Since I've bought ZTE smat phone and I have Android on it, decided to install Viber – iOS, Android and Desktop PC – Free Calls, Text and Picture sharing through the internet app. Viber is used by a lot of my people including many friends already so I installed it as well to be possible to speak for free with close friends …
Why Viber?
What makes this nifty app so great is its capability to make free calls over mobile phones through the Internet Viber.
Viber saves you a lot of money as calls are handled only through the Internet (you need Wifi on your mobile or Mobile 3G Internet access on phone) and you don't need to pay to your mobile operator 0.10 – 0.15 euro / cents per minute. Besides being Free another advantage of Viber is conversations sound quality which is much better than a regular phone call
Viber doesn't need a special registration, but as (login) identificator uses your mobile phone number – you just need to have a working Mobile operator phone num. Once registered under a number even if you change your mobile sim card to other operator (for example moving from country to country) still the Viber account will continue work. Another good reason to use Viber is it makes possible price free calls between different countries (for example if you travel a lot and you want to regularly speak with your wife) – in my case right now I'm in Bulgaria and my wife is in Belarus, so to save money and keep talking daily we use Viber daily.
What Devices and Operating System Viber Supports and what is Viber advantages / disadvantages ?
Another reason why Viber is so great is its multi-platform support it works on iPhone, Blackberry, Windows Phone, Nokia (Symbian), Windows, Mac OS and even (Korean own OS-ed) Bada devices. Some might argue that Viber is inferior to Skype and interms of Voice and Video quality its better because of its enhanced HD voice enhanced codecs, besides that Viber's video is still in Beta. However Viber has one big advantage it makes easy possible to reach people using just their Mobile Phone numbers where in Skype it takes time and effort to register in Skype install application on your Mobile keep yourself logged in in Skype and have all contacts previously added, all this happens automatically in Viber in time of installation of Viber App on your mobile.
Which Is Cheaper Viber or Skype?
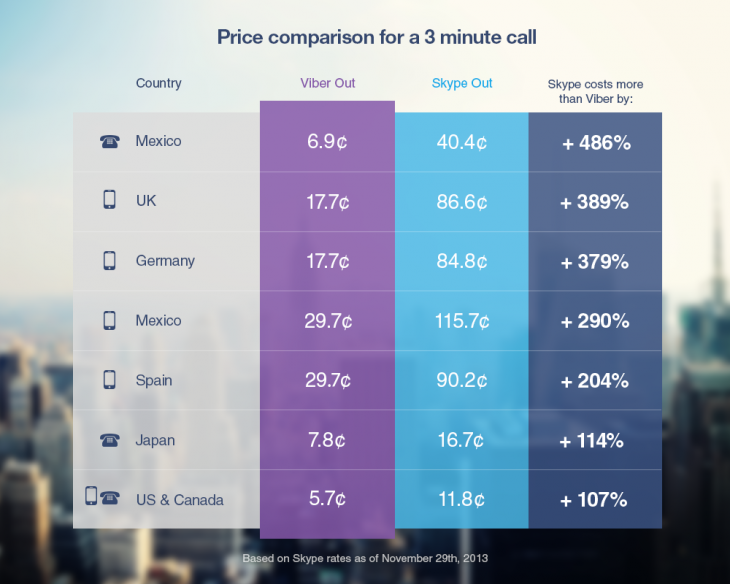
Once installed Viber could integrate itself with rest of your Mobile OS Call Manager and in time of call a friend number you have the opportunity to make it free Viber call. Viber are also selling Viber Credits so if you want to use your Viber Voice Over IP you can call external mobile operator numbers on a very very cheap price. Viber Calls to landline or mobile phones could be up to 400% cheaper than Skype! Whether you own a Smartphone it will be nice to give Viber a try.
Viber – How to make Phone calls between Desktop PC and Smarphone Mobile
One not so standard Viber use is to make Viber calls with no smartphone (at hand) from PC to another Viber equipped Mobile and vice versa.
I needed to make Viber calls from my ZTE Android running mobile to my wife's MacBook Air PC because her mobile is an old Nokia running obscure Symbian version which is not supporting Viber + she doesn't have an Internet access tariff switched on her mobile.
Here is what I had to do to make Phone calls between my Mobile Viber App and my wife's MacbookAir Notebook PC:
- Install BlueStacks Web App Player

BlueStacks App Player is a software designed to enable Android applications to run on Windows PC, Apple Macintosh Computers and Windows tablets. BlueStacks is something like (VMware, Qemu) Virtual Machine which allows you to install and run any Android App on your Desktop PC.
Its curious that app was created by Rosen Sharma in 2008 an ex CTO (Chief Technology Officer) of McAfee
- A mobile phone with a working SIM card (Nokia 6310 or any old mobile no need to be a smartphone
- Desktop PC with Windows 7, 8 or PC with Mac OS
- Working Google Account (Gmail etc.)
- Install Native Viber for Windows or Mac OS
Install Bluestacks
BlueStacks is needed in order to emulate a smartphone on your PC, therefore once setupped Bluestacks. Launch it and inside its necessary to login with your Gmail (Google Account) in order to allow access to Google Play Appstore on your PC.
viber with no mobile phone bluestacks
Installing and Verifying Viber
This is the most crucial and tricky part in order to make Viber working on any device you need to receive a special Viber verification code, you need to fill in this code to confirm Viber installation on PC. Here I assume you have BlueStacks running with Viber Application installed.
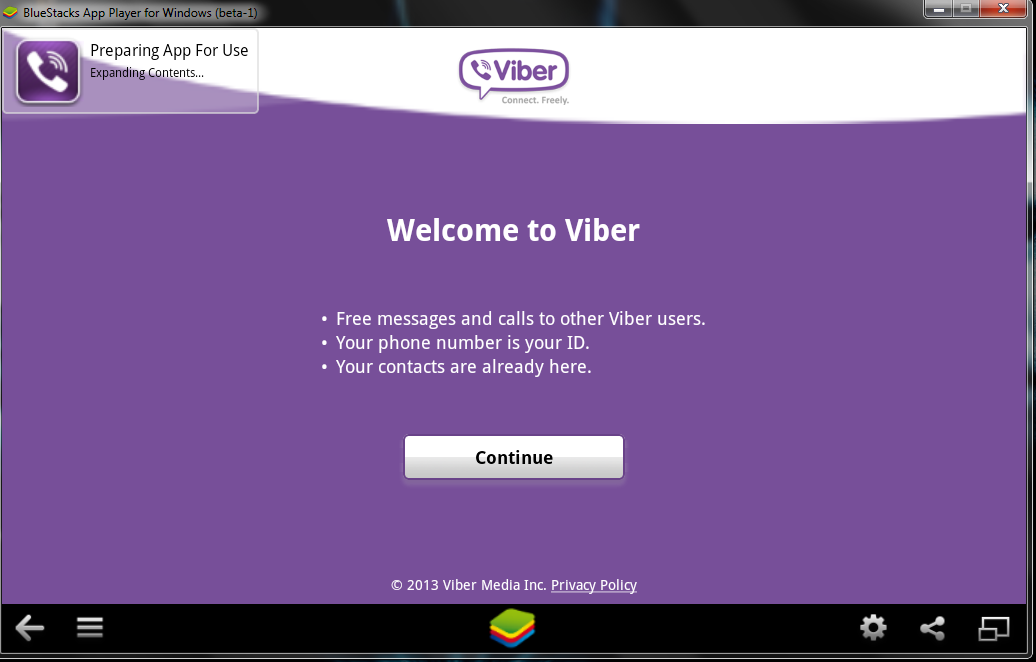
First will be prompted to Agree with Terms and Conditions and provide Mobile Phone number for verification. Tell the Viber app that you have a smartphone with Viber already when prompted. After receving Viber Verification Code you need to fill in this code into BlueStacks Window (inside Viber should be running), go further to next step and you should be done with Desktop PC Viber number registration.
N.B. ! One brackets to open here is you need to have a working Mobile Phone number where you will receive the verification code as SMS, otherwise you cannot get the verification. On your filled in mobile phone number you will get the verification code as SMS.
Making Viber Calls to (Windows Mac) PC without Smartphone
There is no more further need for BlueStacks so you can uninstall it, however I preferred to keep it as its useful to be able to install Android Applications straight on your Desktop PC. To start using Viber on Desktop, just launch Viber application (not through BlueStacks) but the direct install.
Use Viber dial pad to dial your desired remote Smartphone number with Viber equipped.
Enjoy the free Internet calls ! 🙂

 I remember GNU / Linux, 11 years from now, times when ALSA was not standardly shipped with Linux.
I remember GNU / Linux, 11 years from now, times when ALSA was not standardly shipped with Linux.