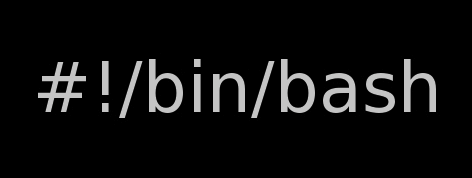Posts Tagged ‘Shell’
Monday, June 11th, 2012 
After writting in previous article on how talk be used to handle interactive chat console sessions on FreeBSD, I thought of dropping a few lines on how same is done on Debian, so here is how:
1.; Install talk and talkd
noah:/home/hipo# apt-get --yes install talk talkd
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following NEW packages will be installed:
talk talkd
0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 93 not upgraded.
Need to get 19.0 kB/42.3 kB of archives.
After this operation, 201 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/ stable/main talkd amd64 0.17-14 [19.0 kB]
Fetched 19.0 kB in 0s (67.1 kB/s)
Selecting previously deselected package talk.
(Reading database ... 90%
Unpacking talk (from .../talk_0.17-14_amd64.deb) ...
Selecting previously deselected package talkd.
Unpacking talkd (from .../talkd_0.17-14_amd64.deb) ...
Processing triggers for man-db ...
Setting up talk (0.17-14) ...
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/netkit-ntalk to provide /usr/bin/talk (talk) in auto mode.
Setting up talkd (0.17-14) ...
2.;; Check and make sure talk and ntalkd lines are present in /etc/inetd.conf
noah:/home/hipo# grep -i talk /etc/inetd.conf
#:BSD: Shell, login, exec and talk are BSD protocols.
talk dgram udp wait nobody.tty /usr/sbin/in.talkd in.talkd
ntalk dgram udp wait nobody.tty /usr/sbin/in.ntalkd in.ntalkd
Now you probably wonder why are there two lines in /etc/inetd.conf for ))
in.talkd and in.ntald
in.talkd daemon's aim is to deliver talk sessions between logged in users on one Linux host with few logged in users willing to talk to each other locally;;
Wheter in.ntalkd is designed to serve interactive user talks between the host where in.ntalkd is installed and remote systems ruwhich have the talk client program installed. Of course in order for remote talks to work properly the firewall (if such has to be modified to allow in.ntalkd chats. I've never used in.ntalkd and on most machines having in.ntald hanging around from inetd, could be a potential security hole so, for people not planning to initiate remote TALKs between Unix / Linux / BSD hosts on a network it is a good practice the ntalkd line seen above in inetd.conf to be commented out ::;
noah:/home/hipo# grep -i talk /etc/inetd.conf
#:BSD: Shell, login, exec and talk are BSD protocols.
talk dgram udp wait nobody.tty /usr/sbin/in.talkd in.talkd
#ntalk dgram udp wait nobody.tty /usr/sbin/in.ntalkd in.ntalkd
3.;;; Restart openbsd-inetd init script and talk is ready to use
noah:~# /etc/init.d/openbsd-inetd restart
* Restarting internet superserver inetd
Onwards to use talk between two users the syntax is same like on other BSD, as a matter of fact TALK – console / terminal interactive chat originally was developed for the 4.2BSD UNIX release ;; the Linux code is a port of this BSD talk and not rewrite from scratch.
Using talk between two logged in users on pts/1 (lets say user test) and tty1 (user logged as root) is done with:
noah:~$ tty
noah:~$ talk root@localhost tty1
/dev/pts/1
On tty1 the user has to have enabled Talk sessions request, by default this behaviour in Debian and probably other Debian based Linuxes (Ubuntu) for instance is configured to have talks disabled, i,e ,,,
root@noah:~# mesg
is n
Enabling it on root console is done with:
root@noah:~# mesg y
Once enabled the root will be able to see the TALK service requests on tty1 otherwise, the user gets nothing. With enabled messaging the root user will get on his tty:
Message from TalkDaemon@his_machine...
talk: connection requested by your_name@your_machine.
talk: respond with: talk your_name@your_machine
So on the root console to reply back to talk chat request:
noah:~$ talk hipo@localhost
Tags: aim, Auto, auto mode, building, configured, confnoah, daemon, deb, debian gnu, dependency, dependency tree, dgram, Disk, disk space, DoneBuilding, Draft, exec, Fetched, freebsd, gnu linux, inetd, information, Install, Installing, interactive user, localhost, login, mesg, network, noah, nobody, ntalk, ntalkd, operation, package, protocols, reading database, reading package, request, root, root user, sbin, sessions, Shell, shell login, state information, tree, tty, wait, work, writting
Posted in Curious Facts, Everyday Life, Linux, Various | No Comments »
Saturday, April 28th, 2012 
If there is necessity to look for a string in all hidden files with all sub-level subdirectories (be aware this will be time consuming and CPU stressing) use:
hipo@noah:~$ grep -rli 'PATH' .*
./.gftp/gftprc
./.gftp/cache/cache.OOqZVP
….
Sometimes its necessery to only grep for variables within the first-level directories (lets say you would like to grep a 'PATH' variable set, string within the $HOME directory, the command is:
hipo@noah:~$ grep PATH .[!.]*
.profile:PATH=/bin:/usr/bin/:${PATH}
.profile:export PATH
.profile:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.profile: PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
.profile.language-env-bak:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.profile.language-env-bak: PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
.viminfo:?/PATH.xcyrillic: XNLSPATH=/usr/X11R6/lib/X11/nls
.xcyrillic: export XNLSPATH
The regular expression .[!.]*, means exclude any file or directory name starting with '..', e.g. match only .* files
Note that to use the grep PATH .[!.]* on FreeBSD you will have to use this regular expression in bash shell, the default BSD csh or tsch shells will not recognize the regular expression, e.g.:
grep PATH '.[!.]*'
grep: .[!.]*: No such file or directory
Hence on BSD, if you need to look up for a string within the home directory, hidden files: .profile .bashrc .bash_profile .cshrc run it under bash shell:
freebsd# /usr/local/bin/bash
[root@freebsd:/home/hipo]# grep PATH .[!.]*
.bash_profile:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.bash_profile:# PATH=~/bin:"${PATH}"
.bash_profile:# do the same with …
Another easier to remember, alternative grep cmd is:
hipo@noah:~$ grep PATH .*
.profile:PATH=/bin:/usr/bin/:${PATH}
.profile:export PATH
.profile:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.profile: PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
….
Note that grep 'string' .* is a bit different in meaning, as it will not prevent grep to match filenames with names ..filename1, ..filename2 etc.
Though grep 'string' .* will work note that it will sometimes output some unwanted matches if filenames with double dot in the beginning of file name are there …
That's all folks 🙂
Tags: Auto, bash shell, bit, BSD, cache cache, cmd, consuming, csh, cshrc, directory name, Draft, export path, expression, file, freebsd, gftp, grep, hipo, home directory, How to, level directories, Linux, MANPATHAnother, nbsp, necessery, noah, note, Path, path profile, private bin, profile path, quot, regular expression, rli, root, set path, Shell, shrc, text, text strings, time, time consuming, tsch, value, XNLSPATH, XNLSPATHThe, zcompdump
Posted in FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration | 2 Comments »
Tuesday, October 4th, 2011 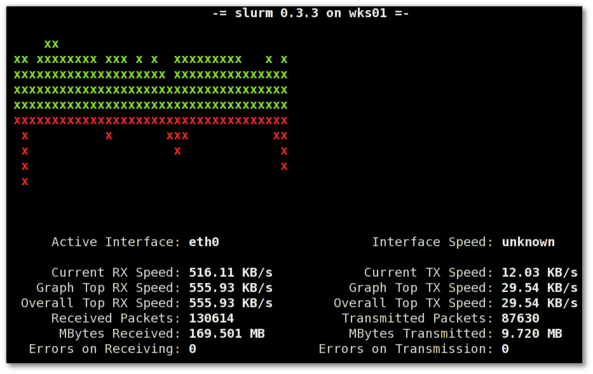
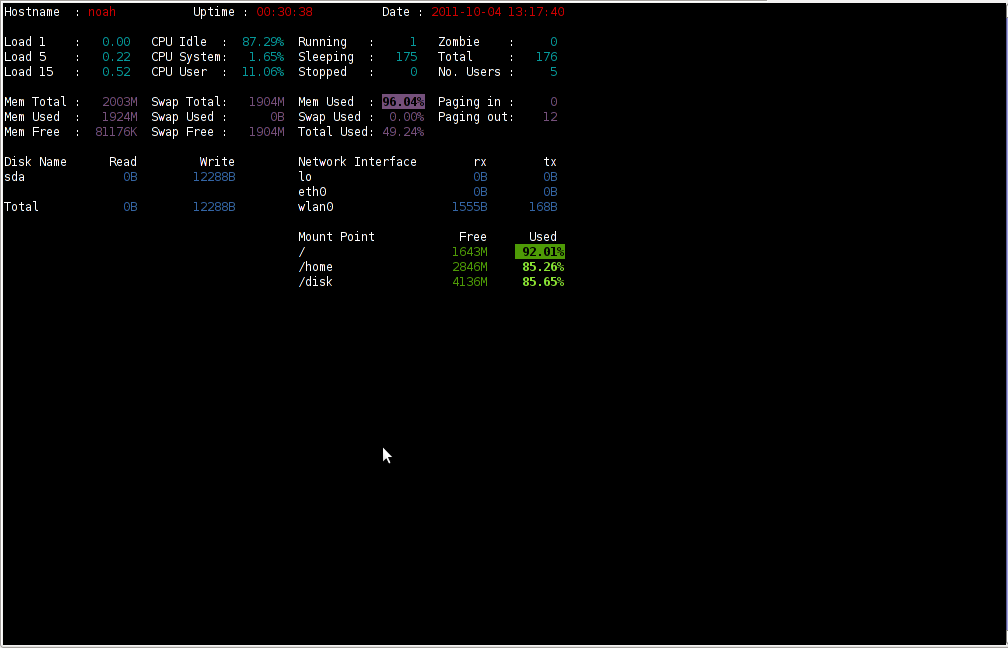
saidar is a text based ncurses program to display live statistics about general system health.
It displays in one refreshable screen (similar to top) statistics about server state of:
CPU, Load, Memory, Swap, Network, I/O disk operations
Besides that saidar supports a ncurses console colors, which makes it more funny to look at.
Saidar extracts the statistics for system state based on libgstrap cross platform statistics library about pc system health.
On Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS Linuxes saider is available for install straight from distribution repositories.
On Debian and Ubuntu saidar is installed with cmd:
debian:~# apt-get install saidar
...
On CentOS and Fedora saidar is bundled as a part of statgrab-tools rpm package.
Installing it on 64 bit CentOS with yum is with command:
[root@centos ~]# yum install statgrab-tools.x86_64
Saidar is also available on FreeBSD as a part of the /usr/ports/devel/libgstrab, hence to use on my FreeBSD I had to install the libgstrab port:
freebsd# cd /usr/ports/devel/libstatgrab
freebsd# make install clean
Here is saidar running on my Desktop Debian on Thinkpad in color output:
debian:~# saidar -c
I've seen many people, who use various shell scripts to output system monitoring information, this scripts however are often written to just run without efficiency in mind and they put some let's say 1% extra load on the system CPU. This is not the case with saidar which is written in C and hence the program is optimized well for what it does.
Update: Next to saidar I recommend you check out Slurm (Real Time Network Interface Monitor) it can visualizes network interface traffic using ascii graph such as on top of the article. On Debian and Ubuntu Slurm is available and easily installable via simple:
apt-get install –yes slurm
Tags: CentOS, cleanHere, cpu load, cross platform, Desktop, desktop system, Disk, disk operations, distribution, extracts, fedora, freebsd, health, information, libgstrab, libgstrap, Linux, Load, load memory, memory, Monitor General Server Desktop, package, platform, ports, repositories, root, rpm, saidar, saider, screen, server desktop, server state, Shell, shell scripts, Slurm Real Time Network Interface Monitor, statistics library, system cpu, system health, text, thinkpad, Ubuntu, use, yum
Posted in FreeBSD, Linux, Monitoring, Networking, System Administration | 1 Comment »
Saturday, March 24th, 2012 
I've written a tiny script to check and restart, Apache if the server encounters, extremely high load avarage like for instance more than (>25). Below is an example of a server reaching a very high load avarage:;
server~:# uptime
13:46:59 up 2 days, 18:54, 1 user, load average: 58.09, 59.08, 60.05
load average: 0.09, 0.08, 0.08
Sometimes high load avarage is not a problem, as the server might have a very powerful hardware. A high load numbers is not always an indicator for a serious problems. Some 16 CPU dual core (2.18 Ghz) machine with 16GB of ram could probably work normally with a high load avarage like in the example. Anyhow as most servers are not so powerful having such a high load avarage, makes the machine hardly do its job routine.
In my specific, case one of our Debian Linux servers is periodically reaching to a very high load level numbers. When this happens the Apache webserver is often incapable to serve its incoming requests and starts lagging for clients. The only work-around is to stop the Apache server for a couple of seconds (10 or 20 seconds) and then start it again once the load avarage has dropped to less than "3".
If this temporary fix is not applied on time, the server load gets increased exponentially until all the server services (ssh, ftp … whatever) stop responding normally to requests and the server completely hangs …
Often this server overloads, are occuring at night time so I'm not logged in on the server and one such unexpected overload makes the server unreachable for hours.
To get around the sudden high periodic load avarage server increase, I've written a tiny bash script to monitor, the server load avarage and initiate an Apache server stop and start with a few seconds delay in between.
#!/bin/sh
# script to check server for extremely high load and restart Apache if the condition is matched
check=`cat /proc/loadavg | sed 's/\./ /' | awk '{print $1}'`
# define max load avarage when script is triggered
max_load='25'
# log file
high_load_log='/var/log/apache_high_load_restart.log';
# location of inidex.php to overwrite with temporary message
index_php_loc='/home/site/www/index.php';
# location to Apache init script
apache_init='/etc/init.d/apache2';
#
site_maintenance_msg="Site Maintenance in progress - We will be back online in a minute";
if [ $check -gt "$max_load" ]; then>
#25 is load average on 5 minutes
cp -rpf $index_php_loc $index_php_loc.bak_ap
echo "$site_maintenance_msg" > $index_php_loc
sleep 15;
if [ $check -gt "$max_load" ]; then
$apache_init stop
sleep 5;
$apache_init restart
echo "$(date) : Apache Restart due to excessive load | $check |" >> $high_load_log;
cp -rpf $index_php_loc.bak_ap $index_php_loc
fi
fi
The idea of the script is partially based on a forum thread – Auto Restart Apache on High Load – http://www.webhostingtalk.com/showthread.php?t=971304Here is a link to my restart_apache_on_high_load.sh script
The script is written in a way that it makes two "if" condition check ups, to assure 100% there is a constant high load avarage and not just a temporal 5 seconds load avarage jump. Once the first if is matched, the script first tries to reduce the server load by overwritting a the index.php, index.html script of the website with a one stating the server is ongoing a maintenance operations.
Temporary stopping the index page, often reduces the load in 10 seconds of time, so the second if case is not necessery at all. Sometimes, however this first "if" condition cannot decrease enough the load and the server load continues to stay too high, then the script second if comes to play and makes apache to be completely stopped via Apache init script do 2 secs delay and launch the apache server again.
The script also logs about, the load avarage encountered, while the server was overloaded and Apache webserver was restarted, so later I can check what time the server overload occured.
To make the script periodically run, I've scheduled the script to launch every 5 minutes as a cron job with the following cron:
# restart Apache if load is higher than 25
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/restart_apache_on_high_load.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
I have also another system which is running FreeBSD 7_2, which is having the same overload server problems as with the Linux host.
Copying the auto restart apache on high load script on FreeBSD didn't work out of the box. So I rewrote a little chunk of the script to make it running on the FreeBSD host. Hence, if you would like to auto restart Apache or any other service on FreeBSD server – get /usr/sbin/restart_apache_on_high_load_freebsd.sh my script and set it on cron on your BSD.
This script is just a temporary work around, however as its obvious that the frequency of the high overload will be rising with time and we will need to buy new server hardware to solve permanently the issues, anyways, until this happens the script does a great job 🙂
I'm aware there is also alternative way to auto restart Apache webserver on high server loads through using monit – utility for monitoring services on a Unix system. However as I didn't wanted to bother to run extra services in the background I decided to rather use the up presented script.
Interesting info to know is Apache module mod_overload exists – which can be used for checking load average. Using this module once load avarage is over a certain number apache can stop in its preforked processes current serving request, I've never tested it myself so I don't know how usable it is. As of time of writting it is in early stage version 0.2.2
If someone, have tried it and is happy with it on a busy hosting servers, please share with me if it is stable enough?
Tags: Anyhow, apache server, apache webserver, Auto, avarage, awk print, bak, bash script, bash shell, bash shell script, condition, cron, cron job, Draft, dual core, host, incoming requests, index, index page, init, instance, job, level, level numbers, Linux, linux servers, loc, location, night time, php, quot, Restart, restart apache, rpf, script, server load, server overloads, server services, server uptime, Shell, ssh, ssh ftp, time, unexpected overload, unreachable, utility
Posted in FreeBSD, Programming, System Administration | 5 Comments »
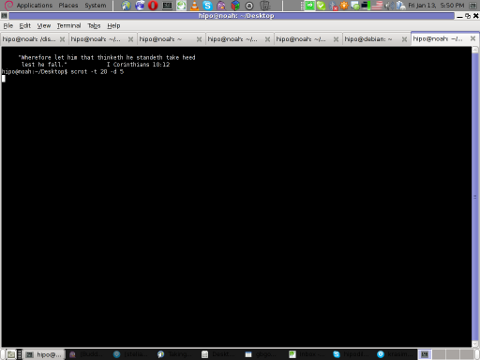
Friday, January 13th, 2012 scrot and import are two commands, which can be used to take screenshot in terminal on Linux and FreeBSD:
To use scrot cmd to take screenshots on Ubuntu and Debian the scrot package has to be installed:
noah:~# apt-get install scrot
...
scrot should also be available on most other Linux distributions in the main repositories, I'll be glad to hear if someone has used it on Fedora, SUSE etc.
On FreeBSD, there is a port called scrot , to install on FreeBSD:
freebsd# cd /usr/ports/graphics/scrot
freebsd# make install clean
...
Scrot has plenty of nice arguments one can use to make a screenshot. Maybe the most handy one in my view is after a preliminary set delay before screenshot is taken.
To take screenshot with it after lets say 5 seconds delay before the screenshot:
hipo@noah:~/Desktop$ scrot -t 20 -d 5
To put an year, month and day and year followed by screen resolution with scrot :
hipo@noah:~$ scrot '%Y-%m-%d_$wx$h.png'
Another way to take a screenshot of screen with command is by using ImageMagick's – import image manipulation package.
To take screenshot of the current screen via terminal using import , type in xterm, gnome-termina or Gnome's Run Application (ALT+F2)
hipo@noah:~$ import -window root ScreenShot.png
To make import command to save the taken screenshot in a format (minute:hour:day:month:year)i :
hipo@noah:~$ import -window root $screenshot_dir/screenshot-$(date +%M_%k_%d_%m_%Y|sed -e 's/^ *//').png
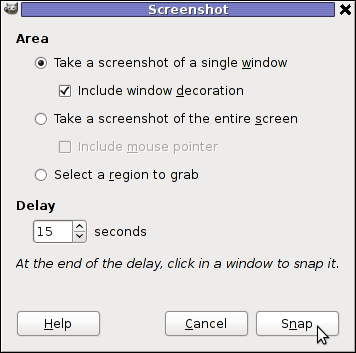
Taking a delayed screenshot is also possible via The GIMP via menus File -> Create -> Screenshot
Now here is an interesting question, what if I would like to take periodic screenshots of what I do on my Desktop to take random movie scenes from a movie I watch with totem or vlc??
This task is quite easily achiavable with a little bash shell script, I wrote:
screenshot_dir='Screenshots';
seconds='60';
if [ ! -d "$screenshot_dir" ]; then
mkdir $screenshot_dir;
fi
while [ 1 ]; do
sleep $seconds;
(import -window root $screenshot_dir/screenshot-$(date +%M_%k_%d_%m_%Y|sed -e 's/^ *//').png) &
done
This script will take screenshot automatically to Screenshots/ directory every (1 min – 60 seconds)
You can also my downloads take_screenshot_every_60_secs_import.sh here
To use take_screenshot_every_60_secs_import.sh just issue the script inside xterm or gnome-terminal, after that simply use your computer as you normally would.
The script will take snapshots every minute and store all taken screenshots in Screenshots dir.
If you prefer to use scrot to take automatically the screenshots every lets say 5 minutes, you can use a script like:
screenshot_dir='Screenshots';
# 300 secs (5 mins)seconds='300';
if [ ! -d "$screenshot_dir" ]; then
mkdir $screenshot_dir;
fi
while [ 1 ]; do
sleep $seconds;
(scrot $screenshot_dir/'%Y-%m-%d_$wx$h.png') &
done
You can fetch take_screenshot_every_60_secs_scrot.sh here
The script using scrot is better in terms of efficiency, the system load scrot will put on your machine will be less.
Using some of this scripts will be handy if you need screenshots to Movies, Programs and favourite Free Software games.
Hope this is educative to someone 😉
Tags: Alt, Auto, bash shell script, Desktop, Draft, fedora, freebsd, GIMP, Gnome, gnu linux, handy one, hipo, How to, image manipulation, ImageMagick, import, import command, import image, import window, linux distributions, manipulation package, multiple, noah, package, png, quot, repositories, root, screen, screenshot, Screenshots, scrot, Shell, someone, SUSE, terminal, totem, type, Ubuntu, wx, xterm, year
Posted in FreeBSD, Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration, Various | No Comments »
Tuesday, May 3rd, 2011 In short I’ll explain here what is Grsecurity http://www.grsecurity.net/ for all those who have not used it yet and what kind of capabilities concerning enhanced kernel security it has.
Grsecurity is a combination of patches for the Linux kernel accenting at the improving kernel security.
The typical application of GrSecurity is in the field of Linux systems which are administered through SSH/Shell, e.g. (remote hosts), though you can also configure grsecurity on a normal Linux desktop system if you want a super secured Linux desktop ;).
GrSecurity is used heavily to protect server system which require a multiple users to have access to the shell.
On systems where multiple user access is required it’s a well known fact that (malicious users, crackers or dumb script kiddies) get administrator (root) privileges with a some just poped in 0 day root kernel exploit.
If you’re an administrator of a system (let’s say a web hosting) server with multiple users having access to the shell it’s also common that exploits aiming at hanging in certain daemon service is executed by some of the users.
In other occasions you have users which are trying to DoS the server with some 0 day Denial of Service exploit.
In all this cases GrSecurity having a kernel with grsecurity is priceless.
Installing grsecurity patched kernel is an easy task for Debian and Ubuntu and is explained in one of my previous articles.
This article aims to explain in short some configuration options for a GrSecurity tightened kernel, when one have to compile a new kernel from source.
I would skip the details on how to compile the kernel and simply show you some picture screens with GrSecurity configuration options which are working well and needs to be set-up before a make command is issued to compile the new kernel.
After preparing the kernel source for compilation and issuing:
linux:/usr/src/kernel-source$ make menuconfig
You will have to select options like the ones you see in the pictures below:
[nggallery id=”8″]
After completing and saving your kernel config file, continue as usual with an ordinary kernel compilation, e.g.:
linux:/usr/src/kernel-source$ make
linux:/usr/src/kernel-source$ make modules
linux:/usr/src/kernel-source$ su root
linux:/usr/src/kernel-source# make modules_install
linux:/usr/src/kernel-source# make install
linux:/usr/src/kernel-source# mkinitrd -o initrd.img-2.6.xx 2.6.xx
Also make sure the grub is properly configured to load the newly compiled and installed kernel.
After a system reboot, if all is fine you should be able to boot up the grsecurity tightened newly compiled kernel, but be careful and make sure you have a backup solution before you reboot, don’t blame me if your new grsecurity patched kernel fails to boot! You’re on your own boy 😉
This article is written thanks to based originally on his article in Bulgarian. If you’re a Bulgarian you might also checkout static’s blog
Tags: administrator, combination, compilation, config, configuration options, configure, crackers, day, Denial, denial of service, Desktop, desktop system, exploits, file, grsecurity, hosting server, How to, img, installlinux, kernel source, Linux, linux desktop, linux kernel, linux systems, make, malicious users, Maximum, maximum linux, menuconfigYou, multiple users, picture, root, root privileges, say, script, script kiddies, server system, Shell, src, system, typical application, Ubuntu, usr
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration | No Comments »
Thursday, April 7th, 2011 
If you’re a a remote Linux many other Unix based OSes, you have defitenily faced the security threat of many failed ssh logins or as it’s better known a brute force attack
During such attacks your /var/log/messages or /var/log/auth gets filled in with various failed password logs like for example:
Feb 3 20:25:50 linux sshd[32098]: Failed password for invalid user oracle from 95.154.249.193 port 51490 ssh2
Feb 3 20:28:30 linux sshd[32135]: Failed password for invalid user oracle1 from 95.154.249.193 port 42778 ssh2
Feb 3 20:28:55 linux sshd[32141]: Failed password for invalid user test1 from 95.154.249.193 port 51072 ssh2
Feb 3 20:30:15 linux sshd[32163]: Failed password for invalid user test from 95.154.249.193 port 47481 ssh2
Feb 3 20:33:20 linux sshd[32211]: Failed password for invalid user testuser from 95.154.249.193 port 51731 ssh2
Feb 3 20:35:32 linux sshd[32249]: Failed password for invalid user user from 95.154.249.193 port 38966 ssh2
Feb 3 20:35:59 linux sshd[32256]: Failed password for invalid user user1 from 95.154.249.193 port 55850 ssh2
Feb 3 20:36:25 linux sshd[32268]: Failed password for invalid user user3 from 95.154.249.193 port 36610 ssh2
Feb 3 20:36:52 linux sshd[32274]: Failed password for invalid user user4 from 95.154.249.193 port 45514 ssh2
Feb 3 20:37:19 linux sshd[32279]: Failed password for invalid user user5 from 95.154.249.193 port 54262 ssh2
Feb 3 20:37:45 linux sshd[32285]: Failed password for invalid user user2 from 95.154.249.193 port 34755 ssh2
Feb 3 20:38:11 linux sshd[32292]: Failed password for invalid user info from 95.154.249.193 port 43146 ssh2
Feb 3 20:40:50 linux sshd[32340]: Failed password for invalid user peter from 95.154.249.193 port 46411 ssh2
Feb 3 20:43:02 linux sshd[32372]: Failed password for invalid user amanda from 95.154.249.193 port 59414 ssh2
Feb 3 20:43:28 linux sshd[32378]: Failed password for invalid user postgres from 95.154.249.193 port 39228 ssh2
Feb 3 20:43:55 linux sshd[32384]: Failed password for invalid user ftpuser from 95.154.249.193 port 47118 ssh2
Feb 3 20:44:22 linux sshd[32391]: Failed password for invalid user fax from 95.154.249.193 port 54939 ssh2
Feb 3 20:44:48 linux sshd[32397]: Failed password for invalid user cyrus from 95.154.249.193 port 34567 ssh2
Feb 3 20:45:14 linux sshd[32405]: Failed password for invalid user toto from 95.154.249.193 port 42350 ssh2
Feb 3 20:45:42 linux sshd[32410]: Failed password for invalid user sophie from 95.154.249.193 port 50063 ssh2
Feb 3 20:46:08 linux sshd[32415]: Failed password for invalid user yves from 95.154.249.193 port 59818 ssh2
Feb 3 20:46:34 linux sshd[32424]: Failed password for invalid user trac from 95.154.249.193 port 39509 ssh2
Feb 3 20:47:00 linux sshd[32432]: Failed password for invalid user webmaster from 95.154.249.193 port 47424 ssh2
Feb 3 20:47:27 linux sshd[32437]: Failed password for invalid user postfix from 95.154.249.193 port 55615 ssh2
Feb 3 20:47:54 linux sshd[32442]: Failed password for www-data from 95.154.249.193 port 35554 ssh2
Feb 3 20:48:19 linux sshd[32448]: Failed password for invalid user temp from 95.154.249.193 port 43896 ssh2
Feb 3 20:48:46 linux sshd[32453]: Failed password for invalid user service from 95.154.249.193 port 52092 ssh2
Feb 3 20:49:13 linux sshd[32458]: Failed password for invalid user tomcat from 95.154.249.193 port 60261 ssh2
Feb 3 20:49:40 linux sshd[32464]: Failed password for invalid user upload from 95.154.249.193 port 40236 ssh2
Feb 3 20:50:06 linux sshd[32469]: Failed password for invalid user debian from 95.154.249.193 port 48295 ssh2
Feb 3 20:50:32 linux sshd[32479]: Failed password for invalid user apache from 95.154.249.193 port 56437 ssh2
Feb 3 20:51:00 linux sshd[32492]: Failed password for invalid user rds from 95.154.249.193 port 45540 ssh2
Feb 3 20:51:26 linux sshd[32501]: Failed password for invalid user exploit from 95.154.249.193 port 53751 ssh2
Feb 3 20:51:51 linux sshd[32506]: Failed password for invalid user exploit from 95.154.249.193 port 33543 ssh2
Feb 3 20:52:18 linux sshd[32512]: Failed password for invalid user postgres from 95.154.249.193 port 41350 ssh2
Feb 3 21:02:04 linux sshd[32652]: Failed password for invalid user shell from 95.154.249.193 port 54454 ssh2
Feb 3 21:02:30 linux sshd[32657]: Failed password for invalid user radio from 95.154.249.193 port 35462 ssh2
Feb 3 21:02:57 linux sshd[32663]: Failed password for invalid user anonymous from 95.154.249.193 port 44290 ssh2
Feb 3 21:03:23 linux sshd[32668]: Failed password for invalid user mark from 95.154.249.193 port 53285 ssh2
Feb 3 21:03:50 linux sshd[32673]: Failed password for invalid user majordomo from 95.154.249.193 port 34082 ssh2
Feb 3 21:04:43 linux sshd[32684]: Failed password for irc from 95.154.249.193 port 50918 ssh2
Feb 3 21:05:36 linux sshd[32695]: Failed password for root from 95.154.249.193 port 38577 ssh2
Feb 3 21:06:30 linux sshd[32705]: Failed password for bin from 95.154.249.193 port 53564 ssh2
Feb 3 21:06:56 linux sshd[32714]: Failed password for invalid user dev from 95.154.249.193 port 34568 ssh2
Feb 3 21:07:23 linux sshd[32720]: Failed password for root from 95.154.249.193 port 43799 ssh2
Feb 3 21:09:10 linux sshd[32755]: Failed password for invalid user bob from 95.154.249.193 port 50026 ssh2
Feb 3 21:09:36 linux sshd[32761]: Failed password for invalid user r00t from 95.154.249.193 port 58129 ssh2
Feb 3 21:11:50 linux sshd[537]: Failed password for root from 95.154.249.193 port 58358 ssh2
This brute force dictionary attacks often succeed where there is a user with a weak a password, or some old forgotten test user account.
Just recently on one of the servers I administrate I have catched a malicious attacker originating from Romania, who was able to break with my system test account with the weak password tset .
Thanksfully the script kiddie was unable to get root access to my system, so what he did is he just started another ssh brute force scanner to crawl the net and look for some other vulnerable hosts.
As you read in my recent example being immune against SSH brute force attacks is a very essential security step, the administrator needs to take on a newly installed server.
The easiest way to get read of the brute force attacks without using some external brute force filtering software like fail2ban can be done by:
1. By using an iptables filtering rule to filter every IP which has failed in logging in more than 5 times
To use this brute force prevention method you need to use the following iptables rules:
linux-host:~# /sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -i eth0 -m state -state NEW -m recent -set
linux-host:~# /sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -i eth0 -m state -state NEW
-m recent -update -seconds 60 -hitcount 5 -j DROP
This iptables rules will filter out the SSH port to an every IP address with more than 5 invalid attempts to login to port 22
2. Getting rid of brute force attacks through use of hosts.deny blacklists
sshbl – The SSH blacklist, updated every few minutes, contains IP addresses of hosts which tried to bruteforce into any of currently 19 hosts (all running OpenBSD, FreeBSD or some Linux) using the SSH protocol. The hosts are located in Germany, the United States, United Kingdom, France, England, Ukraine, China, Australia, Czech Republic and setup to report and log those attempts to a central database. Very similar to all the spam blacklists out there.
To use sshbl you will have to set up in your root crontab the following line:
*/60 * * * * /usr/bin/wget -qO /etc/hosts.deny http://www.sshbl.org/lists/hosts.deny
To set it up from console issue:
linux-host:~# echo '*/60 * * * * /usr/bin/wget -qO /etc/hosts.deny http://www.sshbl.org/lists/hosts.deny' | crontab -u root -
These crontab will download and substitute your system default hosts with the one regularly updated on sshbl.org , thus next time a brute force attacker which has been a reported attacker will be filtered out as your Linux or Unix system finds out the IP matches an ip in /etc/hosts.deny
The /etc/hosts.deny filtering rules are written in a way that only publicly known brute forcer IPs will only be filtered for the SSH service, therefore other system services like Apache or a radio, tv streaming server will be still accessible for the brute forcer IP.
It’s a good practice actually to use both of the methods 😉
Thanks to Static (Multics) a close friend of mine for inspiring this article.
Tags: amanda, apache, brute force, example feb, Failed, fax, ftpuser, hosts, info, invalid user, Linux, log, log messages, logins, logs, majordomo, malicious attacker, mark, maximal protection, oracle, password, peter, port, postgres, protection, root, Secure, secure shell, security, security threat, Shell, sophie, ssh, ssh secure shell, system, temp, test, test1, testuser, threat, tomcat, toto, trac, unix, upload, user1, user2, user3, user5, var, webmaster
Posted in Linux, System Administration | 6 Comments »
Thursday, April 3rd, 2014 
POSITIVE RESULTS FOR RUSSIA DURING REIGN OF VLADIMIR PUTIN
- For last 12 years of government Putin increated Russia's budget 22 times.
- Increated warfare spendings 30 times.
- Increated GDP 12 times (by GDP Russia moved from 36th to 6th place in the World).
- Increated Russian golden reserves 48 times.
- Returned back 256 oil, petrol and other natural resources sources / mine-yards (under non-Russian government curretnly are only 3 of
- Russia's source for natural resources.
- Nationalized 65% of oil industry and 95% of gas industry.
- For a 5th consequential year 2nd / 3rd place in export of grain (just for a comparison USA is currently ranked 4th largest weed exporter). The avarage sallary of national institution employed increased 18.5 times.
- Avarage pension increased 14 times.
- Reduce of population decreased from 1.5 million per year in year 1999 to 21 000 in 2011, i.e. 71 times.
- Prohibited deputies in Government to have bank accounts in foreign banks.Prevented American attack against Syria.
- Put an end to war in Chechnya.
From January y. 2000 to present times Russian ruble rate changed from 28 Rubles per dollar to 29 Rubles per dollar – i.e. severe inflation in Russia ended.Present day Russia is a normal European country not that poor country where approimate pension was 20 dollars and where masters was the financial pyramids and the International Monatery Fund
In 1992 Eltsin cancelled completely export duty of oil products.
In 23 January E. Primakov government forced again oil taxes.
In export price of 9.5 dollars per barrel custom taxes were 2.5 euro per tone and in price 12,5 dollars per barrel 5 euro / tone.Such a minor increase in taxes produced 14 billion rubles in already empty Russian budget.
In August 1999 Eltsin assigned Putin for prime minister.
In just a month later the export taxes Putin increased duty taxes to 7.5 euro/tone and in 8 december to 15 euro/tone. Till then incomes from oil taxes has been steadily increasing and nowadays exporters calculate in national budget half of incomes origin from oil prices and export taxes.
From January to November 2007 Russian customs influxed in national budget 2.57 trillion Rubles.
Oil export takes has drastically raised incomes of citizens.This had major impact on construction business.All Russia nowadays is in reality enormous "construction yard", to illustrate from January to September 2007 375 009 homes were built occupying 34 million square meters.
Cement factories cannot satisfy local market requirements and Russia is forced to import cement from China.
Increased incomes of population led to increase in estates search, this increased apartment prices and as a consequence increased incomes from building activies.
Result is in consutriction business are invested enormous amounts of capital and a real construction boom is observed.
Another consequence of increased income was increase in demand for automobiles. Just for 2006 the quantity of demanded automobiles in Russia increased with 45% and reached 32 billion dollars with a count of sold new cars numbering 2 million. By indicator of sold new cars Russia orders on 5th place after in Europe taking place right after Germany, Great Britain, Italy and France.
Currently are being build a couple of new automobile plants, and existing ones increase production volume.
All this is consequence of increase in demand and therefore from increase in citizens income.
rn>For 10 years budets expenditure for social politics (pensions and social help) increased with 30%.
Before Putin pensions were under existence-minimum with appr. 25% and in 90th pensions were not paid at all.
Now pensions are 50% above existence-minimum and is constantly increasing.
In 2000 approximate sallary in Russia was 2223 Rubles (appr. 80 dollars).
Now approximate sallary in Russia 19174 rubles (apprx. 660 dollars).
Purchase of domestic goods for 10 years increased 10 times. Number of own automobilse increased 3 times.
Putin nationalized YUKOS, without 'making nervous' emering Russian busness in a market manner – with bankruptcy and auction. All this happened lawful, following laws adopted by democratic parliament.
The president doesn't have the right to use other means. Formal occasion for arest of Hodorkovski were taxation frauds of YUKOS. In such machinations are involved practically all large private companies and this is the reason why nobody believes that excuse. It is unbelievable. However Putin simply defended Russia's interests.

The proof for that is transmission of actives of YUKOS to national corporation "Rosneft". It would have been more righteous if this actives were just confiscated … but there are laws and Putin had just stick to them. After all the President can't go out of framework of his jurisdiction.
It can be just added that after Khodorkovsky was injailed, collectivity (incomes)of taxes of ex-actives of YUKOS increased 80 TIMES!
In y. 2004 Putin finally removed law "Agreement for Separation of Production (Separation Agreement)". This law was annexed during Eltsin's regime, in order to benefit Oligarchs (Khodorkovsky, Gusinsky, Beresovsky etc.) in order to make possible Russian oil reserves to be possessed by Western (American and British) oil corporations.
By the power of this law Russian oil and natural fields went into international jurisdiction, and therefore the money from Russian oil doesn't entered budget of Russia but influxed in Western companies.
Money from oil drills went mainly into Dutch "Shell" for covering of corporation expenses. Only after something remained from that they sold it to Russia. In 2006 Putin declared following in that connection "And now we don't get anything from them and if they increase their profit we will not receive it even in 10 years from now."
In fact to this moment Russia didn't get any money from their own oil.
After the law was removed in 2004, revenues in budeg increased from 3 to 4 times.
After cancellation of contracts for oil fields "Sakhalin-1" and "Sakhalin-2" Russia's loans to American company calculated to 700 million dollars, for that time this was too much. The whole Anglo-Saxon world pricked against Putin because of a simple reason: "UK planned to assure its oil reserves for years to come in expense of Russia – only Germany and France who didn't have a direct interest in that process kept neutral …
In 1992 – 1995 the head aparatus of Russia formed its view based on foreign advisors. All legislation from 1990's was hence written by them. In Russian country administration was working 10 000 foreign coaches. George Soros was financing writting of student history books where the Battle for Stalingrad was mentioned in only 2 pages and about the meeting between Elbe and Soviet and American soldiers (Elbe Day) in 10 pages.

: In that mournful times on pupils notebook you can see portrainst of 4 American presidents of USA.
Until this very day there are left relics from that anti-Russian propaganda but hopefully with time Putin will throw away american propaganda from education system.
But why Putin cannot immediately dismiss all this hostile to Russia clerks? The reason is simple: Constitution of Russia written under dictation of Western coaches, does not allow quick changse into it.
Nowadays the President is just one of many clerks with resticted power. Yes truly president power is a bit bigger than other clerks, but country head can't influence everything. The president can't even define his ministers, even though by law this is part of his jurisdiction.
Overfulfilment of budet in times of Putin govern allowed craetion of country Stabilization fund. Nowdays is collected huge golden-currency reserve and practically Russia doesn't have external debt.
War in Kavkaz is over, separatists were destroyed. All famous terrorist leaders were liquidated physically.
Even Zelimkhan_Yandarbiyev was killed in Qatar, Basaev and Umarov were also destoyed. Putin promised "to drawn them if necessary even in their own toilet dish" and he fulfilled his promise. Of course, separatism is not completely destroyed, such conflicts cannot be quickly solved, but nowadays situation in Kakvaz is the best possible. If Chechnya's elite feels the power of Moscow and benefits of being a surrender – then separatism will fade away. This is exactly what happens. The attempts of western spy centrals to supply terrorists are still leading to separate terr. acts but this is the maximum – there will be no war anymore.
For 10 years Putin increased political influence of Russia in world and lifted its image. Today Russia follows its own interests, and not Western ones.
It is not coincidence that Putin was recognized as the most influential world politic of 2013. He prevented Russia's devastation led country out of catastrophe caused by Gorbachov and Eltsin. That's the rason why Western Medias abhor him and compare him with devil.
Everyone interested in political life in Russia seems, that the battle against corruption took unforeseen measures.
At least 2-3 times weekly on TV are shown arrests of clergy and policeman and news inform about sentences against government employees.
Lets not forget Crimea, here is how it was given to Ukraine.
In 1992 on signature of Treaty of Belovesh for dissolution of USSR Ukrainian representative Leonid Kravchuk noticed that Boris Eltsin is "in play with Vodka" and is delaying signature, he urged him with words: –
"Borya if you like take Crimea, please just sign the contract!".
Drunk Eltsin nobly waved hand:
"What for I need Crimea? Here it is your present!"
And signed and by one scratch he "killed" efforts of Prince Grigory Potemkin, Catherina the Great, heros of Sevastopol in 1856, heroes defenders of Sevastopol in 1941 …
Few days ago Putin removed consequences of this "joke with history" – and people of Crimea sung and danced on squares, returning to their motherland.
Here is Why Russophobes hates Putin!
Source Materials from http://rublogers.ru
Translated by: Georgi Georgiev
This translation is copyrighted and copying can only be done with explicit allowance of author Author or link to original translation
http://rublogers.ru/
Tags: American, avarage, bg, blog, consequence, consequences, consequential, country, devil, Dutch Shell, end, euro, existence, export, germany, heroes, Increated Russian, industry, International Monatery Fund, jurisdiction, ldquo, Leonid Kravchuk, market, meeting, mine, place, power, Prevented American, price, reason, Returned, right, ru, russia, Russian, Shell, simple, student, toilet, USA, ussr, Vladimir Putin, year, YUKOS
Posted in Curious Facts, Everyday Life, Various | 1 Comment »
Sunday, October 30th, 2011 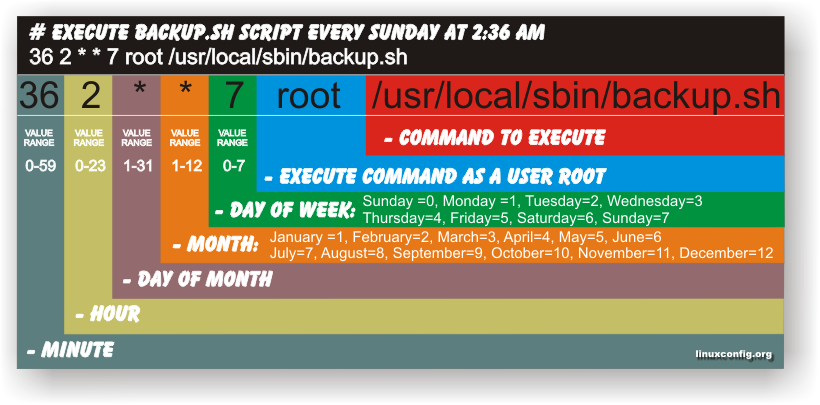
Have you ever been in need to execute some commands scheduled via a crontab, every let’s say 5 seconds?, naturally this is not possible with crontab, however adding a small shell script to loop and execute a command or commands every 5 seconds and setting it up to execute once in a minute through crontab makes this possible.
Here is an example shell script that does execute commands every 5 seconds:
#!/bin/bash
command1_to_exec='/bin/ls';
command2_to_exec='/bin/pwd';
for i in $(echo 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11); do
sleep 5;
$command1_to_exec; $command2_to_exec;
done
This script will issue a sleep every 5 seconds and execute the two commands defined as $command1_to_exec and $command2_to_exec
Copy paste the script to a file or fetch exec_every_5_secs_cmds.sh from here
The script can easily be modified to execute on any seconds interval delay, the record to put on cron to use with this script should look something like:
# echo '* * * * * /path/to/exec_every_5_secs_cmds.sh' | crontab -
Where of course /path/to/exec_every_5_secs_cmds.sh needs to be modified to a proper script name and path location.
Another way to do the on a number of seconds program / command schedule without using cron at all is setting up an endless loop to run/refresh via /etc/inittab with a number of predefined commands inside. An example endless loop script to run via inittab would look something like:
while [ 1 ]; do
/bin/ls
sleep 5;
done
To run the above sample never ending script using inittab, one needs to add to the end of inittab, some line like:
mine:234:respawn:/path/to/script_name.sh
A quick way to add the line from consone would be with echo:
echo 'mine:234:respawn:/path/to/script' >> /etc/inittab
Of course the proper paths, should be put in:
Then to load up the newly added inittab line, inittab needs to be reloaded with cmd:
# init q
I've also red, some other methods suggested to run programs on a periodic seconds basis using just cron, what I found in stackoverflow.com's as a thread proposed as a solution is:
* * * * * /foo/bar/your_script
* * * * * sleep 15; /foo/bar/your_script
* * * * * sleep 30; /foo/bar/your_script
* * * * * sleep 45; /foo/bar/your_script
One guy, even suggested a shorted way with cron:
0/15 * * * * * /path/to/my/script
Tags: bashcommand, basis, com, command, command2, copy, copy paste, course, cron, crontab, echo 1, echo echo, endless loop, exec, file, foo, foo bar, freebsd, gnu linux, How to, init, inittab, interval, line, Linux, location, loop, mine, minute, name, nbsp, number, Path, predefined commands, pwd, record, refresh, respawn, run, script, script name, secs, SHA, Shell, shell script, sleep, something, stackoverflow, thread, time, time interval, way
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration, Various | 1 Comment »
Sunday, September 22nd, 2013 
If you're using some GNU / Linux distribution with GNOME 3 and you would like to show output of screen in two connected Monitors to the machine you will stumble upon really unusual behavior. For some unknown reason GNOME environment developers make second monitor to keep fixed on on First Workspace, so whether you try changing Desktops to second / third etc. Virtual Desktop you end up with your secondary monitor focused on Workspace 1. Logically the use of Dual monitor configuration is to show all GUI output identically on both monitors so this behavior is "wrong" ….
Fortunately there is setting that control this weird behavior in GNOME through gconf-editor and simply changing that switches monitors to show properly.
To fix it:
Start Run Command or Press Alt + F2 to invoke GNOME Run menu
Navigate to registry path Desktop -> Gnome -> Shell -> Windows and Uncheck selection on workspaces_only_on_primary

To make new changes take effect its necessary to Log Off or Restart PC.
There is another easier way for command line oriented people to apply changes without using / having installed gconf-editor by issuing:
gsettings set org.gnome.shell.overrides workspaces-only-on-primary false
Tags: developers, dual monitor, gnome environment, Linux, linux distribution, multiple monitors, registry path, Shell, switches, unusual behavior, virtual desktop, weird behavior, workspace
Posted in Everyday Life, Gnome, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop | 1 Comment »