How to check version of a Linux host's installed Mail server?
Most used mail servers Postfix / Qmail / Exim / Sendmail and usually you have to do a dpkg -l / rpm -qa or whatever package manager to get the package version. But sometimes the package is built to have a different naming convention from the actual installed MTA.
As recently I had to check on a Linux host what kind of version was the installed and used one to the SMTP, below is how to find conrete versions of Postfix / Qmail / Exim / Sendmail.
If none of the 4 is installed and something more cryptic like ssmtp is installed if another one is installed perhaps the best way would be to check with lsof -i :25 command and see what process has binded and listens on TCP port 25.
1. How to check Postfix exact mail server version
Once you can find Postfix is the Network listening MTA, you might think you can simply use postfix -v however, but no …
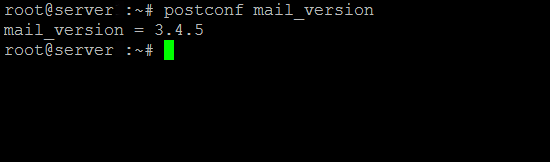
Unlike many other applications, Postfix has no -v or –versions switch. But you can get the version information easily by using the postconf command as shown below:
root@server :~# postconf mail_version
Other approach is to dump all postfix configuration settings (this is useful to get more info on how postfix is configured) and explicitly grep for the version.
How to check version of a Linux host's installeded webserver?
root@server :~# postconf -d | grep mail_version
2. How to check Exim MTA running version ?
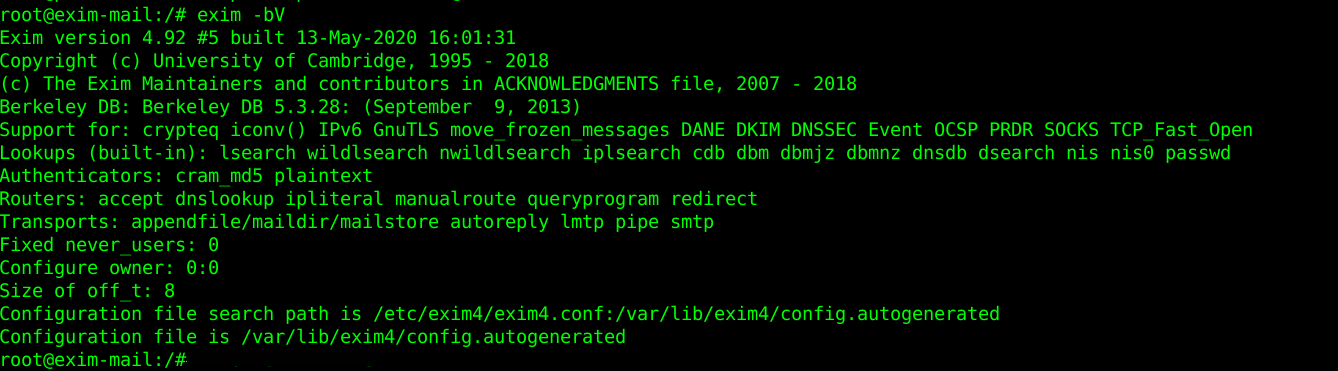
root@exim-mail :/ # exim -bV
Exim version 4.72 #1 built 13-Jul-2010 21:54:55
Copyright (c) University of Cambridge, 1995 – 2007
Berkeley DB: Sleepycat Software: Berkeley DB 4.3.29: (September 19, 2009)
Support for: crypteq iconv() Perl OpenSSL move_frozen_messages Content_Scanning DKIM Old_Demime
Lookups: lsearch wildlsearch nwildlsearch iplsearch cdb dbm dbmnz
Authenticators: cram_md5 plaintext spa
Routers: accept dnslookup ipliteral manualroute queryprogram redirect
Transports: appendfile/maildir/mailstore/mbx autoreply lmtp pipe smtp
Size of off_t: 8
OpenSSL compile-time version: OpenSSL 0.9.8e-fips-rhel5 01 Jul 2008
OpenSSL runtime version: OpenSSL 0.9.8e-fips-rhel5 01 Jul 2008
Configuration file is /etc/exim.conf
3. How to check Sendmail Mail Transport Agent exact Mail version ?
Though sendmail is rarely used this days and it usually works mostly on obsolete old scrap hosts
or in some old fashioned conservative organizations such as Banks and Payment services providers, you might need to invertise it, just like the configuration m4 format complexity with its annoying macros, getting the version is also not straight forward:
# sendmail -d0.4 -bv root | grep Version
Version 8.14.4
Above commands should be working on most Linux distributions such as Debian / Ubuntu / Fedora / CentOS / SuSE and other Linux derivatives
4. How to check Qmail MTA version?
This is a bit of complicated question, as Qmail's base has not been significantly changed for years.
The latest published qmail package is qmail-1.03.tar.gz. 1.03 was released in 1998, Qmail is famous for its unbreakable security. The author of qmail Daniel J. Bernstein is famous for writting Qmail to make the work installation and configuration of SMTP simple as of the time of writting sendmail was the defacto standard and sendmail was hard to configure.
Also sendmail was famous for a set of Security holes that got a lot of Sendmail MTA's on the Net got hacked. Thus the QMAIL was written as a more security-aware mail transport agent.
In contrast to sendmail, qmail has a modular architecture composed of mutually untrusting components; for instance, the SMTP listener component of qmail runs with different credentials from the queue manager or the SMTP sender. qmail was also implemented with a security-aware replacement to the C standard library, and as a result has not been vulnerable to stack and heap overflows, format string attacks, or temporary file race conditions.
The core qmail package has not been updated for many years. New features were initially provided by third party patches, from which the most important at the time were brought together in a single meta-patch set called netqmail.
The current version of netqmail is at 1.06 netqmail-1.06.tar.gz as of year 2020.
One possible way to get some info about installed qmail or components is to use the documentation look up command apropos
qmail:~# apropos qmail
or check the manual or at worst check for the installation source files that the person that installed the qmail used 🙂
A fun fact about qmail few might know is D. Bernstein offered in 1997 a US$500 reward for the first person to publish a verifiable security hole in the latest version of the software, for many years till 2005 no hole was found security researcher Georgi Guninski found an integer overflow in qmail. On 64-bit platforms, in default configurations with sufficient virtual memory, the delivery of huge amounts of data to certain qmail components may allow remote code execution. Bernstein disputes that this is a practical attack, arguing that no real-world deployment of qmail would be susceptible. Configuration of resource limits for qmail components mitigates the vulnerability.
On November 1, 2007, Bernstein raised the reward to US$1000. At a slide presentation the following day, Bernstein stated that there were 4 "known bugs" in the ten-year-old qmail-1.03, none of which were "security holes." He characterized the bug found by Guninski as a "potential overflow of an unchecked counter." "Fortunately, counter growth was limited by memory and thus by configuration, but this was pure luck.
5. Quick way to check the type of Mail server installed on Debian based Linux that doesn't have telnet installed
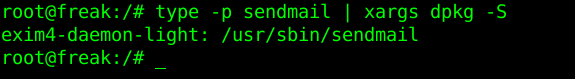
As you know simple telnet localhost 25 or a simple ps -ef could reveal at most times general information on the installed server. However there is another way to do it using package manager. by using embedded bash shell type type command like so:
# type -p sendmail |
xargs dpkg -S
Another hacky way to check whether exim, postfix or sendmail SMTP is installed is with:
hipo@freak:~$ echo $(man sendmail)| grep "exim"|wc -l
1
hipo@freak:~$ echo $(man sendmail)| grep "postfix"|wc -l
0
hipo@freak:~$ echo $(man sendmail)| grep "sendmail"|wc -l
0
I guess there are nice hacks and ways to get versions, so if you're aware of any please share with me.
Enjoy !

 admin
admin
 Kh
Kh













Report haproxy node switch script useful for Zabbix or other monitoring
Tuesday, June 9th, 2020For those who administer corosync clustered haproxy and needs to build monitoring in case if the main configured Haproxy node in the cluster is changed, I've developed a small script to be integrated with zabbix-agent installed to report to a central zabbix server via a zabbix proxy.
The script is very simple it assumed DC1 variable is the default used haproxy node and DC2 and DC3 are 2 backup nodes. The script is made to use crm_mon which is not installed by default on each server by default so if you'll be using it you'll have to install it first, but anyways the script can easily be adapted to use pcs cmd instead.
Below is the bash shell script:
To configure it with zabbix monitoring it can be configured via UserParameterScript.
The way I configured it in Zabbix is as so:
1. Create the userpameter_active_node.conf
Below script is 3 nodes Haproxy cluster
Once pasted to save the file press CTRL + D
The version of the script with 2 nodes slightly improved is like so:
The haproxy_active_DC_zabbix.sh script with a bit of more comments as explanations is available here
2. Configure access for /usr/sbin/crm_mon for zabbix user in sudoers
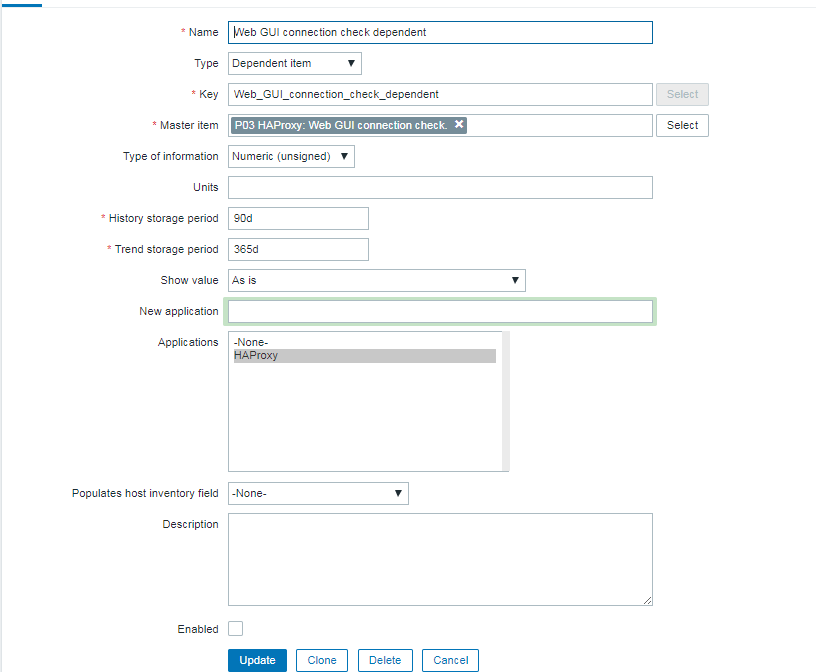
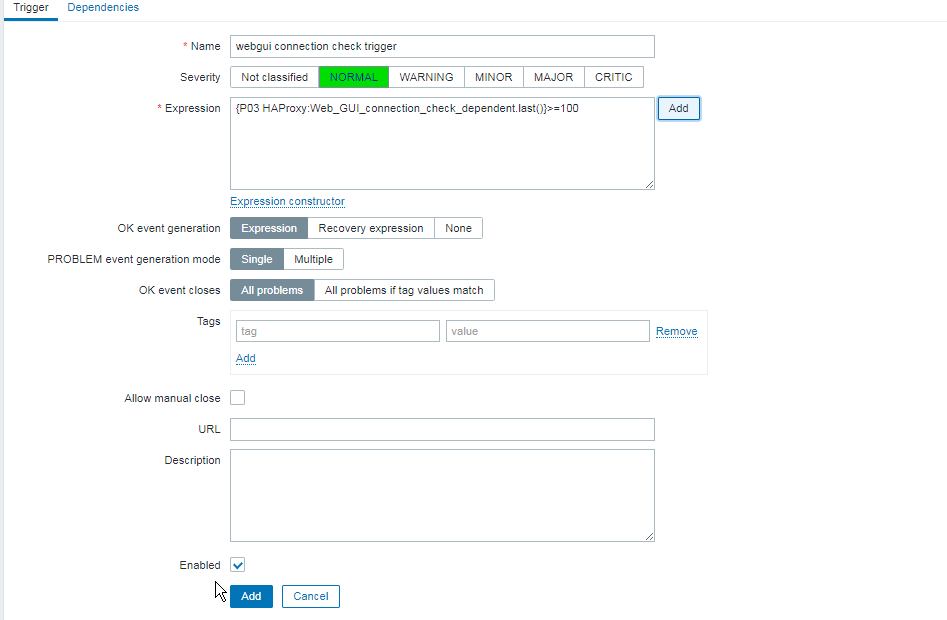
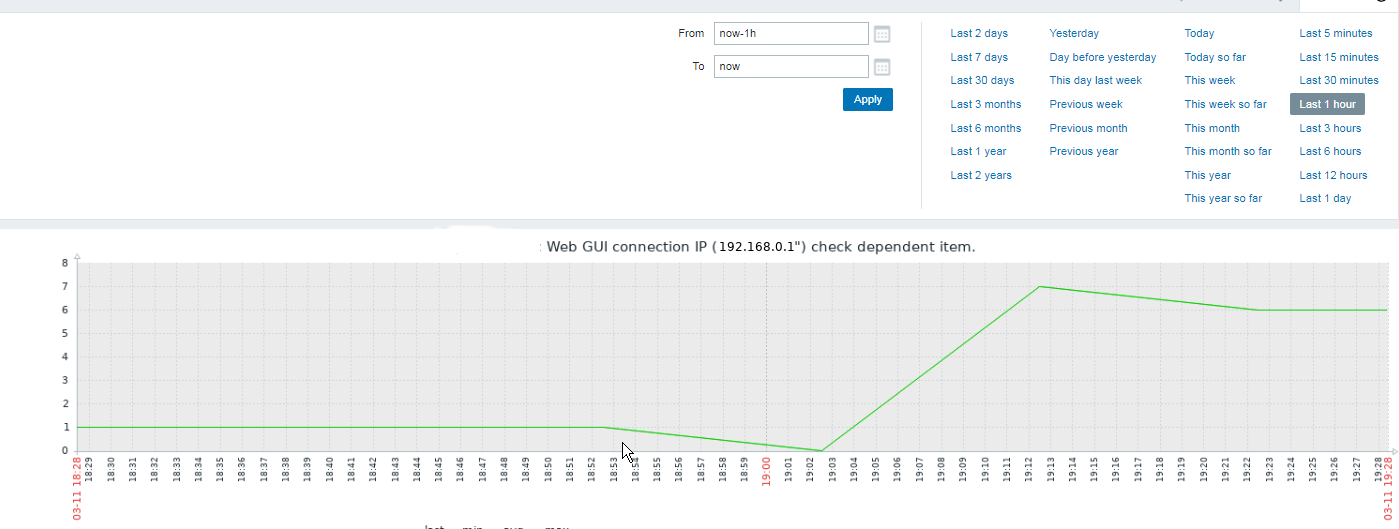
3. Configure in Zabbix for active.dc key Trigger and Item
Tags: access, ALL, and, Anyways, are, available, awk, bash shell, bash shell script, Below, bit, case, cat, Central, check, Cluster, cmd, Comments, conf, configure
Posted in Linux, Monitoring, Zabbix | No Comments »