Many admins might not know about smartmontools Linux package. It provides two useful tools smartctl and smard which use (Self Monitoring and Reporting Technology system) often abreviated as S.M.A.R.T.. SMART support is nowdays available across any modern ATA, SATA and SCSI hard disks. smartontools package is installable via default package repositories on virtually all different Linux distributions. Having smartmontools installed on all critical productive server is a must for the reason it serves as early notification system in case if hard disk is on the down-verge of break-up (i.e. physical media of hard disk storage starts getting damaged). Through the last 14 years I worked as Linux sysadmin. I've used smartmontools on hundreds of servers and on many times it save companies hundreds of dollars by simply reporting a system hdd is dying and by replacing the server or hard disk with identifically configured ones. smartmontools supports monitoring of single hard disks as well as ones configured on a hardware level to work in some RAID array. As of time of writing you can check list of smartmontools supported hardware RAID-Controllers here.
1. Installing smartmontools
a) To install smartmontools on Debian and Ubuntu and other .deb based servers:
debian:~# apt-get install --yes smartmontools
.....
b) On CentOS, Fedora,RHEL and other RPM based install with:
[root@centos ~]# yum --yes install smartmontools
.....
2. Configuring and Enabling smartd hard disk health monitoring
a) on Debian and derivatives
Edit /etc/default/smartmontools:
debian:~# vim /etc/default/smartmontools
By default file looks smth. like;
# Defaults for smartmontools initscript (/etc/init.d/smartmontools)
# This is a POSIX shell fragment
# List of devices you want to explicitly enable S.M.A.R.T. for
# Not needed (and not recommended) if the device is monitored by smartd
#enable_smart="/dev/hda /dev/hdb"
#enable_smart="/dev/hda"
# uncomment to start smartd on system startup
#start_smartd=yes
# uncomment to pass additional options to smartd on startup
#smartd_opts="–interval=1800"
Config file should look something like;
# Defaults for smartmontools initscript (/etc/init.d/smartmontools)
# This is a POSIX shell fragment
# List of devices you want to explicitly enable S.M.A.R.T. for
# Not needed (and not recommended) if the device is monitored by smartd
#enable_smart="/dev/hda /dev/hdb"
enable_smart="/dev/sda"
# uncomment to start smartd on system startup
start_smartd=yes
# uncomment to pass additional options to smartd on startup
#smartd_opts="–interval=1800"
b) on CentOS, RHEL, Fedora for smartd options
By default on RPM based distros there is no need for special configuration. However for some custom cases edit /etc/sysconfig/smartmontools and /etc/smartd.conf
c) Enabling smartmontools
[root@centos default]# /etc/init.d/smartd start
Starting smartd: [ OK ]
3. Checking hard disk failure status with smartctl
Checking whether a SMART hard disk consistency check Passes is done simplest with:
debian:~# /usr/sbin/smartctl -H /dev/sda
smartctl 5.40 2010-07-12 r3124 [x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu] (local build)
Copyright (C) 2002-10 by Bruce Allen, http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net
SMART Health Status: OK
debian:~# /usr/sbin/smartctl -i /dev/sda1
smartctl version 5.38 [i686-redhat-linux-gnu] Copyright (C) 2002-8 Bruce Allen
Home page is http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net/
=== START OF INFORMATION SECTION ===
Model Family: Seagate Barracuda 7200.7 and 7200.7 Plus family
Device Model: ST340014AS
Serial Number: 4MQ0LV3B
Firmware Version: 3.43
User Capacity: 40,020,664,320 bytes
Device is: In smartctl database [for details use: -P show]
ATA Version is: 6
ATA Standard is: ATA/ATAPI-6 T13 1410D revision 2
Local Time is: Fri Mar 15 15:27:12 2013 EET
SMART support is: Available – device has SMART capability.
SMART support is: Enabled
To print as much information as possible for hard disk health status;
[root@centos default]# /usr/sbin/smartctl -a /dev/sda1
smartctl version 5.38 [i686-redhat-linux-gnu] Copyright (C) 2002-8 Bruce Allen
Home page is http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net/
=== START OF INFORMATION SECTION ===
Model Family: Seagate Barracuda 7200.7 and 7200.7 Plus family
Device Model: ST340014AS
Serial Number: 4MQ0LV3B
Firmware Version: 3.43
User Capacity: 40,020,664,320 bytes
Device is: In smartctl database [for details use: -P show]
ATA Version is: 6
ATA Standard is: ATA/ATAPI-6 T13 1410D revision 2
Local Time is: Fri Mar 15 15:14:53 2013 EET
SMART support is: Available – device has SMART capability.
SMART support is: Enabled
=== START OF READ SMART DATA SECTION ===
SMART overall-health self-assessment test result: PASSED
General SMART Values:
Offline data collection status: (0x82) Offline data collection activity
was completed without error.
Auto Offline Data Collection: Enabled.
Self-test execution status: ( 0) The previous self-test routine completed
without error or no self-test has ever
been run.
Total time to complete Offline
data collection: ( 423) seconds.
Offline data collection
capabilities: (0x5b) SMART execute Offline immediate.
Auto Offline data collection on/off support.
Suspend Offline collection upon new
command.
Offline surface scan supported.
Self-test supported.
No Conveyance Self-test supported.
Selective Self-test supported.
SMART capabilities: (0x0003) Saves SMART data before entering
power-saving mode.
Supports SMART auto save timer.
Error logging capability: (0x01) Error logging supported.
General Purpose Logging supported.
Short self-test routine
recommended polling time: ( 1) minutes.
Extended self-test routine
recommended polling time: ( 19) minutes.
SMART Attributes Data Structure revision number: 10
Vendor Specific SMART Attributes with Thresholds:
ID# ATTRIBUTE_NAME FLAG VALUE WORST THRESH TYPE UPDATED WHEN_FAILED RAW_VALUE
1 Raw_Read_Error_Rate 0x000f 052 045 006 Pre-fail Always – 172137473
3 Spin_Up_Time 0x0002 098 098 000 Old_age Always – 0
4 Start_Stop_Count 0x0033 096 096 020 Pre-fail Always – 4198
5 Reallocated_Sector_Ct 0x0033 100 100 036 Pre-fail Always – 0
7 Seek_Error_Rate 0x000f 090 060 030 Pre-fail Always – 945095084
9 Power_On_Hours 0x0032 075 075 000 Old_age Always – 22769
10 Spin_Retry_Count 0x0013 100 100 097 Pre-fail Always – 0
12 Power_Cycle_Count 0x0033 099 099 020 Pre-fail Always – 1084
194 Temperature_Celsius 0x0022 038 046 000 Old_age Always – 38 (0 15 0 0)
195 Hardware_ECC_Recovered 0x001a 052 045 000 Old_age Always – 172137473
197 Current_Pending_Sector 0x0012 100 100 000 Old_age Always – 0
198 Offline_Uncorrectable 0x0010 100 100 000 Old_age Offline – 0
199 UDMA_CRC_Error_Count 0x003e 200 200 000 Old_age Always – 0
200 Multi_Zone_Error_Rate 0x0000 100 253 000 Old_age Offline – 0
202 TA_Increase_Count 0x0032 100 253 000 Old_age Always – 0
SMART Error Log Version: 1
ATA Error Count: 33 (device log contains only the most recent five errors)
CR = Command Register [HEX]
FR = Features Register [HEX]
SC = Sector Count Register [HEX]
SN = Sector Number Register [HEX]
CL = Cylinder Low Register [HEX]
CH = Cylinder High Register [HEX]
DH = Device/Head Register [HEX]
DC = Device Command Register [HEX]
ER = Error register [HEX]
ST = Status register [HEX]
Powered_Up_Time is measured from power on, and printed as
DDd+hh:mm:SS.sss where DD=days, hh=hours, mm=minutes,
SS=sec, and sss=millisec. It "wraps" after 49.710 days.
Error 33 occurred at disk power-on lifetime: 21588 hours (899 days + 12 hours)
When the command that caused the error occurred, the device was active or idle.
After command completion occurred, registers were:
ER ST SC SN CL CH DH
— — — — — — —
40 51 00 77 c3 6a e0 Error: UNC at LBA = 0x006ac377 = 6996855
Commands leading to the command that caused the error were:
CR FR SC SN CL CH DH DC Powered_Up_Time Command/Feature_Name
— — — — — — — — —————- ——————–
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:39.385 READ DMA
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:35.553 IDENTIFY DEVICE
ef 03 45 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:35.550 SET FEATURES [Set transfer mode]
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:35.547 IDENTIFY DEVICE
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:35.543 READ DMA
Error 32 occurred at disk power-on lifetime: 21588 hours (899 days + 12 hours)
When the command that caused the error occurred, the device was active or idle.
After command completion occurred, registers were:
ER ST SC SN CL CH DH
— — — — — — —
40 51 00 77 c3 6a e0 Error: UNC at LBA = 0x006ac377 = 6996855
Commands leading to the command that caused the error were:
CR FR SC SN CL CH DH DC Powered_Up_Time Command/Feature_Name
— — — — — — — — —————- ——————–
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:23.940 READ DMA
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:35.553 IDENTIFY DEVICE
ef 03 45 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:35.550 SET FEATURES [Set transfer mode]
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:35.547 IDENTIFY DEVICE
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:35.543 READ DMA
Error 31 occurred at disk power-on lifetime: 21588 hours (899 days + 12 hours)
When the command that caused the error occurred, the device was active or idle.
After command completion occurred, registers were:
ER ST SC SN CL CH DH
— — — — — — —
40 51 00 77 c3 6a e0 Error: UNC at LBA = 0x006ac377 = 6996855
Commands leading to the command that caused the error were:
CR FR SC SN CL CH DH DC Powered_Up_Time Command/Feature_Name
— — — — — — — — —————- ——————–
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:23.940 READ DMA
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:23.937 IDENTIFY DEVICE
ef 03 45 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:20.071 SET FEATURES [Set transfer mode]
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:20.057 IDENTIFY DEVICE
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:20.044 READ DMA
Error 30 occurred at disk power-on lifetime: 21588 hours (899 days + 12 hours)
When the command that caused the error occurred, the device was active or idle.
After command completion occurred, registers were:
ER ST SC SN CL CH DH
— — — — — — —
40 51 00 77 c3 6a e0 Error: UNC at LBA = 0x006ac377 = 6996855
Commands leading to the command that caused the error were:
CR FR SC SN CL CH DH DC Powered_Up_Time Command/Feature_Name
— — — — — — — — —————- ——————–
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:23.940 READ DMA
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:23.937 IDENTIFY DEVICE
ef 03 45 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:20.071 SET FEATURES [Set transfer mode]
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:20.057 IDENTIFY DEVICE
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:20.044 READ DMA
Error 29 occurred at disk power-on lifetime: 21588 hours (899 days + 12 hours)
When the command that caused the error occurred, the device was active or idle.
After command completion occurred, registers were:
ER ST SC SN CL CH DH
— — — — — — —
40 51 00 77 c3 6a e0 Error: UNC at LBA = 0x006ac377 = 6996855
Commands leading to the command that caused the error were:
CR FR SC SN CL CH DH DC Powered_Up_Time Command/Feature_Name
— — — — — — — — —————- ——————–
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:23.940 READ DMA
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:23.937 IDENTIFY DEVICE
ef 03 45 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:20.071 SET FEATURES [Set transfer mode]
ec 00 00 00 00 00 a0 00 14:07:20.057 IDENTIFY DEVICE
c8 00 08 77 c3 6a e0 00 14:07:20.044 READ DMA
SMART Self-test log structure revision number 1
Num Test_Description Status Remaining LifeTime(hours) LBA_of_first_error
# 1 Extended offline Completed without error 00% 1 –
SMART Selective self-test log data structure revision number 1
SPAN MIN_LBA MAX_LBA CURRENT_TEST_STATUS
1 0 0 Not_testing
2 0 0 Not_testing
3 0 0 Not_testing
4 0 0 Not_testing
5 0 0 Not_testing
Selective self-test flags (0x0):
After scanning selected spans, do NOT read-scan remainder of disk.
If Selective self-test is pending on power-up, resume after 0 minute delay.
4. Visualizing smartd collected data in GUI with gsmartcontrol
For people who prefer to visualize things in Graphical environment smartd service hard disk health data can be viewed in nice graphical interface wth gsmartcontrol tool. Most Linux servers don't have graphical environment as having a X server with any graphics manager is a waste of system resources thus installing gsmartcontrol doesn't make much sense, however for monitoring and reporting for upcoming Hard Disk issues gsmartcontrol is a good one to have.
a) To install gsmartcontrol on Debian and Ubuntu Linux;
debian:~# apt-get install --yes gsmartcontrol
....
b) Installing gsmartcontrol on CentOS, Fedora, RHEL and SuSE;
gsmartcontrol has a binary package builds for all major Linux distributions, except Slackware Linux. For any of RPM based Linux distros. Go and download required smartmontools distro version and type binary from here then install the RPMs one by one with the usual:
[root@centos ~]# rpm -ivh glimm*
....
[root@centos ~]# rpm -ivh libglademm*
....
[root@centos ~]# rpm -ivh libsigc*
....
[root@centos ~]# rpm -ivh cairomm*
....
[root@centos ~]# rpm -ivh gsmartcontrol*
....
Below, are 2 screenshots of GSmartControl taken from my
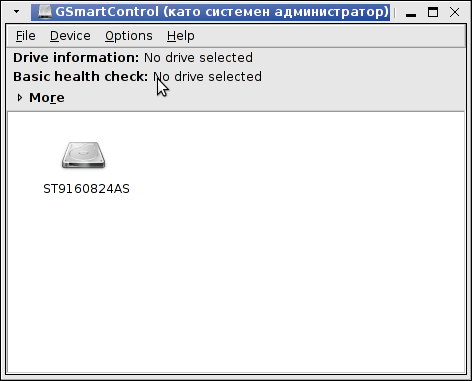
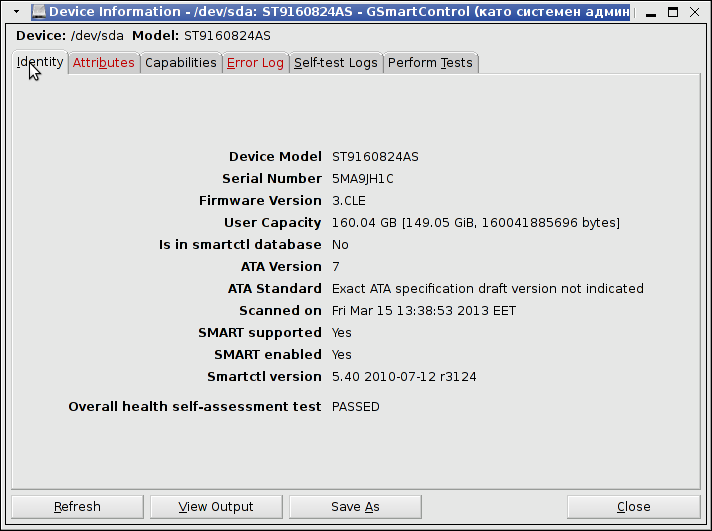
If you get something different from Overall health self-assessment test PASSED, this means hard disk has a surface damage and needs to be replaced ASAP. If during hard disk normal operation HDD hits I/O errors and you can't afford to have a GUI environment just for gsmartcontrol, errors gets logged in dmesg hence dmesg could be useful to provide you with info of a failing hard drive.