After a long time of inavailability, finally TeamViewer 7 for GNU / Linux is out!
Here is the short TeamViewer 7 Linux release note :
In our TeamViewer download area you will now find TeamViewer 7 for Linux.
The final version includes a selection of new features for Linux, e. g. an integrated screenshot feature and the possibility of saving individual connection settings per computer.
You can now establish cross platform connections with other computers running version 7 and hold online meetings and presentations with up to 25 participants.
We wish you best continued success with TeamViewer!
Well, guys it was about time, even later than that… Until now I've so many times experienced troubles with Windows machines which I had to administrate remotely and they only had a TeamViewer 7 installed (a real, real pain in the ass).
The issue comes cause TeamViewer 6 is incompatible with 7 and just until very recently only TV 6 for Linux was available, so trying to access a 7 install directly from Linux was impossible.
Hence to access TeamViewer 7 Windows install, I had to use either a fresh Windows copy with TeamViewer 7 installed or a Virtual Machine like (Qemu, VirtualBox) with Windows version installed in it.
Often back then, when I had to fix remotely a Windows machine behind a firewall, I had to instruct the machine owners to replace the TeamViewer 7 with TeamViewer 6 in order to be able to easily access the remote host from my Debian Linux.
I still remember, it was quite a stuggle to find a link to a Windows .exe install file for TeamViewer 6.
Now thanksfully, TeamViewer guys are starting to make it easier for the user who would for some reason want to stick to older TV version.
I've noticed on TeamViewer's website there is already a new TeamViewer download page offering for download all the old teamviewer version – 1.x, 2.x, 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, 6.x
One example, where old teamviewer release is useful is if you want to run teamviewer on older hardware or old OS (MS Windows 98 or old Linux distro).
I've made a mirror of teamviewer 6 for Debian / Ubuntu amd 32 and 64 bit versions along with all the OS available TeamViewer version 6 and 7, for the sake of preserving it if one day link to old versions of Teamviewer disappear from their website.
Here are the TeamViewer mirrored files:
- mirror of TeamViewer 6 deb 32 bit
- TeamViewer 6 Debian / Ubuntu 64 bit
- TeamViewer 7 deb for Debian / Ubuntu (32 bit)
- TeamViewer 7 Debian / Ubuntu Linux (64 bit)
- Here is also a link to the mirror of Teamviewer 6 and 7 for Windows, Linux and Android
Below you see a screenshot of teamviewer 7 running on my Debian Squeeze 🙂
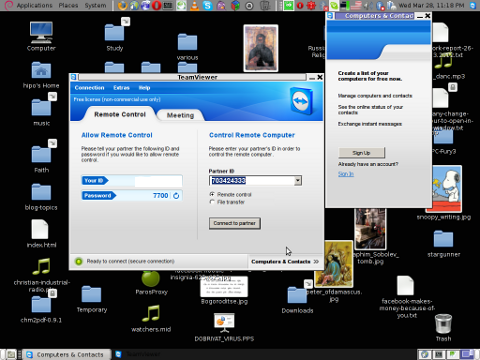
It is great teamviewer produced a Linux working application, however if you run it you realize just like the previous releases TeamViewer is not natively supposed (compiled) to run on GNU / Linux OS but uses wine (windows emulator) to launch through…
Instead of porting the application to be natively for the Linux distros once again with this new release, teamviewer developers just "hacked" it to run on top of windows emulation. Though this is working its performance, is probably a bit degraded and it depends on having install on the Linux host a bunch of useless packages which wine depends on.
Besides that even if it "works" on Linux , TeamViewer has still non-free software essense. I still use it because unfortunately, I don't know of a better remote access program capable to connect to servers behind NAT / machines located behind a tight firewalled routers.
If only (I knew of?) a TeamViewer free software / open source equivalent …
I will be glad to hear if someone know a (free software / open source) TeamViewer like program able to access remote hosts with no a real (public inet) IP address?P.S.: By similar TV program I don't mean VNC, UltraVNC and this kind of other VNC derivative programs but mean close TeamViewer alternative.




