Often it happens, that some old hosted websites were created in a way so no Web Statistics are available. Almost all modern created websites nowadays are already set to use Google Analytics. Anyhow every now and then I stumble on hosting clients whose websites creator didn't thought on how to track how many hits or unique visitors site gets in a month / year etc.
Thanksfully this is solvable by good "uncle" admin with help with of Webalizer (with custom configuration) and a little bit of shell scripting.
The idea is simple, we take the old website logs located in lets say
/var/log/apache2/www.website-access.log*, move files to some custom created new directory lets say /root/www.website-access-logs/ and then configure webalizer to read and generate statistics based on log in there.
For the purpose, we have to have webalizer installed on Linux system. In my case this is Debian GNU / Linux.
For those who hear of Webalizer for first time here is short package description:
debian:~# apt-cache show webalizer|grep -i description -A 2
Description-en: web server log analysis program
The Webalizer was designed to scan web server log files in various formats
and produce usage statistics in HTML format for viewing through a browser.
—
If webalizer is not installed still install it with:
debian:~# apt-get install --yes webalizer
...
.....
Then make backup copy of original / default webalizer.conf (very important step especially if server is already processing Apache log files with some custom webalizer configuration:
debian:~# cp -rpf /etc/webalizer/webalizer.conf /etc/webalizer/webalizer.conf.orig
Next step is to copy webalizer.conf with a name reminding of website of which logs will be processed, e.g.:
debian:~# cp -rpf /etc/webalizer/webalizer.conf /etc/webalizer/www.website-webalizer.conf
In www.website-webalizer.conf config file its necessary to edit at least 4 variables:
LogFile /var/log/apache2/access.log
OutputDir /var/www
#Incremental no
ReportTitle Usage statistics for
Make sure after modifying 3 vars read something like:
LogFile /root/www.website/access_log_merged_1.log
OutputDir /var/www/www.website
Incremental yes
ReportTitle Usage statistics for Your-Website-Host-Name.com
Next create /root/www.website and /var/www/www.website, then copy all files you need to process from /var/log/apache2/www.website* to /root/www.website:
debian:~# mkdir -p /root/www.website
debian:~# cp -rpf /var/log/apache2/www.website* /root/www.website
On Debian Apache uses logrotate to archive old log files, so all logs except www.website-access.log and wwww.website-access.log.1 are gzipped:
debian:~# cd /root/www.website
debian:~# ls
www.website-access.log.10.gz
www.website-access.log.11.gz
www.website-access.log.12.gz
www.website-access.log.13.gz
www.website-access.log.14.gz
www.website-access.log.15.gz
www.website-access.log.16.gz
www.website-access.log.17.gz
www.website-access.log.18.gz
www.website-access.log.19.gz
www.website-access.log.20.gz
...
Then we have to un-gzip zipped logs and create one merged file from all of them ready to be red later by Webalizer. To do so I use a tiny shell script like so:
for n in {52..1}; do gzip -d www.dobrudzhatour.net-access.log.$n.gz; done
for n in {52..1}; do cat www.dobrudzhatour.net-access.log.$n >> access_log_merged_1.log;
done
First look de-gzips and second one does create a merged file from all with name access_merged_1.log The range of log files in my case is from www.website-access.log.1 to www.website-access.log.52, thus I have in loop back number counting from 52 to 1.
Once access_log_merged_1.log is ready we can run webalizer to process file (Incremental) and generate all time statistics for www.website:
debian:~# webalizer -c /etc/webalizer/webalizer-www.website-webalizer.conf
Webalizer V2.01-10 (Linux 2.6.32-27-server) locale: en_US.UTF-8
Using logfile /root/www.website/access_log_merged_1.log (clf)
Using default GeoIP database Creating output in /var/www/webalizer-www.website
Hostname for reports is 'debian'
Reading history file… webalizer.hist
Reading previous run data.. webalizer.current
333474 records (333474 ignored) in 37.50 seconds, 8892/sec
To check out just generated statistics open in browser:
http://yourserverhost/webalizer-www.website/
or
http://IP_Address/webalizer-www.website
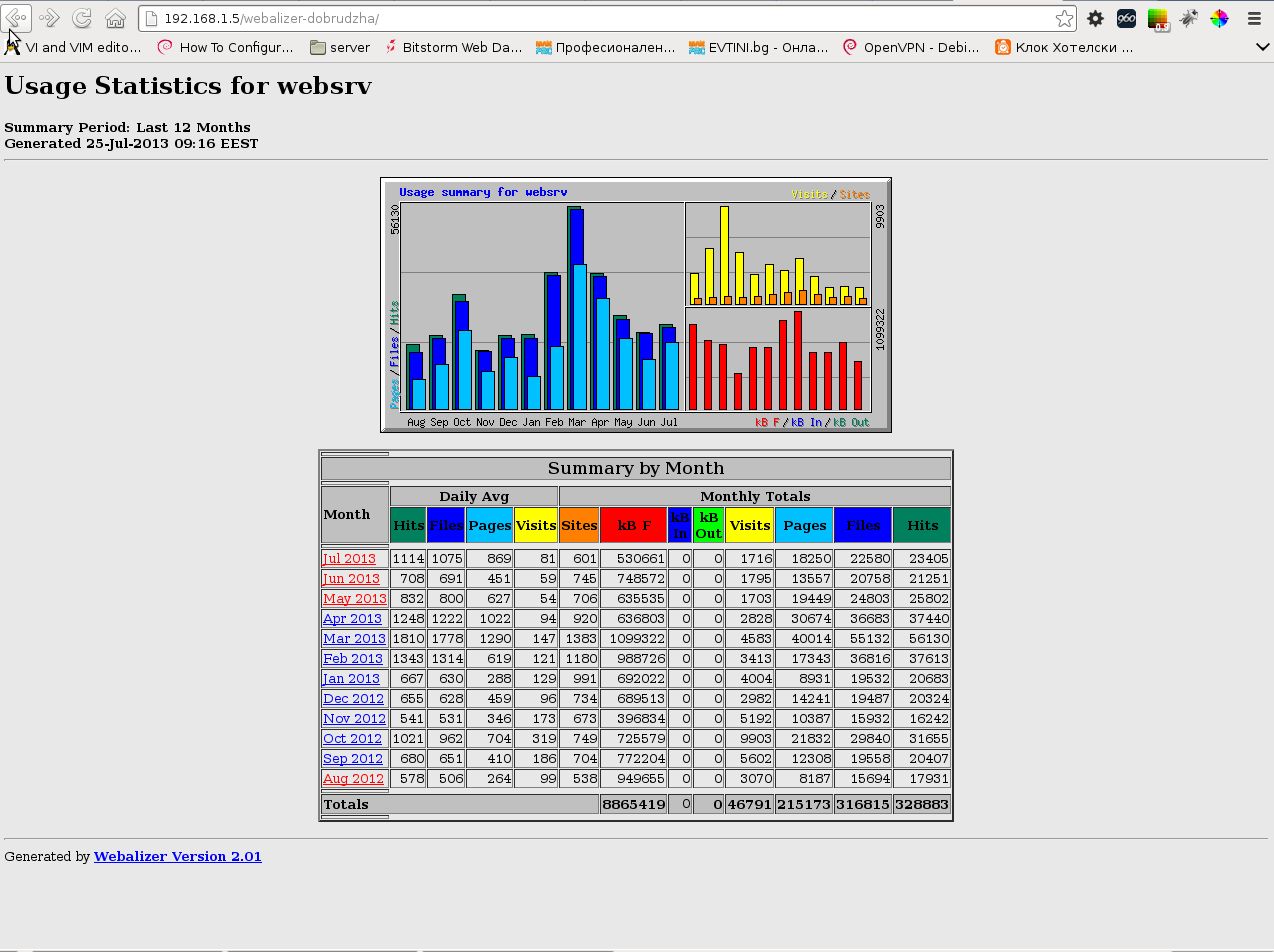
You should see statistics pop-up, below is screenshot with my currently generated stats: