH Tunnels on Linux and BSD and how to create SSH Tunnels with Putty Terminal client on Windows.
Creating SSH Tunnels is a precious knowledge every advanced computer user, a system administrator or security expert should be well aware of.
Probably still there are plenty of people for which the SSH Tunnelling is something never heard of or even if heard it is a mythical term covered by ancient shadows 🙂
So What is an SSH Tunnel? – SSH Tunnels shortly explained.
A SSH tunnel consists of an encrypted tunnel created through a SSH protocol
connection.
An SSH tunnel can be used to transfer unencrypted traffic over a
network through an encrypted channel between two hosts (host A and Host B) usually using remote and local port.
Requirements for SSH tunnel
Where Host B has to be running a version of OpenSSH server on some reachable port from Host B, (lets say 22).
Host B OpenSSH server has to be with (enabled X11Forwarding – X11Forwarding yes in /etc/ssh/sshd_config) and Host A needs to have some SSH client supporting port forwarding (ssh command on Linux – part of (openssh-client package) and on Windows – Putty / Plink or any other of the many available ssh tunneling clients).
Probably most common SSH Tunnel use is to bypass firewalls that prohibits or filter certain internet services.
In other words SSH Tunnels can be used to get around firewall filtering. If you never heard of Bypassing firewalls with port forwarding I recommend to check this article
We can use a ssh tunnel to securely transfer files between a FTP server and a client even though the FTP
protocol itself is not encrypted, Tnnel traffic to an SQL server, Tunnel traffic from your Desktop PC to a Proxy
SSH tunnels can be used to tunnel outbound E-mail traffic back to your work PC to avoid having to change SMTP servers etc.
A very common SSH Tunnel use is by office workers who don't want their Custom Web browsing habbits and Web history be tracked,
For people who has to travel a lot tunneling SSH traffic from notebook to your home based SMTP is mandatory, otherwise your e-mail passwords, might end up captured by someone who manages the Free WI-FI used by you somewhere on the road or cafeteria. Another good case use of SSH Tunnel is to tunnel VNC traffic.
SSH Tunneling was historically very famous in days where IRC (Internet Relay Chat) and used to be common way (for people who want to prevent their real IP address from publicly visible) on the Internet.
SSH Tunneling is great way to maintain high communication security, however because it requires some basic technical knowledge most people neglect it or never heard of it, so I hope this article will give at least basic ideas to people new to tunneling.
How to create SSH Tunnels on Microsoft Windows
SSH Tunneling has been originally invented on UNIX / Linux platform, luckily nowdays it is easily possible to create SSH tunnels on almost any moden OS (including Mac OS X and M$ Windows).
Using Plink it is possible to create easily (batch) scriptable SSH tunnels on Windows
Generally here is example of basic plink use syntax:
plink.exe {remote-host} -P 22 -C -D 10080 -l username -pw password
To make a Tunnel with Plink to remote SSH Server (remote-ssh-server.com) listening for connections on port 22 on localhost 10022
"C:Program Files (x86)PuTTYplink.exe" -ssh remote-username@tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com -pw PASSWORD123 -C -T -D 127.0.0.1:10022 -N
-D – option instructs Plink to make "Dynamic SOCKS-based port forwarding"
Dynamic Socks-based port forwarding will make your ssh client a simple socks server which listen to port 10022 for incoming connections.
-T – tells plink not to open interactive shell on remote server (disable pty allocation)
-C – enables traffic compression
Using the -D option you can prepare tunnel to traffic all your outgoing server traffic via the SSH tunneling host.
E. g. -D allows you to use the remote ssh server as a proxy server with no need for remote server to run anything except SSH service and have Internet connection.
-N – stands for "don't start shell/command SSH-2 only"
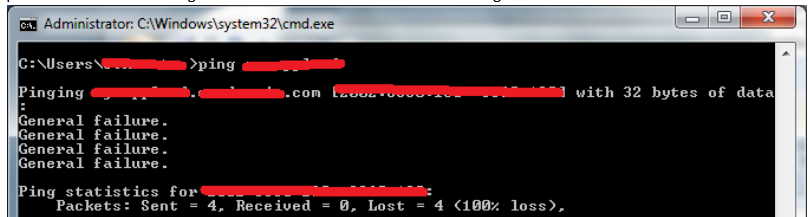
On success of SSH Tunnel establishing you will get a pop-up window similar to below screenshot (note that some of the messages in cmd line are from a batch script – if no batch script is used you wil only get a window with "Using Username":
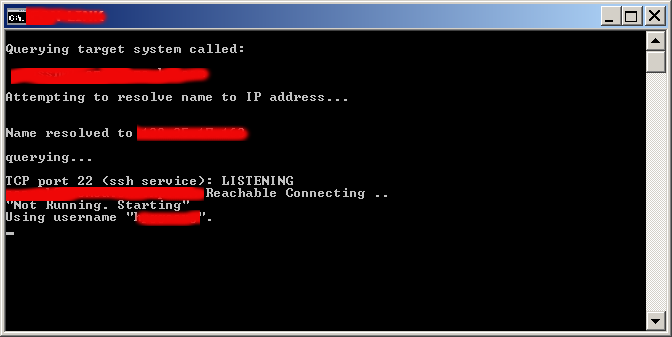
Note: That if you're about to be using Plink command frequently add it to your Windows SYSTEM PATH (check my previous article – how to add Putty to System PATH) to enable it invokable without writting the full command path location.
Once this Window is open if you still have doubt, where the tunnel is established, the quickest way to test whether tunnel is working is to open telnet to localhost port 10022.
In Windows command prompt type:
C:> telnet localhost 10022
…
You will get a remote server SSH version printed, like on below shot:
Now lets say now you would like to access the internet via just created SSH tunnel.
You can do it by simply setting Socks Proxy in your Firefox / Opera (or whatever browser you use).
Whether you want to run the SSH Tunnel permanent and periodically check whether tunnel is allve and respawn it in case plink quit, you can use a very simple batch script like one below:
@ECHO OFF
tasklist /FI "IMAGENAME eq plink.exe" 2>NUL | find /I /N "plink.exe">NUL
if "%ERRORLEVEL%"=="0" ( echo Programm is running exiting
exit
)
echo "Not Running"
start /b "C:Program Files (x86)PuTTYplink.exe" -ssh remote-username@tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com -pw Password123 -T -C -D 127.0.0.1:10022 -N"
If you're a Linux guy and you don't want to mess around with Plink but still want to create your SSH tunnels following SSH client UNIX command line syntax, setup the Cygwin port of OpenSSH for Windows.
Or if you're unsure whether remote server is always reachable (you're moving with your notebook from (Country) network to network), you can use also portqry – windows port scanner to check whether remote ssh server port is opened:
@ECHO OFF
tasklist /FI "IMAGENAME eq plink.exe" 2>NUL | find /I /N "plink.exe">NUL
if "%ERRORLEVEL%"=="0" ( echo Programm is running exiting
pause
exit
)
portqry -n tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com -p tcp -e 22
if %ERRORLEVEL%==0 echo tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com Reachable Connecting ..
if NOT %ERRORLEVEL%==0 (echo tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com.com Unreachable
exit)
echo "Not Running. Starting"
"C:Program Files (x86)PuTTYplink.exe" -ssh remote-username@tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com -pw Password123 -T -C -D 127.0.0.1:10080 –N
Here is another sample use of Plink to create tunnel via SSH host tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com to listen for connections on localhost port 1234 and forward all incoming traffic to squid proxy server on 192.168.1.5 on port 3128.
C:Usersgeorgi>plink.exe -v -x -a -T -C -noagent -ssh -L 127.0.0.1:1234:192.168.1.5:3128 remote-username@tunnel-to-ssh-server-host.com
Setting then 127.0.0.1:1234 in Firefox Proxy browser settings will make all traffic from your browser to flow securily to your own proxy server (letting you hide your "custom traffic" from company Web sniffers (Proxying) and Web filtering.
A remark to make here is 192.168.1.5 is (a internal server with Squid Proxy, configured to pass traffic to the internet ).
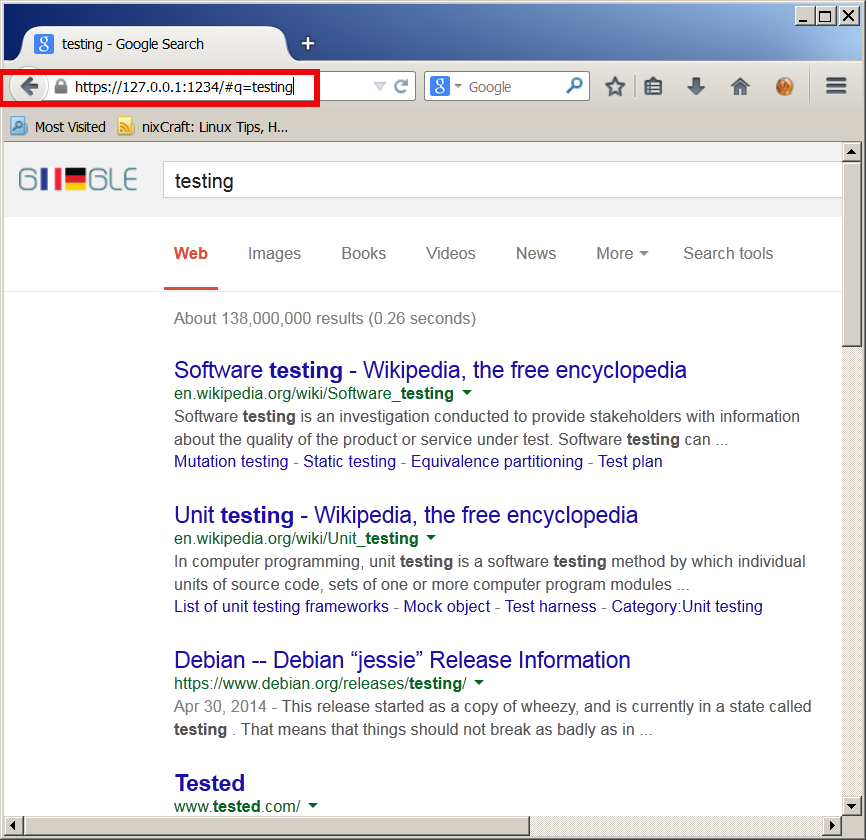
Here is a way to make tunnel between your remote SSH server and local Desktop PC to make Google queries without being logged by your ISP or company where you're working:
plink.exe "-v -x -a -T -C -noagent -ssh -L 127.
0.0.1:1234:95.158.130.242:443 -pw SecretPassword123 -l hipo www.pc-freak.net"
95.158.130.242 – is one of the IPs www.google.com resolves to
www.pc-freak.net – is name of my home router.
To make tunneled queries to Google then open in browser https://127.0.0.1:1234
If you're a lazy windows user and don't want to bother to make your tunnels from command line and you want need nice gui way to manage multiple tunnels – check out putty-tunnel-manager.
I myself am not a SSH Tunnel expert and thus Iwould be happy to learn further from people for some interesting cases and custom ways to do SSH Tunnels. If you know of better advantageous ways to tunnel traffic, please share.
Happy tunneling ! 🙂