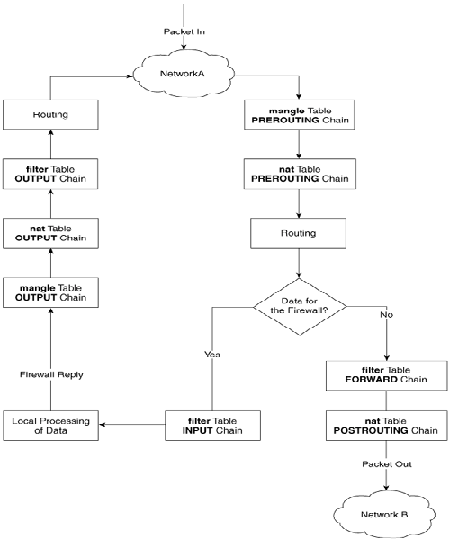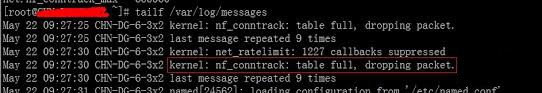
On many busy servers, you might encounter in /var/log/syslog or dmesg kernel log messages like
nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet
to appear repeatingly:
[1737157.057528] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.160357] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.260534] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.361837] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.462305] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.564270] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.666836] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.767348] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.868338] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.969828] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
[1737157.969928] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet
[1737157.989828] nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet
[1737162.214084] __ratelimit: 83 callbacks suppressed
There are two type of servers, I've encountered this message on:
1. Xen OpenVZ / VPS (Virtual Private Servers)
2. ISPs – Internet Providers with heavy traffic NAT network routers
I. What is the meaning of nf_conntrack: table full dropping packet error message
In short, this message is received because the nf_conntrack kernel maximum number assigned value gets reached.
The common reason for that is a heavy traffic passing by the server or very often a DoS or DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack. Sometimes encountering the err is a result of a bad server planning (incorrect data about expected traffic load by a company/companeis) or simply a sys admin error…
– Checking the current maximum nf_conntrack value assigned on host:
linux:~# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_max
65536
– Alternative way to check the current kernel values for nf_conntrack is through:
linux:~# /sbin/sysctl -a|grep -i nf_conntrack_max
error: permission denied on key 'net.ipv4.route.flush'
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 65536
error: permission denied on key 'net.ipv6.route.flush'
net.nf_conntrack_max = 65536
– Check the current sysctl nf_conntrack active connections
To check present connection tracking opened on a system:
:
linux:~# /sbin/sysctl net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_count
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_count = 12742
The shown connections are assigned dynamicly on each new succesful TCP / IP NAT-ted connection. Btw, on a systems that work normally without the dmesg log being flooded with the message, the output of lsmod is:
linux:~# /sbin/lsmod | egrep 'ip_tables|conntrack'
ip_tables 9899 1 iptable_filter
x_tables 14175 1 ip_tables
On servers which are encountering nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet error, you can see, when issuing lsmod, extra modules related to nf_conntrack are shown as loaded:
linux:~# /sbin/lsmod | egrep 'ip_tables|conntrack'
nf_conntrack_ipv4 10346 3 iptable_nat,nf_nat
nf_conntrack 60975 4 ipt_MASQUERADE,iptable_nat,nf_nat,nf_conntrack_ipv4
nf_defrag_ipv4 1073 1 nf_conntrack_ipv4
ip_tables 9899 2 iptable_nat,iptable_filter
x_tables 14175 3 ipt_MASQUERADE,iptable_nat,ip_tables
II. Remove completely nf_conntrack support if it is not really necessery
It is a good practice to limit or try to omit completely use of any iptables NAT rules to prevent yourself from ending with flooding your kernel log with the messages and respectively stop your system from dropping connections.
Another option is to completely remove any modules related to nf_conntrack, iptables_nat and nf_nat.
To remove nf_conntrack support from the Linux kernel, if for instance the system is not used for Network Address Translation use:
/sbin/rmmod iptable_nat
/sbin/rmmod ipt_MASQUERADE
/sbin/rmmod rmmod nf_nat
/sbin/rmmod rmmod nf_conntrack_ipv4
/sbin/rmmod nf_conntrack
/sbin/rmmod nf_defrag_ipv4
Once the modules are removed, be sure to not use iptables -t nat .. rules. Even attempt to list, if there are any NAT related rules with iptables -t nat -L -n will force the kernel to load the nf_conntrack modules again.
Btw nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet. message is observable across all GNU / Linux distributions, so this is not some kind of local distribution bug or Linux kernel (distro) customization.
III. Fixing the nf_conntrack … dropping packets error
– One temporary, fix if you need to keep your iptables NAT rules is:
linux:~# sysctl -w net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=131072
I say temporary, because raising the nf_conntrack_max doesn't guarantee, things will get smoothly from now on.
However on many not so heavily traffic loaded servers just raising the net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=131072 to a high enough value will be enough to resolve the hassle.
– Increasing the size of nf_conntrack hash-table
The Hash table hashsize value, which stores lists of conntrack-entries should be increased propertionally, whenever net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max is raised.
linux:~# echo 32768 > /sys/module/nf_conntrack/parameters/hashsize
The rule to calculate the right value to set is:
hashsize = nf_conntrack_max / 4
– To permanently store the made changes ;a) put into /etc/sysctl.conf:
linux:~# echo 'net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_count = 131072' >> /etc/sysctl.conf
linux:~# /sbin/sysct -p
b) put in /etc/rc.local (before the exit 0 line):
echo 32768 > /sys/module/nf_conntrack/parameters/hashsize
Note: Be careful with this variable, according to my experience raising it to too high value (especially on XEN patched kernels) could freeze the system.
Also raising the value to a too high number can freeze a regular Linux server running on old hardware.
– For the diagnosis of nf_conntrack stuff there is ;
/proc/sys/net/netfilter kernel memory stored directory. There you can find some values dynamically stored which gives info concerning nf_conntrack operations in "real time":
linux:~# cd /proc/sys/net/netfilter
linux:/proc/sys/net/netfilter# ls -al nf_log/
total 0
dr-xr-xr-x 0 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 ./
dr-xr-xr-x 0 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 10
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 11
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 12
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 3
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 5
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 6
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 7
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 23 23:02 9
IV. Decreasing other nf_conntrack NAT time-out values to prevent server against DoS attacks
Generally, the default value for nf_conntrack_* time-outs are (unnecessery) large.
Therefore, for large flows of traffic even if you increase nf_conntrack_max, still shorty you can get a nf_conntrack overflow table resulting in dropping server connections. To make this not happen, check and decrease the other nf_conntrack timeout connection tracking values:
linux:~# sysctl -a | grep conntrack | grep timeout
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_generic_timeout = 600
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_sent = 120
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_recv = 60
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 432000
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_last_ack = 30
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close = 10
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_max_retrans = 300
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_unacknowledged = 300
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_udp_timeout = 30
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_udp_timeout_stream = 180
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_icmp_timeout = 30
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_events_retry_timeout = 15
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_generic_timeout = 600
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_sent = 120
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_sent2 = 120
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_recv = 60
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 432000
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_last_ack = 30
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close = 10
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_max_retrans = 300
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_udp_timeout = 30
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_udp_timeout_stream = 180
net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_icmp_timeout = 30
All the timeouts are in seconds. net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_generic_timeout as you see is quite high – 600 secs = (10 minutes).
This kind of value means any NAT-ted connection not responding can stay hanging for 10 minutes!
The value net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 432000 is quite high too (5 days!)
If this values, are not lowered the server will be an easy target for anyone who would like to flood it with excessive connections, once this happens the server will quick reach even the raised up value for net.nf_conntrack_max and the initial connection dropping will re-occur again …
With all said, to prevent the server from malicious users, situated behind the NAT plaguing you with Denial of Service attacks:
Lower net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_generic_timeout to 60 – 120 seconds and net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established to stmh. like 54000
linux:~# sysctl -w net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_generic_timeout = 120
linux:~# sysctl -w net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 54000
This timeout should work fine on the router without creating interruptions for regular NAT users. After changing the values and monitoring for at least few days make the changes permanent by adding them to /etc/sysctl.conf
linux:~# echo 'net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_generic_timeout = 120' >> /etc/sysctl.conf
linux:~# echo 'net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 54000' >> /etc/sysctl.conf




 Screenshot of my installed list of Joomla Language Packs (Multi-Language setup)
Screenshot of my installed list of Joomla Language Packs (Multi-Language setup)