Saint Confessor Nikolay Sofijski (Nikolay of Sofia) Short Biography
![]()
St. Nikolay (Nicolas) of Sofia has been born in Ioannina (city now in territory of Greece). He was a pious and with his honorable craft of shoemaking going through the stormy sea of life. When he arrived in Sofia (Serdica / Sredetz), one of the main cities of the Ottoman Empire of that time, a long remain of the glorious past when even the righteous emperor Constantine The great was considering to set as a capital of the Eastern empire either Constantinople today's Istanbul in Turkey or Sofia (Fortress of Serdika).
When Nikolay came to Sofia, he was immediately recognized by the Turkish authorities and rich people of the city and to have him part of their "nobel" turkish society and enrich the city ruleship, the Turkish tried to push Nikolay to accept Islam.
Once a time Turkish invited Nikolay, put a somniferous herb in his offered drink and once he fall asleep without his knowledge they have circumcised him according to Islamic tradition observance.
Once awaken Nikolay realised what has been done to him and fall in a deep regret and mourned over the abuse of his body which according the Christian faith is a temple of the Holy Spirit. Once he started appearing on the streets of Sofia, Turkish immediately invited him to attend the mosque considering him already a muslim due to the circumcision ritual commited on him.
He firmly rejected the offer publicly, considering himself a Christian as he never publicly resigned his Christian faith and never ever wanted to be muslim and never ever has attended another temple apart from the Eastern Orthodox Christian Church he belonged to.
Facing the rejection, the powerful of the day turks cannot believe their eyes as they already thought Nikolay accepted the fact he is already a muslim, not understanding that for a Christian the temporary flesh is nothing but a temporary hut and the Spiritual and Eternal Soul and The Spirit of God which enlightens it as well as the Eternal Kingdom of Heaven is everything. The turks thouhgt over it fleshly, thinking that having a sign of circumcision already puts a person belonging to his faith, not knowing that the the first desciples of Christ, the most holy apostles as belonging to the Jewish faith had their circumcision themselves, and this circumcision never ever hindered their faith in the Resurrected Messiah Jesus Christ.
Immediately facing the rejecting the Turks, arrested him as a traitor of their faith and put him into a harsh torments.
![]()
![]()
Combined icon with the living of saint Nikolay of Sofia
Putting him on trial In the local court, the judge announced his opinion that Nikolay doesn't hold a fault, neither against Islam neither against the claimants.
Nevertheless the crowd put Nikolay outside of Sofia (in a similar way the Jews resurrected Christ outside of the city of Jerusalem) in Sofia's near region called "Yuch Bunar", translated from Turkish as the ("The Tree Wells"), there they stoned to death on 17th of May year 1555 A.D., (the stoning a transgressor of the Islamic law, tradition is still followed by some countries even today, for example I heard similar cases do happen still in Saudi Arabia for sinners against islamic law).
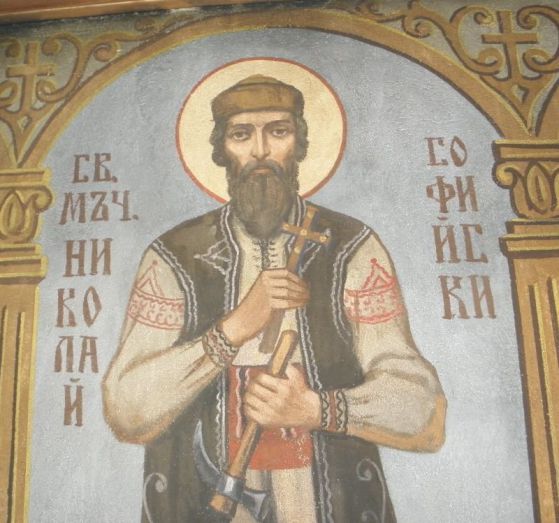

Saint Nikolay icon in his traditional Bulgarian clothes wear (Nosia)
holding his shoemaking instrument
His holy body has been moved to the graveyear called (Търница) Térnitza and has been burned – and the dust has been scattered through the four directions of the world North, East, South, West following islamic tradition and in attempt to completely irradicate the memory of the saint in the relatives and the living Christians of that time. Even though due to the request of Matey Gramatik (Mathew the Gramatik – translated as Chronicler / Annalist), a boy managed to collect little burned part remains of the relics and a pious christian, secretly made a burial prayer for his Soul (Опело – called Opelo in the Slavonic Eastern Orthodox Church) according to the Christian tradition and buried him with honor.
Soon after the martyrdom of saint Nikolay the New, the Metropolitan of Sredetz Iakov (Jacob), announced the canonization of st. Nikolay on a specially summoned for the consideration of saintship of St. Nikolay, a Local Church Metropolitan Council. Jacob received parts from holy relics (parts of the skull and the bones) of st. Nikolay, that has been secretly kept by a faithful Christians till then and placed the new received saint relics and placed them together in the ark (coffin) with the incorruptable holy relics of Saint King Stephan Milutin at that time located in Church of St. Archangel Michael, see my previous article pilgrimage to the incorruptable Holy relics of Saint Stephan Milutin in Cathedral Saint Nedelya, Sofia Bulgaria. Later parts of the holy relics has been housed in in a Wood maden Church.
The grave of saint Nikolay of Sofia is one of the few known graves of Bulgarian saints. Today, it is situated in the city center of Sofia capital city of Bulgaria in the district "Три кладенци" / "The Three Wells". Three hundred meters from there (in the tiny park like garden between the streets of "Pirotska" and "Opalchenska") lays a Beatiful Majestic Church, dedicated to the Holy Martyr st. Nikolay Sofijski. The Church of Saint Nicolas of Sofia is one of the biggest Cathedral Churches in Bulgaria (it is second by size in city of Sofia). The Temple has been rised following a project of architecture created by Anton Tornyov after the Liberation of Bulgarian following the Russian/Bulgarian-Turkish war on 3-rd of December 1900. Church saint Nikolay Sofijski has been consecrated by Metropolitan Partenij (Parthenius of Sofia was a senior Bulgarian clergyman and church figure, Metropolitan of Sofia from 1892 to 1918. Metropolitan Parthenius is an exceptional clergyman who has left a lasting mark in the history of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church.).
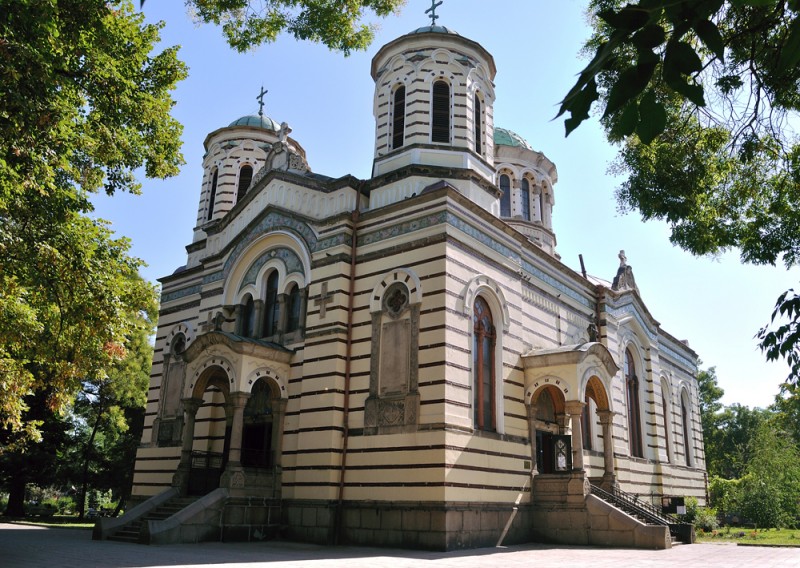

Church of Saint Nikolay of Sofia in Sofia Bulgaria (corner of street "Opalchenska" and "Pirotska").
![]()
Church Nikolay Sofijski view to Iconostasis Church interior
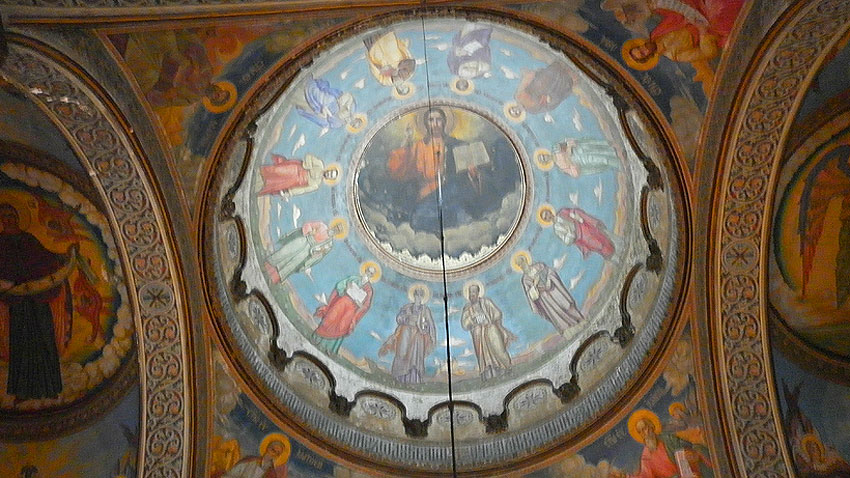

Church dome paintings of St. Nikolay Sofijski
![]()
Iconostasis of the Church (notice the beatiful flower forms curved wood)
In the beginning of XXth century in 1870s on the exact place of the grave of the saint has been built a small chapel in his memoriam. It is situated in a small yard on today's Street of "Tzar Simeon / King Simeon" it is opened for pilgrim visitors everyday in the early afternoon every working day.
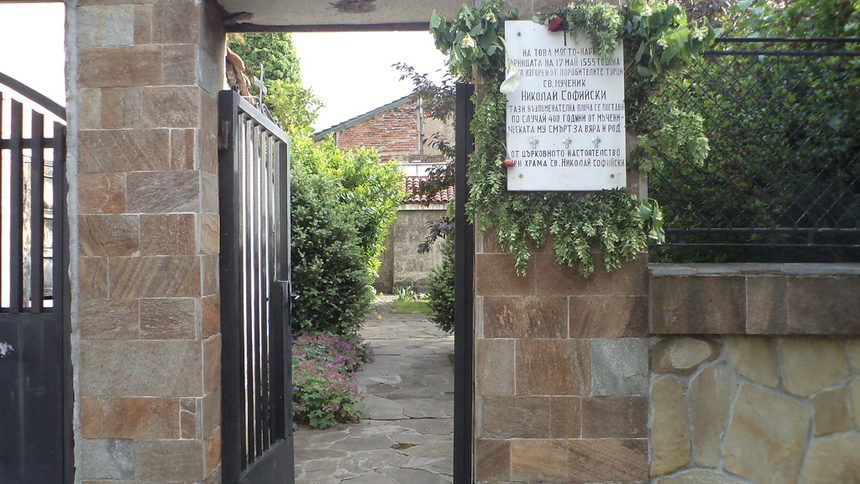

The Chapel entrance door
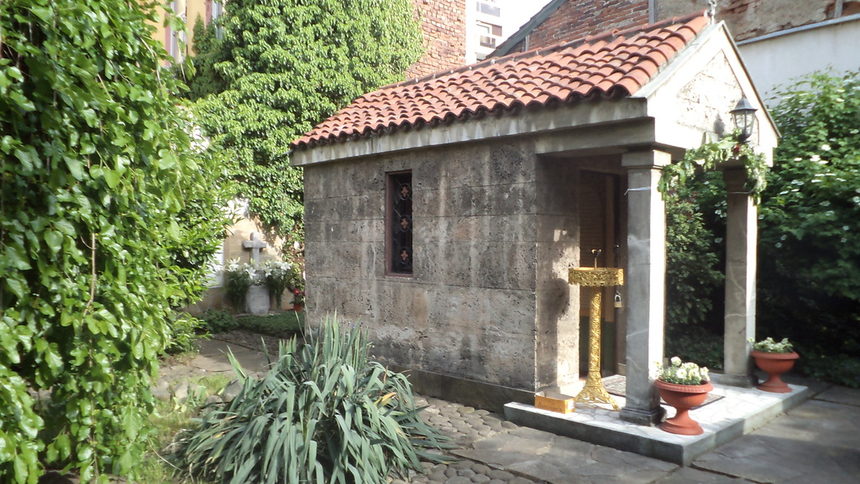

A Heavenly beauty roman like chapel
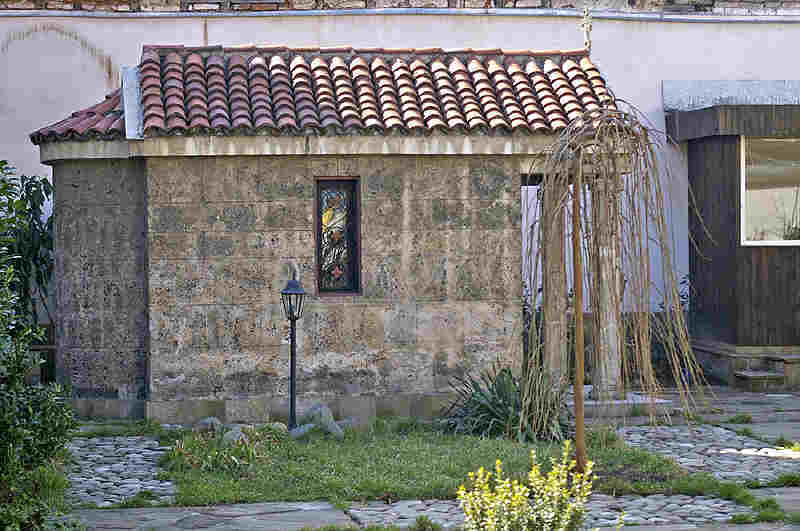

The Chapel on the grave of Saint Nikolas of Sofia, built on the place called "Terniza" (Tzar Simeon Street), where on 17-th of May, year 1555 A.D. where remains of the saint has been burned by turks – photo by Martin Mitov (C)
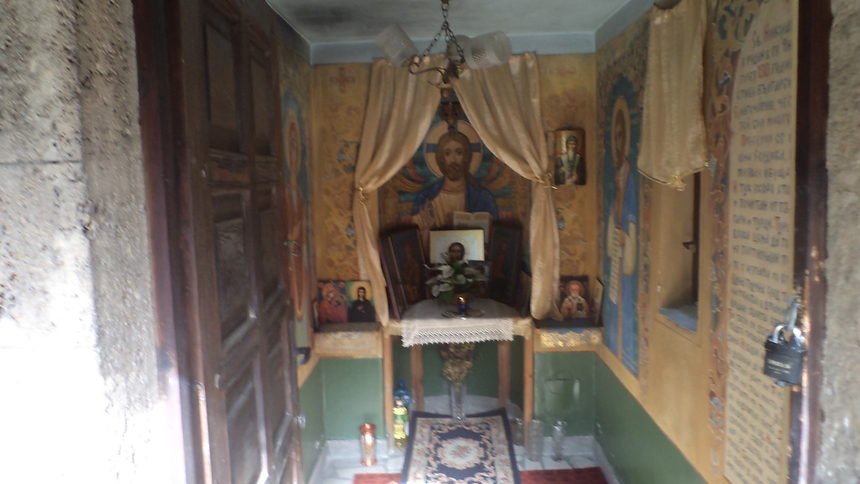

The Grave of Saint Nikolay of Sofia (View to Alter dedicated to the matryr saint)
The holy relics of Saint Nikolay the new are now preserved in his Church and are brought for veneration by believers and pilgrims on each 16 and 17 of May and sometimes in a Church feasts of a higher importance.
Each 17-th of May in Sofia it is a tradition for clirics (clergy) to gather together with pilgrims and layman for a Lithia with the holy relics of saint Nikolay from the Church to the chapel, and for the following two days 18, 19th of May his holy relics are publicly displayed for veneration.
Sofia's mediaval historian and clergyman deacon Matey Gramatik (upmentioned), was a comtemporary of the saint and eyewitness of his martyrdom and death, soon after wrote his Church service and Biography (Saint Living). Today the original manuscript is preserved in the the Library of the church "St. Martyr Nikolai Novi Sofiyski" in Sofia.
Let by the holy prayers of Saint Nikolay Sofijski our homeland Bulgaria is given peace prosperity in The Hope, Faith and Love and every Good and firmness in the True faith given by Christ the Holy Eastern Orthodox faith. Let by his Holy prayers God gives peace and love to everyone in the world and grant, repentance for us the lost and spiritually poor and "fatherless" children of the 21st century.
![]()
![]()