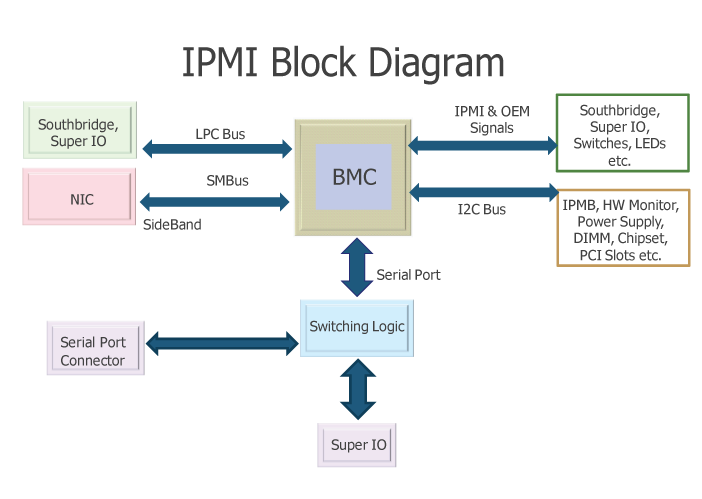
IPMI – Intelligent Platform Management Interface is a standardized computer interface also accessible remotely via Java applet allowing remote management and monitoring access to PC BIOS. IPMI is a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or a keyboard physical / screen login shell. The IPMI server standard was introduced by Intel and nowadays supported by more than 200 computer vendors i.e. – Super Micro, Hewlett Packard, Cisco, Dell etc.
Intelligent Platform Management Interface is an open, industry-standard interface that was designed for the management of server systems over network. IPMI interfaces by various vendors have also Virtual Media support (i.e. – Operating System ISO files could be mounted remotely to a Virtual CD / DVD rom and you can approach installing a bare-metal server without physical presense to it). Just like Power Off / Restart, BIOS Entrance and Virtual Media access is done directly through a web-browser interface over the network or the internet.
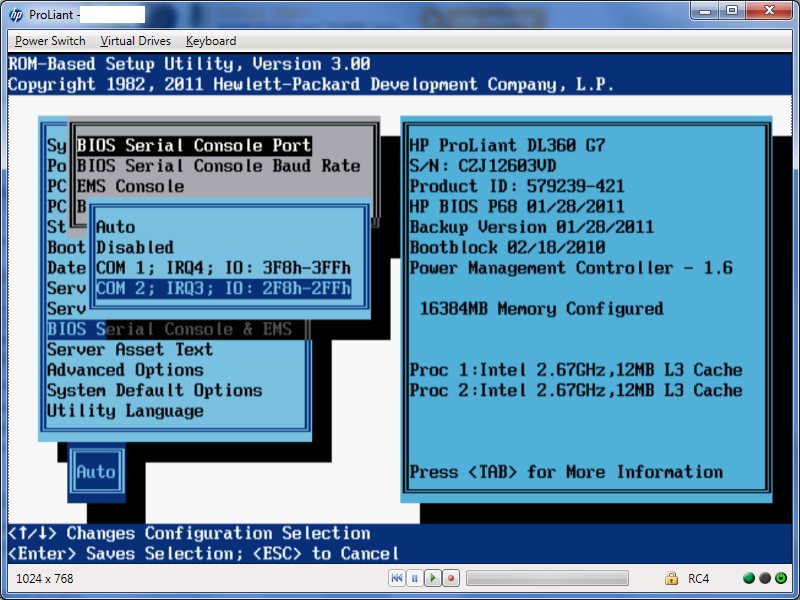
ILO – stands for Integrated Lights-Out and is HP Proliant servers remote console to PC / server physical screen. ILO is server integrated chip on HP servers and doesn't need further installations. It gives you a web console using Java showing you server screen just like there is a Monitor connected to the server it is precious for remote system administration purposes as often when there is no SSH or Remote Desktop to server you can see directly whether the server has completed hanged and try to recover or see a failing hardware notification on the screen to a server with a partially accessible services. Using ILO console access to an HP server one can have a BIOS access remotely to machines already colocated in data canters. In other words ILO is HP's variation of IPMI remote interface also known under business buzz word IPKVM.
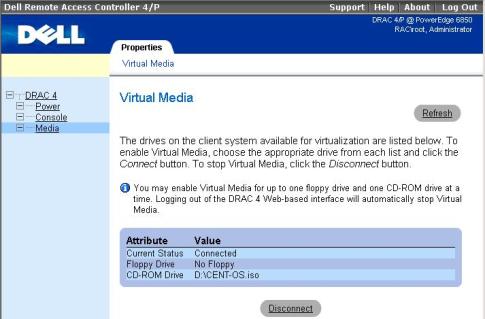
DRAC (iDRAC)- Dell's Remote Access Controller is interface card from Dell Inc. offering remote access (out-of-band) management facilities – i.e. DRAC is Dell's variant of HP's ILO – an implementation of Intel's IPMI out-of-band standard. DRAC is also giving you remote way to access no other means accessible server on a software level. Interesting and nice things is Dell provides their DRAC source code, so if you're a developer you can learn how DRAC technology works on a lower level.
ILO, iDRAC (Dell's new generation DRAC for Blade servers) and ILO's remote management interfaces's (IPMI tools) most valuable features is it allows remote system Power On / Shutdown and Remote Restart while monitoring the server screen (hardware output) messages and allowing you see critical hardware issue messages on pre-OS boot time, failure with memory, hard disks etc. and remote interface to do BIOS tuning.




