Intro
Main console package install apt-get / apt and / aptitude did not use the HTTP Proxy environment variables by default as there is no default proxy set on Debian / Ubuntu / Mint and other deb based distros after OS Install. Under some circunstances for DMZ placed or firewall secured servers, direct access to internet address or even Package repository is only allowed via a proxy and hence the package manager needs to have a proxy host set.
Setting a global wide proxy on Linux is easily possible by setting http_proxy="http://yourhost.com:8080" and https_proxy or if FTP connection via ftp_proxy somewhere in /etc/profile , /etc/bashrc or via /etc/environment but as using this Shell variables set it global wide for all applications lynx / links / wget / curl, sometimes it is useful to set the Proxy host only for deb package management tools.
Note that if you want to set a proxy host for deb operations this can be done during initial OS install installation, the Apt configuration file would have been automatically updated then.
Creating an Apt Proxy Conf File
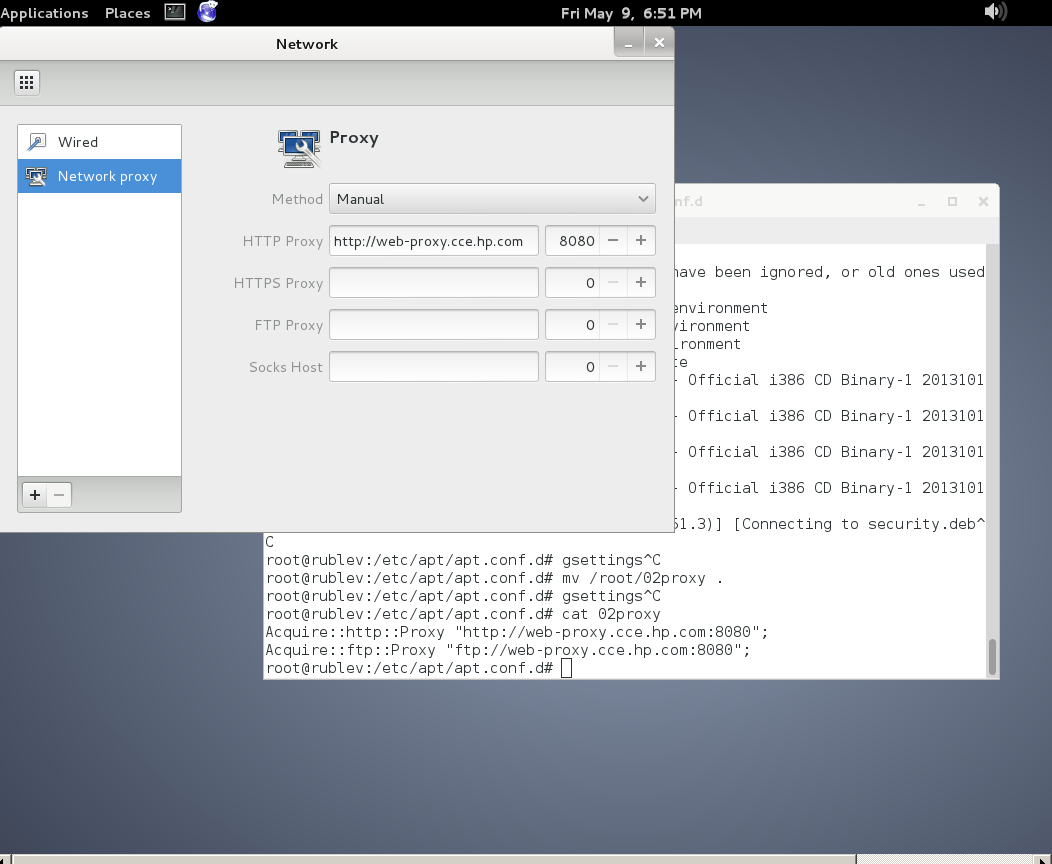
Apt loads all configuration files under /etc/apt/apt.conf.d. We can create a configuration specifically for our proxy there, keeping it separate from all other configurations.
- Create a new configuration file named proxy.conf.
# touch /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/proxy.conf
- Open the proxy.conf file in a text editor.
# vi /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/proxy.conf
- Add the following line to set your HTTP proxy for apt.
Acquire::http::Proxy "http://username:password@proxy.server:port/";
- Add the following line to set your HTTPS proxy.
Acquire::https::Proxy "http://username:passw0rd@proxy.server:port/";
- Save your changes and exit the text editor.
Your proxy settings will be applied the next time you run Apt.
Simplifying the Configuration
As mentioned by a user in the comments below, there is an alternative way for defining the proxy settings. While similar, it removes some redundancy.
Just like in the first example, create a new file under the /etc/apt/apt.conf.d directory for example /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/proxies, and then add the lines as.
Acquire { HTTP::proxy "http://127.0.0.1:8080"; HTTPS::proxy "http://127.0.0.1:8080"; }