I've just reinstalled my CentOS 7 Virtual Machine since after I tried to migrate a .vdi Virtual Box image to the new company laptop using a copy of Virtualbox VM via Microsoft OneDrive was a failure.
Thus I have rebuild all my CentOS Linux programs preinstalled on the old Virtual Machines from scratch, I use this virtual machine for a very simple tasks, so basicly most imporant tools I use is a plain SSH and VNC and Remote Desktop clients just to be able to remotely connect to remote Home based server.
1.Install GNOME Graphical Environment from command line on CentOS 7 with yum and configure it to start GUI on next OS boot
I've used a minimal CentOS installation – ISO CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1908.iso and this brings up the OS with a text mode only as usually CentOS is used to roll on Servers and rarely and many times admins did not want to have GUI at all, however my case is different since I do like to use Graphical Environment as I use my CentOS for all kind of testing that can be later applied to a Production machines that doesn't have a GUI, hence to install GNOME on CentOS run below cmds:
[root@centos ~ ]# yum group list
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
There is no installed groups file.
Maybe run: yum groups mark convert (see man yum)
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
Available Environment Groups:
Minimal Install
Compute Node
Infrastructure Server
File and Print Server
Basic Web Server
Virtualization Host
Server with GUI
GNOME Desktop
KDE Plasma Workspaces
Development and Creative Workstation
Available Groups:
Compatibility Libraries
Console Internet Tools
Development Tools
Graphical Administration Tools
Legacy UNIX Compatibility
Scientific Support
Security Tools
Smart Card Support
System Administration Tools
System Management
Done
[root@centos ~ ]# yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop" "Graphical Administration Tools" -y
Enable GUI to be automatically start on CentOS VM boot in systemd this is configured with the "targets" instead of the well known classical runlevels (the well known /etc/inittab) is now obsolete in newer Linux distros.
[root@centos ~ ]# ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/runlevel5.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
2. Install Guest Additions Tools on CentOS
The most basic thing to do once I've had the CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core) rolled out on the VirtualBox is of course to enable Guest Additions Tools
First I had to install of course Guest Additions Tools to allow myself to have a copy paste in clip board via the Host Machine (Windows 10) and the Guest Machine.
To do I had to:
[root@centos ~ ]# yum install kernel-headers.x86_64 -y
[root@centos ~ ]# rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
[root@centos ~ ]# yum install perl gcc dkms kernel-devel kernel-headers make bzip2
To check the required VBoxLinuxAdditions.run script kernel headers are at place:
[root@centos ~ ]# ls -l /usr/src/kernels/$(uname -r)
…
You should get a list of kernel header files
Then once I've done the Insert Guest Additions CD Image from the VirtualBox VM upper menu. I've had to mount and load the guest additions via the script:
[root@centos ~ ]# mkdir /mnt/cdrom
[root@centos ~ ]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
[root@centos ~ ]# sh VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
After rebooting the Virtual Machine, I've used the full screen functionality to test and configured immediately Shared Clipboard and Drag and Drop to be both set to (Bidirectional) as well as configured a Shared folder to provide my Windows Desktop under /mnt/shared_folder (as read write) as I usually do to be able to easily copy files from the VM and to the Windows.
3. Install Google Chrome on the CentOS Virtual Machine with yum
Next I've installed the chrome browser that was pretty trivial it is up to fetching the required 32 or 64 bit latest chrome binary this is usually on URL:
[root@centos ~ ]# wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64.rpm
and installing Google Chrome with superuser with command:
[root@centos ~ ]# yum install ./google-chrome-stable_current_*.rpm -y
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
Examining ./google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64.rpm: google-chrome-stable-92.0.4515.107-1.x86_64
Marking ./google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64.rpm to be installed
Resolving Dependencies
–> Running transaction check
—> Package google-chrome-stable.x86_64 0:92.0.4515.107-1 will be installed
–> Processing Dependency: liberation-fonts for package: google-chrome-stable-92.0.4515.107-1.x86_64
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirror.digitalnova.at
* epel: fedora.ipacct.com
* extras: mirror.digitalnova.at
* updates: mirror.digitalnova.at
–> Processing Dependency: libvulkan.so.1()(64bit) for package: google-chrome-stable-92.0.4515.107-1.x86_64
–> Running transaction check
—> Package liberation-fonts.noarch 1:1.07.2-16.el7 will be installed
–> Processing Dependency: liberation-narrow-fonts = 1:1.07.2-16.el7 for package: 1:liberation-fonts-1.07.2-16.el7.noarch
—> Package vulkan.x86_64 0:1.1.97.0-1.el7 will be installed
–> Processing Dependency: vulkan-filesystem = 1.1.97.0-1.el7 for package: vulkan-1.1.97.0-1.el7.x86_64
–> Running transaction check
—> Package liberation-narrow-fonts.noarch 1:1.07.2-16.el7 will be installed
—> Package vulkan-filesystem.noarch 0:1.1.97.0-1.el7 will be installed
–> Finished Dependency ResolutionDependencies Resolved
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
google-chrome-stable x86_64 92.0.4515.107-1 /google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64
259 M
Installing for dependencies:
liberation-fonts noarch 1:1.07.2-16.el7 base 13 k
liberation-narrow-fonts noarch 1:1.07.2-16.el7 base 202 k
vulkan x86_64 1.1.97.0-1.el7 base 3.6 M
vulkan-filesystem noarch 1.1.97.0-1.el7 base 6.3 kTransaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 1 Package (+4 Dependent packages)Total size: 263 M
Total download size: 3.8 M
Installed size: 281 M
Is this ok [y/d/N]: y
Downloading packages:
(1/4): liberation-fonts-1.07.2-16.el7.noarch.rpm | 13 kB 00:00
(2/4): liberation-narrow-fonts-1.07.2-16.el7.noarch.rpm | 202 kB 00:00
(3/4): vulkan-filesystem-1.1.97.0-1.el7.noarch.rpm | 6.3 kB 00:00
(4/4): vulkan-1.1.97.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpm | 3.6 MB 00:00
——————————————————————————–
Total 3.0 MB/s | 3.8 MB 00:01
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : vulkan-filesystem-1.1.97.0-1.el7.noarch 1/5
Installing : vulkan-1.1.97.0-1.el7.x86_64 2/5
Installing : 1:liberation-narrow-fonts-1.07.2-16.el7.noarch 3/5
Installing : 1:liberation-fonts-1.07.2-16.el7.noarch 4/5
Installing : google-chrome-stable-92.0.4515.107-1.x86_64 5/5
Verifying : vulkan-1.1.97.0-1.el7.x86_64 1/5
Verifying : 1:liberation-narrow-fonts-1.07.2-16.el7.noarch 2/5
Verifying : 1:liberation-fonts-1.07.2-16.el7.noarch 3/5
Verifying : google-chrome-stable-92.0.4515.107-1.x86_64 4/5
Verifying : vulkan-filesystem-1.1.97.0-1.el7.noarch 5/5Installed:
google-chrome-stable.x86_64 0:92.0.4515.107-1Dependency Installed:
liberation-fonts.noarch 1:1.07.2-16.el7
liberation-narrow-fonts.noarch 1:1.07.2-16.el7
vulkan.x86_64 0:1.1.97.0-1.el7
vulkan-filesystem.noarch 0:1.1.97.0-1.el7
…
4. Install usable Windows VNC and remote desktop (RDP Client) for CentOS Linux
There is a plenty of clients to choice from if you need to have an RDP client for Linux, but perhaps the most useful ones I usually use are remmina / rdesktop and freerdp. Usually I use remmina on Debian Linux, but under the VM somehow I was not able to make remmina work in Full Screen mode while connected to remote Windows 7 VPS server, thus I've first tried xfreerdp (that comes from default CentOS repositories) and is open source alternative to rdesktop (which is non free distributed binary).
[root@centos ~ ]$ sudo yum -y install freerdp
The basic use is:
[hipo@centos ~ ]$ xfreerdp –toggle-fullscreen <remote-server-address>
Unfortunately I did not succeeded to make xfreerdp be able to show me remote desktop in FullScreen mode so had to use additional repository package called nux-dextop to have rdesktop at my disposal.
To install it had to run:
[root@centos ~ ]# rpm –import http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/RPM-GPG-KEY-nux.ro
[root@centos ~ ]# rpm -Uvh http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el7/x86_64/nux-dextop-release-0-1.el7.nux.noarch.rpm
[root@centos ~ ]# yum install rdesktop
To connect to the remote RDP host in Fullscreen with rdesktop :
rdesktop -f <remote-server-address>
As telnet is not installed by default and it is so useful to check ports
5. Install GNU Image Manipulation Program for better screnshotting and Graphic edits
I usually do install GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program) since this is my favourite tool to make screenshot on Linux as well as do some minor graphic edits whenever necessery. I warmly recommend gimp to anyone. If you don't have basic GIMP tool and you plan to be daily working a lot with Linux sooner or later some skills with the program will be of a major use even for the most advanced sysadmin :)_
root@centos ~ ]# yum install -y gimp
6. Install useful administration tools for daily sysadmin work – telnet, nmap, iftop, htop, iotop, iptraf-ng, tcpdump
Having basic analys tools and remote communication port testing, DNS, resolving and connection, cpu, mem statistics I find mostly useful.
[root@centos .ssh]# yum install telnet nmap iftop htop vnstat sysstat iptraf-ng bind-utils -y
…
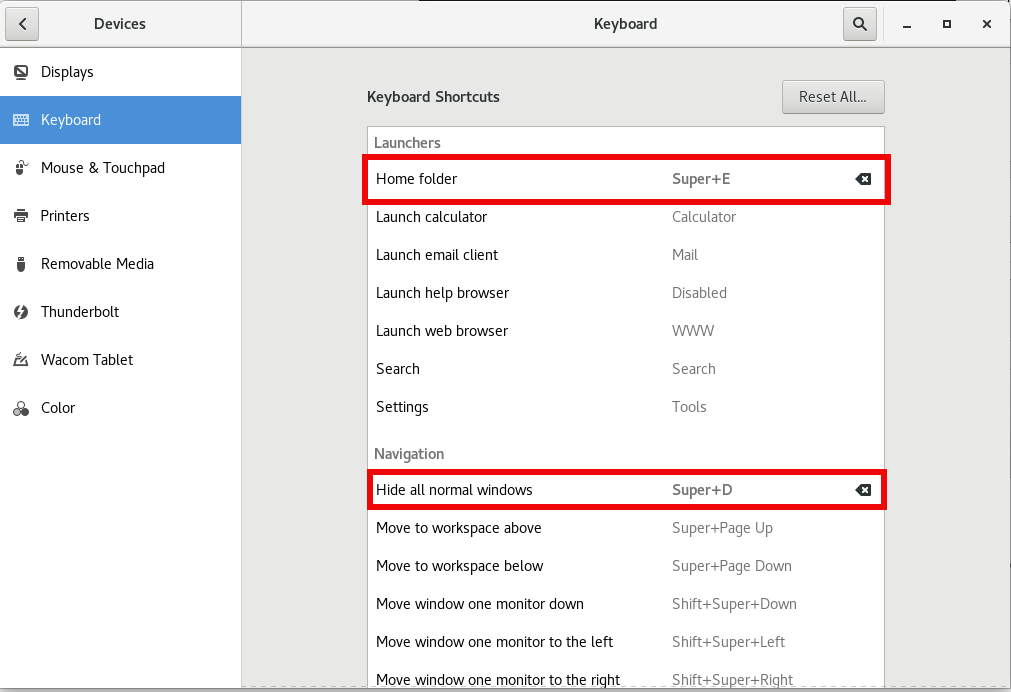
7. Set Open Explorer and SHOW Desktop key binding shortcuts for GNOME (to make daily work easier)
Another useful I do use in my newly installed Virtual Machines is the key combination of Windows (button key) + E – to easily open the GNOME equivalent of Windows Explorer (Nautilus) and Windows (key) + D to hide the active selected Window and Show Desktop. This is configured pretty easy in GNOME through:
$ gnome-control-center
Keyboard (Section)
Perhaps there is other stuff I need to add on the freshly installed Operating System if I remember something else interesting
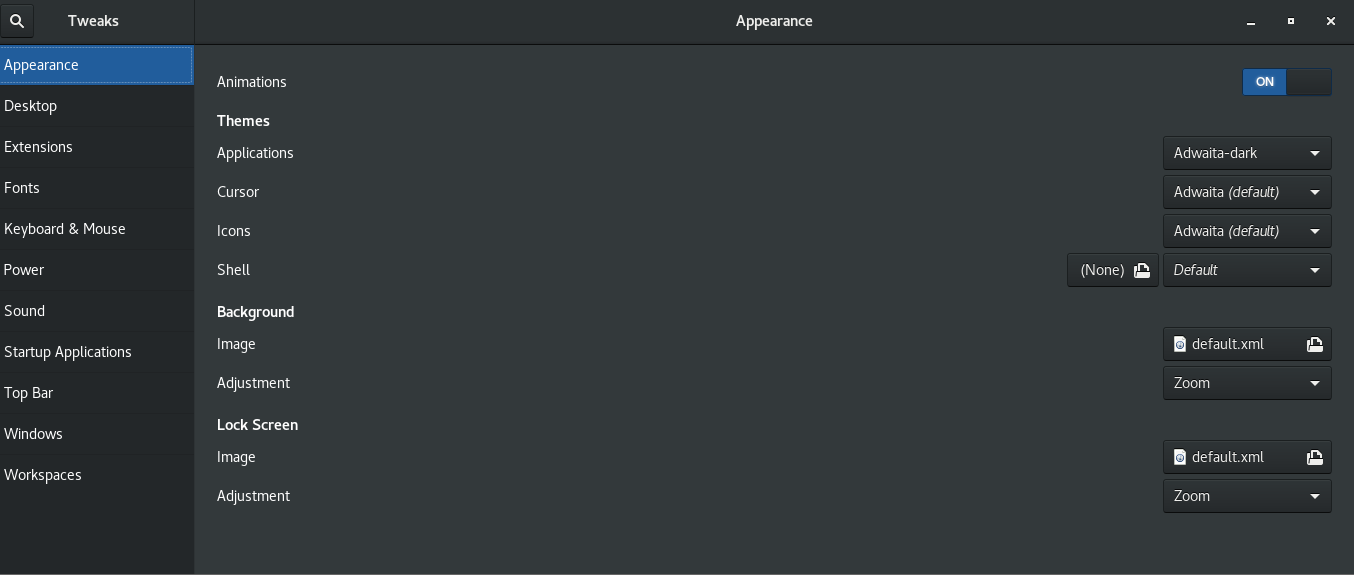
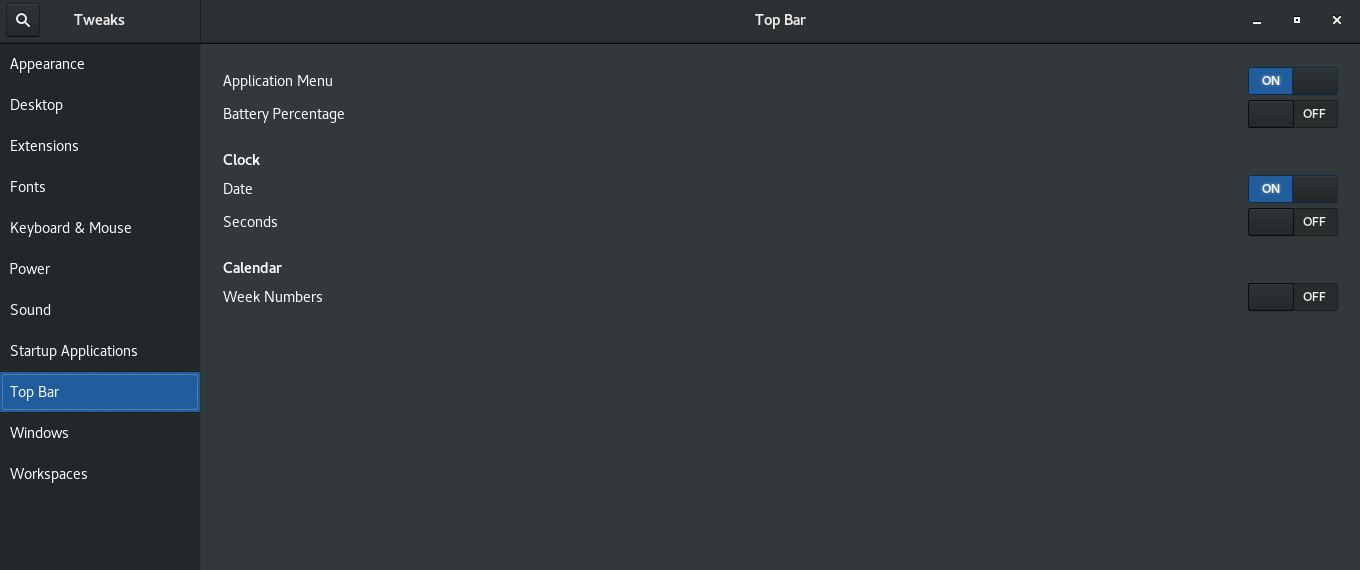
8. Install gnome-tweaks to tweak a bit the desktop icon positionsing and additional gnome-shell extras
[root@centos hipo]# yum install -y gnome-shell-extension-workspace-indicator.noarch gnome-shell-extension-workspace-indicator.noarch gnome-shell-extension-suspend-button.noarch gnome-shell-extension-refresh-wifi.noarch gnome-shell-extension-updates-dialog.noarch gnome-shell-extension-windowoverlay-icons.noarch gnome-shell-extension-places-menu.noarch gnome-shell-extension-drive-menu.noarch gnome-shell-extension-apps-menu.noarch gnome-shell-extension-auto-move-windows.noarch gnome-tweaks gnome-shell-extension-systemMonitor.noarch gnome-shell-extension-openweather.noarch gnome-shell-extension-user-theme.noarch gnome-shell-extension-topicons-plus.noarch
Next step is to use gnome-tweaks to set multiple custom preference stuff you like on the gnome 3.28 GUI
9. Change ( Fix) timezone to correct time on the Virtual Machine
[root@localhost ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Fri 2021-07-30 12:20:51 CEST
Universal time: Fri 2021-07-30 10:20:51 UTC
RTC time: Fri 2021-07-30 10:20:48
Time zone: Europe/Berlin (CEST, +0200)
NTP enabled: yes
NTP synchronized: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: yes
Last DST change: DST began at
Sun 2021-03-28 01:59:59 CET
Sun 2021-03-28 03:00:00 CEST
Next DST change: DST ends (the clock jumps one hour backwards) at
Sun 2021-10-31 02:59:59 CEST
Sun 2021-10-31 02:00:00 CET
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /etc/localtime
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 35 Jul 29 14:03 /etc/localtime -> ../usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Berlin
To change to correct timezone, you need to find out the long name for the timezone you want to use. The timezone naming convention usually uses “Region/City” format.
To list all available time zones, you can either list the files in the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory or use the timedatectl command.
[root@centos ~]# timedatectl list-timezones|tail -n 10
Pacific/Pohnpei
Pacific/Port_Moresby
Pacific/Rarotonga
Pacific/Saipan
Pacific/Tahiti
Pacific/Tarawa
Pacific/Tongatapu
Pacific/Wake
Pacific/Wallis
UTC
As I'm situated in Sofia Bulgaria to set the correct timezone to UTC (Universal Time Clock) + 2 Hrs, i've checked the correct Continent/Country like so:
[root@centos ~]# timedatectl list-timezones|grep -i Sofia
Europe/SofiaOnce I've my Capital / Country time location identified to set to it:
[root@centos ~]# timedatectl set-timezone your_time_zone
10. Configure remote connection hostname SSH aliases via ssh config ( ~/.ssh/config)
I'm having separate Virtual Machines running on my OpenXen virtualization Hypervisor server at different ports which I remember by heart under different hostnames, this saves me time to always type on command line long commands such as:
# ssh long-hostname -p Port_number
to make accessibility to remote machines via a simple Hostname Aliases, that forwards to remote port (that gets forwarded via a Local Network configure Netwrork Address Translation), I use the .ssh/config nice Host / Hostname / User / Port directives like below samples:
[hipo@centos .ssh]$ cat config
Host pcfreak
User root
Port 2248
HostName 83.228.93.76Host freak
User root
Port 2249
HostName 213.91.190.233
Host pcfrxenweb
User root
Port 2251
Hostname 83.228.93.76Host pcfrxen
User root
Port 2250
Hostname 213.91.190.233
…
Now to connect to pcfrxen for example I simply type:
ssh pcfrxen
type in the password to remote VM and I'm in 🙂
The same could be achieved also with Adding Custom Hostname IP Aliases via ~/.bashrc or iteration script as I've explained earlier that fakes like custom /etc/hosts, but I usuaully prefer to use .ssh/config instead like explained above.
Note that above steps should work also on RHEL / Fedora Linux with a minor modifications, as usually this two distros share the RPM package manager. If someone tries to follow the guide and have success on any of this distros please drop a comment with feedback.