Below are some valuable advices on Wireless Access Point initial install and configuration to better off your Wireless connection.It’s worthy to note that the 2.4 GHz
Wi-Fi signal range is divided into a number of smaller bands or “channels,” similar to television channels. I decided to run my wireless on channel 12 since this there was no other wireless routers operating on that frequency, though most routers are preconfigured to spread it’s signal on channel 6.
There is a difference in channels available for setup for 802.11b and 802.11g wireless networks in the United States and the European Union. In the USA the wireless channels available are from (1 to 11) whether in the EU it’s in the range of (1-13). Each of the Wireless channels run on a different frequency.
The lower the number of the channel is the lowest the radiating frequence band on which data is transmitted .Subsequently, increasing the channel increases the frequency slightly. Therefore the higher the channel you select on your AP the lesser the overlap with other devices running on the same channel and thus the lesser the possibility to overlap and interference.
It’s quite likely that you experience problems, if you use the default wireless channel which is 6.
If that’s the case it’s recommended to use either channel 1 or channel 11. In case of interference, i.e. overlap with other wireless networks, cellphones etc., there are 2 possible ways to approach the situation. In case of smaller interference, any change in channel on which there is no wireless device running could fix it up. The second way is to choose a wireless channel for your router in between 1,6 or 11 in (The USA) or 1,7,13 in Europe.
Up to 3 networks can run on the same space with minimum interference, therefore it would be a wise idea to check the list of wireless routers in your and check if there are others running on the same frequency.
As I mentioned in the beginning of the post I initially started running my wireless on channel 12, however after I discovered it is recommended to run your wireless router either on channel 1 7 or 13 in Europe I switched my D-Link DI-524 wireless router to transmit it’s signal on Channel 13.
I should testify that after changing the wireless channel, there was quite an improvement in my wireless connection.For instance before I change to Channel 13 (when my wireless internet was still streamed on channel 12) my wireless had constantly issues with disconnects because of low wireless signal.
Back then My wireless located physically in like 35 meters away set in another room, I can see my wireless router hardly connected on like 35%, changing to channel 13 enhanced my connection to the current 60% wireless router availability.
It’s also an interesting fact that Opened Wireless networks had better network thoroughput, so if you’re living in a house with a neighbors a bit distant from your place then you might consider it as a good idea to completely wipe out Wireless Router security encryption and abandon the use of WEP or WPA network encryption.
In case if all of the above is not working for you, you might consider take a close look at your Wireless Wireless LAN pc card and see if there are no any kind of bumps there. Another really interesting fact to know is that many people here in Bulgaria tend to configure there Wireless Access Points on channels either 1,6 or 11 which is quite inadequate considering that we’re in the EU and we should use a wireless channel between 1, 7 or 13 as prescribed for EU citizens.
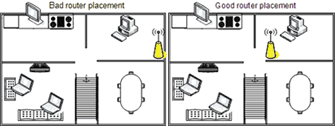
Another thing not to forget is to place your wireless in a good way and prevent it from interferences with other computer equipment. For example keep the router at least few meters away from PC equipment, printers, scanners, cellphones, microwaves. Also try to put your wireless router on some kind of central place in your home, if you want to have the wireless signal all around your place.
At my place I have a microwave in the Kitchen which is sometimes an obstacle for the Wireless signal to flow properly to my notebook, fortunately this kind of interference happens rare (only when the Microwove is used to warm-up food etc.).Upgrading 802.11b wireless card / router to a better one as 802.11g is a wise idea too. 802.11g are said to be like 5 times faster than 802.11b.
You can expect 802.11b wireless network to transfer maximum between 2-5 Mbp/s whether 802.11g is claimed to transfer at approximately (12 to 23 Mbp/s). If even though the above prescriptions there is no wireless signal at some remote place at your home, you might consider adding a wireless repeater or change the AP router antenna.
By default wireless Routers are designed to be omni-directional (in other terms they broadcast the wireless signal all around the place. Thus is quite unhandy if you intend to use your Wireless net only in certain room or location at your place. If that’s the case for you, you might consider upgrading to a hi-gain antenna that will focus the wireless signal to an exact direction. Let me close this article with a small diagram taken from the net which illustrates a good router placement that will enable you to have a wwireless connection all over your place.