Sometimes you have to work with Windows 7 / 8 / 10 PCs etc. that has a very small partition C:\
drive or othertimes due to whatever the disk got filled up with time and has only few megabytes left
and this totally broke up the windows performance as Windows OS becomes terribly sluggish and even
simple things as opening Internet Browser (Chrome / Firefox / Opera ) or Windows Explorer stones the PC performance.
You might of course try to use something like Spacesniffer tool (a great tool to find lost data space on PC s short description on it is found in my previous article how to
delete temporary Internet Files and Folders to to speed up and free disk space ) or use CCleaner to clean up a bit the pc.
Sometimes this is not enough though or it is not possible to do at all the main
partition disk C:\ is anyhow too much low (only 30-50MB are available on HDD) or the Physical or Virtual Machine containing the OS is filled with important data
and you couldn't risk to remove anything including Internet Temporary files, browsing cookies … whatever.
Lets say you are the fate chosen guy as sysadmin to face this uneasy situation and have no easy
way to add disk space from another present free space partition or could not add a new SATA hard drive
SSD drive, what should you do?
The solution wipe off pagefile.sys and hiberfil.sys
Usually every Windows installation has a pagefile.sys and hiberfil.sys.
- pagefile.sys – is the default file that is used as a swap file, immediately once the machine runs out of memory. For Unix / Linux users better understanding pagefile.sys is the equivallent of Linux's swap partition. Of course as the pagefile is in a file and not in separate partition the swapping in Windows is perhaps generally worse than in Linux.
- hiberfil.sys – is used to store data from the machine on machine Hibernation (for those who use the feature)
Pagefile.sys which depending on the configured RAM memory on the OS could takes up up to 5 – 8 GB, there hanging around doing nothing but just occupying space. Thus a temporary workaround that could free you some space even though it will degrade performance and on servers and production machines this is not a good solution on just user machines, where you temporary need to free space any other important task you can free up space
by seriously reducing the preconfigured default size of pagefile.sys (which usually is 1.5 times the active memory on the OS – hence if you have 4GB you would have a 6Gigabytes of pagefile.sys).
Other possibility especially on laptop and movable devices running Win OS is to disable hiberfil.sys, read below how this is done.
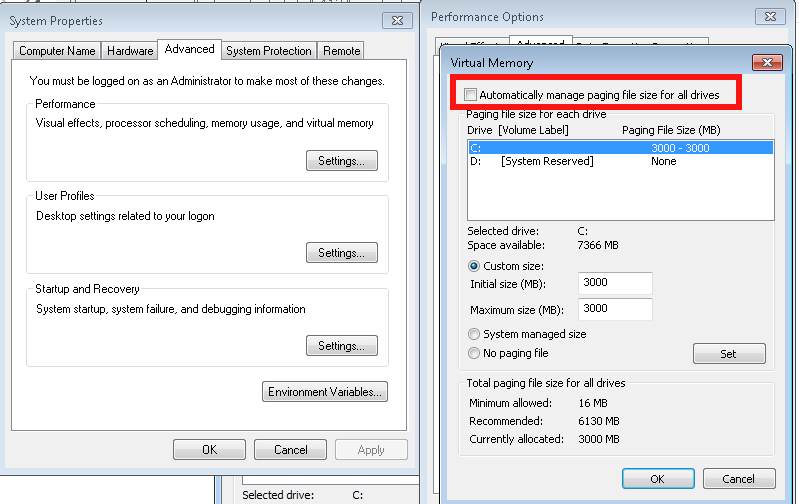
The temporary solution here is to simply free space by either reducing the pagefile.sys or completely disabling it
1. Disable pagefile.sys on Windows XP, Windows 7 / 8 / 10 / 11
The GUI interface to disable pagefile across all NT based Windows OS-es is quite similar, the only difference is newer versions of Windows has slightly more options.
1.1 Disable pagefile on Windows XP
Quickest way is to find pagefile.sys settings from GUI menus
1. Computer (My Computer) – right click mouse
2. Properties (System Preperties will appear)
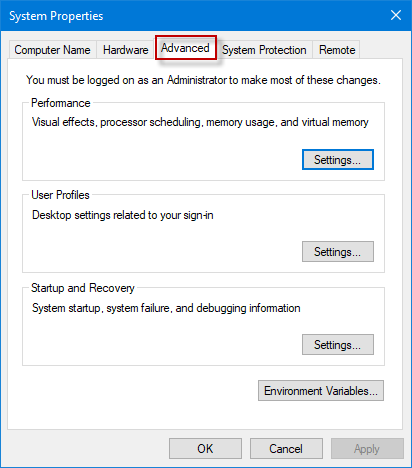
3. Advanced (tab)
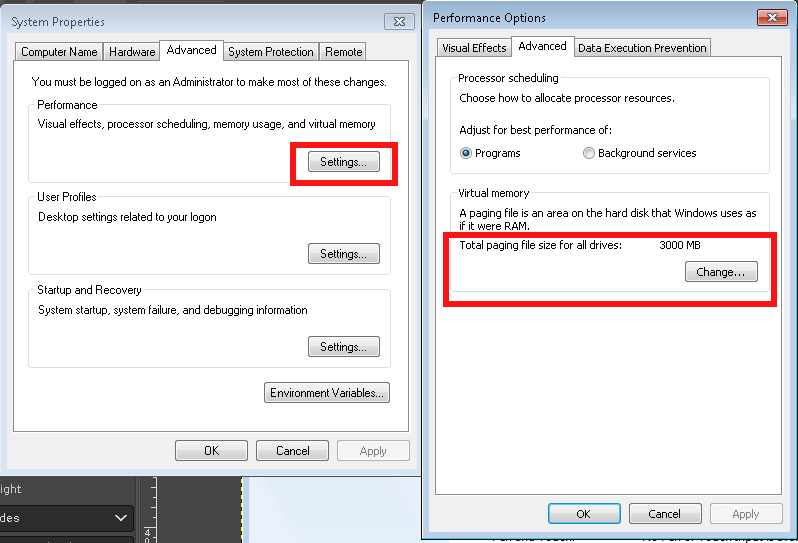
4. Settings
5. Advanced (tab)
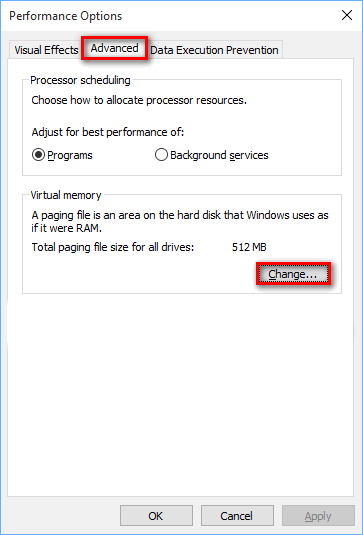
6. Change button
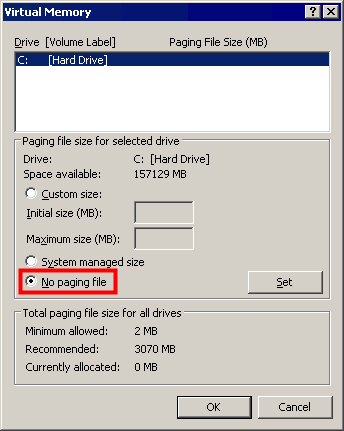
1.2 Disable pagefile on Windows 7
Once applied you'll be required to reboot the PC
1.3 Disable Increase / Decrease pagefile.sys on Windows 10 / Win 11
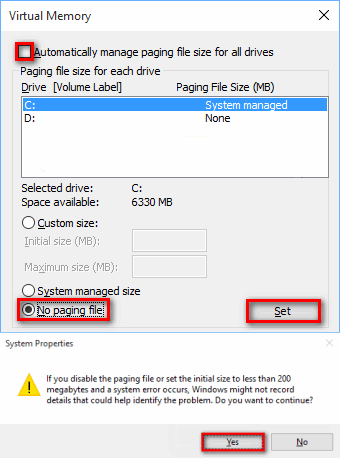
1.4 Make Windows clear pagefile.sys on shutdown
On home PCs it might be useful thing to clear up ( nullify) pagefile.sys on shutdown, that could save you some disk space on every reboot, until file continuously grows to its configured Maximum.
Run
regedit
Modify registry key at location
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management
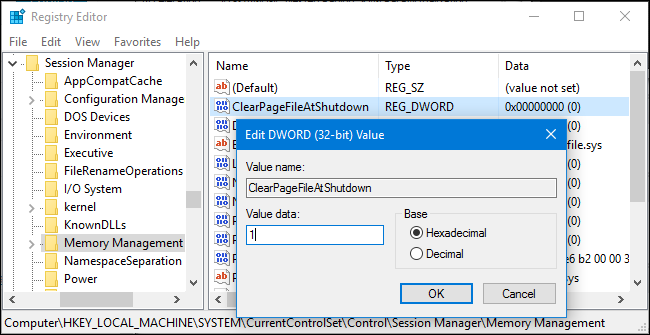
You can apply the value also via a registry file you can get the Enable Clearpagefile at shutdown here .reg.
2. Manipulating pagefile.sys size and file delete from command line with wmic tool
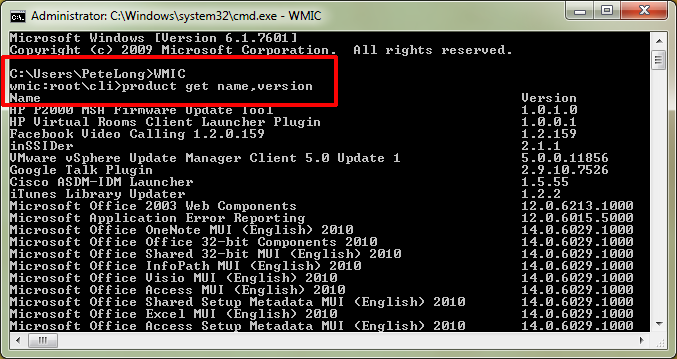
For scripting purposes you might want to use the wmic pagefile which can do increase / decrase or delete the file without GUI, that is very helpful if you have to admin a Windows Domain (Active Directory)
[hipo.WINDOWS-PC] ➤ wmic pagefile /?
PAGEFILE – Virtual memory file swapping management.
HINT: BNF for Alias usage.
(<alias> [WMIObject] |[ ] | [ ] ) [ ]. USAGE:
PAGEFILE ASSOC [
]
PAGEFILE CREATE <assign list>
PAGEFILE DELETE
PAGEFILE GET [] [ ]
PAGEFILE LIST [] [
]
[hipo.WINDOWS-PC] ➤ wmic pagefile
AllocatedBaseSize Caption CurrentUsage Description InstallDate Name PeakUsage Status TempPageFile
4709 C:\pagefile.sys 499 C:\pagefile.sys 20200912061902.938000+180 C:\pagefile.sys 525 FALSE
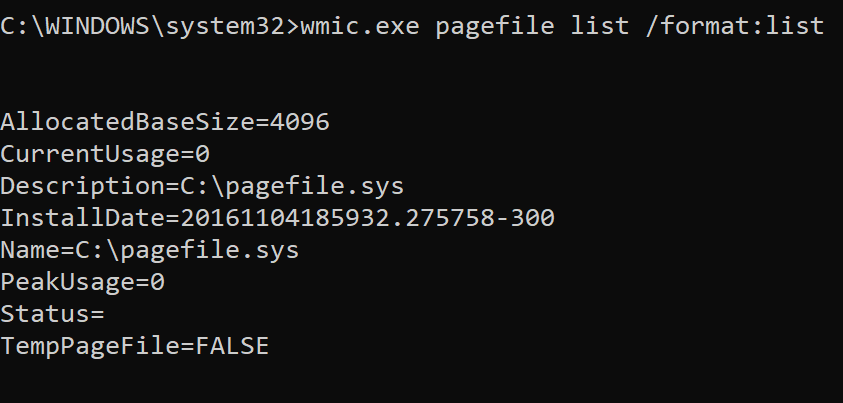
[hipo.WINDOWS-PC] ➤ wmic pagefile list /format:list
AllocatedBaseSize=4709
CurrentUsage=499
Description=C:\pagefile.sys
InstallDate=20200912061902.938000+180
Name=C:\pagefile.sys
PeakUsage=525
Status=
TempPageFile=FALSE
- To change the Initial Size or Maximum Size of Pagefile use:
➤ wmic pagefileset where name="C:\\pagefile.sys" set InitialSize=2048,MaximumSize=2048
- To move the pagefile / change location of pagefile to less occupied disk drive partition (i.e. D:\ drive)
Sometimes you might have multiple drives on the PC and some of them might be having multitudes of gigabytes while main drive C:\ could be fully occupied due to initial install bad drive organization, in that case a good work arount to save you space so you can work normally with the server is just to temporary or permanently move pagefile to another drive.
wmic pagefileset where name="D:\\pagefile.sys" set InitialSize=2048,MaximumSize=2048
!! CONSIDER !!!
That if you have the option to move the pagefile.sys for best performance it is advicable to place the file inside another physical disk, preferrably a Solid State Drive one, SATA disks are too slow and reduced Input / Output disk operations will lead to degraded performance, if there is lack of memory (i.e. pagefile.sys is actively open read and wrote in).
- To delete pagefile.sys
➤ wmic pagefileset where name="C:\\pagefile.sys" delete
If for some reason you prefer to not use wmic but simple del command you can delete pagefile.sys also by:
Removing file default "Hidden" and "system" file attributes – set for security reasons as the file is a system file usually not touched by user. This will save you from "permission denied" errors:
➤ attrib -s -h %systemdrive%\pagefile.sys
Delete the file:
➤ del /a /q %systemdrive%\pagefile.sys
3. Disable hibernation on Windows 7 / 8 and Win 10 / 11
Disabling hibernation file hiberfil.sys can also free up some space, especially if the hibernation has been actively used before and the file is written with data. Of course, that is more common on notebooks.
Windows hibernation has significantly improved over time though i didn't have very pleasant experience in the past and I prefer to disable it just in case.
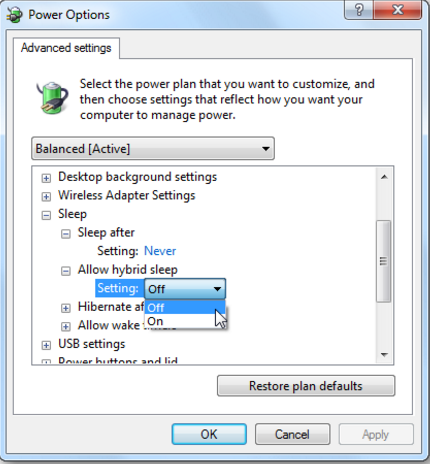
3.1 Disable Windows 7 / 8 / 10 / 11 hibernation from GUI
Disable it through:
Control Panel -> All Control Panel Items -> Power Options -> Edit Plan Settings -> Change advanced power settings
like shown in below screenshot:
3.2 Disable Windows 7 / 8 / 10 / 11 hibernation from command line
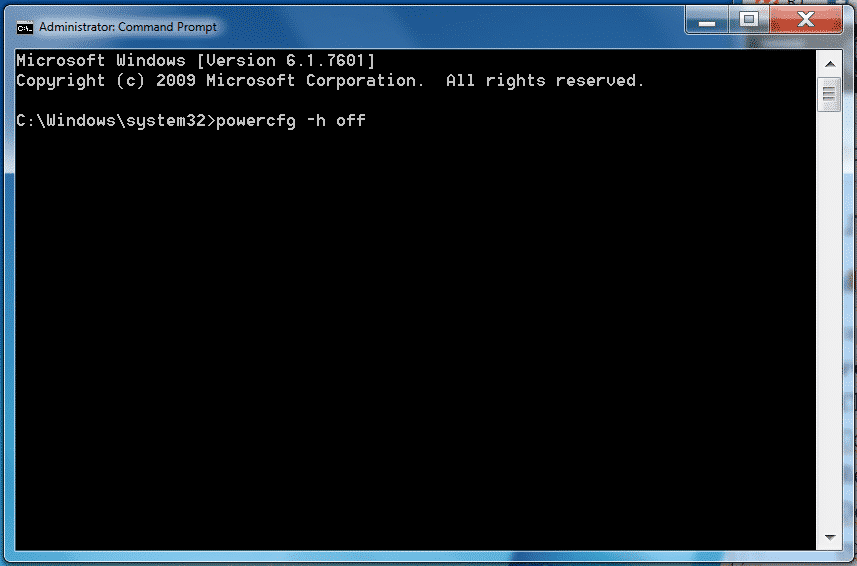
Disable hibernation Is done in the same way through the powercfg.exe command, to disable it
if you're cut of disk space and you want to save space from it:
run as Administrator in Command Line Windows (cmd.exe)
powercfg.exe /hibernate off
If you later need to switch on hibernation
powercfg.exe /hibernate on
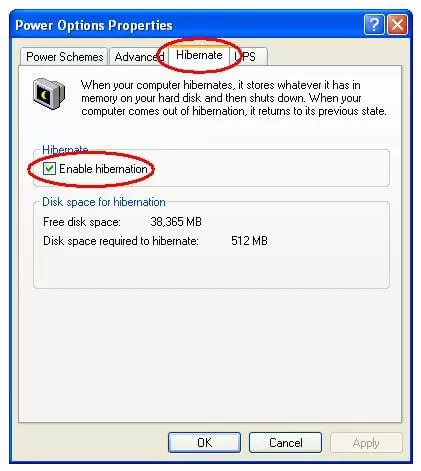
3.3 Disable Windows hibernation on legacy Windows XP
On XP to disable hibernation open
1. Power Options Properties
2. Select Hibernate.
3. Select Enable Hibernation to clear the checkbox and disable Hibernation mode.
4. Select OK to apply the change.
Close the Power Options Properties box.
To sum it up
We have learned some basics on Windows swapping and hibernation and i've tried to give some insight on how thiese files if misconfigured could lead to degraded Win OS performance. In any case using SSD as of 2022 to store both files is a best practice for machines that has plenty of memory always try to completely disable / remove the files. It was shown how to manage pagefile.sys and hiberfil.sys across Windows Operating Systems different versions both from GUI and via command line as well as how you can configure pagefile.sys to be cleared up on pc reboot.