On one of the servers, I'm administrating the websites started showing some Mysql database table corrup errors like:
Table './database_name/site_news_list_com' is marked as crashed and last (automatic?) repair failed
…
The server is using Oracle MySQL server community stable edition on Debian GNU / Linux 6.0, so I first thought during work the server crashed either due to some bug issue in MySQL or it crashed due to some PHP cron job that did something messy. Thus to solve the crashed tables, tried using mysqlcheck tool which helped pretty fine, at many times whether there were database / table corruptions. I've run the following set of mysqlcheck commands with root (superuser) in a bash shell after logging in through SSH:
:
server:~# /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–check –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
server:~# /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf –analyze –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
server:~# /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–auto-repair –optimize –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
server:~# /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–optimize –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
In order for above commands to work, I've created the /root/.my.cnf containing my root (mysql CLI) mysql username and password, e.g. file has content like below:
[client]
user=root
password=MySecretPassword8821238
Btw a good note here is its generally a good idea (if you want to have consistent mysql databases) to automatically execute via a cron job 2 times a month, I've in root cronjob the following:
crontab -u root -l |grep -i mysqlcheck
04 06 5,10,15,20,25,1 * * /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–check –all-databases –silent -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log 07 06 5,10,15,20,25,1 * * /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf –analyze –all-databases –silent -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log 12 06 5,10,15,20,25,1 * * /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–auto-repair –optimize –all-databases –silent -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log 17 06 5,10,15,20,25,1 * * /usr/bin/mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–optimize –all-databases –silent -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
Strangely I got a lot of errors that some .MYI / .MYD .frm temp files, necessery for the mysql tables recovery can't be written inside /home/mysql/database_name
That was pretty weird and I thought there might be some issues with permissions, causing the inability to write, due to some bug or something so I went straight and checked /home/mysql/database_name permissions, e.g.::
server:/home/mysql/database_name# ls -ld soccerfame
drwx—— 2 mysql mysql 36864 Nov 17 12:00 soccerfame
server:/home/mysql/database_name# ls -al1|head -n 10
total 1979012
drwx—— 2 mysql mysql 36864 Nov 17 12:00 .
drwx—— 36 mysql mysql 4096 Nov 17 11:12 ..
-rw-rw—- 1 mysql mysql 8712 Nov 17 10:26 1_campaigns_diez.frm
-rw-rw—- 1 mysql mysql 14672 Jul 8 18:57 1_campaigns_diez.MYD
-rw-rw—- 1 mysql mysql 1024 Nov 17 11:38 1_campaigns_diez.MYI
-rw-rw—- 1 mysql mysql 8938 Nov 17 10:26 1_campaigns.frm
-rw-rw—- 1 mysql mysql 8738 Nov 17 10:26 1_campaigns_logs.frm
-rw-rw—- 1 mysql mysql 883404 Nov 16 22:01 1_campaigns_logs.MYD
-rw-rw—- 1 mysql mysql 330752 Nov 17 11:38 1_campaigns_logs.MYI
As seen from above output, all was perfect with permissions, so it should have been something else, so I decided to try to create a random file with touch command inside /home/mysql/database_name directory:
touch /home/mysql/database_name/somefile-to-test-writtability.txt touch: cannot touch ‘/scr1/data/somefile-to-test-writtability.txt‘: No space left on device
Then logically I thought the /home/mysql/ mounted ext4 partition got filled, because of crashed SQL database or a bug thus, checked with disk free command df whether there is enough space on server:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/md1 20G 7.6G 11G 42% /
udev 10M 0 10M 0% /dev
tmpfs 13G 1.3G 12G 10% /run
tmpfs 32G 0 32G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
tmpfs 32G 0 32G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/md2 256G 134G 110G 55% /home
Well that's weird? Obviously only 55% of available disk space is used and available 134G which was more than enough so I got totally puzzled why, files can't be written.
Then very logically, I thought it might be that /home directory has remounted as read only, because the SSD memory disk on server is failing and checked for errors in dmesg, i.e.:
server:~# dmesg|grep -i error
Also checked how exactly was partition mounted, to check whether it is (RO) read-only:
server:~# mount -l|grep -i /home
/dev/md2 on /home type ext4 (rw,relatime,discard,data=ordered)
Now everything become even more weirder, as obviously the disk continued to be claiming no space left on device, while in reality there was plenty of disk space.
Then after running a quick research on the internet for the no space left on device with free disk space, I've come across this great superuser.com thread which let me realize the partition run out of inodes and that's why no new file inodes could be assigned and therefore, the linux kernel is refusing to write the file on ext4 partition.
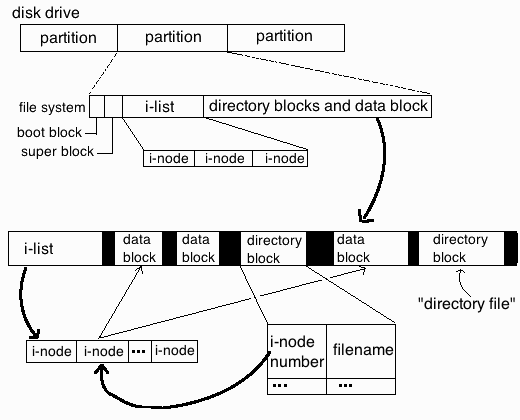
For those who haven't heard of Linux Partition Inodes here is link to Wikipedia and a quick quote:
In a Unix-style file system, the inode is a data structure used to represent a filesystem object, which can be one of various things including a file or a directory. Each inode stores the attributes and disk block location(s) of the filesystem object's data.[1] Filesystem object attributes may include manipulation metadata (e.g. change,[2] access, modify time), as well as owner and permission data (e.g. group-id, user-id, permissions).[3]
Directories are lists of names assigned to inodes. The directory contains an entry for itself, its parent, and each of its children.
Once I understood it is the inodes, I checked how many of them are occupied with cmd:
server:~# df -i /home
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
/dev/md2 17006592 17006592 0 100% /home
You see, there were 0 (zero) free file inodes on server and that was the reason for no space left on device while there was actually free disk space
To clean up (free) some inodes on partition, first thing I did is to delete all old logs which were inside /home and files I positively know not to be necessery, then to find which directories allocating most innodes used:
server:~# find . -xdev -type f | cut -d "/" -f 2 | sort | uniq -c | sort -n
If you're on a regular old fashined IDE Hard Drive and not SSD or you have too much files inside this command will take really long …:
Therefore a better solution might be to frist:
a) Try to find root folders with large inodes count:
for i in /home/*; do echo $i; find $i |wc -l; done
Try to find specific folders:
You should get output like:
/home/new_website
606692
/home/common
73
/home/pcfreak
5661
/home/hipo
33
/home/blog
13570
/home/log
123
/home/lost+found
1
…
b) Then once you know the directory allocating most inodes, run the command again to see the sub-directories with most files (eating) partition innodes:
for i in /home/webservice/*; do echo $i; find $i |wc -l; done
…
One usual large folder which could free you some nodes is the linux source headers, but in my case it was simply a lot of tiny old logs being logged on the system for few years in the past without cleaning:
After deleting the log dirs and cache folder in my case /home/new_website/{log,cache}:
server:~# rm -rf /home/new_website/log/*
server:~# rm -rf /home/new_website/cache/*
a) Then, stopping Apache webserver to check prevent Apache to use MySQl databases while running database repair and restaring MySQL:
server:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 stop Restarting MySQL server
..
server:~# /etc/init.d/mysql restart
..
b) And re-issuing MySQL Check / Repair / Optimize database commands:
mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–check –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
…
mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf –analyze –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
…
mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–auto-repair –optimize –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
…
mysqlcheck –defaults-extra-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf \–optimize –all-databases -u root -p`grep -i password /root/.my.cnf |sed -e 's#password=##g'`>> /var/log/cronwork.log
…
c) And finally starting the Apache Webserver again:
server:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 start
Some innodse got freed up:
server:~# df -i /home Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
/dev/md2 17006592 16797196 209396 99% /home
And hooray by God's Grace and with help of prayers of The most Holy Theotokos (Virgin) Mary, websites started again !