If you happen to buy or already own or just have to install a Smart TV to be connected with a LAN Network to a Linux based custom built NAS (Network Attached Storage) server. You might benefit of the smart TV to Share and Watching the Disk Storage Pictures, Music, Video files from the NAS to the Smart TV using the Media Server protocol.
You have certainly already faced the Media Server at your life on many locations in stores and Mall Buildings, because virtually any reoccuring advertisements, movies projected on the TVs, Kids entertainment or Floor and Buildings Room location schedules or timeline promition schedules are streamed using the Media Server protocol, for many years now. Thus having a brief idea about Media Server proto existence is foundamental stuff to be aware of for sysadmins and programmers.
Shortly about DLNA UPnP Media Streaming Protocol
Assuming that your Smart TV has been already connected to your Wireless Router 2.4Ghz or 5Ghz Wifi, one would think that the easiest way to share the files with the SmartTV is via something like a simple SAMBA Linux server via smb:// cifs:// protocols or via the good old NFS Server, however most of Samsung Smart TV and many other in year 2022 does not have embedded support for Samba SMB / CIFS Protocol but instead have support for the DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance) streaming support. DLNA is part of the UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) Protocols, UPnP is also known to those using and familiar with Windows Operating Systems realm simply as UPnP AV Media server or Windows Media server.
Windows Media server for those who never heard it or used it allows you to build a Playlists with Media files Video and Audio data files, that can be then later played remotely via a Local LAN or even long distance over TCP / IP remote side connected Internet network.
1. Set up and Stream data via Media server on Windows PC / notebook with integrated Windows Media server
Windows Media server configuration on Windows 7, 10 and 11 is a relatively easy to configure via:
Network and Sharing Center -> Media Streaming Options -> Turn on Media Streaming
Then you have to define the name of the Media Library, configure whether Media server should show
on the Local Netework for other conected devices and Allow or Block access from the other network present devices.
2. Using a more advanced Media Server to get rid about the limitation of DLNA set of supported file codecs.
The Windows default embedded DLNA server is the easiest and fastest one to set up, but it’s not necessarily the best option.
Due to the way DLNA works, you can only stream certain types of media codecs supported by the server. If you have other types of media not defaultly supported and defined by DLNA win server, it just won’t work.
Thus thanksfully it was developed other DLNA servers improve this by offering real-time transcoding.
If you try to play an unsupported file, they’ll transcode it on-the-fly, streaming the video in a supported format to your DLNA device.
Just to name few of the DLNA Media Streaming servers that have supported for larger MPG Video, MP3 / MP4 and other Audio formats encodings,
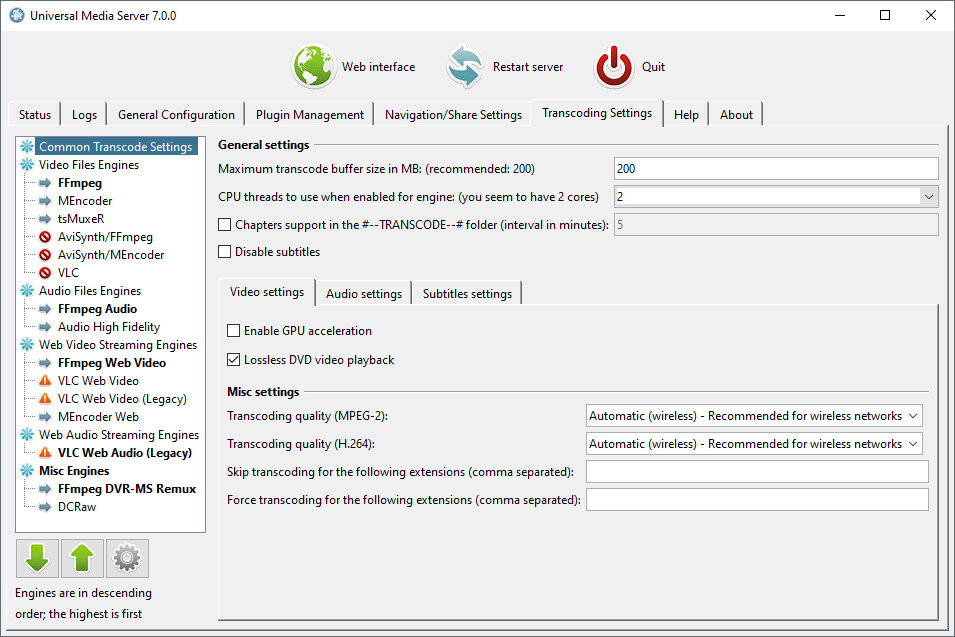
you can try Plex or the Universal Media Server both of which are free to use under freeware license and have versions for Linux and Mac OS.
3. Setting up a free as in freedom DLNA server MiniDLNA (ReadyMedia) on GNU / Linux
ReadyMedia (formerly known as MiniDLNA) is a simple media server software, with the aim of being fully compliant with DLNA/UPnP-AV clients. It was originally developed by a NETGEAR employee for the ReadyNAS product line.
MiniDNLA daemon serves media files (music, pictures, and video) to clients on a network. Linux Media servers clients you can use to test or scan your network for existent Media servers are multiple perhaps the most famous ones are applications such as totem (for QT users) and Kodi (for KDE).
The devices that can be used with minidlna are devices such as portable media players (iPod), Smartphones, Televisions, Tablets, and gaming systems (such as PS3 and Xbox 360) etc.
ReadyMedia is a simple, lightweight, the downside of it is It does not have a web interface for administration and must be configured by editing a text file. But for a simple Video streaming in most cases does a great job.
3.1 Install the minidlna software package
Minidlna is available out of the box on most linux distributions (Fedora / CentOS / Debian / Ubuntu etc.) as of year 2022.
- Install on Debian Linux (Deb based distro)
media-server:~# apt install minidlna –yes
- Install on Fedora / CentOS (other RPM based distro)
media-server:~# yum install -y minidlna
3.2 Configure minidlna
– /etc/minidlna.conf – main config file
Open with text editor and set user= , media_dir= , port=, friendly_name= , network_interface= variables as minimum.
To be add minidlnad support symlinks to external file locations, set also wide_links=yes
media-server:~# vim /etc/minidlna.conf
#user=minidlna
user=root
media_dir=/var/www/owncloud/data
network_interface=eth0,eth1# Port number for HTTP traffic (descriptions, SOAP, media transfer).
# This option is mandatory (or it must be specified on the command-line using
# "-p").
port=8200
# Name that the DLNA server presents to clients.
# Defaults to "hostname: username".
#friendly_name=
friendly_name=DLNAServer Linux
# set this to yes to allow symlinks that point outside user-defined media_dirs.
wide_links=yes
# Automatic discovery of new files in the media_dir directory.
#inotify=yes
Keep in mind that it is supported to provide separete media_dir and provide different USB / External Hard Drive or SD Card sources separated only by content be it Video, Audio or Pictures short named in config as (A,V,P).
media_dir=P,/media/usb/photos
media_dir=V,/media/external-disk/videos
media_dir=A,/media/sd-card/music
You might want to diasble / ineable the inotify depending on your liking, if you don't plan to place new files automated to the NAS and don't care to get indexed and streamed from the Media server you can disable it with inotify=no otherwise keep that on.
– /etc/default/minidlna – additional startup config to set minidlnad (daemon) options such as setup to run with admin superuser root:root
(usually it is safe to leave it empty and set the user=root, whether needed straight from /etc/minidlna.conf
That's all now go on and launch the minidlna and enable it to automatically boot on Linux boot.
media-server:~# systemctl start minidlna
media-server:~# systemctl enable minidlna
media-server:~# systemctl status minidlna
3.3 Rebuilt minidlna database with data indexed files
If you need to re- generate minidlna's database.
To do so stop the minidlna server with the
media-server:~# systemctop stop minidlna
command, then issue the following command (both commands should be run as root):
media-server:~# minidlna -R
Since this command might kept in the background and keep the minidlna server running with incorrect flags, after a minute or two kill minidlna process and relaunch the server via sysctl.
media-server:~# killall -9 minidlna
media-server:~# systemctl start minidlna
3.4 Permission Issues / Scanning issues
If you plan to place files in /home directory. You better have a seperate partition or folder *outside* your "home" directory devoted to your media. Default user with which minidlna runs is minidlna, this could prevent some files with root or other users being red. So either run minidlna daemon as root or as other user with whom all media files should be accessible.
If service runs as root:root, and still getting some scanning issues, check permissions on your files and remove special characters from file names.
media-server:~# tail -10 /var/log/minidlna/minidlna.log
[2022/02/17 22:51:36] scanner.c:489: warn: Unsuccessful getting details for /var/www/owncloud/data/Videos/Family-Videos/FILE006.MPG
[2022/02/17 22:52:08] scanner.c:819: warn: Scanning /var/www/owncloud/data finished (10637 files)!
[2022/02/17 22:52:08] playlist.c:135: warn: Parsing playlists…
[2022/02/17 22:52:08] playlist.c:269: warn: Finished parsing playlists.
minidlna.c:1126: warn: Starting MiniDLNA version 1.3.0.
minidlna.c:1186: warn: HTTP listening on port 8200
scanner.c:489: warn: Unsuccessful getting details for /var/www/owncloud/data/admin/files/origin/External SD card/media/Viber Images/IMG-4477de7b1eee273d5e6ae25236c5c223-V.jpg
scanner.c:489: warn: Unsuccessful getting details for /var/www/owncloud/data/Videos/Family-Video/FILE006.MPG
playlist.c:135: warn: Parsing playlists…
playlist.c:269: warn: Finished parsing playlists.
3.5. Fix minidlna Inotify errors
In /etc/sysctl.conf
Add:
fs.inotify.max_user_watches=65536
in a blank line at end of file and do
media-server:~# sysctl -p
Debugging minidlna problems, index errors, warnings etc
minidlna does write by default to /var/log/minidlna/minidlna.log inspect the log closely and you should get most of the time what is wrong with it.
Note that some files might not get indexed because minidlna won't support the strange file codecs such as SWF encoding, if you have some important files to stream that are not indexed by minidlna, then install and try one of the more sophisticated free software Media Servers for Linux:
- MediaTomb
- UniversalMediaServer
- Plex
Note that most Linux users from my quick research shows, MediaTomb is the preferred advanced features Open Source Linux Media Server of choice for most of the guys.
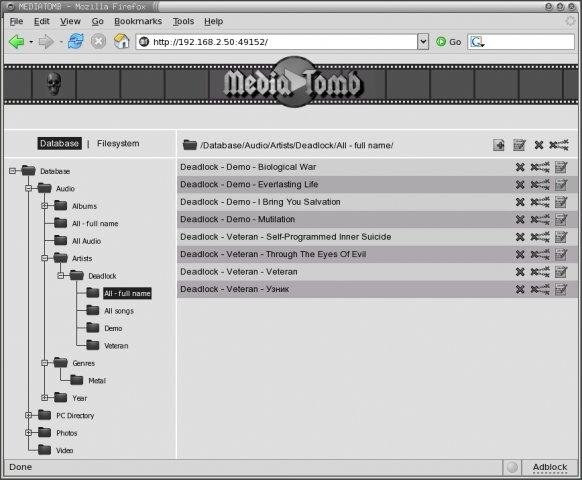
4. Test minidlna Linux servers works, getting information of other DLNA Servers on the network
media-server:~# lynx -dump http://127.0.0.1:8200
MiniDLNA status
Media library
Audio files 0
Video files 455
Image files 10182
Connected clients
ID Type IP Address HW Address Connections
0 Samsung Series [CDEFJ] 192.168.1.11 7C:0A:3D:88:A6:FA 0
1 Generic DLNA 1.5 192.168.0.241 00:16:4E:1D:48:05 0
2 Generic DLNA 1.5 192.168.1.18 00:16:3F:0D:45:05 0
3 Unknown 127.0.0.1 FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF 0
-1 connections currently open
Note that there is -1 connections (no active connections) currently to the server.
The 2 Generic DLNA 1.5 IPs are another DLNA servers provided by a OpenXEN hosted Windows 7 Virtual machines, that are also broadcasting their existence in the network. The Samsung Series [CDEFJ] is the DLNA client on the Samsung TV found, used to detect and stream data from the just configured Linux dlna server.
The DLNA Protocol enabled devices on a network as you can see are quite easy to access, querying localhost on the 8200 server dumps, what minidlna knows, the rest of IPs connecting should not be able to receive this info. But anyways since the minidlna does not have a special layers of security to access it, but the only way to restrict is filtering the 8200 port, it is a very good idea to put a good iptables firewall on the machine to allow only the devices that should have access to the data.
Further more if you happen to need to access the Media files on Linux from GUI you might use some client as upmentioned totem, VLC or if you need something more feature rich Java eezUPnP .
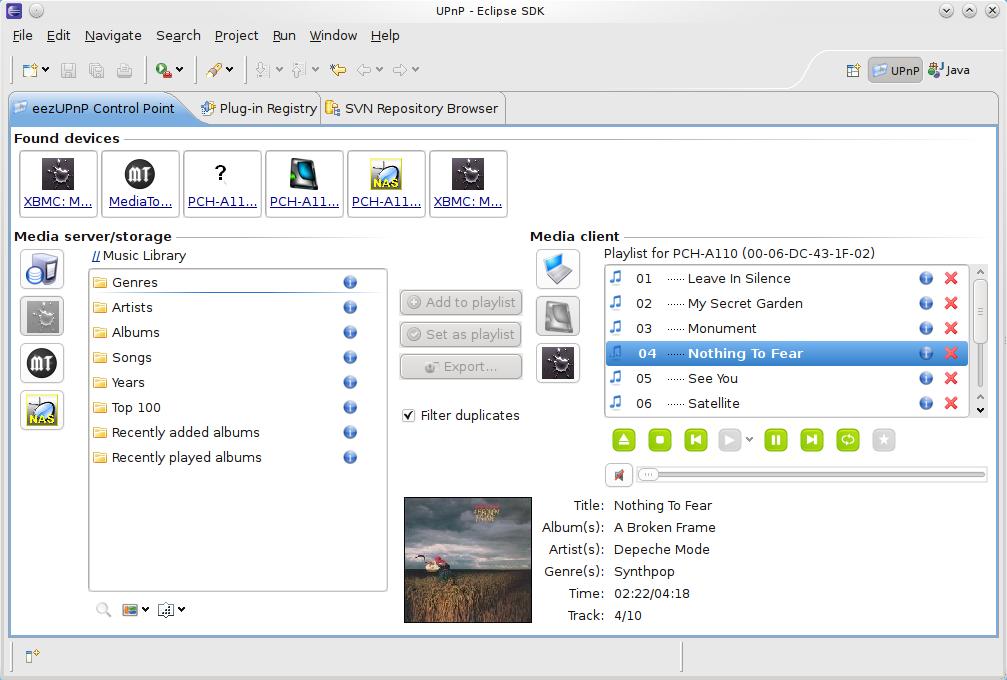
That's all folks !
Enjoy your media on the TV 🙂