Getting CPU information, RAM info and other various hardware specifics on Windows from the GUI interface is pretty trivial from Computer -> Properties
even more specifics could be obtained using third party Windows software such as CPU-Z
Perhaps there are plenty of many other ones to get and log info about hardware on PC or notebook system, but for Windwos sysadmins especially ones who are too much in love with command prompt way of behaving and ones who needs to automatizate server deployment processes with BATCH (.BAT) scripts getting quickly info about hardware on freshly installed remote host Win server with no any additional hardware info tools, you'll be happy to know there are command line tools you can use to get extra hardware information on Windows PC / server:
The most popular tool available to present you with some basic hardware info is of course systeminfo
C:\> systeminfo
Host Name: REMHOST
OS Name: Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard
OS Version: 6.3.9600 N/A Build 9600
OS Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation
OS Configuration: Member Server
OS Build Type: Multiprocessor Free
Registered Owner: Registrar
Registered Organization: Registrar
Product ID: 00XXX-X0000-00000-XX235
Original Install Date: 17/02/2016, 11:38:39
System Boot Time: 18/02/2016, 14:16:48
System Manufacturer: VMware, Inc.
System Model: VMware Virtual Platform
System Type: x64-based PC
Processor(s): 1 Processor(s) Installed.
[01]: Intel64 Family 6 Model 45 Stepping 7 GenuineInt
el ~2600 Mhz
BIOS Version: Phoenix Technologies LTD 6.00, 11/06/2014
Windows Directory: C:\Windows
System Directory: C:\Windows\system32
Boot Device: \Device\HarddiskVolume1
System Locale: de;German (Germany)
Input Locale: de;German (Germany)
Time Zone: (UTC+01:00) Amsterdam, Berlin, Bern, Rome, Stockholm,
Vienna
Total Physical Memory: 4,095 MB
Available Physical Memory: 2,395 MB
Virtual Memory: Max Size: 10,239 MB
Virtual Memory: Available: 8,681 MB
Virtual Memory: In Use: 1,558 MB
Page File Location(s): C:\pagefile.sys
Domain: dom1.domain.com
Logon Server: \\DOM
Hotfix(s): 148 Hotfix(s) Installed.
[01]: KB2894852
[02]: KB2894856
[03]: KB2918614
[04]: KB2919355
…..
Now though systeminfo's hardware details and installed Windows KBXXXXX OS Hotfix patches are getting lists the command does not provide you with info about system’s BIOS, thus to get this info you'll have to use also wmic (Windows Management Instrumentation Command).
So What Is WMIC?
WMIC extends WMI for operation from several command-line interfaces and through batch scripts. Before WMIC, you used WMI-based applications (such as SMS), the WMI Scripting API, or tools such as CIM Studio to manage WMI-enabled computers. Without a firm grasp on a programming language such as C++ or a scripting language such as VBScript and a basic understanding of the WMI namespace, do-it-yourself systems management with WMI was difficult. WMIC changes this situation by giving you a powerful, user-friendly interface to the WMI namespace.
WMIC is more intuitive than WMI, in large part because of aliases. Aliases take simple commands that you enter at the command line, then act upon the WMI namespace in a predefined way, such as constructing a complex WMI Query Language (WQL) command from a simple WMIC alias Get command. Thus, aliases act as friendly syntax intermediaries between you and the namespace. For example, when you run a simple WMIC command such as
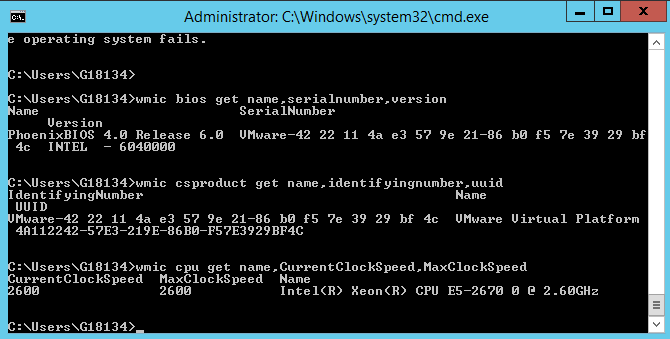
Here is how to wmic to get PC Motherboard serial numbers, CPU and BIOS details:
C:\> wmic bios get name,serialnumber,version
Above will print name if your BIOS, current version and it’s serial number if there is any.
If you need to get more info about the specific Motherboard installed on host:
C:\> wmic csproduct get name,identifyingnumber,uuid
This command will show motherboard modification and it’s UUID
If you want to quickly get what is Windows running hardware CPU clock speed
C:\> wmic cpu get name,CurrentClockSpeed,MaxClockSpeed
Also if you have turbo boost CPUs above command will help you find what’s the Max Clock Speed your system is capable of for the current hardware configuration.
If you do have dynamic clock speed running, then add this line, will refresh and monitor the Clock speed every 1 second.
C:\> wmic cpu get name,CurrentClockSpeed,MaxClockSpeed /every:1
Actually wmic is a great tool