Posts Tagged ‘BSD’
Monday, June 28th, 2021 This post is just informative for Text Geeks who are in love with ASCII Art, it is a bit of rant as I will say nothing new, but I thought it might be of interest to some console maniac out there 🙂
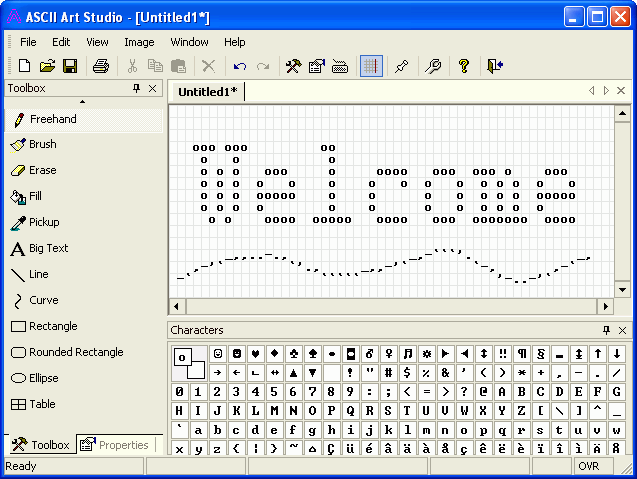
While checking stuff on Internet I've stumbled on interesting ASCII arts freak software – >ASCII Art Studio. ASCII Art Studio is unfortunately needs licensing is not Free Software. But anyways, for anyone willing to draw pro ASCII art pictures it is a must see. Check it out;
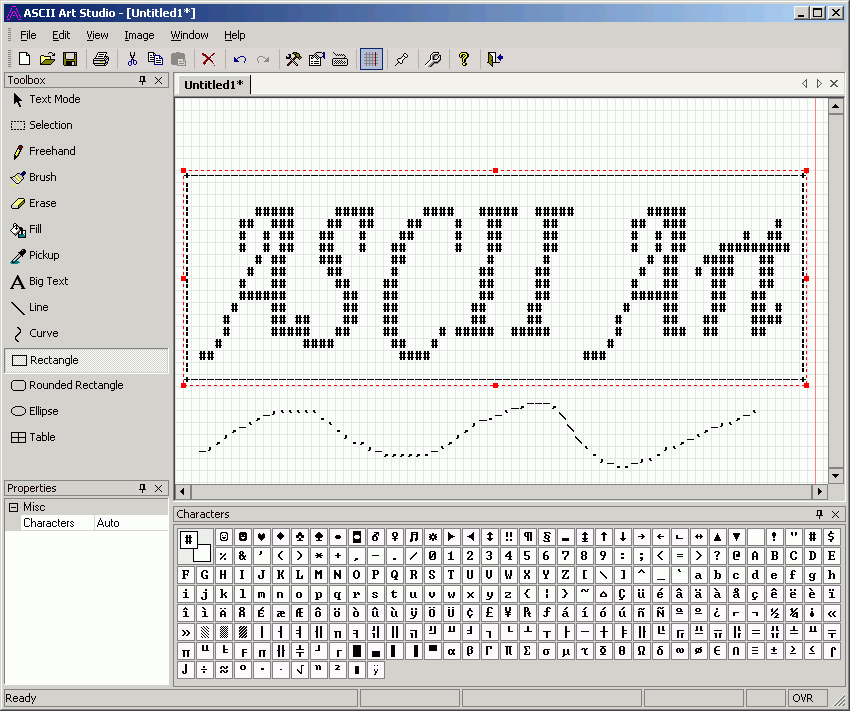
Isn't it like a Plain Text pro Photoshop ? 🙂 Its a pity we don't have a Linux / BSD Release of this wonderful piece of software. I've tried with WINE (Windows Emulator) on Linux to make the Ascii Art Studio work but that was a fail. It seems only way to make it work is have Windows as a worst case install a Virtual Machine with VirtualBox / Vmware and run it inside if you don't have a Windows PC at hand.
Of course there are stuff on Linux to ascii art edit you can use if you want to have a native software to edit ASCIIs such as Playscii. Unfortunately Playscii is not an easy one to install and the software doesn't have a prepared rpm or deb binary you can easily roll on the OS and you have to manually build all required python modules and have a working version of python3 to be able to make it work.
I did not have much time to test to install it and since I faced issues with plascii install I just abandoned it. If some geek has some more time anyways I guess it is worse to give it a try below is 2 screenshots from PLAYSCII official download page.
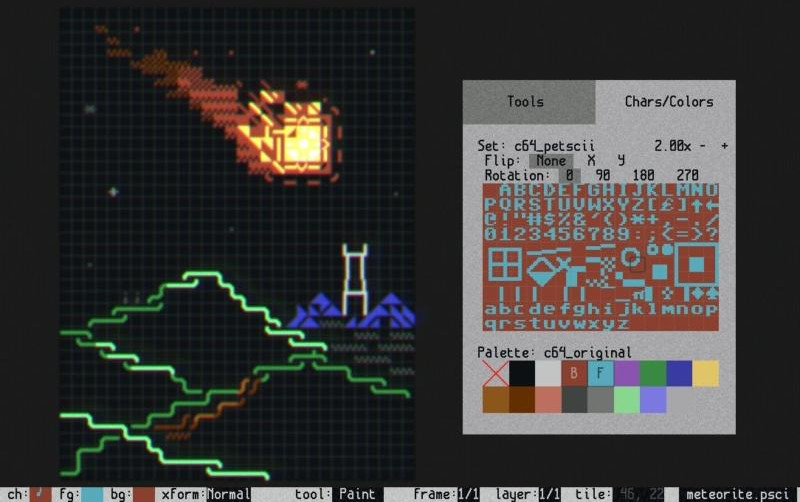
As you see authors of the open source playscii whose source is available via github choose to have an amazing looking ascii art text menus, though for daily ASCII art editing it is perhaps much more complicated to use than the simlistic ASCII Art Studio
There is other stuff for Linux to do ASCII Art files text edit like:
JaVE (this one I don't personally like because it is Java Based), Ascii Art Maker or Pablow Draw Linux (unfortunately this 2 ones are proprietary).
Tags: ALL, Amazing, and, Anyways, are, art, art editor, art files, Arts, Ascii, ascii art, available, based, Below, binary, bit, BSD, case, check, checking
Posted in Curious Facts, Entertainment, Everyday Life, Rant | No Comments »
Wednesday, April 14th, 2021 
Say you have access to a remote Linux / UNIX / BSD server, i.e. a jump host and you have to remotely access via ssh a bunch of other servers
who have existing IP addresses but the DNS resolver recognized hostnames from /etc/resolv.conf are long and hard to remember by the jump host in /etc/resolv.conf and you do not have a way to include a new alias to /etc/hosts because you don't have superuser admin previleges on the hop station.
To make your life easier you would hence want to add a simplistic host alias to be able to easily do telnet, ssh, curl to some aliased name like s1, s2, s3 … etc.
The question comes then, how can you define the IPs to be resolvable by easily rememberable by using a custom User specific /etc/hosts like definition file?
Expanding /etc/hosts predefined host resolvable records is pretty simple as most as most UNIX / Linux has the HOSTALIASES environment variable
Hostaliases uses the common technique for translating host names into IP addresses using either getaddrinfo(3) or the obsolete gethostbyname(3). As mentioned in hostname(7), you can set the HOSTALIASES environment variable to point to an alias file, and you've got per-user aliases
create ~/.hosts file
linux:~# vim ~/.hosts
with some content like:
g google.com
localhostg 127.0.0.1
s1 server-with-long-host1.fqdn-whatever.com
s2 server5-with-long-host1.fqdn-whatever.com
s3 server18-with-long-host5.fqdn-whatever.com
…
linux:~# export HOSTALIASES=$PWD/.hosts
The caveat of hostaliases you should know is this will only works for resolvable IP hostnames.
So if you want to be able to access unresolvable hostnames.
You can use a normal alias for the hostname you want in ~/.bashrc with records like:
alias server-hostname="ssh username@10.10.10.18 -v -o stricthostkeychecking=no -o passwordauthentication=yes -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null"
alias server-hostname1="ssh username@10.10.10.19 -v -o stricthostkeychecking=no -o passwordauthentication=yes -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null"
alias server-hostname2="ssh username@10.10.10.20 -v -o stricthostkeychecking=no -o passwordauthentication=yes -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null"
…
then to access server-hostname1 simply type it in terminal.
The more elegant solution is to use a bash script like below:
# include below code to your ~/.bashrc
function resolve {
hostfile=~/.hosts
if [[ -f “$hostfile” ]]; then
for arg in $(seq 1 $#); do
if [[ “${!arg:0:1}” != “-” ]]; then
ip=$(sed -n -e "/^\s*\(\#.*\|\)$/d" -e "/\<${!arg}\>/{s;^\s*\(\S*\)\s*.*$;\1;p;q}" "$hostfile")
if [[ -n “$ip” ]]; then
command "${FUNCNAME[1]}" "${@:1:$(($arg-1))}" "$ip" "${@:$(($arg+1)):$#}"
return
fi
fi
done
fi
command "${FUNCNAME[1]}" "$@"
}
function ping {
resolve "$@"
}
function traceroute {
resolve "$@"
}
function ssh {
resolve "$@"
}
function telnet {
resolve "$@"
}
function curl {
resolve "$@"
}
function wget {
resolve "$@"
}
Now after reloading bash login session $HOME/.bashrc with:
linux:~# source ~/.bashrc
ssh / curl / wget / telnet / traceroute and ping will be possible to the defined ~/.hosts IP addresses just like if it have been defined global wide on System in /etc/hosts.
Enjoy
Tags: access, adding, addresses, admin, after, alias, ALLOW, and, are, Arg, based, bash script, bashrc, Below, BSD, bunch, code, com, command, common
Posted in Educational, Hacks, System Administration, Various | No Comments »
Thursday, June 18th, 2020 
Have you logged in through SSH to remote servers with the brand new given UNIX account in your company just to be prompted for your current Password immediately after logging and forced to change your password?
The smart sysadmins or security officers use this trick for many years to make sure the default set password for new user is set to a smarter user to prevent default password leaks which might later impose a severe security risk for a company Demiliterized networks confidential data etc.
If you haven't seen it yet and you're in the beautiful world of UNIX / Linux as a developer qa tester or sysadmin sooner or later you will face it.
Here of course I'm talking about plain password local account authentication using user / pass credentials stored in /etc/passwd or /etc/shadow.
Lets Say hello to the main command chage that is used to do this sysadmin trick.
chage command is used to change user password expiry information and set and alter password aging parameters on user accounts.
1. Force chage to make password expire on next user login for a new created user
# chage -d 0 {user-name}
Below is a real life example
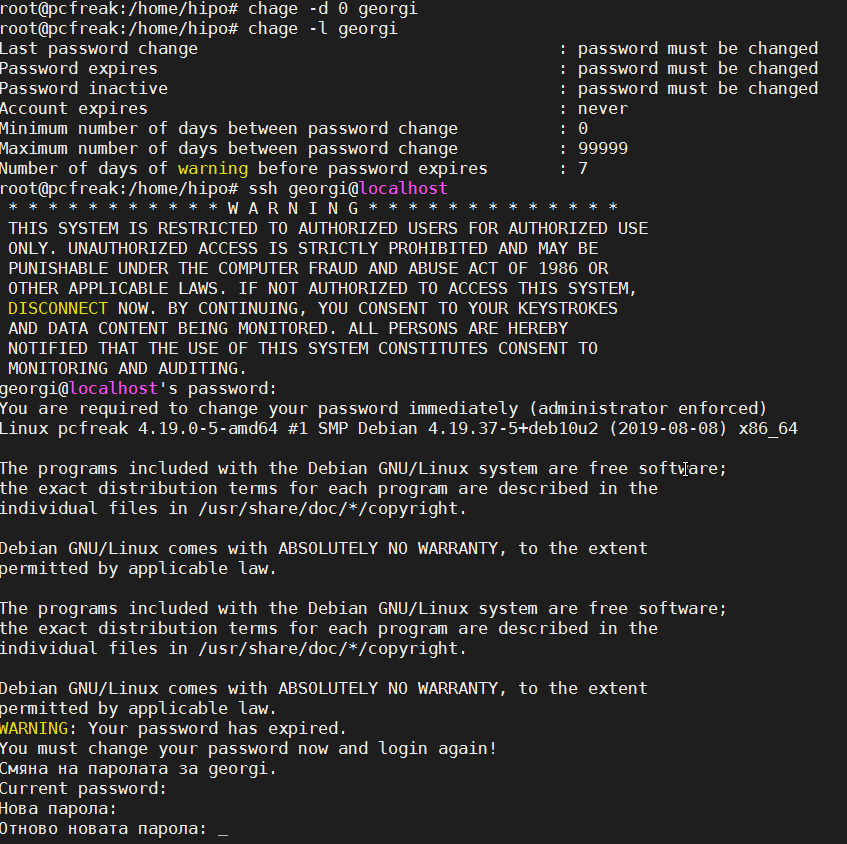
2. Get information on when account expires
[hipo@linux ~]$ chage -l hipo
Last password change : Apr 03, 2020
Password expires : Jul 08, 2020
Password inactive : never
Account expires : never
Minimum number of days between password change : 0
Maximum number of days between password change : 90
Number of days of warning before password expires : 14
3. Use chage to set user account password expiration
The most straight forward way to set an expiration date for an active user acct is with:
# chage -E 2020-08-16 username
To make the account get locked automatically if the password has expired and the user did not logged in to it for 2 days after its expiration.
# chage -I 2 username
– Set Password expire with Minimum days 7 (-n mindays 7), (-x maxdays 28) and (-w warndays 5)
# passwd -n 7 -x 28 -w 5 username
To check the passwod expiration settings use list command:
# chage -l username
Last password change : юни 18, 2020
Password expires : юли 16, 2020
Password inactive : never
Account expires : never
Minimum number of days between password change : 7
Maximum number of days between password change : 28
Number of days of warning before password expires : 5
chage is a command is essential sysadmin command that is mentioned in every Learn Linux book out there, however due to its often rare used many people and sysadmins either, don't know it or learn of it only once it is needed.
A note to make here is some sysadmins prefer to use usermod to set a password expire instead of chage.
usermod -e 2020-10-14 username
For those who wonder how to set password expiry on FreeBSD and other BSD-es is done, there it is done via the pw system user management tool as chage is not present there.
A note to make here is chage usually does not provide information for Linux user accounts that are stored in LDAP. To get information of such you can use ldapsearch with a query to the LDAP domain store with something like.
ldapsearch -x -ZZ -LLL -b dc=domain.com,dc=com objectClass=*
It is worthy to mention also another useful command when managing users this is getent used to get entries from Name Service Switch libraries.
getent is useful to get various information from basic /etc/ stored db files such as /etc/services /etc/shadow, /etc/group, /etc/aliases, /etc/hosts and even do some simple rpc queries.
Tags: BSD, chage, force password change, freebsd, getent, hosts, ldapsearch, linux?, passwd, password expire, pw, shadow
Posted in Computer Security, Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration | No Comments »
Monday, March 14th, 2011 
I'm experimenting this days with Elgg – An Open Source Free Software GPLed Social Network which enables users to quickly create Communities.
Elgg is really easy to install and all it requires is a Linux/BSD or Windows system with PHP, MySQL and Apache installed.
Elgg is provided with dozens of nice plugins which for a short time enables individual to create fully operational Social Network like facebook.
Many people nowdays use facebook without realizing how bad facebook is how it breaks their privacy.
Facebook is actually a spy network, it stores data and pictures, likings and user behaviour of million of users around the world.
This needs to be stopped somehow, maybe if people start using the free software networks like elgg to build a mini-community which has profound interests in a certain spheres of work, life and amusement.
The evil empire of facebook will slowly start to loose it's position and the small projects networks based on Elgg and the other Free Software Social Networks which are currently available will start to rise up.
I'm currently really a novice into Elgg but I'm more convinced that the guys who develop it and contribute to it in terms of handy plugins have done really a great job.
It's ultra easy even for non professional middle level user to setup himself an Elgg install.
The installation procedure is not much harder than a simple wordpress blog or joomla based website install.
The installation of elgg takes no more than 10 to 20 minutes, the plugin installation and setup time further could take few days but in the end you have a full featured Social Network! This is really amazing.
The installation of new plugins in elgg is also fool proof / easy all you have to do to equip a newly installed elgg with plugins is to go to it's root directory and look for the mod directory. The new plugins which needs to be installed, could be directly downloaded and saved via links, elinks, lynx or even wget to the elgg installation directory.
Most of the elgg plugins comes in a form of zip files so after being installed simply executing:
server:/home/elgg/mysocialnetwork/mod# unzip walltowall.zip
....
The above cmd will for example unzip the WallToWall elgg plugin and the plugin will be further ready to be enabled via the administrator user set upped during your elgg installation.
The configurations of elgg are being accomplished via:
Administration -> Tool Administration
I should I'm still experimenting with Elgg social, until this very moment I've installed the following elgg plugins:
aaudio
akismet
artfolio
blog
bookmarks
buddytalk
captcha
categories
chat
crontrigger
custom_index
custom_profile_fields
default_widgets
diagnostics
elgg-ebuddy
embed
embedvideo
emoticons
externalpages
family
fbconnect
file
file_tree
flyers
forum
friend_request
friends
garbagecollector
groups
htmlawed
invitations
invitefriends
izap_videos
kaltura_video
lastfm
likes
logbrowser
logrotate
lucygames
members
messageboard
messages
milockergames_frameme
noscript_message
notifications
pages
polls
profile
reportedcontent
resume
river_comments
riverdashboard
riverfaces
search
siteaccess
tagcloud
theme_simpleneutral
thewire
tidypics
tidypicsExt
tinymce
twitter
twitterservice
user_contact_list
uservalidationbyemail
walltowall
weather
wp1
zaudio
One very handy feature I truly enjoy about Elgg is that it gives every user an own blog which or in other words when somebody registers in Elgg, he automatically gets a personal blog! How cool this is Yeash 😉
The Elgg photo upload plugin is also another interesting story. The photo plugin is a way better from my first impressions than facebook's buggy upload client.
Elgg also uses heavily jquery for it's various operations and the user experience feels very interactive.
Of course as with all free software things are not perfect some of the elgg plugins or (mods) as they are called are not working.
For example I couldn't make by so far the weather plugin which is supposed to report the weather.
Maybe some tweakening of the not working plugins will easily make them working. What is really important is that the Elgg basis system looks and seems to work really good and enpowers the user with a social network alternatives to the ugly facebook.
In order to experiment with Elgg and I've established a small social network targetting at University College and School Students called MockATeacher – mockateacher.com>/i>. The idea behind is to help students in their report writting by providing them with a place where they can meet other students and share files.
Some other aspects I've planned for MockATeacher is to build a small community of people who would like to share about idiot teachers, teacher stupid sayings as well as to mock the idiotic type of education that we and our children are up to in this age.
Just to close up, if you're looking for some time to spend in experimenting in an enjoyable way you definitely need to install elgg and play with it 😉
Tags: BSD, bsd system, custom, dozens, elgg, evil empire, facebook, fool, fool proof, Free, free software networks, GPLed, installation, level, likings, Lynx, mod, novice, Open, php mysql, plugin, plugin installation, Privacy, root, root directory, setup time, short time, social networks, software, spheres, spy, spy network, time, unzip, weather, which enables users, windows system, wordpress blog, work, working
Posted in Entertainment, Everyday Life, Joomla, Linux, Various, Web and CMS | 2 Comments »
Friday, November 2nd, 2012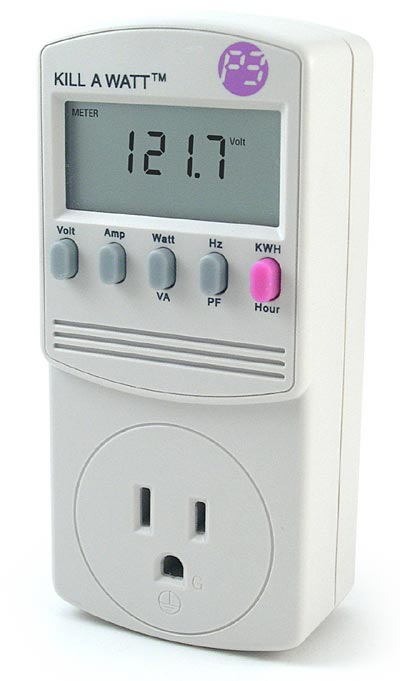 
A friend of mine today ask me if I have clue if it is possible to track his home computer Consumption with some piece of Software?
The question is quite interesting, since I run a home server with Linux and it would have been nice if I can exactly track how much electricity per month it consumes
Now knowing, the answer I first checked online for some kind of software and all I can find something that does something similar but all can find is powertop.
Though powertop is nice Linux tool to keep an eye which program on PC consumes most from overall consumed electricity and order the programs and modules based on electricity consumption it is not providing information on overall electricity consumption.
As the topic seem to be some interesting, I've decided to ask in irc.freenode.net #deiban
Here is a paste from irssi channel log:
17:21 < hipodilski> hi any idea, how can I find how much electricity a server conmuses per month
17:21 < hipodilski> is there some some kind of software
17:21 -!- digdilem [~digdilem@plague.digdilem.org] has joined #debian
17:22 < babilen> hipodilski: I would recommend an electricity meter rather than software
17:22 -!- tommy_e [~tommy@81.27.221.202] has quit [Ping timeout: 260 seconds]
17:22 < jelly-home> watt meters ftw
17:22 -!- msx [~msx@190.194.114.10] has joined #debian
17:22 -!- blackshirt [~najwa@103.3.223.5] has left #debian []
17:23 < hipodilski> yes but i don't have electricity metter, if there is software it would be interesting to try it
17:23 -!- badiane [~gdurand@D8FF67fa.cst.lightpath.net] has quit [Remote host closed the connection]
17:23 < xand> hipodilski: no, you need a hardware device.
17:23 < jelly-home> now everything can be solved in software, hipodilski
17:23 < jelly-home> not*
17:23 < jelly-home> dammit
17:23 < xand> unless you have a very fancy PSU, software can't find that out
17:23 < babilen> jelly-home: hehe, nice typo !
17:23 < vacuous> hipodilski yes
17:24 < HelloShitty> nsadmin, are you out of ideas for me?
17:24 < vacuous> there's various devices that do it
17:24 -!- firecode [~irc@unaffiliated/firecode] has joined #debian
17:24 < vacuous> you can either get a killawat which are highly innacurate but it might give you a clue
17:24 < vacuous> and they're very cheap too
17:25 < vacuous> you can get a device which measures your entire houses electric, then you just turn off all the appliances and run the
server only
17:25 -!- trysten [~trysten@37-251-103-145.FTTH.ispfabriek.nl] has quit [Quit: be back]
17:25 * babilen likes that approach
17:25 < babilen> But this is getting a bit too off-topic. Maybe hipodilski wants to take it to #debian-offtopic
17:25 < vacuous> or you can keep all fridges on, check what the reading is and then negate that from the total
17:25 < hipodilski> yes thanks 🙂
The answer makes it clear right of time of writing this post there is no software for Linux or BSD that keeps track electricity consumption daily or monthly
I've googled to see what is Kill-A-Watt hardware? and found fuzzy named device Kill-A-Watt for sale on ThinkGeek's website for the not so expensive 24.99$
To use Kill-A-Watt device is to be connected inside the power plug and then PC or Server has to be plugged into Kill-A-Watt dev. I've red also (while researching) many Intelligent UPS devs has support for keeping log of discharged energy, so just buying a good UPS with web administrator or even a cheap one providing statistical information of UPS use via serial port should be another alternative to track ur server consumption.
Tags: BSD, clue, consumption, electricity, find out server ups capacity, How to, kind, Linux, Pc, PSU, server electricity consumption, software, something, ups, website
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration | No Comments »
Tuesday, October 12th, 2010 I'm studying Project Management, right now. In that spirit of thoughts I and a couple of other guys are building a Project Plan.
As it Project Plan it's necessary to put a GANTT Chart in it to show visually the project timeline (the phases), the duration and the inter-relation between the different tasks which leads the project to an actual completion.
After a bit of thorough research online on available software to deal with project management and particularly, ones that are capable to build a GANTT charts on Linux / BSD.
I've come with the following list of software capable to be a substitute for the Microsoft Project software.
Redmine GANTT Chart
1. Gantt Project
 GANTTProject Chart
GANTTProject Chart
2. Gnome Planner
 Planner GANTT Chone Chart
Planner GANTT Chone Chart
3. Task Juggler Project Manager with GANTT Capability for (KDE)
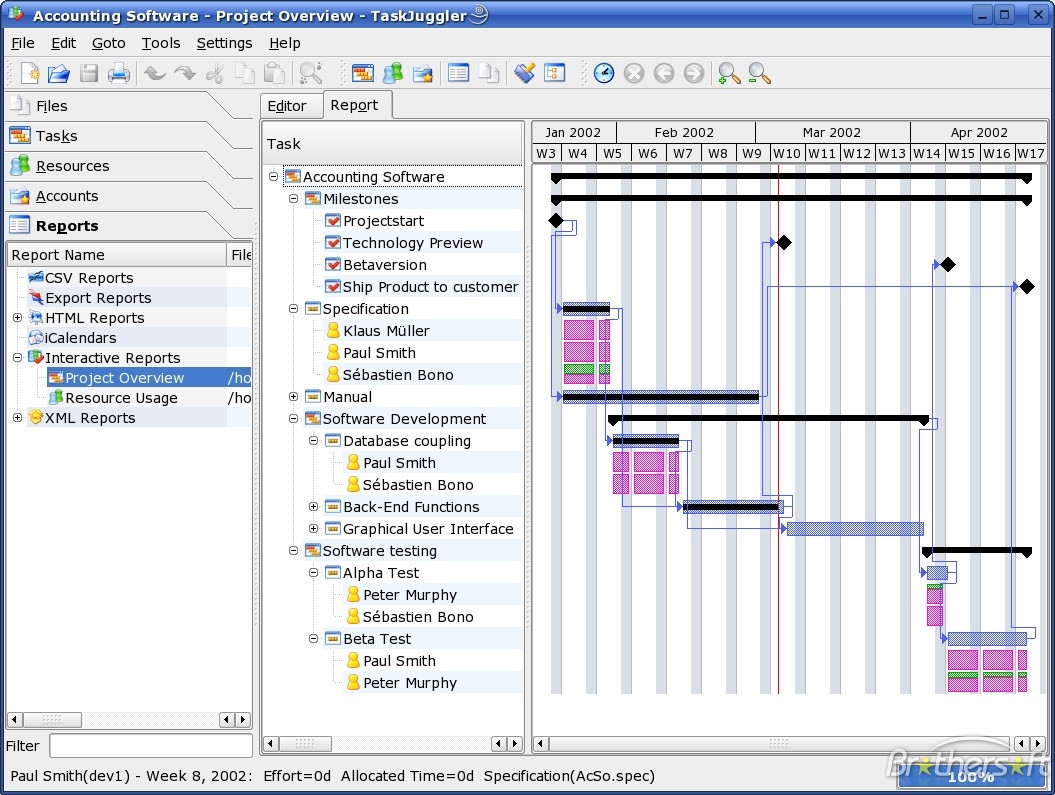 Task Juggler
Task Juggler
4. JxProject – This software is not free, though it can be considered almost free
Take a look also at:
5. Trac , though it doesn't really support GANTT charts it's a lovely software to be used for PM.
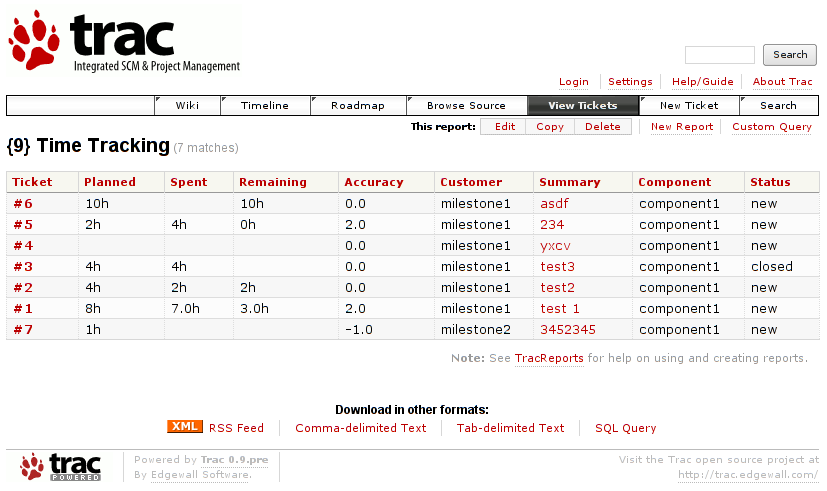
Another option you have is to try out:
6. PHProjekt
Update 20.09.2016 – PHPProject Old download link is no longer active
It is this link http://www.phprojekt.com/, but the page doesn’t seem to be active any more. I thought you might want to update.
If you are looking for an alternative please check out http://wiht.link/PHProjekt-PM, it may make a suitable replacement.
Kind Regards,
Tom Wilcox
That piece of softwre really looks promising, especially if we consider that it's web based and how much essential is today to have an anline tools for doing the ordinary desktop jobs.
You can even check an online demo of the PHPProjekt software here
If you're a type of KDE user you definitely has to try out Kplato
As I've tested the software the software is easy to be used, however it still is missing some essential parts that Microsoft Project includes so it's not 100% substitute.
Also it's not able to open Microsoft Project (MPP) files, neither able to save the charts in the .mpp format.
Moving ahead I've came across DotProject 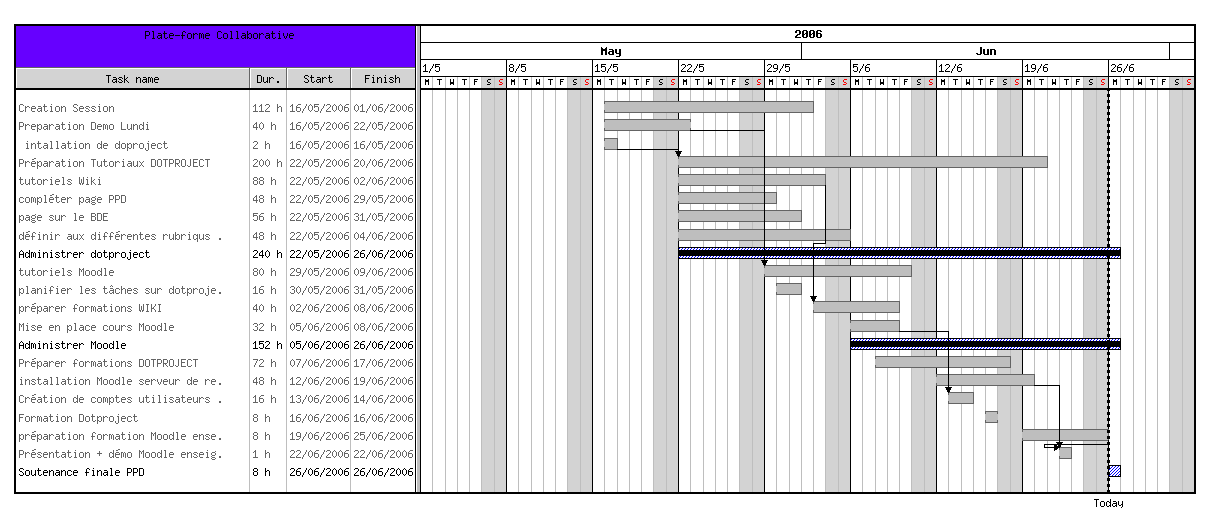
DottProject Gantt Chart
I haven't took the time to test it myself but however, as I go through the software website the project looked quite good.
Lastly you can take a look at: 7. PStricks as a mean of project management, however I think it doesn't support GANTT chart building.
>
Tags: anline, available software, BSD, building, capability, Chart, check, completion, demo, Desktop, doesn, Drawing GANTT Charts and Project Management on Linux, duration, GANTT, gantt chart, gantt charts, Gnome, jobs, Juggler, Linux, linux microsoft, look, Microsoft, Microsoft Project, microsoft project software, mpp, mpp format, online, option, page doesn, PHProjekt, piece, project, project management, project mpp, Project Plan, project timeline, software, software website, Spirit, substitute, support, time, trac, type, unix
Posted in Business Management, Curious Facts, Everyday Life, Linux | 1 Comment »
Tuesday, May 8th, 2012 
I believe, the quickest way to take notes on Linux and BSD and later view the notes is to use the command line.
A very easy simple way to keep record of various short notes is just to use a simple text editor like (vim) and store each note in a separate file in lets say ~/notes/ directory.
Actually, I'm using this way to take notes and store sensitive info for various important information I need for further reference, since 5 years or so..
Opening a new text editor for each note and then doing cd ~/notes/; ls |grep -i 'string' is a bit time consuming.
Fortunately there is a quick two shell functions hack that shortens time for note taking. The following two bash functions has to be added in ~/.bashrc:
n() {
vim ~/notes/"$*".txt
}
nls() {
ls -c ~/notes/ | grep "$1"
}
Copy / Paste this two functions in the beginning or the end of ~/.bashrc in order to use them.
Also if ~/notes directory is not existing, yet create it:
hipo@noah:~$ mkdir notes
To make the two new input functions active across opened bash shells on console or terminal either re-login or reread the .bashrc by "sourcing it", e.g.
hipo@noah:~$ source ~/.bashrc
Afterwards, note taking becomes a piece of cake to store a new note with login credentials (user/password) for a new registration to a random named website, type something like:
hipo@noah:~$ n my_website_name-user-pass
This will open for editting ~/.notes/my_website_name-user-pass.txt, type the new desired note content and do save and exit from vim (press esc and type :x!.
Then to get a quick list of all previously stored notes use:
hipo@noah:~$ nls website
my_website_name-user-pass.txt
If you already have a directory containing subdirectories with various taken notes (like me), you will need to use an improved version nls written by Jason Ryan, the nls improved is like this:
nls () { tree -CR --noreport ~/notes | awk '{
if ((NR >) gsub(/.txt/,"")); if
(NF==1) print $1; else if (NF==2)
print $2; else if (NF==3)
printf " %s\n", $3}';
}
This two functions, were not my creation but was suggested in Linux Magazine issue 135 article entitled Command-line task managers and note-taking tools written by Dmitri Popov.
Hope this two functions, will be helpful to console geeks out there.
Tags: Auto, BSD, cake, consuming, copy paste, cr, Draft, file, freebsd, gnu linux, hack, hipo, important information, info, information, input functions, jason ryan, Linux, login, login credentials, mkdir, need, nls, noah, opening, password, piece, piece of cake, sensitive info, Shell, shell functions, shells, something, store, subdirectories, terminal, text, time, time consuming, Tip Quick Note, txtIf, type, use, vim, websitemy
Posted in Curious Facts, Linux, System Administration, vim editor | 2 Comments »
Monday, May 21st, 2012 
I'm running FreeBSD with Apache and PHP on it and I got in dmesg (kernel log), following error:
freebsd# dmesg|grep -i vm.pmap.shpgperproc
Approaching the limit on PV entries, consider increasing either the vm.pmap.shpgperproc or the vm.pmap.pv_entry_max tunable.
Approaching the limit on PV entries, consider increasing either the vm.pmap.shpgperproc or the vm.pmap.pv_entry_max tunable.
Approaching the limit on PV entries, consider increasing either the vm.pmap.shpgperproc or the vm.pmap.pv_entry_max tunable.
Approaching the limit on PV entries, consider increasing either the vm.pmap.shpgperproc or the vm.pmap.pv_entry_max tunable.
Approaching the limit on PV entries, consider increasing either the vm.pmap.shpgperproc or the vm.pmap.pv_entry_max tunable.
The exact FreeBSD, Apache and php versions I have installed are:
freebsd# uname -a ; httpd -V ; php –version
FreeBSD pcfreak 7.2-RELEASE-p4 FreeBSD 7.2-RELEASE-p4 #0: Fri Oct 2 12:21:39 UTC 2009 root@i386-builder.daemonology.net:/usr/obj/usr/src/sys/GENERIC i386
Server version: Apache/2.0.64
Server built: Mar 13 2011 23:36:25Server's Module Magic Number: 20050127:14
Server loaded: APR 0.9.19, APR-UTIL 0.9.19
Compiled using: APR 0.9.19, APR-UTIL 0.9.19
Architecture: 32-bit
Server compiled with….
-D APACHE_MPM_DIR="server/mpm/prefork"
-D APR_HAS_SENDFILE
-D APR_HAS_MMAP
-D APR_HAVE_IPV6 (IPv4-mapped addresses enabled)
-D APR_USE_FLOCK_SERIALIZE
-D APR_USE_PTHREAD_SERIALIZE
-D SINGLE_LISTEN_UNSERIALIZED_ACCEPT
-D APR_HAS_OTHER_CHILD
-D AP_HAVE_RELIABLE_PIPED_LOGS
-D HTTPD_ROOT="/usr/local"
-D SUEXEC_BIN="/usr/local/bin/suexec"
-D DEFAULT_PIDLOG="/var/run/httpd.pid"
-D DEFAULT_SCOREBOARD="logs/apache_runtime_status"
-D DEFAULT_LOCKFILE="/var/run/accept.lock"
-D DEFAULT_ERRORLOG="logs/error_log"
-D AP_TYPES_CONFIG_FILE="etc/apache2/mime.types"
-D SERVER_CONFIG_FILE="etc/apache2/httpd.conf"
PHP 5.3.5 with Suhosin-Patch (cli) (built: Mar 14 2011 00:29:17)
Copyright (c) 1997-2009 The PHP Group
Zend Engine v2.3.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2010 Zend Technologies
with eAccelerator v0.9.6.1, Copyright (c) 2004-2010 eAccelerator, by eAccelerator
After a bunch of research a FreeBSD forums thread , I've found the fix suggested by a guy.
The solution suggested in the forum is to raise up vm.pmap.pv_entry_ma to vm.pmap.pv_entry_max=1743504, however I've noticed this value is read only and cannot be changed on the BSD running kernel;
freebsd# sysctl vm.pmap.pv_entry_max=1743504
sysctl: oid 'vm.pmap.pv_entry_max' is read only
Instead to solve the;
Approaching the limit on PV entries, consider increasing either the vm.pmap.shpgperproc or the vm.pmap.pv_entry_max tunable.
, I had to add in /boot/loader.conf
vm.pmap.pde.mappings=68
vm.pmap.shpgperproc=500
vm.pmap.pv_entry_max=1743504
Adding this values through /boot/loader.conf set them on kernel boot time. I've seen also in the threads the consider increasing either the vm.pmap.shpgperproc is also encountered on FreeBSD hosts running Squid, Dansguardion and other web proxy softwares on busy hosts.
This problems are not likely to happen for people who are running latest FreeBSD releases (>8.3, 9.x), I've read in same above post in newer BSD kernels the vm.pmap is no longer existing in newer kernels.
Tags: apache 2, apache2, architecture, Auto, boot time, BSD, dmesg, Draft, eeBSDI, errorlog, Fix Approaching, flock, freebsd, freebsd apache, Fri, GENERIC, grep, httpd, kernel, limit, loader, logs apache, magic number, Mar, mime types, mmap, Module, mpm, net usr, number, Oct, patc, pcfreak, php version, php versions, PV, RELEASE-p, root, scoreboard, sendfile, serialize, server, server config, server version, shpgperproc, suexec, threads, uname, UTC, vm, Zend
Posted in FreeBSD, System Administration | No Comments »
Saturday, April 28th, 2012 
If there is necessity to look for a string in all hidden files with all sub-level subdirectories (be aware this will be time consuming and CPU stressing) use:
hipo@noah:~$ grep -rli 'PATH' .*
./.gftp/gftprc
./.gftp/cache/cache.OOqZVP
….
Sometimes its necessery to only grep for variables within the first-level directories (lets say you would like to grep a 'PATH' variable set, string within the $HOME directory, the command is:
hipo@noah:~$ grep PATH .[!.]*
.profile:PATH=/bin:/usr/bin/:${PATH}
.profile:export PATH
.profile:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.profile: PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
.profile.language-env-bak:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.profile.language-env-bak: PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
.viminfo:?/PATH.xcyrillic: XNLSPATH=/usr/X11R6/lib/X11/nls
.xcyrillic: export XNLSPATH
The regular expression .[!.]*, means exclude any file or directory name starting with '..', e.g. match only .* files
Note that to use the grep PATH .[!.]* on FreeBSD you will have to use this regular expression in bash shell, the default BSD csh or tsch shells will not recognize the regular expression, e.g.:
grep PATH '.[!.]*'
grep: .[!.]*: No such file or directory
Hence on BSD, if you need to look up for a string within the home directory, hidden files: .profile .bashrc .bash_profile .cshrc run it under bash shell:
freebsd# /usr/local/bin/bash
[root@freebsd:/home/hipo]# grep PATH .[!.]*
.bash_profile:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.bash_profile:# PATH=~/bin:"${PATH}"
.bash_profile:# do the same with …
Another easier to remember, alternative grep cmd is:
hipo@noah:~$ grep PATH .*
.profile:PATH=/bin:/usr/bin/:${PATH}
.profile:export PATH
.profile:# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
.profile: PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
….
Note that grep 'string' .* is a bit different in meaning, as it will not prevent grep to match filenames with names ..filename1, ..filename2 etc.
Though grep 'string' .* will work note that it will sometimes output some unwanted matches if filenames with double dot in the beginning of file name are there …
That's all folks 🙂
Tags: Auto, bash shell, bit, BSD, cache cache, cmd, consuming, csh, cshrc, directory name, Draft, export path, expression, file, freebsd, gftp, grep, hipo, home directory, How to, level directories, Linux, MANPATHAnother, nbsp, necessery, noah, note, Path, path profile, private bin, profile path, quot, regular expression, rli, root, set path, Shell, shrc, text, text strings, time, time consuming, tsch, value, XNLSPATH, XNLSPATHThe, zcompdump
Posted in FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration | 2 Comments »
Wednesday, April 18th, 2012 
The default behaviour of lynx – console text browser on Linuces, BSD and other free OSes is to always ask, for the accept cookies prompt once an internet web page is opened that requires browser cookies to be enabled.
I should admin, having this "secure by default" (always ask for new cookies) behaviour in lynx was a good practice from a security point of view.
Another reason, why this cookies prompt is enabled by default is back in the days, when lynx was actively developed by programmers the websites with cookies support was not that many and even cookies was mostly required for user/pass authentication (all those who still remember this days the websites that requires authentication was a way less than today) …
With this said the current continuing security cautious behaviour in the browser, left from its old days is understandable.
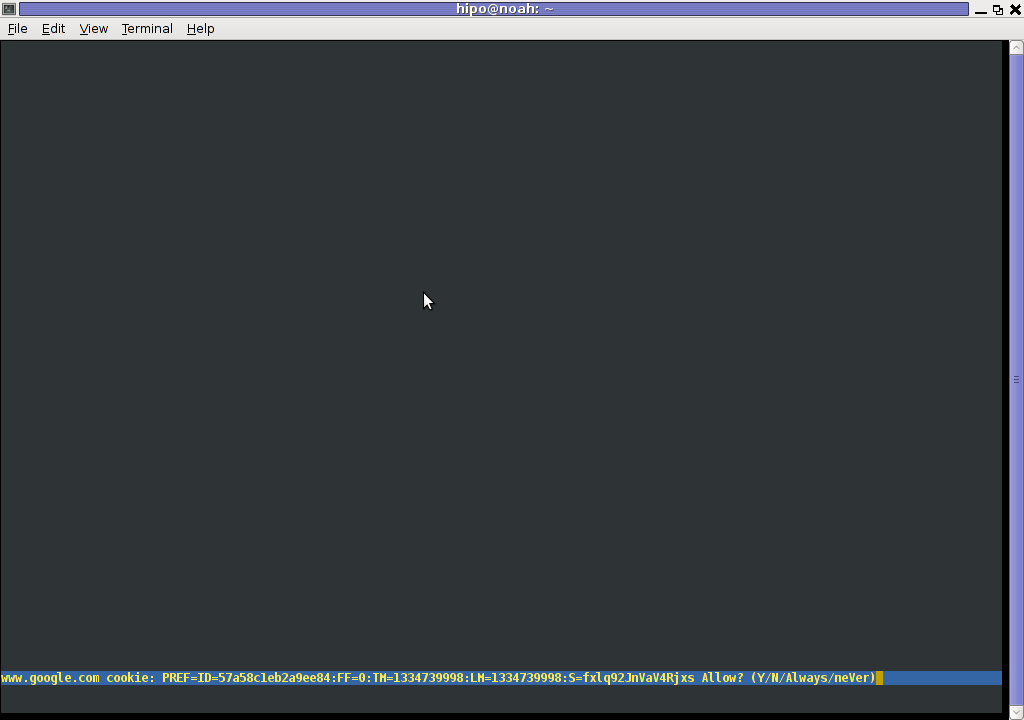
However I personally sometimes, need to use lynx more frequently and this behaviour of always opening a new website in text mode in console to prompts me for a cookie suddenly becomes a big waste of time if you use lynx to browser more than few sites. Hence I decided to change the default way lynx handles cookies and make them enabled by default instead.
Actually even in the past, when I was mainly using internet in console on every new server or home Linux install, I was again making the cookies to be permanently accepted.
Everyone who used lynx a few times already knows its "annoying" to all time accept cookie prompts … This provoked me to write this short article to explain how enabling of constant cookie accepting in lynx is done
To enable the persistent cookies in lynx, one needs to edit lynx.cfg on different GNU / Linux and BSD* distributions lynx.cfg is located in different directory.
Most of the lynx.cfg usual locations are /etc/lynx/lynx.cfg or /etc/lynx.cfg as of time of writting this post in Debian Squeeze GNU / Linux the lynx.cfg is located in /etc/lynx-cur/lynx.cfg, whether for FreeBSD / NetBSD / OpenBSD users the file is located in /usr/local/etc/lynx.cfg
What I did to allow all cookies is open lynx.cfg in vim edit and change the following lines:
a)
#FORCE_SSL_COOKIES_SECURE:FALSE
with
FORCE_SSL_COOKIES_SECURE:TRUE
b)
#SET_COOKIES:TRUE
uncomment it to:
SET_COOKIES:TRUE
c) next, change
ACCEPT_ALL_COOKIES:FALSE
ACCEPT_ALL_COOKIES:TRUE
Onwards opening any website with lynx auto-accepts the cookies.
For people who care about there security (who still browse in console (surely not many anymore)), permanently allowing the cookies is not a good idea. But for those who are ready to drop off little security for convenience its ok.
Tags: ALL, authentication, Auto, browser cookies, BSD, bsd distributions, cfg, change, convenience, Cookie, default behaviour, Draft, everyone, file, free oses, GNU, gnu linux, good, How to, internet web, Linux, Lynx, lynx one, NetBSD, Onwards, OpenBSD, page, persistent cookies, point of view, programmers, quot, reason, security point, squeeze, support, text, text browser, text mode, time, TRUEb, TRUEc, TRUEuncomment, uncomment, use, using internet, vim, waste, waste of time, web page, writ
Posted in Curious Facts, Everyday Life, FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration | 1 Comment »










 GANTTProject Chart
GANTTProject Chart  Planner GANTT Chone Chart
Planner GANTT Chone Chart  Task Juggler
Task Juggler 








How to permanently enable Cookies in Lynx text browser – Disable accept cookies prompt in lynx console browser
Wednesday, April 18th, 2012The default behaviour of lynx – console text browser on Linuces, BSD and other free OSes is to always ask, for the accept cookies prompt once an internet web page is opened that requires browser cookies to be enabled.
I should admin, having this "secure by default" (always ask for new cookies) behaviour in lynx was a good practice from a security point of view.
Another reason, why this cookies prompt is enabled by default is back in the days, when lynx was actively developed by programmers the websites with cookies support was not that many and even cookies was mostly required for user/pass authentication (all those who still remember this days the websites that requires authentication was a way less than today) …
With this said the current continuing security cautious behaviour in the browser, left from its old days is understandable.
However I personally sometimes, need to use lynx more frequently and this behaviour of always opening a new website in text mode in console to prompts me for a cookie suddenly becomes a big waste of time if you use lynx to browser more than few sites. Hence I decided to change the default way lynx handles cookies and make them enabled by default instead.
Actually even in the past, when I was mainly using internet in console on every new server or home Linux install, I was again making the cookies to be permanently accepted.
Everyone who used lynx a few times already knows its "annoying" to all time accept cookie prompts … This provoked me to write this short article to explain how enabling of constant cookie accepting in lynx is done
To enable the persistent cookies in lynx, one needs to edit lynx.cfg on different GNU / Linux and BSD* distributions lynx.cfg is located in different directory.
Most of the lynx.cfg usual locations are /etc/lynx/lynx.cfg or /etc/lynx.cfg as of time of writting this post in Debian Squeeze GNU / Linux the lynx.cfg is located in /etc/lynx-cur/lynx.cfg, whether for FreeBSD / NetBSD / OpenBSD users the file is located in /usr/local/etc/lynx.cfg
What I did to allow all cookies is open lynx.cfg in vim edit and change the following lines:
a)
#FORCE_SSL_COOKIES_SECURE:FALSEwith
FORCE_SSL_COOKIES_SECURE:TRUEb)
#SET_COOKIES:TRUEuncomment it to:
SET_COOKIES:TRUEc) next, change
ACCEPT_ALL_COOKIES:FALSEACCEPT_ALL_COOKIES:TRUEOnwards opening any website with lynx auto-accepts the cookies.
For people who care about there security (who still browse in console (surely not many anymore)), permanently allowing the cookies is not a good idea. But for those who are ready to drop off little security for convenience its ok.
Tags: ALL, authentication, Auto, browser cookies, BSD, bsd distributions, cfg, change, convenience, Cookie, default behaviour, Draft, everyone, file, free oses, GNU, gnu linux, good, How to, internet web, Linux, Lynx, lynx one, NetBSD, Onwards, OpenBSD, page, persistent cookies, point of view, programmers, quot, reason, security point, squeeze, support, text, text browser, text mode, time, TRUEb, TRUEc, TRUEuncomment, uncomment, use, using internet, vim, waste, waste of time, web page, writ
Posted in Curious Facts, Everyday Life, FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration | 1 Comment »