Historically Email sending has been very different from what most people use it in the Office, there was no heavy Email clients such as Outlook Express no MX Exchange, no e-mail client capabilities for Calendar and Meetings schedule as it is in most of the modern corporate offices that depend on products such as Office 365 (I would call it a connectedHell 365 days a year !).
There was no free webmail and pop3 / imap providers such as Mail.Yahoo.com, Gmail.com, Hotmail.com, Yandex.com, RediffMail, Mail.com the innumerous lists goes and on.
Nope back in the day emails were doing what they were originally supposed to like the post services in real life simply send and receive messages.
For those who remember that charming times, people used to be using BBS-es (which were basicly a shared set-up home system as a server) or some of the few University Internal Email student accounts or by crazy sysadmins who received their notification and warnings logs about daemon (services) messages via local DMZ-ed network email servers and it was common to read the email directly with mail (mailx) text command or custom written scripts … It was not uncommon also that mailx was used heavily to send notification messages on triggered events from logs. Oh life was simple and clear back then, and even though today the email could be used in a similar fashion by hard-core old school sysadmins and Dev Ops / simple shell scriptings tasks or report cron jobs such usage is already in the deep history.
The number of ways one could send email in text format directly from the GNU / Linux / *BSD server to another remote mail MTA node (assuming it had properly configured Relay server be it Exim or Postifix) were plenty.
In this article I will try to rewind back some of the UNIX history by pinpointing a few of the most common ways, one used to send quick emails directly from a remote server connection terminal or lets say a cheap VPS few cents server, through something like (SSH or Telnet) etc.
1. Using the mail command client (part of bsd-mailx on Debian).
In my previous article Linux: "bash mail command not found" error fix
I ended the article with a short explanation on how this is done but I will repeat myself one more time here for the sake of clearness of this article.
root@linux:~# echo "Your Sample Message Body" | mail -s "Whatever … Message Subject" remote_receiver@remote-server-email-address.com
…
The mail command will connect to local server TCP PORT 25 on local configured MTA and send via it. If the local MTA is misconfigured or it doesn't have a proper MX / PTR DNS records etc. or not configure as a relay SMTP remote mail will not get delivered. Sent Email should be properly delivered at remote recipient address.
How to send HTML formatted emails using mailx command on Linux console / terminal shell using remote server through SSH ?
Connect to remote SSH server (VPS), dedicated server, home Linux router etc. and run:
root@linux:~# mailx -a 'Content-Type: text/html'
-s "This is advanced mailx indeed!" < email_content.html
"first_email_to_send_to@gmail.com, mail_recipient_2@yahoo.com"
email_content.html should be properly formatted (at best w3c standard compliant) HTML.
Here is an example email_content.html (skeleton file)
To: your_customer@gmail.com
Subject: This is an HTML message
From: marketing@your_company.com
Content-Type: text/html; charset="utf8"
<html>
<body>
<div style="
background-color:
#abcdef; width: 300px;
height: 300px;
">
</div>
Whatever text mixed with valid email HTML tags here.
</body>
</html>
Above command sends to two email addresses however if you have a text formatted list of recipients you can easily use that file with a bash shell script for loop and send to multiple addresses red from lets say email_addresses_list.txt .
To further advance the one liner you can also want to provide an email attachment, lets say the file email_archive.rar by using the -A email_archive.rar argument.
root@linux:~# mailx -a 'Content-Type: text/html'
-s "This is advanced mailx indeed!" -A ~/email_archive.rar < email_content.html
"first_email_to_send_to@gmail.com, mail_recipient_2@yahoo.com"
For those familiar with Dan Bernstein's Qmail MTA (which even though a bit obsolete is still a Security and Stability Beast across email servers) – mailx command had to be substituted with a custom qmail one in order to be capable to send via qmail MTA daemon.
2. Using sendmail command to send email
Do you remember that heavy hard to configure MTA monster sendmail ? It was and until this very day is the default Mail Transport Agent for Slackware Linux.
Here is how we were supposed to send mail with it:
[root@sendmail-host ~]# vim email_content_to_be_delivered.txt
Content of file should be something like:
Subject: This Email is sent from UNIX Terminal Email
Hi this Email was typed in a file and send via sendmail console email client
(part of the sendmail mail server)
It is really fun to go back in the pre-history of Mail Content creation 🙂
[root@sendmail-host ~]# sendmail -v user_name@remote-mail-domain.com < /tmp/email_content_to_be_delivered.txt
-v argument provided, will make the communication between the mail server and your mail transfer agent visible.
3. Using ssmtp command to send mail
ssmtp MTA and its included shell command was used historically as it was pretty straight forward you just launch it on the command line type on one line all your email and subject and ship it (by pressing the CTRL + D key combination).
To give it a try you can do:
root@linux:~# apt-get install ssmtp
Reading package lists… Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information… Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
libgnutls-openssl27
The following packages will be REMOVED:
exim4-base exim4-config exim4-daemon-heavy
The following NEW packages will be installed:
libgnutls-openssl27 ssmtp
0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 3 to remove and 1 not upgraded.
Need to get 239 kB of archives.
After this operation, 3,697 kB disk space will be freed.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y
Get:1 http://ftp.us.debian.org/debian stretch/main amd64 ssmtp amd64 2.64-8+b2 [54.2 kB]
Get:2 http://ftp.us.debian.org/debian stretch/main amd64 libgnutls-openssl27 amd64 3.5.8-5+deb9u3 [184 kB]
Fetched 239 kB in 2s (88.5 kB/s)
Preconfiguring packages …
dpkg: exim4-daemon-heavy: dependency problems, but removing anyway as you requested:
mailutils depends on default-mta | mail-transport-agent; however:
Package default-mta is not installed.
Package mail-transport-agent is not installed.
Package exim4-daemon-heavy which provides mail-transport-agent is to be removed.
(Reading database … 169307 files and directories currently installed.)
Removing exim4-daemon-heavy (4.89-2+deb9u3) …
dpkg: exim4-config: dependency problems, but removing anyway as you requested:
exim4-base depends on exim4-config (>= 4.82) | exim4-config-2; however:
Package exim4-config is to be removed.
Package exim4-config-2 is not installed.
Package exim4-config which provides exim4-config-2 is to be removed.
exim4-base depends on exim4-config (>= 4.82) | exim4-config-2; however:
Package exim4-config is to be removed.
Package exim4-config-2 is not installed.
Package exim4-config which provides exim4-config-2 is to be removed.
Removing exim4-config (4.89-2+deb9u3) …
Selecting previously unselected package ssmtp.
(Reading database … 169247 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack …/ssmtp_2.64-8+b2_amd64.deb …
Unpacking ssmtp (2.64-8+b2) …
(Reading database … 169268 files and directories currently installed.)
Removing exim4-base (4.89-2+deb9u3) …
Selecting previously unselected package libgnutls-openssl27:amd64.
(Reading database … 169195 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack …/libgnutls-openssl27_3.5.8-5+deb9u3_amd64.deb …
Unpacking libgnutls-openssl27:amd64 (3.5.8-5+deb9u3) …
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.24-11+deb9u3) …
Setting up libgnutls-openssl27:amd64 (3.5.8-5+deb9u3) …
Setting up ssmtp (2.64-8+b2) …
Processing triggers for man-db (2.7.6.1-2) …
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.24-11+deb9u3) …
As you see from above output local default Debian Linux Exim is removed …
Lets send a simple test email …
hipo@linux:~# ssmtp user@remote-mail-server.com
Subject: Simply Test SSMTP Email
This Email was send just as a test using SSMTP obscure client
via SMTP server.
^d
What is notable about ssmtp is that even though so obsolete today it supports of STARTTLS (email communication encryption) that is done via its config file
/etc/ssmtp/ssmtp.conf
4. Send Email from terminal using Mutt client
Mutt was and still is one of the swiff army of most used console text email clients along with Alpine and Fetchmail to know more about it read here
Mutt supports reading / sending mail from multiple mailboxes and capable of reading IMAP and POP3 mail fetch protocols and was a serious step forward over mailx. Its syntax pretty much resembles mailx cmds.
root@linux:~# mutt -s "Test Email" user@example.com < /dev/null
Send email including attachment a 15 megabytes MySQL backup of Squirrel Webmail
root@linux:~# mutt -s "This is last backup small sized database" -a /home/backups/backup_db.sql user@remote-mail-server.com < /dev/null
5. Using simple telnet to test and send email (verify existence of email on remote SMTP)
As a Mail Server SysAdmin this is one of my best ways to test whether I had a server properly configured and even sometimes for the sake of fun I used it as a hack to send my mail 🙂
telnet is and will always be a great tool for doing SMTP issues troubleshooting.
It is very useful to test whether a remote SMTP TCP port 25 is opened or a local / remote server firewall prevents connections to MTA.
Below is an example connect and send example using telnet to my local SMTP on www.pc-freak.net (QMail powered (R) 🙂 )
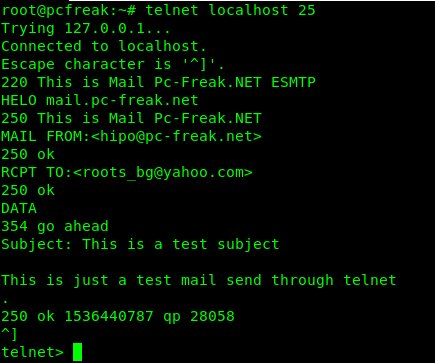
root@pcfreak:~# telnet localhost 25
Trying 127.0.0.1…
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 This is Mail Pc-Freak.NET ESMTP
HELO mail.www.pc-freak.net
250 This is Mail Pc-Freak.NET
MAIL FROM:<hipo@www.pc-freak.net>
250 ok
RCPT TO:<roots_bg@yahoo.com>
250 ok
DATA
354 go ahead
Subject: This is a test subject
This is just a test mail send through telnet
.
250 ok 1536440787 qp 28058
^]
telnet>
Note that the returned messages are native to qmail, a postfix would return a slightly different content, here is another test example to remote SMTP running sendmail or postfix.
root@pcfreak:~# telnet mail.servername.com 25
Trying 127.0.0.1…
Connected to localhost.localdomain (127.0.0.1).
Escape character is '^]'.
220 mail.servername.com ESMTP Sendmail 8.13.8/8.13.8; Tue, 22 Oct 2013 05:05:59 -0400
HELO yahoo.com
250 mail.servername.com Hello mail.servername.com [127.0.0.1], pleased to meet you
mail from: systemexec@gmail.com
250 2.1.0 hipo@www.pc-freak.net… Sender ok
rcpt to: hip0d@yandex.ru
250 2.1.5 hip0d@yandex.ru… Recipient ok
data
354 Enter mail, end with "." on a line by itself
Hey
This is test email only
Thanks
.
250 2.0.0 r9M95xgc014513 Message accepted for delivery
quit
221 2.0.0 mail.servername.com closing connection
Connection closed by foreign host.
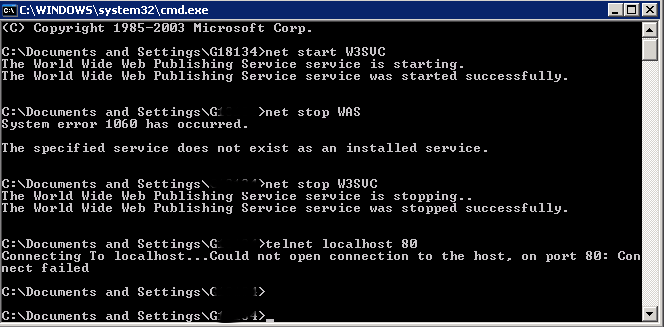
It is handy if you want to know whether remote MTA server has a certain Emailbox existing or not with telnet by simply trying to send to a certian email and checking the Email server returned output (note that the message returned depends on the remote MTA version and many qmails are configured to not give information on the initial SMTP handshake but returns instead a MAILER DAEMON failure error sent back to your sender address. Some MX servrers are still vulnerable to this attack yet, historically dreamhost.com. Below attack screenshot is made at the times before dreamhost.com fixed the brute force email issue.
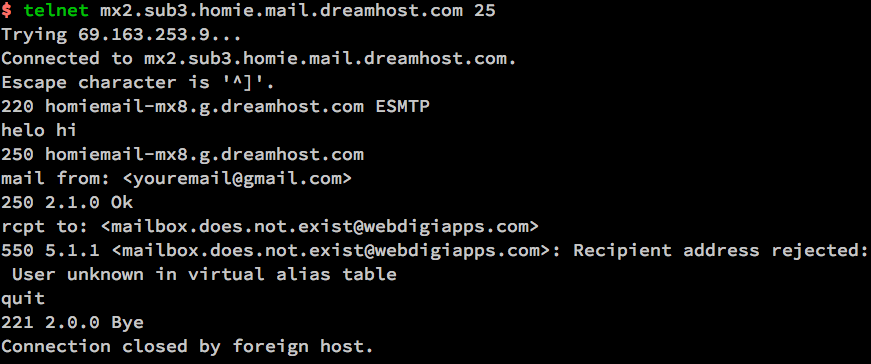
6. Using simple netcat TCP/IP Swiss Army Knife to test and send email in console

Other tool besides telnet of testing remote / local SMTP is netcat tool (for reading and writting data across TCP and UDP connections).
The way to do it is analogous but since netcat is not present on most Linux OSes by default you need to install it through the package manager first be it apt or yum etc.
# apt-get –yes install netcat
…
First lets create a new file test_email_content.txt using bash's echo cmd.
# echo 'EHLO hostname
MAIL FROM: hip0d@yandex.ru
RCPT TO: solutions@www.pc-freak.net
DATA
From: A tester <hip0d@yandex.ru>
To: <solutions@www.pc-freak.net>
Date: date
Subject: A test message from test hostname
Delete me, please
.
QUIT
' >>test_email_content.txt
# netcat -C localhost 25 < test_email_content.txt
220 This is Mail Pc-Freak.NET ESMTP
250-This is Mail Pc-Freak.NET
250-STARTTLS
250-SIZE 80000000
250-PIPELINING
250 8BITMIME
250 ok
250 ok
354 go ahead
451 See http://pobox.com/~djb/docs/smtplf.html.
Because of its simplicity and the fact it has a bit more capabilities in reading / writing data over network it was no surprise it was among the favorite tools not only of crackers and penetration testers but also a precious debug tool for the avarage sysadmin. netcat's advantage over telnet is you can push-pull over the remote SMTP port (25) a non-interactive input.
7. Using openssl to connect and send email via encrypted channel
root@linux:~# openssl s_client -connect smtp.gmail.com:465 -crlf -ign_eof
===
Certificate negotiation output from openssl command goes here
===
220 smtp.gmail.com ESMTP j92sm925556edd.81 – gsmtp
EHLO localhost
250-smtp.gmail.com at your service, [78.139.22.28]
250-SIZE 35882577
250-8BITMIME
250-AUTH LOGIN PLAIN XOAUTH2 PLAIN-CLIENTTOKEN OAUTHBEARER XOAUTH
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250-PIPELINING
250-CHUNKING
250 SMTPUTF8
AUTH PLAIN *passwordhash*
235 2.7.0 Accepted
MAIL FROM: <hipo@pcfreak.org>
250 2.1.0 OK j92sm925556edd.81 – gsmtp
rcpt to: <systemexec@gmail.com>
250 2.1.5 OK j92sm925556edd.81 – gsmtp
DATA
354 Go ahead j92sm925556edd.81 – gsmtp
Subject: This is openssl mailing
Hello nice user
.
250 2.0.0 OK 1339757532 m46sm11546481eeh.9
quit
221 2.0.0 closing connection m46sm11546481eeh.9
read:errno=0
8. Using CURL (URL transfer) tool to send SSL / TLS secured crypted channel emails via Gmail / Yahoo servers and MailGun Mail send API service
Using curl webpage downloading advanced tool for managing email send might be a shocking news to many as it is idea is to just transfer data from a server.
curl is mostly used in conjunction with PHP website scripts for the reason it has a Native PHP implementation and many PHP based websites widely use it for download / upload of user data.
Interestingly besides support for HTTP and FTP it has support for POP3 and SMTP email protocols as well
If you don't have it installed on your server and you want to give it a try, install it first with apt:
root@linux:~# apt-get install curl
To learn more about curl capabilities make sure you check cURL –manual arg.
root@linux:~# curl –manual
a) Sending Emails via Gmail and other Mail Public services
Curl is capable to send emails from terminal using Gmail and Yahoo Mail services, if you want to give that a try.
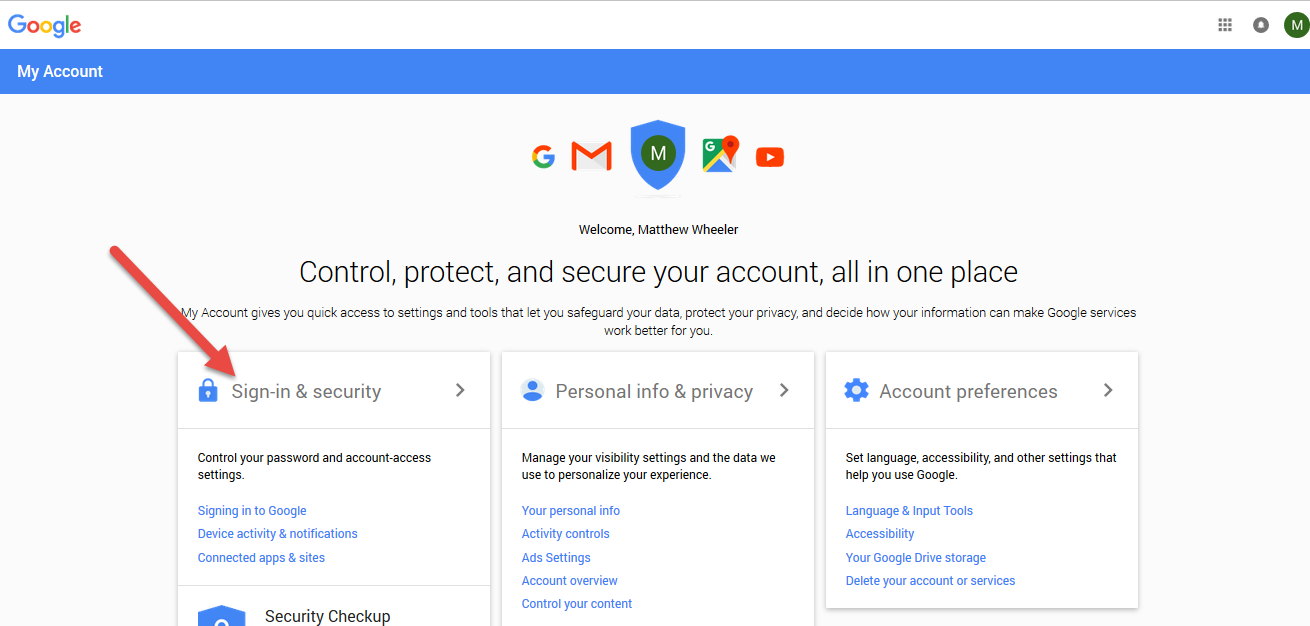
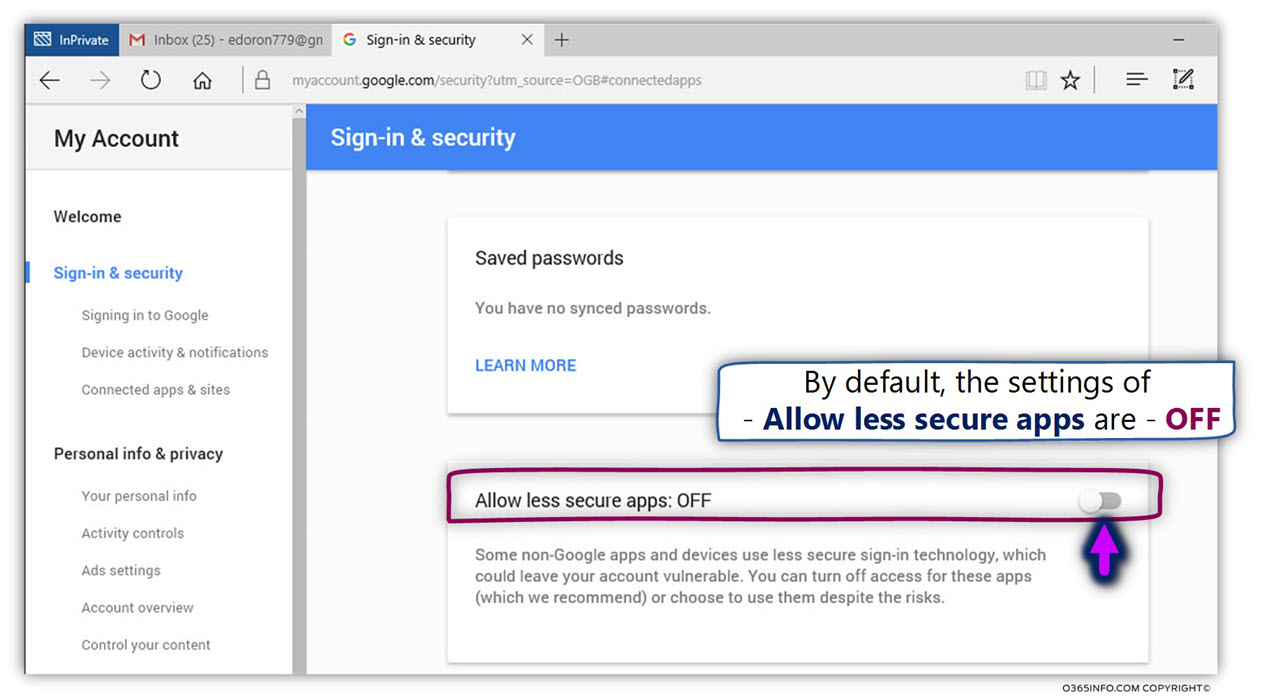
Go to myaccount.google.com URL and login from the web interface choose Sign in And Security choose Allow less Secure Apps to be -> ON and turn on access for less secure apps in Gmail. Though I have not tested it myself so far with Yahoo! Mail, I suppose it should have a similar security settings somewhere.
Here is how to use curl to send email via Gmail.
root@linux:~# curl –url 'smtps://smtp.gmail.com:465' –ssl-reqd \
–mail-from 'your_email@gmail.com' –mail-rcpt 'remote_recipient@mail.com' \
–upload-file mail.txt –user 'your_email@gmail.com:your_accout_password'
b) Sending Emails using Mailgun.com (Transactional Email Service API for developers)
To use Mailgun to script sending automated emails go to Mailgun.com and create account and generate new API key.
Then use curl in a similar way like below example:
curl -sv –user 'api:key-7e55d003b…f79accd31a' \
https://api.mailgun.net/v3/sandbox21a78f824…3eb160ebc79.mailgun.org/messages \
-F from='Excited User <developer@yourcompany.com>' \
-F to=sandbox21a78f824…3eb160ebc79.mailgun.org \
-F to=user_acc@gmail.com \
-F subject='Hello' \
-F text='Testing Mailgun service!' \
–form-string html='<h1>EDMdesigner Blog</h1><br /><cite>This tutorial helps me understand email sending from Linux console</cite>' \
-F attachment=@logo_picture.jpg
The -F option that is heavy present in above command lets curl (Emulate a form filled in button in which user has pressed the submit button).
For more info of the options check out man curl.
9. Using swaks command to send emails from
root@linux:~# apt-cache show swaks|grep "Description" -B 10
Package: swaks
Version: 20170101.0-1
Installed-Size: 221
Maintainer: Andreas Metzler <ametzler@debian.org>
Architecture: all
Depends: perl
Recommends: libnet-dns-perl, libnet-ssleay-perl
Suggests: perl-doc, libauthen-sasl-perl, libauthen-ntlm-perl
Description-en: SMTP command-line test tool
swaks (Swiss Army Knife SMTP) is a command-line tool written in Perl
for testing SMTP setups; it supports STARTTLS and SMTP AUTH (PLAIN,
LOGIN, CRAM-MD5, SPA, and DIGEST-MD5). swaks allows one to stop the
SMTP dialog at any stage, e.g to check RCPT TO: without actually
sending a mail.
.
If you are spending too much time iterating "telnet foo.example 25"
swaks is for you.
Description-md5: f44c6c864f0f0cb3896aa932ce2bdaa8
root@linux:~# apt-get instal –yes swaks
root@linux:~# swaks –to mailbox@example.com -s smtp.gmail.com:587
-tls -au <user-account> -ap <account-password>
The -tls argument (in order to use gmail encrypted TLS channel on port 587)
If you want to hide the password not to provide the password from command line so (in order not to log it to user history) add the -a options.
10. Using qmail-inject on Qmail mail servers to send simple emails
Create new file with content like:
root@qmail:~# vim email_file_content.text
To: user@mail-example.com
Subject: Test
This is a test message.
root@qmail:~# cat email_file_content.text | /var/qmail/bin/qmail-inject
qmail-inject is part of ordinary qmail installation so it is very simple it even doesn't return error codes it just ships what ever given as content to remote MTA.
If the linux host where you invoke it has a properly configured qmail installation the email will get immediately delivered. The advantage of qmail-inject over the other ones is it is really lightweight and will deliver the simple message more quickly than the the prior heavy tools but again it is more a Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) for quick debugging, if MTA is not working, than for daily email writting.
It is very useful to simply test whether email send works properly without sending any email content by (I used qmail-inject to test local email delivery works like so).
root@linux:~# echo 'To: mailbox_acc@mail-server.com' | /var/qmail/bin/qmail-inject
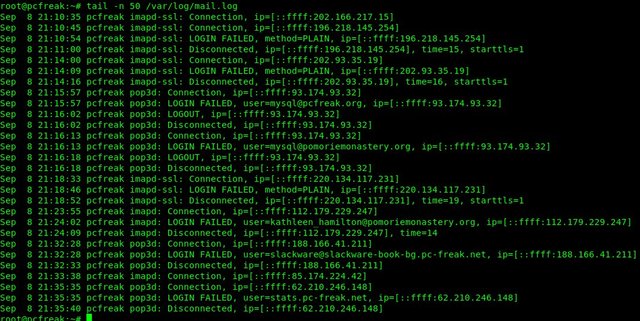
11. Debugging why Email send with text tool is not being send properly to remote recipient
If you use some of the above described methods and email is not delivered to remote recipient email addresses check /var/log/mail.log (for a general email log and postfix MTAs – the log is present on many of the Linux distributions) and /var/log/messages or /var/log/qmal (on Qmail installations) /var/log/exim4 (on servers running Exim as MTA).
Closure
The ways to send email via Linux terminal are properly innumerous as there are plenty of scripted tools in various programming languages, I am sure in this article, also missing a lot of pre-bundled installable distro packages. If you know other interesting ways / tools to send via terminal I would like to hear it.
Hope you enjoyed, happy mailing !