If you don't have tried it yet Redhat and CentOS and other RPM based Linux operationg systems that use anaconda installer is generating a kickstart file after being installed under /root/{anaconda-ks.cfg,initial-setup- ks.cfg,original-ks.cfg} immediately after the OS installation completes. Using this Kickstart file template you can automate installation of Redhat installation with exactly the same configuration as many times as you like by directly loading your /root/original-ks.cfg file in RHEL installer.
Here is the official description of Kickstart files from Redhat:
"The Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation process automatically writes a Kickstart file that contains the settings for the installed system. This file is always saved as /root/anaconda-ks.cfg. You may use this file to repeat the installation with identical settings, or modify copies to specify settings for other systems."
Kickstart files contain answers to all questions normally asked by the text / graphical installation program, such as what time zone you want the system to use, how the drives should be partitioned, or which packages should be installed. Providing a prepared Kickstart file when the installation begins therefore allows you to perform the installation automatically, without need for any intervention from the user. This is especially useful when deploying Redhat based distro (RHEL / CentOS / Fedora …) on a large number of systems at once and in general pretty useful if you're into the field of so called "DevOps" system administration and you need to provision a certain set of OS to a multitude of physical servers or create or recreate easily virtual machines with a certain set of configuration.
1. Create /vmprivate storage directory where Virtual machines will reside
First step on the Hypervisor host which will hold the future created virtual machines is to create location where it will be created:
[root@redhat ~]# lvcreate –size 140G –name vmprivate vg00
[root@redhat ~]# mkfs.ext4 -j -b 4096 /dev/mapper/vg00-vmprivate
[root@redhat ~]# mount /dev/mapper/vg00-vmprivate /vmprivate
To view what is the situation with Logical Volumes and VG group names:
[root@redhat ~]# vgdisplay -v|grep -i vmprivate -A7 -B7
Segments 1
Allocation inherit
Read ahead sectors auto
– currently set to 8192
Block device 253:0
— Logical volume —
LV Path /dev/vg00/vmprivate
LV Name vmprivate
VG Name vg00
LV UUID VVUgsf-FXq2-TsMJ-QPLw-7lGb-Dq5m-3J9XJJ
LV Write Access read/write
LV Creation host, time main.hostname.com, 2021-01-20 17:26:11 +0100
LV Status available
# open 1
LV Size 150.00 GiB
Note that you'll need to have the size physically available on a SAS / SSD Hard Drive physically connected to Hypervisor Host.
To make the changes Virtual Machines storage location directory permanently mounted add to /etc/fstab
/dev/mapper/vg00-vmprivate /vmprivate ext4 defaults,nodev,nosuid 1 2
[root@redhat ~]# echo '/dev/mapper/vg00-vmprivate /vmprivate ext4 defaults,nodev,nosuid 1 2' >> /etc/fstab
2. Second we need to install the following set of RPM packages on the Hypervisor Hardware host
[root@redhat ~]# yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img libvirt virt-install libvirt-client virt-manager libguestfs-tools virt-install virt-top -y
3. Enable libvirtd on the host
[root@redhat ~]# lsmod | grep -i kvm
[root@redhat ~]# systemctl enable libvirtd
4. Configure network bridging br0 interface on Hypervisor
In /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 you need to include:
NM_CONTROLED=NO
Next use nmcli redhat configurator to create the bridge (you can use ip command instead) but since the tool is the redhat way to do it lets do it their way ..
[root@redhat ~]# nmcli connection delete eno3
[root@redhat ~]# nmcli connection add type bridge autoconnect yes con-name br0 ifname br0
[root@redhat ~]# nmcli connection modify br0 ipv4.addresses 10.80.51.16/26 ipv4.method manual
[root@redhat ~]# nmcli connection modify br0 ipv4.gateway 10.80.51.1
[root@redhat ~]# nmcli connection modify br0 ipv4.dns 172.20.88.2
[root@redhat ~]# nmcli connection add type bridge-slave autoconnect yes con-name eno3 ifname eno3 master br0
[root@redhat ~]# nmcli connection up br0
5. Prepare a working kickstart.cfg file for VM
Below is a sample kickstart file I've used to build a working fully functional Virtual Machine with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.3 (Ootpa) .
#version=RHEL8 #install # Run the Setup Agent on first boot firstboot --enable ignoredisk --only-use=vda # Use network installation #url --url=http://hostname.com/rhel/8/BaseOS ##url --url=http://171.23.8.65/rhel/8/os/BaseOS # Use text mode install text #graphical # System language #lang en_US.UTF-8 keyboard --vckeymap=us --xlayouts='us' # Keyboard layouts ##keyboard us lang en_US.UTF-8 # Root password rootpw $6$gTiUCif4$YdKxeewgwYCLS4uRc/XOeKSitvDJNHFycxWVHi.RYGkgKctTMCAiY2TErua5Yh7flw2lUijooOClQQhlbstZ81 --iscrypted # network-stuff # place ip=your_VM_IP, netmask, gateway, nameserver hostname network --bootproto=static --ip=10.80.21.19 --netmask=255.255.255.192 --gateway=10.80.21.1 --nameserver=172.30.85.2 --device=eth0 --noipv6 --hostname=FQDN.VMhost.com --onboot=yes # if you need just localhost initially configured uncomment and comment above ##network В --device=lo --hostname=localhost.localdomain # System authorization information authconfig --enableshadow --passalgo=sha512 --enablefingerprint # skipx skipx # Firewall configuration firewall --disabled # System timezone timezone Europe/Berlin # Clear the Master Boot Record ##zerombr # Repositories ## Add RPM repositories from KS file if necessery #repo --name=appstream --baseurl=http://hostname.com/rhel/8/AppStream #repo --name=baseos --baseurl=http://hostname.com/rhel/8/BaseOS #repo --name=inst.stage2 --baseurl=http://hostname.com ff=/dev/vg0/vmprivate ##repo --name=rhsm-baseos В В --baseurl=http://172.54.8.65/rhel/8/rhsm/x86_64/BaseOS/ ##repo --name=rhsm-appstream --baseurl=http://172.54.8.65/rhel/8/rhsm/x86_64/AppStream/ ##repo --name=os-baseos В В В --baseurl=http://172.54.9.65/rhel/8/os/BaseOS/ ##repo --name=os-appstream В --baseurl=http://172.54.8.65/rhel/8/os/AppStream/ #repo --name=inst.stage2 --baseurl=http://172.54.8.65/rhel/8/BaseOS # Disk partitioning information set proper disk sizing ##bootloader --location=mbr --boot-drive=vda bootloader --append=" crashkernel=auto tsc=reliable divider=10 plymouth.enable=0 console=ttyS0 " --location=mbr --boot-drive=vda # partition plan zerombr clearpart --all --drives=vda --initlabel part /boot --size=1024 --fstype=ext4 --asprimary part swap --size=1024 part pv.01 --size=30000 --grow --ondisk=vda ##part pv.0 --size=80000 --fstype=lvmpv #part pv.0 --size=61440 --fstype=lvmpv volgroup s pv.01 logvol / --vgname=s --size=15360 --name=root --fstype=ext4 logvol /var/cache/ --vgname=s --size=5120 --name=cache --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,nosuid" logvol /var/log --vgname=s --size=7680 --name=log --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,noexec,nosuid" logvol /tmp --vgname=s --size=5120 --name=tmp --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,nosuid" logvol /home --vgname=s --size=5120 --name=home --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,nosuid" logvol /opt --vgname=s --size=2048 --name=opt --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,nosuid" logvol /var/log/audit --vgname=s --size=3072 --name=audit --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,nosuid" logvol /var/spool --vgname=s --size=2048 --name=spool --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,nosuid" logvol /var --vgname=s --size=7680 --name=var --fstype=ext4 --fsoptions="defaults,nodev,nosuid" # SELinux configuration selinux --disabled # Installation logging level logging --level=debug # reboot automatically reboot ### %packages @standard python3 pam_ssh_agent_auth -nmap-ncat #-plymouth #-bpftool -cockpit #-cryptsetup -usbutils #-kmod-kvdo #-ledmon #-libstoragemgmt #-lvm2 #-mdadm -rsync #-smartmontools -sos -subscription-manager-cockpit # Tune Linux vm.dirty_background_bytes (IMAGE-439) # The following tuning causes dirty data to begin to be background flushed at # 100 Mbytes, so that it writes earlier and more often to avoid a large build # up and improving overall throughput. echo "vm.dirty_background_bytes=100000000" >> /etc/sysctl.conf # Disable kdump systemctl disable kdump.service %end
Important note to make here is the MD5 set root password string in (rootpw) line this string can be generated with openssl or mkpasswd commands :
Method 1: use openssl cmd to generate (md5, sha256, sha512) encrypted pass string
[root@redhat ~]# openssl passwd -6 -salt xyz test
$6$xyz$rjarwc/BNZWcH6B31aAXWo1942.i7rCX5AT/oxALL5gCznYVGKh6nycQVZiHDVbnbu0BsQyPfBgqYveKcCgOE0
Note: passing -1 will generate an MD5 password, -5 a SHA256 encryption and -6 SHA512 encrypted string (logically recommended for better security)
Method 2: (md5, sha256, sha512)
[root@redhat ~]# mkpasswd –method=SHA-512 –stdin
The option –method accepts md5, sha-256 and sha-512
Theoretically there is also a kickstart file generator web interface on Redhat's site here however I never used it myself but instead use above kickstart.cfg
6. Install the new VM with virt-install cmd
Roll the new preconfigured VM based on above ks template file use some kind of one liner command line like below:
[root@redhat ~]# virt-install -n RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine –description "CentOS 8.3 Virtual Machine" –os-type=Linux –os-variant=rhel8.3 –ram=8192 –vcpus=8 –location=/vmprivate/rhel-server-8.3-x86_64-dvd.iso –disk path=/vmprivate/RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine.img,bus=virtio,size=70 –graphics none –initrd-inject=/root/kickstart.cfg –extra-args "console=ttyS0 ks=file:/kickstart.cfg"
7. Use a tiny shell script to automate VM creation
For some clarity and better automation in case you plan to repeat VM creation you can prepare a tiny bash shell script:
#!/bin/sh
KS_FILE='kickstart.cfg';
VM_NAME='RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine';
VM_DESCR='CentOS 8.3 Virtual Machine';
RAM='8192';
CPUS='8';
# size is in Gigabytes
VM_IMG_SIZE='140';
ISO_LOCATION='/vmprivate/rhel-server-8.3-x86_64-dvd.iso';
VM_IMG_FILE_LOC='/vmprivate/RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine.img';virt-install -n "$VMNAME" –description "$VM_DESCR" –os-type=Linux –os-variant=rhel8.3 –ram=8192 –vcpus=8 –location="$ISO_LOCATION" –disk path=$VM_IMG_FILE,bus=virtio,size=$IMG_VM_SIZE –graphics none –initrd-inject=/root/$KS_FILE –extra-args "console=ttyS0 ks=file:/$KS_FILE"
A copy of virt-install.sh script can be downloaded here
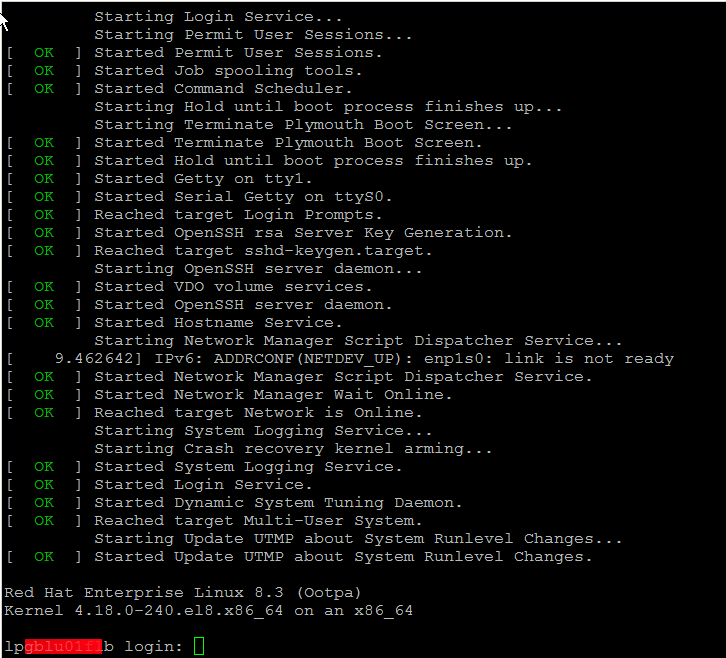
Wait for the installation to finish it should be visualized and if all installation is smooth you should get a login prompt use the password generated with openssl tool and test to login, then disconnect from the machine by pressing CTRL + ] and try to login via TTY with
[root@redhat ~]# virst list –all
Id Name State
—————————
2 RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine running…
[root@redhat ~]# virsh console RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine
One last thing I recommend you check the official documentation on Kickstart2 from CentOS official website
In case if you later need to destroy the VM and the respective created Image file you can do it with:
[root@redhat ~]# virsh destroy RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine
[root@redhat ~]# virsh undefine RHEL8_3-VirtualMachine
Don't forget to celebreate the success and give this nice article a credit by sharing this nice tutorial with a friend or by placing a link to it from your blog 🙂
Enjoy !