Recently my Mother asked me to prepare a Music Audio CD for her from a popular musician accordionist Stefan Georgiev from Dobrudja who has a unique folklore Bulgarian music.
As some of older people who still remember the age of the CD and who had most likely been into the CD burning Copy / Piracy business so popular in the countries of the ex-USSR so popular in the years 1995-2000 audio , Old CD Player Devices were not able to play the MP3 file format due to missing codecs (as MP3 was a proprietary compression that can't be installed on every device without paying the patent to the MP3 compression rights holder.
The revolutionary MP3 compression used to be booming standard for transferring Music data due to its high compression which made an ordinary MP3 of 5 minutes of 5MB (10+ times more compression than an ordinary classic WAV Audio the CPU intensiveness of MP3 files that puts on the reading device, requiring the CD Player to have a more powerful CPU.
Hence due to high licensing cost and requirement for more powerful CPU enabled Audio Player many procuders of Audio Players never introduced MP3 to their devices and MP3 Neve become a standard for the Audio CD that was the standard for music listening inside almost every car out there.
Nowdays it is very rare need to create a Audio CD as audio CDs seems to be almost dead (As I heard from a Richard Stallman lecture In USA nowadays there is only 1 shop in the country where you can still buy CD or DVD drives) and only in third world as Africa Audio CDs perhaps are still in circulation.
Nomatter that as we have an old Stereo CD player on my village and perhaps many others, still have some old retired CD reading devices being able to burn out a CD is a useful thing.
Thus to make mother happy and as a learning excercise, I decided to prepare the CD for her on my Linux notebook.
Here I'll shortly describe the takes I took to make it happen which hopefully will be useful for other people that need to Convert and burn Audio CD from MP3 Album.
1. First I downloaded the Album in Mp3 format from Torrent tracker
My homeland Bulgaria and specific birth place place the city of Dobrich has been famous its folklore: Galina Durmushlijska and Stefan Georgiev are just 2 of the many names along with Оркестър Кристал (Orchestra Crystal) and the multitude of gifted singers. My mother has a santiment for Stefan Georgiev, as she listened to this gifted accordinist on her Uncle's marriage.
Thus In my case this was (Стефан Георгиев Хора и ръченици от Добруджа) the album full song list here If you're interested to listen the Album and Enjoy unique Folklore from Dobrudja (Dobrich) my home city, Stefan Georgiev's album Hora and Rachenica Dances is available here

I've downloaded them from Bulgarian famous torrent tracker zamunda.net in MP3 format.
Of course you need to have a CD / DVD readed and write device on the PC which nowdays is not present on most modern notebooks and PCs but as a last resort you can buy some cheap External Optical CD / DVD drive for 25 to 30$ from Amazon / Ebay etc.
2. You will need to install a couple of programs on Linux host (if you don't have it already)
To be able to convert from command line from MP3 to WAV you will need as minimum ffmpeg and normalize-audio packages as well as some kind of command line burning tool like cdrskin wodim which is
the fork of old good known cdrecord, so in case if you you're wondering what happened with it just
use instead wodim.
Below is a good list of tools (assuming you have enough HDD space) to install:
root@jeremiah:/ # apt-get install –yes dvd+rw-tools cdw cdrdao audiotools growisofs cdlabelgen dvd+rw-tools k3b brasero wodim ffmpeg lame normalize-audio libavcodec58
Note that some of above packages I've installed just for other Write / Read operations for DVD drives and you might not need that but it is good to have it as some day in future you will perhaps need to write out a DVD or something.
Also the k3b here is specific to KDE and if you're a GNOME user you could use Native GNOME Desktop app such brasero or if you're in a more minimalistic Linux desktop due to hardware contrains use XFCE's native xfburn program.
If you're a console / terminal geek like me you will definitely enjoy to use cdw
root@jeremiah:/ # apt-cache show cdw|grep -i description -A 1
Description-en: Tool for burning CD's – console version
Ncurses-based frontend for wodim and genisoimage. It can handle audio and
—
Description-md5: 77dacb1e6c00dada63762b78b9a605d5
Homepage: http://cdw.sourceforge.net/
3. Selecting preferred CD / DVD / BD program to use to write out the CD from Linux console
cdw uses wodim (which is a successor of good old known console cdrecord command most of use used on Linux in the past to burn out new Redhat / Debian / different Linux OS distro versions for upgrade purposes on Desktop and Server machines.
To check whether your CD / DVD drive is detected and ready to burn on your old PC issue:
root@jeremiah:/# wodim -checkdrive
Device was not specified. Trying to find an appropriate drive…
Detected CD-R drive: /dev/cdrw
Using /dev/cdrom of unknown capabilities
Device type : Removable CD-ROM
Version : 5
Response Format: 2
Capabilities :
Vendor_info : 'HL-DT-ST'
Identification : 'DVDRAM GT50N '
Revision : 'LT20'
Device seems to be: Generic mmc2 DVD-R/DVD-RW.
Using generic SCSI-3/mmc CD-R/CD-RW driver (mmc_cdr).
Driver flags : MMC-3 SWABAUDIO BURNFREE
Supported modes: TAO PACKET SAO SAO/R96P SAO/R96R RAW/R16 RAW/R96P RAW/R96R
You can also use xorriso (whose added value compared to other console burn cd tools is is not using external program for ISO9660 formatting neither it use an external or an external burn program for CD, DVD or BD (Blue Ray) drive but it has its own libraries incorporated from libburnia-project.org libs.
Below output is from my Thinkpad T420 notebook. If the old computer CD drive is there and still functional in most cases you should not get issues to detect it.
cdw ncurses text based CD burner tool's interface is super intuitive as you can see from below screenshot:
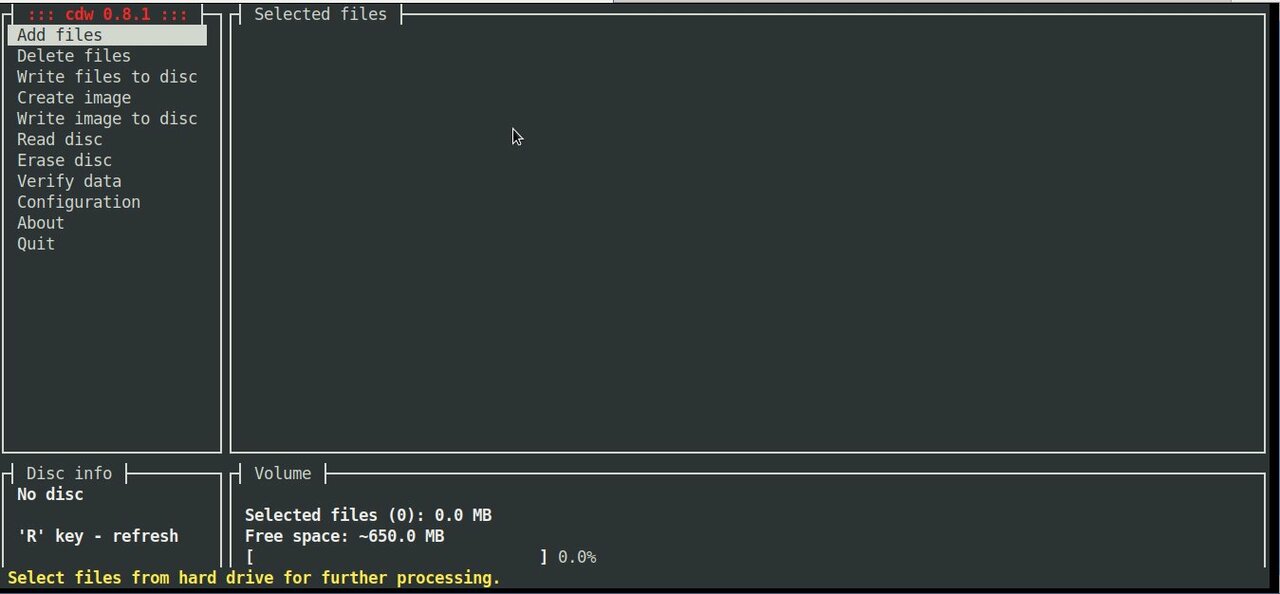
CDW has many advanced abilities such as “blanking” a disk or ripping an audio CD on a selected folder. To overcome the possible problem of CDW not automatically detecting the disk you have inserted you can go to the “Configuration” menu, press F5 to enter the Hardware options and then on the first entry press enter and choose your device (by pressing enter again). Save the setting with F9.
4. Convert MP3 / MP4 Files or whatever format to .WAV to be ready to burn to CD
Collect all the files you want to have collected from the CD album in .MP3 a certain directory and use a small one liner loop to convert files to WAV with ffmpeg:
cd /disk/Music/Mp3s/Singer-Album-directory-with-MP3/
for i in $( ls *.mp3); do ffmpeg -i $i $i.wav; done
If you don't have ffmpeg installed and have mpg123 you can also do the Mp3 to WAV conversion with mpg123 cmd like so:
for i in $( ls ); do mpg123 -w $i.wav $i.mp3; done
Another alternative for conversion is to use good old lame (used to create Mp3 audio files but abling to also) decode
mp3 to wav.
lame –decode somefile.mp3 somefile.wav
In the past there was a burn command tool that was able to easily convert MP3s to WAV but in up2date Linux modern releases it is no longer available most likely due to licensing issues, for those on older Debian Linux 7 / 8 / 9 / Ubuntu 8 to 12.XX / old Fedoras etc. if you have the command you can install burn and use it (and not bother with shell loops):
apt-get install burn
or
yum install burn
…
Once you have it to convert
$ burn -A -a *.mp3
5. Fix file naming to remove empty spaces such as " " and substitute to underscores as some Old CD Players are
unable to understand spaces in file naming with another short loop.
for f in *; do mv "$f" `echo $f | tr ' ' '_'`; done
6. Normalize audio produced .WAV files (set the music volume to a certain level)
In case if wondering why normalize audio is needed here is short extract from normalize-audio man page command description to shed some light.
"normalize-audio is used to adjust the volume of WAV or MP3 audio files to a standard volume level. This is useful for things like creating mp3 mixes, where different recording levels on different albums can cause the volume to vary greatly from song to song."
cd /disk/Music/Mp3s/Singer-Album-directory-with-MP3/
normalize-audio -m *.wav
7. Burn the produced normalized Audio WAV files to the the CD
wodim -v -fix -eject dev='/dev/sr0' -audio -pad *.wav
Alternatively you can conver all your MP3 files to .WAV with anything be it audacity
or another program or even use
GNOME's CDBurn tool brasero (if gnome user) or KDE's CDBurn which in my opinion is
the best CD / DVD burning application for Linux K3B.
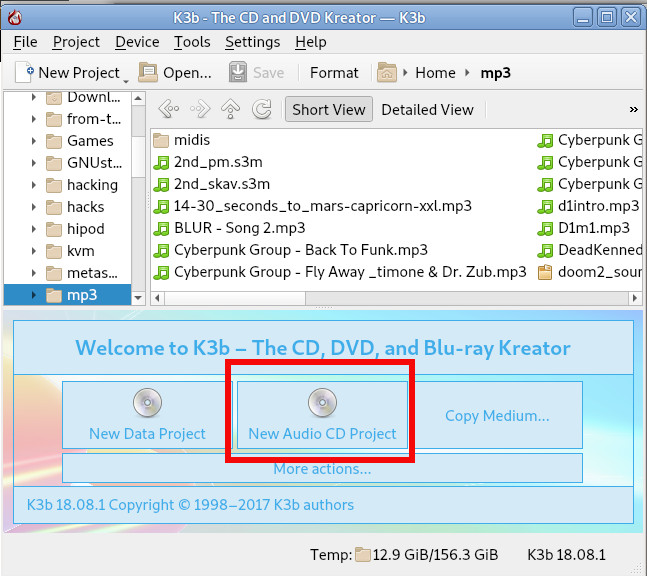
Burning Audio CD with K3b is up to few clicks and super easy and even k3b is going to handle the MP3 to WAV file Conversion itself. To burn audio with K3B just run it and click over 'New Audio CD Project'.
For those who want to learn a bit more on CD / DVD / Blue-Ray burning on GNU / Linux good readings are:
Linux CD Burning Mini Howto, is Linux's CD Writing Howto on ibiblio (though a bit obsolete) or Debian's official documentation on BurnCD.
8. What we learned here
Though the accent of this tutorial was how to Create Audio Music CD from MP3 on GNU / Linux, the same commands are available in most FreeBSD / NetBSD / OpenBSD ports tree so you can use the same method to build prepare Audio Music CD on *BSDs.
In this article, we went through few basic ways on how to prepare WAV files from MP3 normalize the new created WAV files on Linux, to prepare files for creation of Audio Music CD for the old mom or grandma's player or even just for fun to rewind some memories. For GUI users this is easily done with k3b, brasero or xfburn.
I've pointed you to cdw a super useful text ncurses tool that makes CD Burninng from plain text console (on servers) without a Xorg / WayLand GUI installed super easy. It was shortly reviewed what has changed over the last few years and why and why cdrecord was substituted for wodim. A few examples were given on how to handle conversion through bash shell loops and you were pointed to some extra reading resources to learn a bit more on the topic.
There are plenty of custom scripts around for doing the same CD Burn / Covnersion tasks, so pointing me to any external / Shell / Perl scripts is mostly welcome.
Hope this learned you something new, Enjoy ! 🙂

















