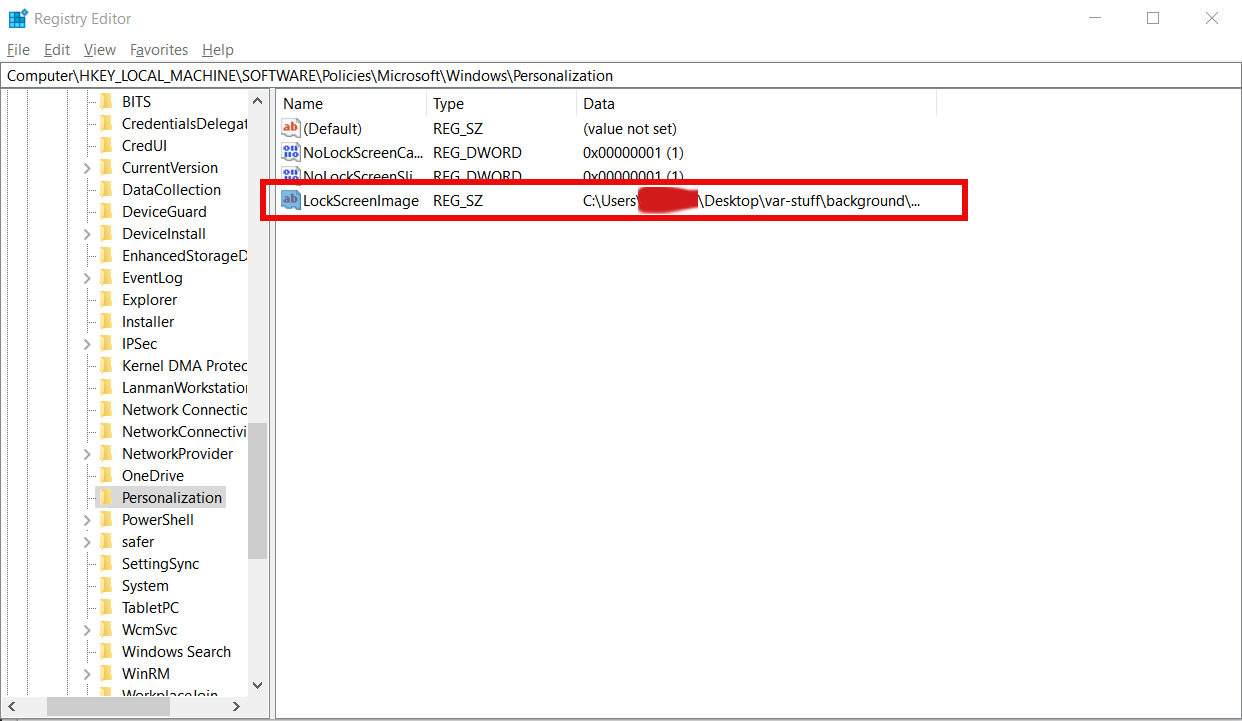
I've started to work as a External Consultant for Equens Worldline, who lately merged with Atos – a French multinational information technology.
As the company is mostly into the financial business and as any company that is involved with OLTP Online transaction processing , an information systems that typically facilitate and manage transaction-oriented applications, e.g. in a mortal language takes care for a numerous companies Credit / Debit card online payments.
Of course the technologies used both on a Server / Data Center level and for Employee personal used are a bit old fashioned. In that relation, most of the computers, I've seen used by Worldline – Atos including my work PC notebook is still running a custom version of Windows 7.
Once I had the Computer ready with the OS from the HelpDesk colleague, then it was ready to install, unfortunately, I didn't have administrator account on the Lenovo L serie laptop so I couldn't install applications. To get around this I've used PortableApps – the world's most popular portable software solution allowing you to take your favorite software with you with no need for any Installation and on Win OS computers, where you have limited access.
PortableApps is fully open source and free platform, it works from any synced cloud folder (DropBox, Google Drive, Box, etc), from your local PC on an internal or external drive, or on any portable storage device (USB flash drive, memory card, portable hard drive, etc). Because the applicatons are installed without being really binded to the Win OS, once the PortableApps ported Application is installed it can be easily moved by simply copying between PCs.
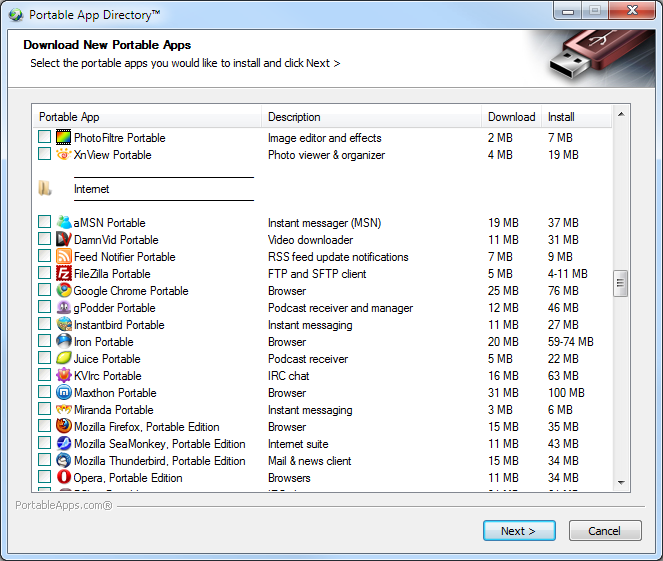
PortableApps.com is currently used by millions of users all over the world and is the Largest Portable full collection of open source and freeware software, compatible commercial software, and partners in hardware industry for Microsoft Windows.
As I do often with the Windows fresh installed Windows machines I have to work on, install the great set of tools prior described in must have software on any fresh installed Windows OS as this is essential if you're a sysadmin or Advanced user for the daily work with the WinBlows
OS Graphical Interface simplicity is a crucial thing to me, cause if I have to work with Windows and spendan 8 hours each day 5 days a week in front of the Computer Display with this Complex unnecessery coloring (that Windows 7 / Windows 10 default Theme introduced), together with the visual aids on the Window Minimize and Maximize, puts a useless additional eye strain and besides that "fries" the brain (as the brain has to process all this mambo-jambo "virtual" reality graphics turning all down and up and mixing up the gamma of unreal colors for nothing …
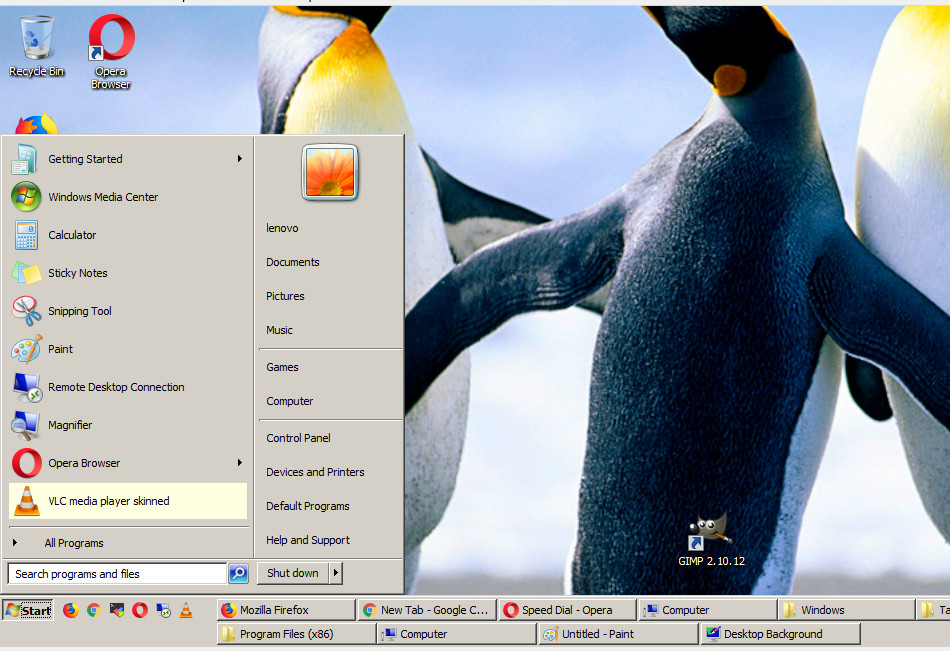
So far so good I've set the needed software from above list and continued further to Change my Windows start menu to look like Windows 2000. Start menu and Theme To be the Classic Theme.
After setting up the Windows Classic Theme (which by the way is unfortunately, no longer available in Windows 10), I love to set my Windows Background picture to be a Sold Black Color, I do this as Black color is the less exhausting for the eyes – as one views the desktop picture thousand times and this is extra unnecessery work for the brain.
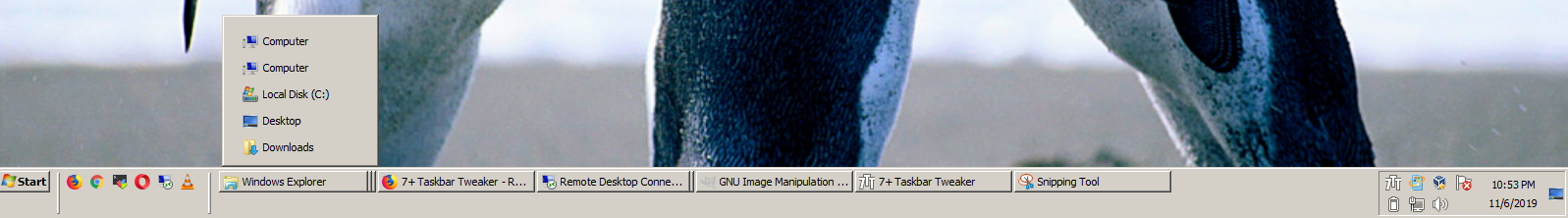
However next, unpleasant thing faced is even though now my Windows Start and Windows borders looked old-fashioned in the Windows 2000 Server, "wooden" style, the order of my (Open) Running applicaitons on the start menu bar were not isolated but were mixing, with the rest of my Pinned Program Starter icons
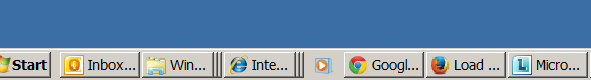
! Notice the Windows Media player icon being in the middle between the Lync, Firefox, Chrome and Internet Explorer line … !
I spend some time to rewind some memories on how I did make the pinned program to distinguish itself (separate) from the rest of the Opened Runnign Windows, and had in mind that I used some kind of separator added custom Toolbar, but the bad thing was I couldn't remember exactly how so I spend some good amount of time to Google around.
And found few articles on the topic proposing to add a new Custom empty launcher program of cmd.exe and change the icon of the empty launcher to a | graphical string
I've tried a lot of this approach but it didn't work and after some experimentations, finally I figured it out. The way to do it is to add a New Toolbar that is Pointing to a Directory with a list of Programs whose icons you want to have listed with icon launchers next to Start menu.
Here is step by step what I've done to achieve configuration of Hard Separator Delimiter between my Program Launchers and Running Applications.
1. Create a New Folder somewhere under your User Home directory, lets say:
C:\Users\Username\TaskbarPrograms
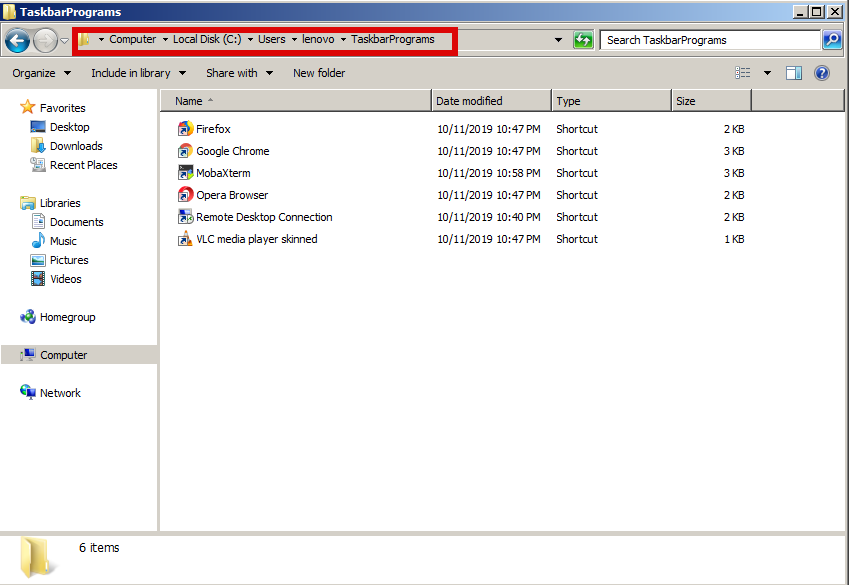
2. Add a shortcut or copy the programs starters (icons) to the TaskBar Programs
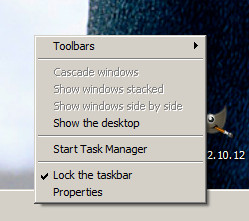
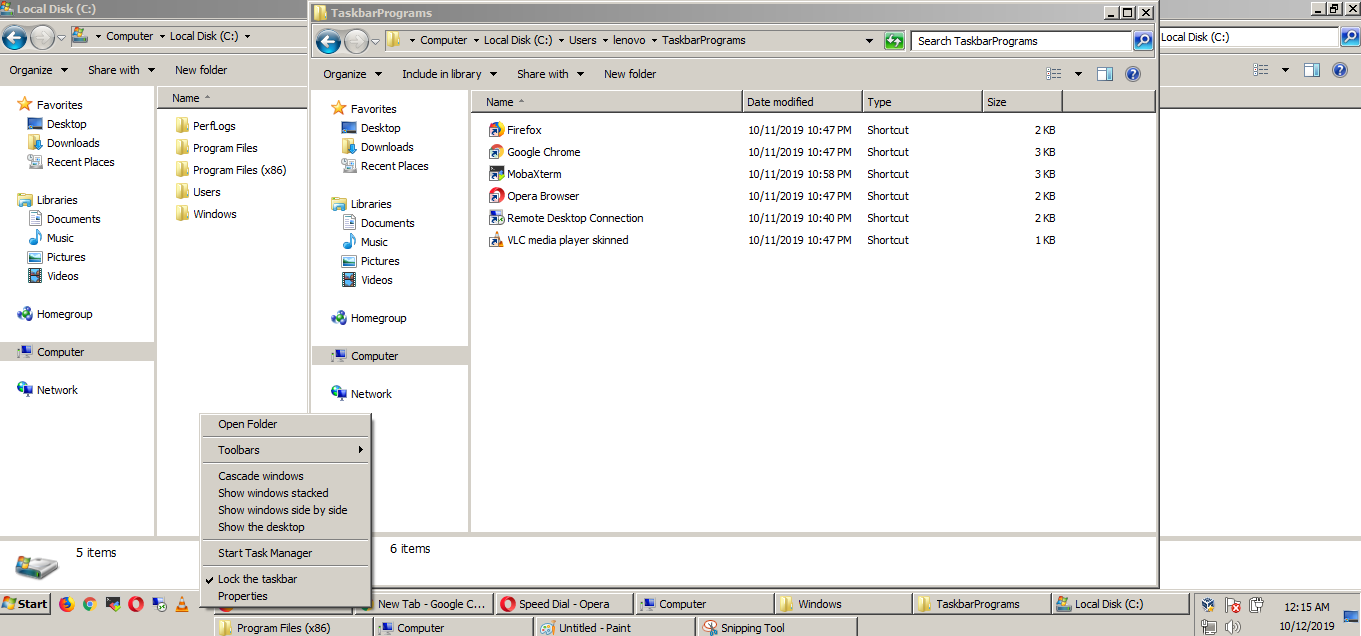
3. Unlock the Windows 7 Taskbar
E.g. Click over on any of the empty space on the taskbar after Windows Start menu button and untick Lock the Taskbar
4. Remove any Pinned programs (you have placed there earlier)
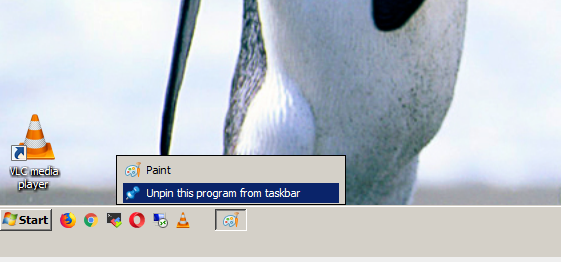
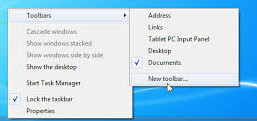
5. Again On an empty place on the Taskbar press the last button Mouse (Rightest button) to open Taskbar properties menu and
Go to ToolBars menu and Choose (New Toolbar)
6. As a location for the new toolbar place C:\Users\Username\TaskbarPrograms
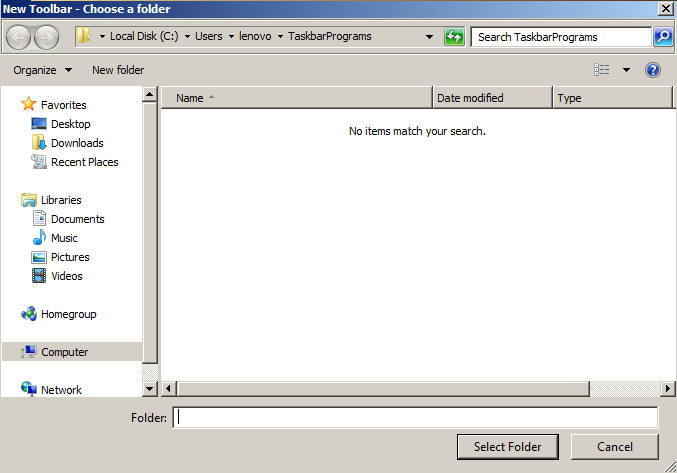
The result should be that all the programs in the selected folder will appear in the Windows pane
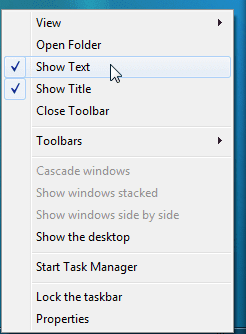
8. Now go over the empty space of the Windows start menu bar
and untick Show Text / Show Title
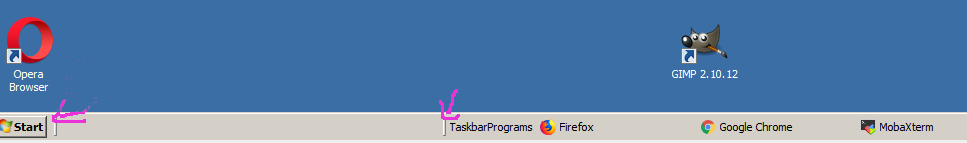
9. Hold over the Taskbar Programs holder and drag and drop it constantly holding the left mouse button
and place it over the default separator Holder (for clarity marked in below screenshot as Marked over here).
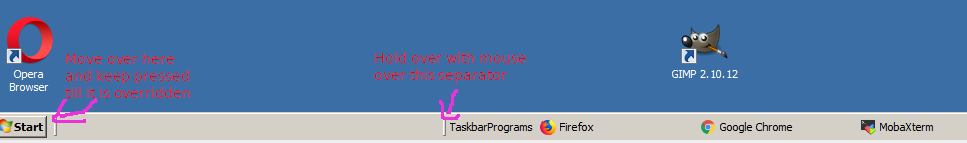
10. Move the default separator that will appear on the left close to the list of shown applications
(shown in screenshot)

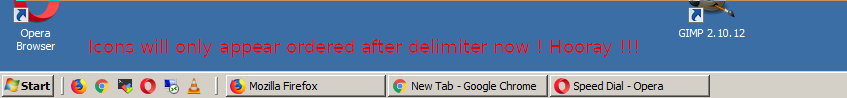
11. Open any of the applications (e.g. Firefox, Chrome, MobaXterm, Opera, RDP, VLC) the result should be a fine ordered icons. Hooray !!!
12. To make more space for the Opened Active (Running) Windows, a good hint is to stretch the start menu pane field – this is done by holding a right mouse button on the edge of the gray line, like shown in below screenshot.
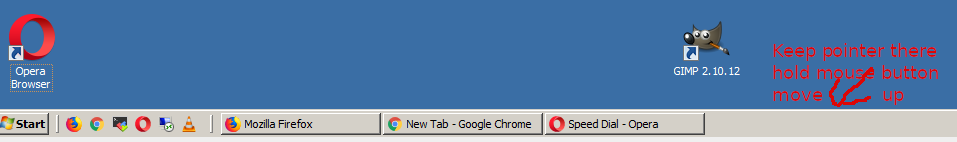
Note that, you will need to remove any icons that are left over binded to the default separator (holder).
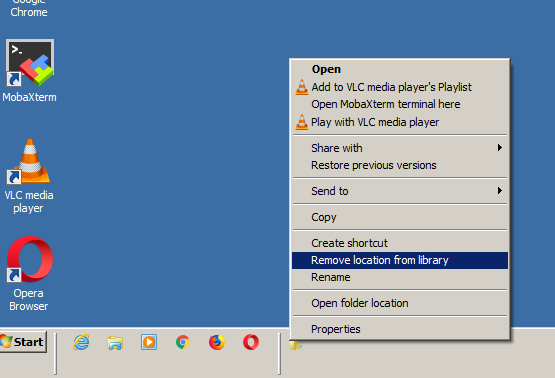
13. Finally on the Taskbar (empty space) menu with the Mouse, click again right mouse button and tick on the Lock the Taskbar
That's it now your Windows 7 start menu bar will look pretty much like Linux's GNOME 2.x and GNOME Mate, and if you're a a long years Linux Desktop user you will feel at home even on Windows 7.
To further tweak the Taskbar a very useful Program is Windows 7+ Taskbar Tweaker
"7+ Taskbar Tweaker allows you configure various aspects of the Windows taskbar which can't be tweaked via registry or taskbar properties. The tweaker is designed for Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, and Windows 10.
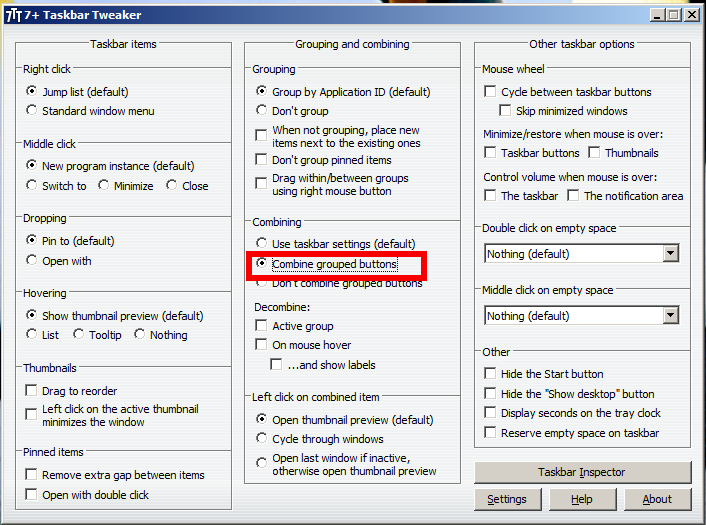
I install it mostly because one single feature Combined Grouped Buttons which makes similar Windows to group together. Just having a number of Windows of the same type floating around the Taskbar is really irritating and becomes really confusing once multiple windows.
For example if you have opened 10 Windows of Explorer they will be group under the same window title pointer.

To make the Windows even more bizarre and feel more like a Linux powered Box go on and install MobaXterm as a substitute for Linux's gnome-terminal as well as the rest of things such as CygWin / GNUWin32 / GVim etc.
Also some good start up list of software I do install on new Windows Desktop PCs is described in my previous article Some standard software programs to install on Windows to make your Windows feel more like a Linux / Unix Desktop host
This time I did not needed that but on other locations another Windows useful hint I use every now and then is to set some custom programs (Lets say a PortableApps program) to Automatically run – described earlier in my earlier article how to add startup Windows 7 / 8 program run on startup.
P.S. I've tried to setup the same Classic Theme and Start menu button with the same order on Windows 10 OS, but even though a similar interface could be achieved, I've had problems with setting up the proper Running application Ordering, due to a different behavior of the Delimiter / Separators in Windows 10.
For me this Custom Windows interface and Window ordering works pretty well it saves me a lot of the eye strain and brain overcalculation for nothing.
After all, Lets not forget that God is in the Simplicity ! 🙂
![]()