Tracking the Problem of MAC duplicates on Linux routers
If you have two networks that see each other and they're not separated in VLANs but see each other sharing a common netmask lets say 255.255.254.0 or 255.255.252.0, it might happend that there are 2 dhcp servers for example (isc-dhcp-server running on 192.168.1.1 and dhcpd running on 192.168.0.1 can broadcast their services to both LANs 192.168.1.0.1/24 (netmask 255.255.255.0) and Local Net LAN 192.168.1.1/24. The result out of this is that some devices might pick up their IP address via DHCP from the wrong dhcp server.
Normally if you have a fully controlled little or middle class home or office network (10 – 15 electronic devices nodes) connecting to the LAN in a mixed moth some are connected via one of the Networks via connected Wifi to 192.168.1.0/22 others are LANned and using static IP adddresses and traffic is routed among two ISPs and each network can see the other network, there is always a possibility of things to go wrong. This is what happened to me so this is how this post was born.
The best practice from my experience so far is to define each and every computer / phone / laptop host joining the network and hence later easily monitor what is going on the network with something like iptraf-ng / nethogs / iperf – described in prior how to check internet spepeed from console and in check server internet connectivity speed with speedtest-cli) iftop / nload or for more complex stuff wireshark or even a simple tcpdump. No matter the tools network monitoring is only part on solving network issues. A very must have thing in a controlled network infrastructure is defining every machine part of it to easily monitor later with the monitoring tools. Defining each and every host on the Hybrid computer networks makes administering the network much easier task and tracking irregularities on time is much more likely.
Since I have such a hybrid network here hosting a couple of XEN virtual machines with Linux, Windows 7 and Windows 10, together with Mac OS X laptops as well as MacBook Air notebooks, I have followed this route and tried to define each and every host based on its MAC address to pick it up from the correct DHCP1 server 192.168.1.1 (that is distributing IPs for Internet Provider 1 (ISP 1), that is mostly few computers attached UTP LAN cables via LiteWave LS105G Gigabit Switch as well from DHCP2 – used only to assigns IPs to servers and a a single Wi-Fi Access point configured to route incoming clients via 192.168.0.1 Linux NAT gateway server.
To filter out the unwanted IPs from the DHCPD not to propagate I've so far used a little trick to Deny DHCP MAC Address for unwanted clients and not send IP offer for them.
To give you more understanding, I have to clear it up I don't want to have automatic IP assignments from DHCP2 / LAN2 to DHCP1 / LAN1 because (i don't want machines on DHCP1 to end up with IP like 192.168.0.50 or DHCP2 (to have 192.168.1.80), as such a wrong IP delegation could potentially lead to MAC duplicates IP conflicts. MAC Duplicate IP wrong assignments for those older or who have been part of administrating large ISP network infrastructures makes the network communication unstable for no apparent reason and nodes partially unreachable at times or full time …
However it seems in the 21-st century which is the century of strangeness / computer madness in the 2022, technology advanced so much that it has massively started to break up some good old well known sysadmin standards well documented in the RFCs I know of my youth, such as that every electronic equipment manufactured Vendor should have a Vendor Assigned Hardware MAC Address binded to it that will never change (after all that was the idea of MAC addresses wasn't it !).
Many mobile devices nowadays however, in the developers attempts to make more sophisticated software and Increase Anonimity on the Net and Security, use a technique called MAC Address randomization (mostly used by hackers / script kiddies of the early days of computers) for their Wi-Fi Net Adapter OS / driver controlled interfaces for the sake of increased security (the so called Private WiFi Addresses). If a sysadmin 10-15 years ago has seen that he might probably resign his profession and turn to farming or agriculture plant growing, but in the age of digitalization and "cloud computing", this break up of common developed network standards starts to become the 'new normal' standard.
I did not suspected there might be a MAC address oddities, since I spare very little time on administering the the network. This was so till recently when I accidently checked the arp table with:
Hypervisor:~# arp -an
192.168.1.99 5c:89:b5:f2:e8:d8 (Unknown)
192.168.1.99 00:15:3e:d3:8f:76 (Unknown)..
and consequently did a network MAC Address ARP Scan with arp-scan (if you never used this little nifty hacker tool I warmly recommend it !!!)
If you don't have it installed it is available in debian based linuces from default repos to install
Hypervisor:~# apt-get install –yes arp-scan
…
It is also available on CentOS / Fedora / Redhat and other RPM distros via:
Hypervisor:~# yum install -y arp-scan
…
Hypervisor:~# arp-scan –interface=eth1 192.168.1.0/24
…192.168.1.19 00:16:3e:0f:48:05 Xensource, Inc.
192.168.1.22 00:16:3e:04:11:1c Xensource, Inc.
192.168.1.31 00:15:3e:bb:45:45 Xensource, Inc.
192.168.1.38 00:15:3e:59:96:8e Xensource, Inc.
192.168.1.34 00:15:3e:d3:8f:77 Xensource, Inc.
192.168.1.60 8c:89:b5:f2:e8:d8 Micro-Star INT'L CO., LTD
192.168.1.99 5c:89:b5:f2:e8:d8 (Unknown)
192.168.1.99 00:15:3e:d3:8f:76 (Unknown)
192.168.x.91 02:a0:xx:xx:d6:64 (Unknown)
192.168.x.91 02:a0:xx:xx:d6:64 (Unknown) (DUP: 2)
…
N.B. !. I found it helpful to check all available interfaces on my Linux NAT router host.
As you see the scan revealed, a whole bunch of MAC address mess duplicated MAC hanging around, destroying my network topology every now and then
So far so good, the MAC duplicates and strangely hanging around MAC addresses issue, was solved relatively easily with enabling below set of systctl kernel variables.
1. Fixing Linux ARP common well known Problems through disabling arp_announce / arp_ignore / send_redirects kernel variables disablement
Linux answers ARP requests on wrong and unassociated interfaces per default. This leads to the following two problems:
ARP requests for the loopback alias address are answered on the HW interfaces (even if NOARP on lo0:1 is set). Since loopback aliases are required for DSR (Direct Server Return) setups this problem is very common (but easy to fix fortunately).
If the machine is connected twice to the same switch (e.g. with eth0 and eth1) eth2 may answer ARP requests for the address on eth1 and vice versa in a race condition manner (confusing almost everything).
This can be prevented by specific arp kernel settings. Take a look here for additional information about the nature of the problem (and other solutions): ARP flux.
To fix that generally (and reboot safe) we include the following lines into
Hypervisor:~# cp -rpf /etc/sysctl.conf /etc/sysctl.conf_bak_07-feb-2022
Hypervisor:~# cat >> /etc/sysctl.conf# LVS tuning
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore=1
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce=2
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore=1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce=2net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects=0
net.ipv4.conf.eth0.send_redirects=0
net.ipv4.conf.eth1.send_redirects=0
net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects=0Press CTRL + D simultaneusly to Write out up-pasted vars.
To read more on Load Balancer using direct routing and on LVS and the arp problem here
2. Digging further the IP conflict / dulicate MAC Problems
Even after this arp tunings (because I do have my Hypervisor 2 LAN interfaces connected to 1 switch) did not resolved the issues and still my Wireless Connected devices via network 192.168.1.1/24 (ISP2) were randomly assigned the wrong range IPs 192.168.0.XXX/24 as well as the wrong gateway 192.168.0.1 (ISP1).
After thinking thoroughfully for hours and checking the network status with various tools and thanks to the fact that my wife has a MacBook Air that was always complaining that the IP it tried to assign from the DHCP was already taken, i"ve realized, something is wrong with DHCP assignment.
Since she owns a IPhone 10 with iOS and this two devices are from the same vendor e.g. Apple Inc. And Apple's products have been having strange DHCP assignment issues from my experience for quite some time, I've thought initially problems are caused by software on Apple's devices.
I turned to be partially right after expecting the logs of DHCP server on the Linux host (ISP1) finding that the phone of my wife takes IP in 192.168.0.XXX, insetad of IP from 192.168.1.1 (which has is a combined Nokia Router with 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz Wi-Fi and LAN router provided by ISP2 in that case Vivacom). That was really puzzling since for me it was completely logical thta the iDevices must check for DHCP address directly on the Network of the router to whom, they're connecting. Guess my suprise when I realized that instead of that the iDevices does listen to the network on a wide network range scan for any DHCPs reachable baesd on the advertised (i assume via broadcast) address traffic and try to connect and take the IP to the IP of the DHCP which responds faster !!!! Of course the Vivacom Chineese produced Nokia router responded DHCP requests and advertised much slower, than my Linux NAT gateway on ISP1 and because of that the Iphone and iOS and even freshest versions of Android devices do take the IP from the DHCP that responds faster, even if that router is not on a C class network (that's invasive isn't it??). What was even more puzzling was the automatic MAC Randomization of Wifi devices trying to connect to my ISP1 configured DHCPD and this of course trespassed any static MAC addresses filtering, I already had established there.
Anyways there was also a good think out of tthat intermixed exercise 🙂 While playing around with the Gigabit network router of vivacom I found a cozy feature SCHEDULEDING TURNING OFF and ON the WIFI ACCESS POINT – a very useful feature to adopt, to stop wasting extra energy and lower a bit of radiation is to set a swtich off WIFI AP from 12:30 – 06:30 which are the common sleeping hours or something like that.
3. What is MAC Randomization and where and how it is configured across different main operating systems as of year 2022?
Depending on the operating system of your device, MAC randomization will be available either by default on most modern mobile OSes or with possibility to have it switched on:
- Android Q: Enabled by default
- Android P: Available as a developer option, disabled by default
- iOS 14: Available as a user option, disabled by default
- Windows 10: Available as an option in two ways – random for all networks or random for a specific network
Lately I don't have much time to play around with mobile devices, and I do not my own a luxury mobile phone so, the fact this ne Androids have this MAC randomization was unknown to me just until I ended a small mess, based on my poor configured networks due to my tight time constrains nowadays.
Finding out about the new security feature of MAC Randomization, on all Android based phones (my mother's Nokia smartphone and my dad's phone, disabled the feature ASAP:
4. Disable MAC Wi-Fi Ethernet device Randomization on Android
MAC Randomization creates a random MAC address when joining a Wi-Fi network for the first time or after “forgetting” and rejoining a Wi-Fi network. It Generates a new random MAC address after 24 hours of last connection.
Disabling MAC Randomization on your devices. It is done on a per SSID basis so you can turn off the randomization, but allow it to function for hotspots outside of your home.
- Open the Settings app
- Select Network and Internet
- Select WiFi
- Connect to your home wireless network
- Tap the gear icon next to the current WiFi connection
- Select Advanced
- Select Privacy
- Select "Use device MAC"
5. Disabling MAC Randomization on MAC iOS, iPhone, iPad, iPod
To Disable MAC Randomization on iOS Devices:
Open the Settings on your iPhone, iPad, or iPod, then tap Wi-Fi or WLAN
- Tap the information button next to your network
- Turn off Private Address
- Re-join the network
Of course next I've collected their phone Wi-Fi adapters and made sure the included dhcp MAC deny rules in /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf are at place.
The effect of the MAC Randomization for my Network was terrible constant and strange issues with my routings and networks, which I always thought are caused by the openxen hypervisor Virtualization VM bugs etc.
That continued for some months now, and the weird thing was the issues always started when I tried to update my Operating system to the latest packetset, do a reboot to load up the new piece of software / libraries etc. and plus it happened very occasionally and their was no obvious reason for it.
6. How to completely filter dhcp traffic between two network router hosts
IP 192.168.0.1 / 192.168.1.1 to stop 2 or more configured DHCP servers
on separate networks see each other
To prevent IP mess at DHCP2 server side (which btw is ISC DHCP server, taking care for IP assignment only for the Servers on the network running on Debian 11 Linux), further on I had to filter out any DHCP UDP traffic with iptables completely.
To prevent incorrect route assignments assuming that you have 2 networks and 2 routers that are configurred to do Network Address Translation (NAT)-ing Router 1: 192.168.0.1, Router 2: 192.168.1.1.
You have to filter out UDP Protocol data on Port 67 and 68 from the respective source and destination addresses.
In firewall rules configuration files on your Linux you need to have some rules as:
# filter outgoing dhcp traffic from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.0.1
-A INPUT -p udp -m udp –dport 67:68 -s 192.168.1.1 -d 192.168.0.1 -j DROP
-A OUTPUT -p udp -m udp –dport 67:68 -s 192.168.1.1 -d 192.168.0.1 -j DROP
-A FORWARD -p udp -m udp –dport 67:68 -s 192.168.1.1 -d 192.168.0.1 -j DROP-A INPUT -p udp -m udp –dport 67:68 -s 192.168.0.1 -d 192.168.1.1 -j DROP
-A OUTPUT -p udp -m udp –dport 67:68 -s 192.168.0.1 -d 192.168.1.1 -j DROP
-A FORWARD -p udp -m udp –dport 67:68 -s 192.168.0.1 -d 192.168.1.1 -j DROP-A INPUT -p udp -m udp –sport 67:68 -s 192.168.1.1 -d 192.168.0.1 -j DROP
-A OUTPUT -p udp -m udp –sport 67:68 -s 192.168.1.1 -d 192.168.0.1 -j DROP
-A FORWARD -p udp -m udp –sport 67:68 -s 192.168.1.1 -d 192.168.0.1 -j DROP
You can download also filter_dhcp_traffic.sh with above rules from here
Applying this rules, any traffic of DHCP between 2 routers is prohibited and devices from Net: 192.168.1.1-255 will no longer wrongly get assinged IP addresses from Network range: 192.168.0.1-255 as it happened to me.
7. Filter out DHCP traffic based on MAC completely on Linux with arptables
If even after disabling MAC randomization on all devices on the network, and you know physically all the connecting devices on the Network, if you still see some weird MAC addresses, originating from a wrongly configured ISP traffic router host or whatever, then it is time to just filter them out with arptables.
## drop traffic prevent mac duplicates due to vivacom and bergon placed in same network – 255.255.255.252
dchp1-server:~# arptables -A INPUT –source-mac 70:e2:83:12:44:11 -j DROP
To list arptables configured on Linux host
dchp1-server:~# arptables –list -n
If you want to be paranoid sysadmin you can implement a MAC address protection with arptables by only allowing a single set of MAC Addr / IPs and dropping the rest.
dchp1-server:~# arptables -A INPUT –source-mac 70:e2:84:13:45:11 -j ACCEPT
dchp1-server:~# arptables -A INPUT –source-mac 70:e2:84:13:45:12 -j ACCEPT
dchp1-server:~# arptables -L –line-numbers
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
1 -j DROP –src-mac 70:e2:84:13:45:11
2 -j DROP –src-mac 70:e2:84:13:45:12
3
Once MACs you like are accepted you can set the INPUT chain policy to DROP as so:
dchp1-server:~# arptables -P INPUT DROP
If you later need to temporary, clean up the rules inside arptables on any filtered hosts flush all rules inside INPUT chain, like that
dchp1-server:~# arptables -t INPUT -F



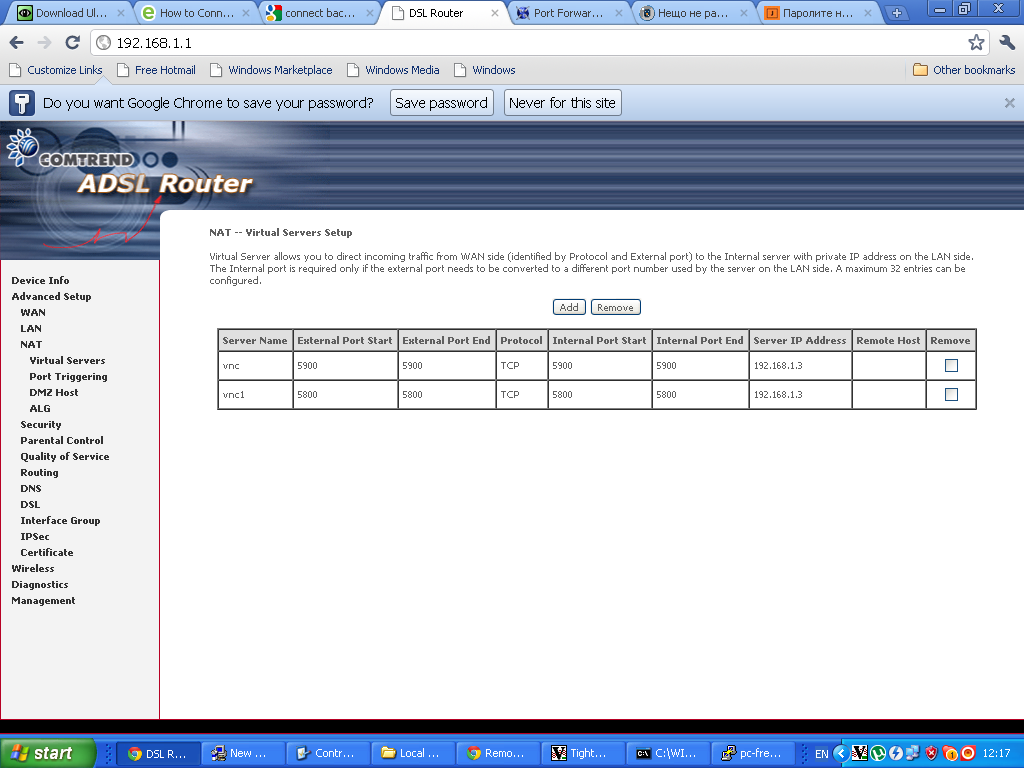
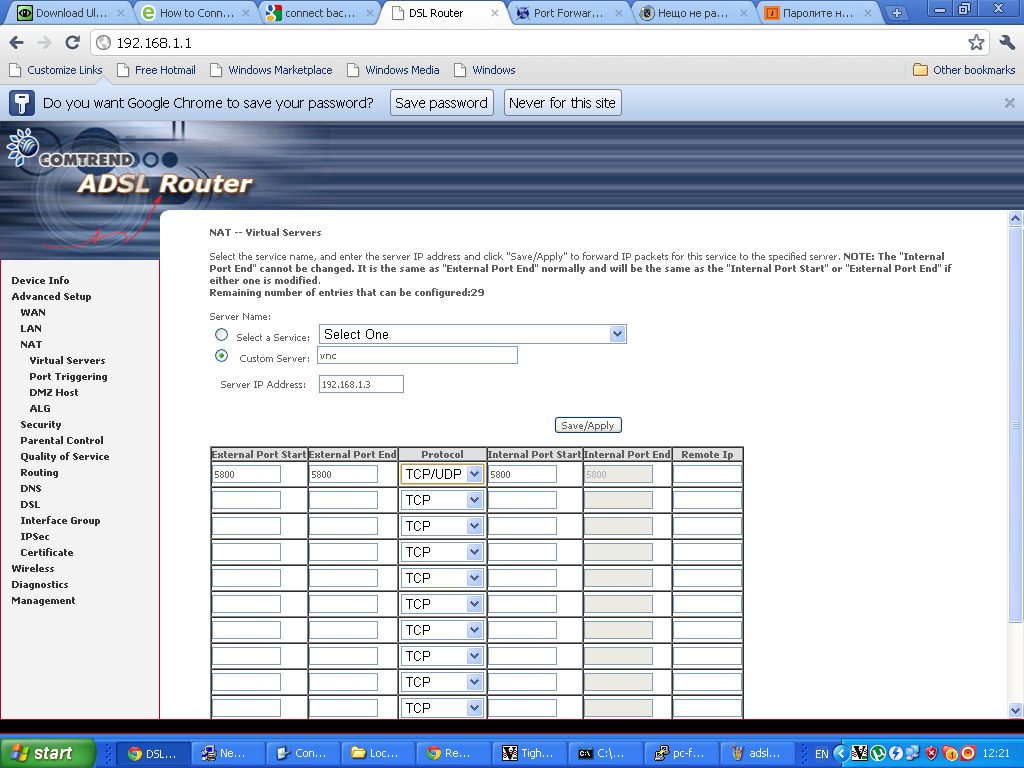 Configuring ADSL SmartAX MT882 TightVNC NAT port redirection screenTightVNC requires also NAT port redirection rule for port 5900 in order to be able to connect to the VNC server behind the dsl, so analogically I added a Virtual Server NAT rule for port 5900.
Configuring ADSL SmartAX MT882 TightVNC NAT port redirection screenTightVNC requires also NAT port redirection rule for port 5900 in order to be able to connect to the VNC server behind the dsl, so analogically I added a Virtual Server NAT rule for port 5900.



