Linux's surprises and disorganization is continuously growing day by day and I start to realize it is becoming mostly impossible to support easily this piece of hackware bundled together.
Usually so far during the last 5 – 7 years, I rarely had any general issues with using:
apt-get update && apt-get upgrade && apt-get dist-upgrade
to raise a server's working stable Debian Linux version packages e.g. version X.Y to verzion X.Z (for example up the release from Debian Jessie from 8.1 to 8.2).
Today I just tried to follow this well known and established procedure that, of course nowdays is better to be done with the newer "apt" command instead with the legacy "apt-get"
And the set of
# apt-get update && apt-get upgrade && apt-get dist-upgrade
has triggered below shitty error:
root@zabbix:~# apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
Get:1 http://security.debian.org buster/updates InRelease [65.4 kB]
Get:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster InRelease [122 kB]
Get:3 http://security.debian.org buster/updates/non-free Sources [688 B]
Get:4 http://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/5.0/debian buster InRelease [7096 B]
Get:5 http://security.debian.org buster/updates/main Sources [198 kB]
Get:6 http://security.debian.org buster/updates/main amd64 Packages [300 kB]
Get:7 http://security.debian.org buster/updates/main Translation-en [157 kB]
Get:8 http://security.debian.org buster/updates/non-free amd64 Packages [556 B]
Get:9 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/main Sources [7836 kB]
Get:10 http://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/5.0/debian buster/main Sources [1192 B]
Get:11 http://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/5.0/debian buster/main amd64 Packages [4785 B]
Get:12 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/non-free Sources [85.7 kB]
Get:13 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/contrib Sources [42.5 kB]
Get:14 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/main amd64 Packages [7907 kB]
Get:15 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/main Translation-en [5968 kB]
Get:16 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/main amd64 Contents (deb) [37.3 MB]
Get:17 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/contrib amd64 Packages [50.1 kB]
Get:18 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/non-free amd64 Packages [87.7 kB]
Get:19 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/non-free Translation-en [88.9 kB]
Get:20 http://deb.debian.org/debian buster/non-free amd64 Contents (deb) [861 kB]
Fetched 61.1 MB in 22s (2774 kB/s)
Reading package lists… Done
N: Repository 'http://deb.debian.org/debian buster InRelease' changed its 'Version' value from '10.9' to '10.10'
…
As I used to realize nowdays, as Linux started originally as 'Hackers' operating system, its legacy is just one big hack and everything from simple maintenance up to the higher and more sophisticated things requires a workaround 'hack''.
This time the hack to resolve error:
N: Repository 'http://deb.debian.org/debian buster InRelease' changed its 'Version' value from '10.9' to '10.10'
is up to running cmd:
debian-server:~# apt-get update –allow-releaseinfo-change
Поп:1 http://ftp.de.debian.org/debian buster-backports InRelease
Поп:2 http://ftp.debian.org/debian stable InRelease
Поп:3 http://security.debian.org stable/updates InRelease
Изт:5 https://packages.sury.org/php buster InRelease [6837 B]
Изт:6 https://download.docker.com/linux/debian stretch InRelease [44,8 kB]
Изт:7 https://packages.sury.org/php buster/main amd64 Packages [317 kB]
Игн:4 https://attic.owncloud.org/download/repositories/production/Debian_10 InRelease
Изт:8 https://download.owncloud.org/download/repositories/production/Debian_10 Release [964 B]
Изт:9 https://packages.sury.org/php buster/main i386 Packages [314 kB]
Изт:10 https://download.owncloud.org/download/repositories/production/Debian_10 Release.gpg [481 B]
Грш:10 https://download.owncloud.org/download/repositories/production/Debian_10 Release.gpg
Следните подписи са невалидни: DDA2C105C4B73A6649AD2BBD47AE7F72479BC94B
Грш:11 https://ookla.bintray.com/debian generic InRelease
403 Forbidden [IP: 52.39.193.126 443]
Четене на списъците с пакети… Готово
N: Repository 'https://packages.sury.org/php buster InRelease' changed its 'Suite' value from '' to 'buster'
W: An error occurred during the signature verification. The repository is not updated and the previous index files will be used. GPG error: https://download.owncloud.org/download/repositories/production/Debian_10 Release:
…
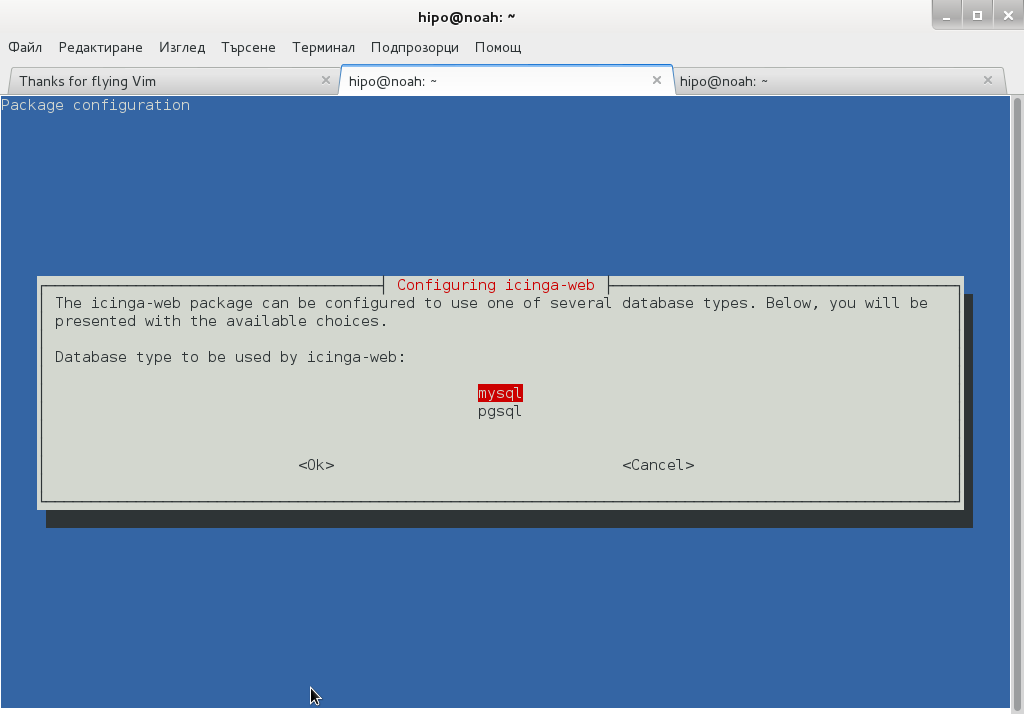
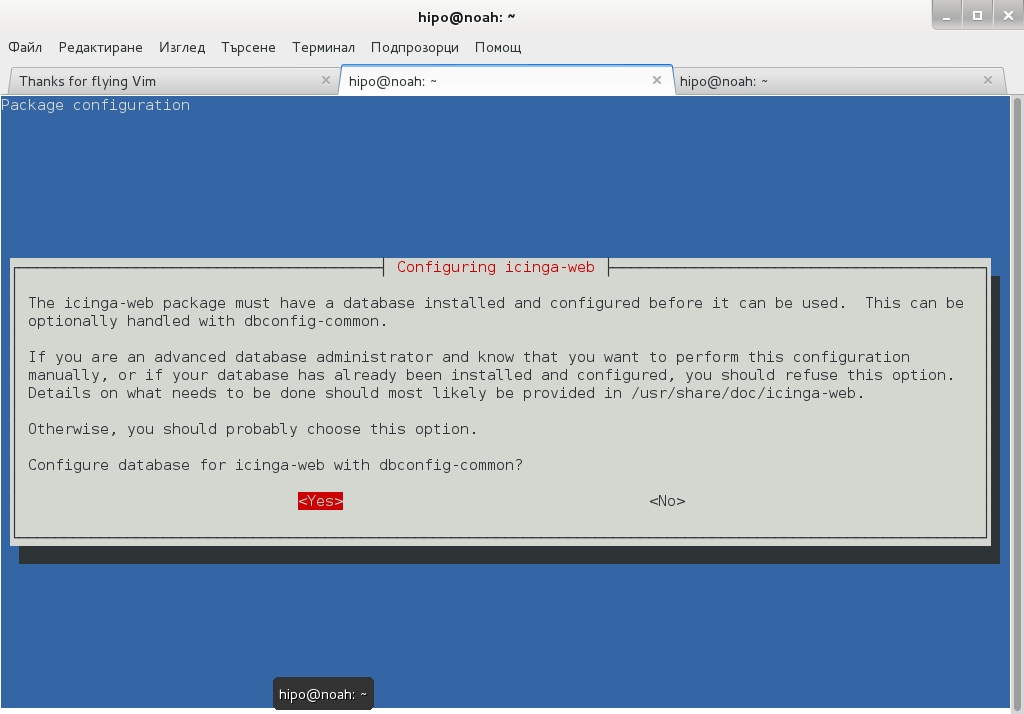
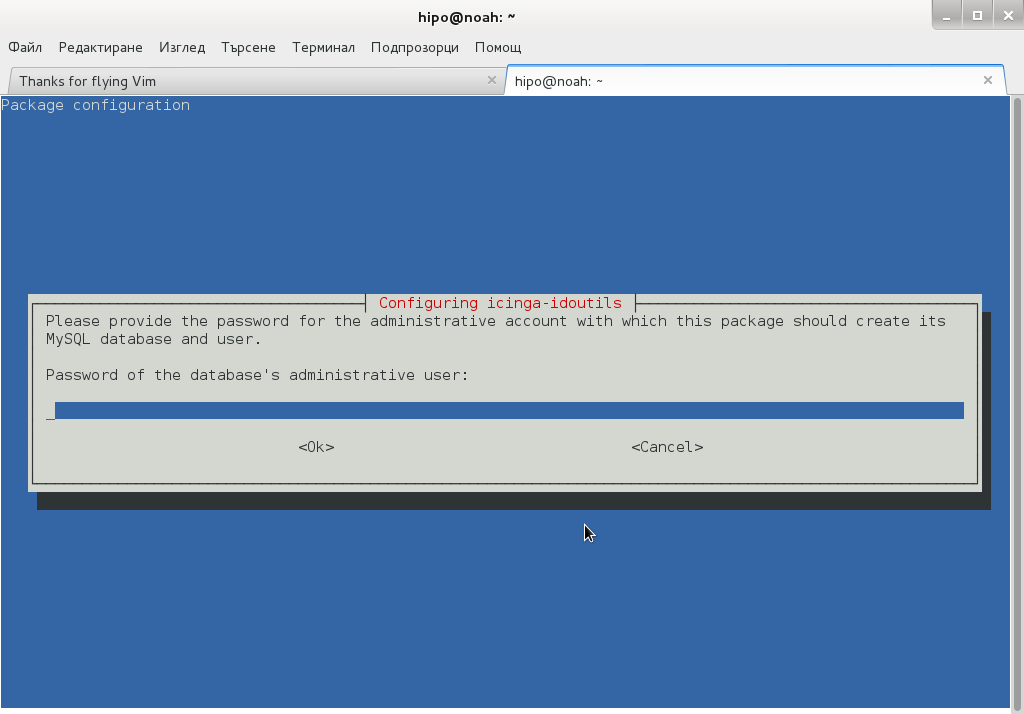
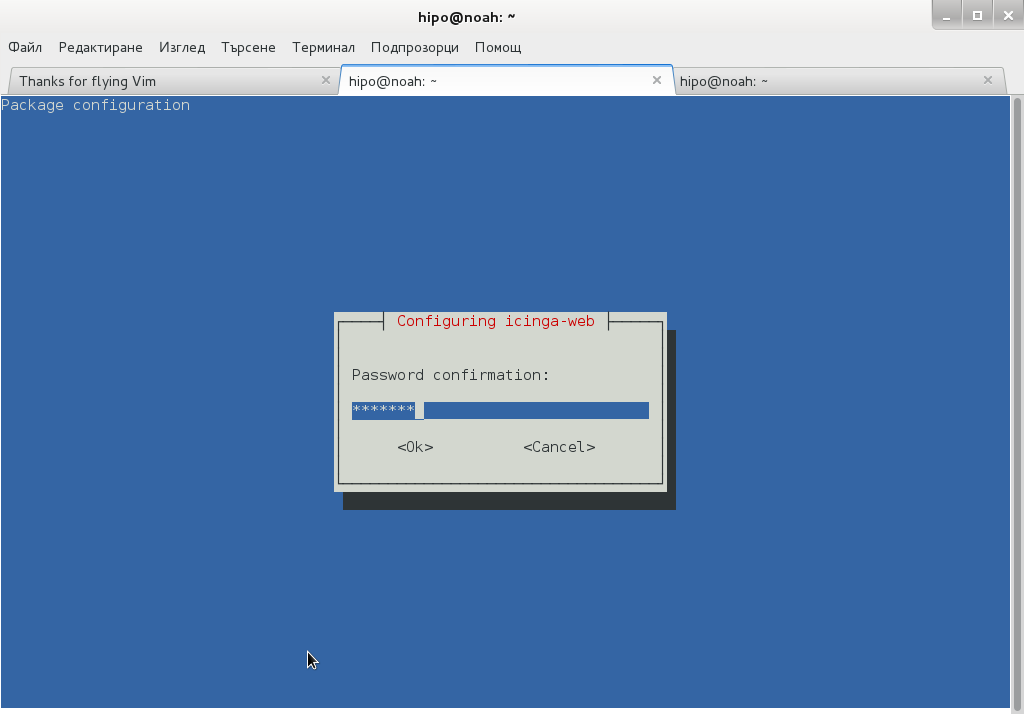
Onwards to upgrade the system up to the latest .deb packages, as usual run:
# apt-get -y update && apt-get upgrade -y
…
and updates should be applied as usual with some prompts on whether you prefer to keep or replace existing service configuration and some information on some general changes that might affect your installed services. In a few minutes and few prompts hopefully your Debian OS should be up to the latest stable.