If you're working for a company that is following high security / PCI Security Standards and you're using m$ Windows OS that belongs to the domain it is useful to know when your user is set to expiry
to know how many days are left until you'll be forced to change your Windows AD password.
In this short article I'll explain how to check Windows AD last password set date / date expiry date and how you can list expiry dates for other users, finally will explain how to set your expiry date to Never
to get rid of annoying change password every 90 days.
1. Query domain Username for Password set / Password Expires set dates
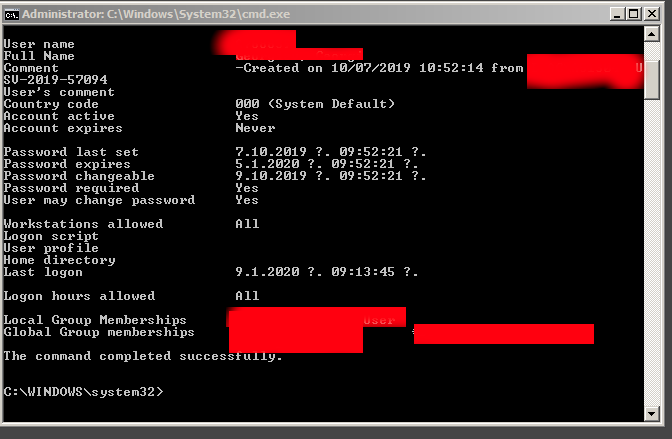
To know this info you need to know the Password expiration date for Active Directory user account, to know it just open Command Line Prompt cmd.exe
And run command:
NET USER Your-User-Name /domain
Note that, many companies does only connect you to AD for security reason only on a VPN connect with something like Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client whatever VPN connect tool is used to encrypt the traffic between you and the corporate DMZ-ed network
Below is basic NET USER command usage args:
Net User Command Options
Item Explanation
net user Execute the net user command alone to show a very simple list of every user account, active or not, on the computer you're currently using.
username This is the name of the user account, up to 20 characters long, that you want to make changes to, add, or remove. Using username with no other option will show detailed information about the user in the Command Prompt window.
password Use the password option to modify an existing password or assign one when creating a new username. The minimum characters required can be viewed using the net accounts command. A maximum of 127 characters is allowed1.
* You also have the option of using * in place of a password to force the entering of a password in the Command Prompt window after executing the net user command./add Use the /add option to add a new username on the system.
options See Additional Net User Command Options below for a complete list of available options to be used at this point when executing net user./domain This switch forces net user to execute on the current domain controller instead of the local computer.
/delete The /delete switch removes the specified username from the system.
/help Use this switch to display detailed information about the net user command. Using this option is the same as using the net help command with net user: net help user.
/? The standard help command switch also works with the net user command but only displays the basic command syntax. Executing net user without options is equal to using the /? switch.
2. Listing all Active Directory users last set date / never expires and expiration dates
If you have the respective Active Directory rights and you have the Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows (RSAT Tools), you are able to do also other interesting stuff,
such as
– using PowerShell to list all user last set dates, to do so use Open Power Shell and issue:
get-aduser -filter * -properties passwordlastset, passwordneverexpires |ft Name, passwordlastset, Passwordneverexpires
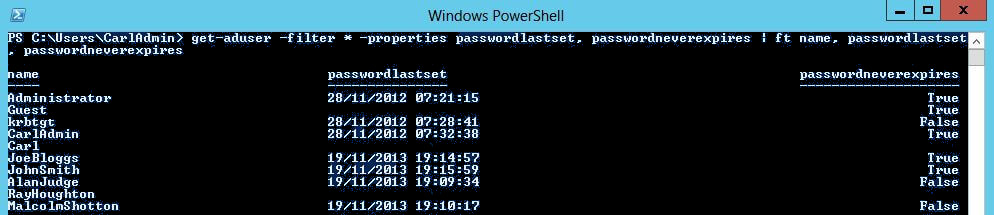
This should show you info as password last set date and whether password expiration is set for account.
– Using PS to get only the password expirations for all AD existing users is with:
Get-ADUser -filter {Enabled -eq $True -and PasswordNeverExpires -eq $False} –Properties "DisplayName", "msDS-UserPasswordExpiryTimeComputed" |
Select-Object -Property "Displayname",@{Name="ExpiryDate";Expression={[datetime]::FromFileTime($_."msDS-UserPasswordExpiryTimeComputed")}}
If you need the output data to get stored in CSV file delimitered format you can add to above PS commands
| export-csv YOUR-OUTPUT-FILE.CSV
3. Setting a user password to never Expiry
If the user was created with NET USER command by default it will have been created to have a password expiration.
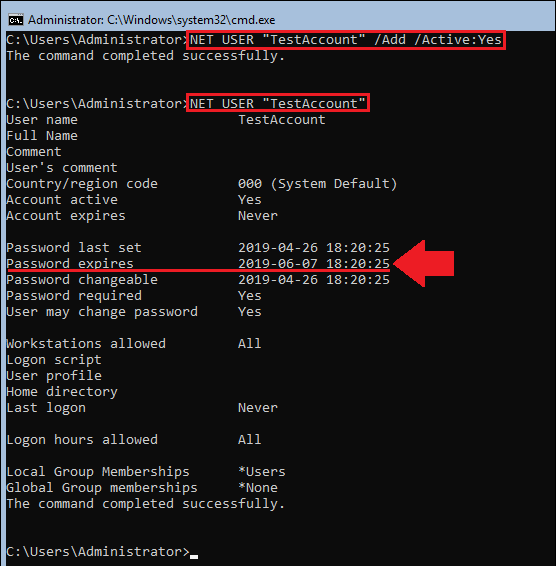
However if you need to create new users for yourself (assuming you have the rights), with passwords that never expire on lets say Windows Server 2016 – (if you don't care about security so much), use:
NET USER "Username" /Add /Active:Yes
WMIC USERACCOUNT WHERE "Name='Username' SET PasswordExpires=False
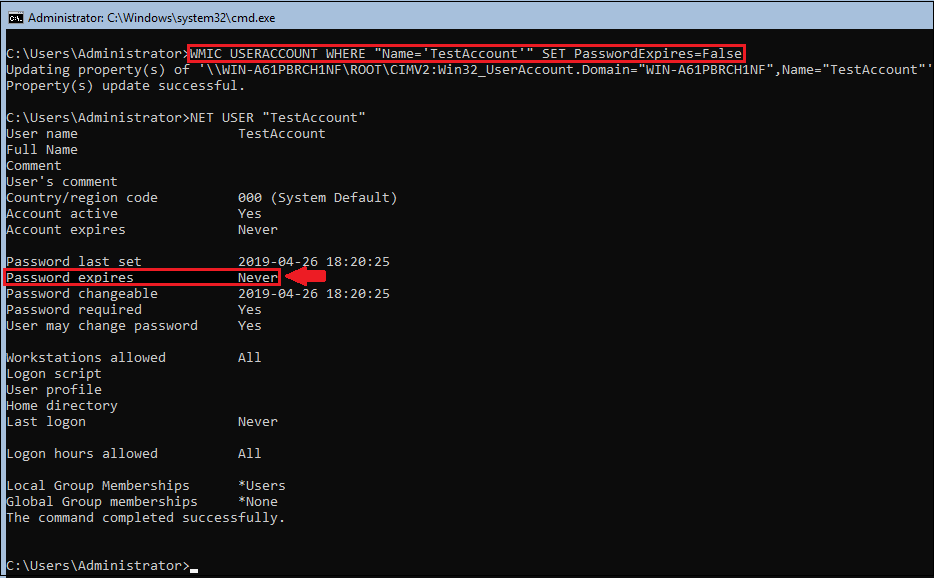
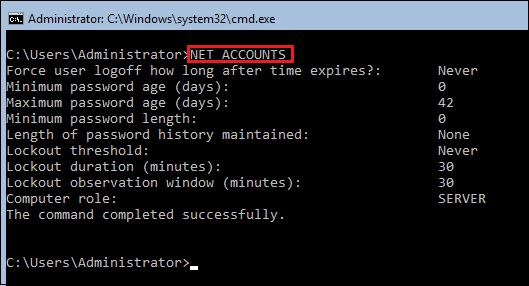
To view the general password policies, type following:
NET ACCOUNTS
More helpful Articles

Tags: active, check, directory, User, when, Windows







