In this article I'll explain how to install IBM Spectrum Protect client well known over the years with TSM (Tivoli Service Manager) which as of time of writting perhaps the best backup solution for Linux / Unix server. The install process is rather trivial, but there are few configuration things worthy to mention and explain. IBM Tivoli is a 2 component system consisting of Client and Server just like most solutions, we know thus before proceeding you should already have setup a functional backup server with attached and configured storages but this is a topic for another future article.
1. Login and configure TSM server to add the backup host machine you'll be connecting
If you don't have the access to remote server if you're in a Corporation network and you don't have the Admin credentials to Tivoli Server, ask a colleague who has access to add you the hostname you would like to backup.
He should generate you as a minimum a connect password and hand it back to you in encrypted form (GPG / PGP etc.). Besides setting the new client to connect password, it is necessery to communicate when and how frequently the backup is to be prepared and respectively he should set the required backup schedule configuration etc.
2. Check OS version
As minimum this article assumes you'll be using some kind of RPM based distribution.
[root@centos ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
In my case this was CentOS, any other RPM based distribution should work. For specifics check out
README_*.htm
3. Remove version lock If version lock is there
On our servers we do use one feature of yum called versionlock to prepare some colleague to install or update some package with yum by mistake.
If you don't know versionlock and you want to install and use it you will have to install RPM package yum-plugin-versionlock
[root@centos ~]# yum install -y yum-plugin-versionlock
…
Versionlock is used for Restricting a Package to a Fixed Version Number with yum.
In case if you have versionlock installed to list the versionlock restricted versions to not be ovewritten do:
[root@centos ~]# yum versionlock list
…
….
……
0:gskcrypt64-8.0-55.14.*
0:lm_sensors-libs-3.4.0-8.20160601gitf9185e5.el7.*
0:sysstat-10.1.5-19.el7.*
0:TIVsm-API64-8.1.10-0.*
versionlock list done
- To clean up already set lock for current installed packages
[root@centos ~]# yum versionlock clear
4. Install TSM Backup API and Backup Archiver Client RPMs
If you have already created a /etc/yum.repos.d/3party.repo with a mirror of IBM binaries and repository is enabled you can perhaps do something like:
[root@centos ~]# yum install -y Tivsm-BA
Otherwise go and follow official IBM Tivoli installation instructions
In short once .rpms are downloaded from IBM’s site, this comes to:
4.1. Install the required dependent library gskcrypt64
[root@centos ~]# rpm -U gskcrypt64-8.x.x.x.linux.x86_64.rpm gskssl64-8.x.x.x.linux.x86_64.rpm
4.2. Install Tivoli Storage Manager API
Application programming interface (API) is API which contains the Tivoli Storage Manager API shared libraries and samples, default directory install location is /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/api/bin64
[root@centos ~]# rpm -i TIVsm-API64.x86_64.rpm
4.3. Install the backup-archive client
[root@centos ~]# rpm -i TIVsm-BA.x86_64.rpm
Its most files will be stored under dir /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin.
This directory is considered to be the default installation directory for many backup-archive client files. The sample system-options file (dsm.sys.smp) is written to this directory. If the DSM_DIR environment variable is not set, the dsmc executable file, the resource files, and the dsm.sys file are stored in this directory.
If DSM_CONFIG is not set, the client user-options file must be in this directory.
If you do not define DSM_LOG, writes messages to the dsmerror.log and dsmsched.log files in the current working directory.
Optionally: Install the Common Inventory Technology package that is used by the API. This package depends on the API so it must be installed after the API package is installed.
[root@centos ~]# rpm -i TIVsm-APIcit.x86_64.rpm
Optionally: Install the Common Inventory Technology package the client uses to send PVU metrics to the server. This package depends on the client package so it must be installed after the client package is installed.
[root@centos ~]# rpm -i TIVsm-BAcit.x86_64.rpm
If finally no optional stuff is installed the minumum for operational (Tivoli) Spectrum Protect is to at least below 2 RPMs being installed:
[root@centos ~]# rpm -qa |grep -i TivSM
TIVsm-BA-8.1.10-0.x86_64
TIVsm-API64-8.1.10-0.x86_64
5. Create /var/tsm log directory
[root@centos ~]# mkdir /var/tsm
[root@centos ~]# chown root:root /var/tsm
6. Hardcode to /etc/hosts TSM server hosts / addresses somewhere at File EOF
[root@centos ~]# vim /etc/hosts
Includfe at End of File
### TSM Server Records ###
10.50.8.1 tsmserver1.backup-server-fqdn.com tsmserver1
10.50.8.2 tsmserver2.backup-server-fqdn.com tsmserver2
Hardcoding records is a good idea if you don't use DNS at all, e.g. for security /etc/resolv.conf is empty or if you have configured the machine Name Record resolve order to be first read from /etc/hosts. For those who don't know in Linux this is done via /etc/nsswitch.conf (for more how it is configured – man nsswitch.conf command)
7. Create /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/{dsm.sys,dsm.opt,inclexcl.tsm}
configs
- dsm.sys main config mandatory file
[root@centos ~]# vi /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/dsm.sys
Paste inside and save :wq!:
*=================================================================
*
* File: /usr/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/dsm.sys
*
* Who:
*
* Project: TSM
*
* Purpose: Tivoli Storage Manager client user options
*
* Release: Tivoli BA client 5.3.4
*
* Author:
*
*=================================================================
*
* Modification history:
*
* [Chg.] [When] [Who] [What]
* 1. 19.11.2021 Georgi Georgiev Creation.
*
*=================================================================
* TSM Server Location
* Servername tsmserver1
* COMMmethod TCPip
* TCPPort 1500
* TCPServeraddress tsmserver1.backup-server-fqdn.com
* Passwordaccess generate
* SCHEDLOGNAME /logs/tivoli/sched.log
* SCHEDLOGRETENTION 21 D
* SCHEDMODE PROMPT
* ERRORLOGNAME /logs/tivoli/dsmerror.log
* ERRORLOGRETENTION 30 D
* INCLEXCL /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/inclexcl.tsm
*=========================================================================
*TSM SERVER
Servername tsmserver2
COMMmethod TCPip
TCPPort 1400
TCPServeraddress tsmserver2.backup-server-fqdn.com
NodeName server-hostname1
Passwordaccess generate
SCHEDLOGNAME /var/tsm/sched.log
SCHEDLOGRETENTION 21 D
SCHEDMODE prompted
MANAGEDServices schedule
ERRORLOGNAME /var/tsm/dsmerror.log
ERRORLOGRETENTION 30 D
* INCLEXCL /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/inclexcl.tsm
##########
TCPServeraddress – should equal to the complete hostname where the TSM backup server is configured
Nodename – should be your server hostname from where you create backup usually returned by hostname command
- dsm.opt Additional options file
[root@centos ~]# vi /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/dsm.opt
*=================================================================
*
* File: /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/dsm.opt
*
*
* Project: TSM
*
* Purpose: Tivoli Storage Manager client user options
*
* Release: Tivoli BA client 5.3.4
*
* Author:
*
*=================================================================
*
* Modification history:
*
* [Chg.] [When] [Who] [What]
*
*
*=================================================================
* Quiet
SERVERNAME TSMSERVER2
* Sample config you might want to modify it according to your preferences
Archsymlinkasfile no
Subdir yes
dateformat 2
followsymbolic yes
guitreeviewafterbackup yes
quiet
DOMAIN "/"
DOMAIN "/boot"
DOMAIN "/home"
* below line is commented
* DOMAIN "/var"
########
- Define what directories files / shuld be excluded from backup
# vi /opt/tivoli/tsm/client/ba/bin/inclexcl.tsm
exclude.dir /tmp
exclude.dir /var/cache
exclude /var/lock/*
exclude.dir /var/log
exclude /var/spool/*
exclude.dir /var/tmp
exclude.dir /var/tsm
exclude.dir /var/run
- Note ! Within dsm.sys you have also to have define SCHEDMODE prompted instead of SCHEDMODE polling:
Config should be as:
SCHEDMODE prompted
managedservices schedule
8. Authenticate to tsmserver2 host for a first time to remote Tivoli Backup Serv
Run the Tivoli connect client dsmc
# dsmc
→ empty username (if TSMServer configured so or otherwise provide the user provided by an Admin)
→ enter password given by TSM Admin
q sched → should answer with a schedule
tsm> q sched
Schedule Name: INC_DAILY_PROD
Description: 03:30 Days Schedule Prod
Schedule Style: Classic
Action: Incremental
Options:
Objects:
Priority: 5
Next Execution: 13 Hours and 38 Minutes
Duration: 2 Hours
Period: 1 Day
Day of Week: Any
Month:
Day of Month:
Week of Month:
Expire: Never
Schedule Name: Archives_365_DAYS_prod
Description: 365 Days Archive monthly Prod
Schedule Style: Classic
Action: Archive
Options: -archmc=ARCHIVE_365_DAYS-description="Archive of Logfiles" -deletefiles
Objects: /var/log/*.gz
Priority: 5
Next Execution: 492 Hours and 38 Minutes
Duration: 2 Hours
Period: 1 Month
Day of Week: Any
Month:
Day of Month:
Week of Month:
Expire: Never
tsm>
As you see above you get some details on when backup is to be executed, e.g. what time it is scheduled (in this case it is 03:30 Days Schedule Prod early morning), how often it is supposed to re-run, what is it priority, what is the type of backup (i.e. incremental) and how long is left until next execution.
incr command→ Start the backup (will create first incremental full backup)
q fi command→ To show (list) backuped FileSystems
tsm> q fi
# Last Incr Date Type File Space Name
——————————————————————————–
1 10-11-2021 12:08:43 EXT2 /
2 10-11-2021 12:09:01 EXT4 /boot
3 10-11-2021 12:09:03 EXT4 /home
4 10-11-2021 12:09:24 EXT4 /var
5 10-11-2021 12:03:17 EXT4 /vz
As you can see we have a recent backup of our OpenVZ machine Hypervisor host 🙂
quit → logout from dsmc
9. Check entires within defined /var/tsm/{dsmsched.log, sched.log, dsmerror.log}
If problems connecting check /var/tsm/dsmerror.log
Once incr backup command is finished check that all is backupped normal within /var/tsm/sched.log
10. Start dsmcad process
[root@centos ~]# /etc/init.d/dsmcad start
Or
[root@centos ~]# systemctl start dsmcad
11. Add service to auto start on server boot time
Depending on where, the machine is old legacy System V system or a systemd RedHat / CentOS you should either add it in chkconfig tool to auto start or enable the systemctl service.
11.1. Enable dsmcad autoboot on SystemV legacy machine
[root@centos ~]# chkconfig –add dsmcad
11.2 Enable dmscad boot on recent systemd machine as of year 2021
[root@centos ~]# systemctl enable dsmcad.service
or
[root@centos ~]# systemctl start dsmcad.service
12. Enable back yum versionlock for all installed RPM packages (Optional)
[root@centos ~]# yum versionlock \*

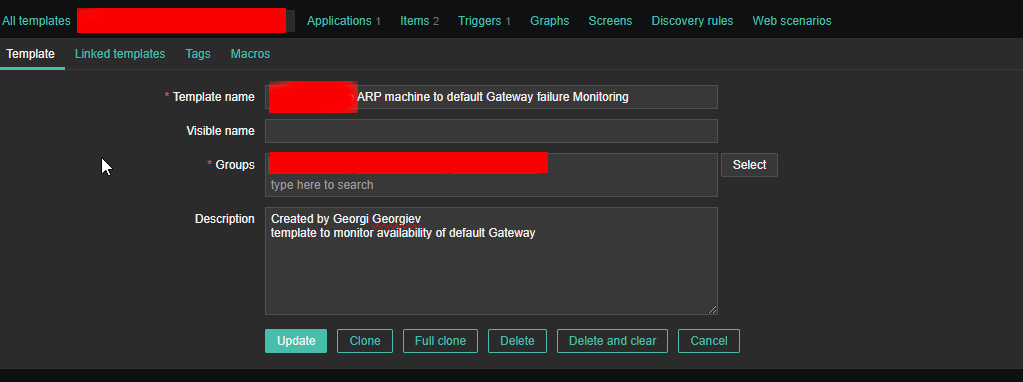

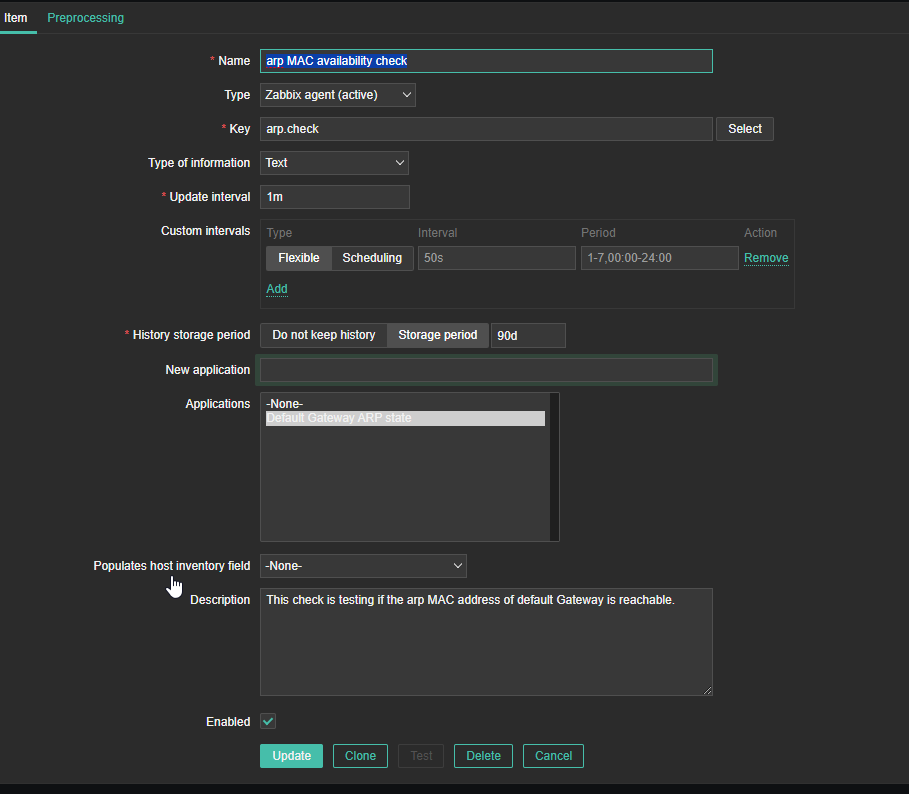
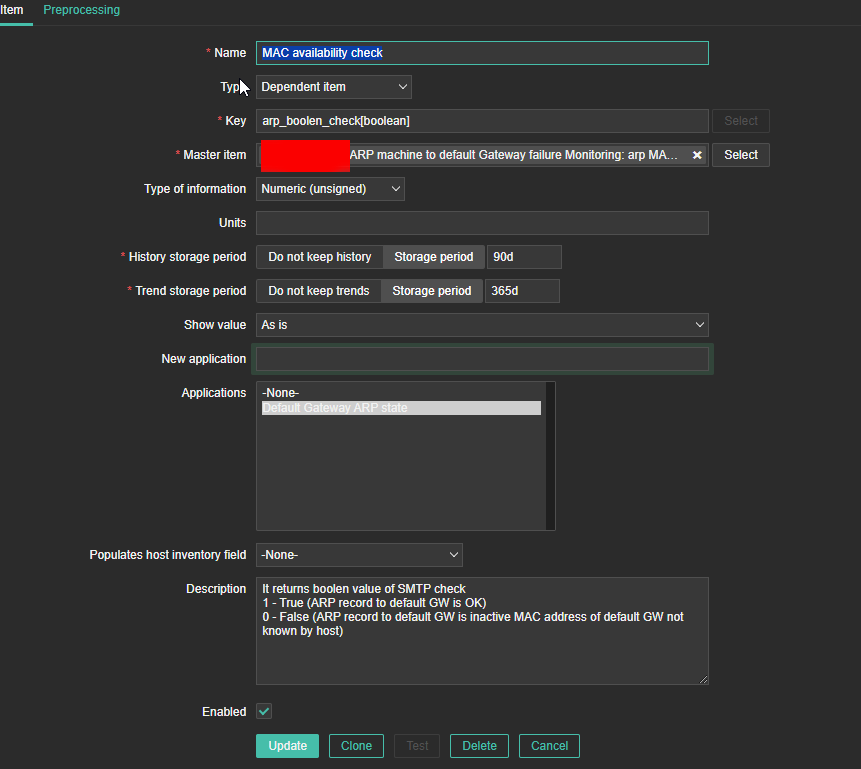
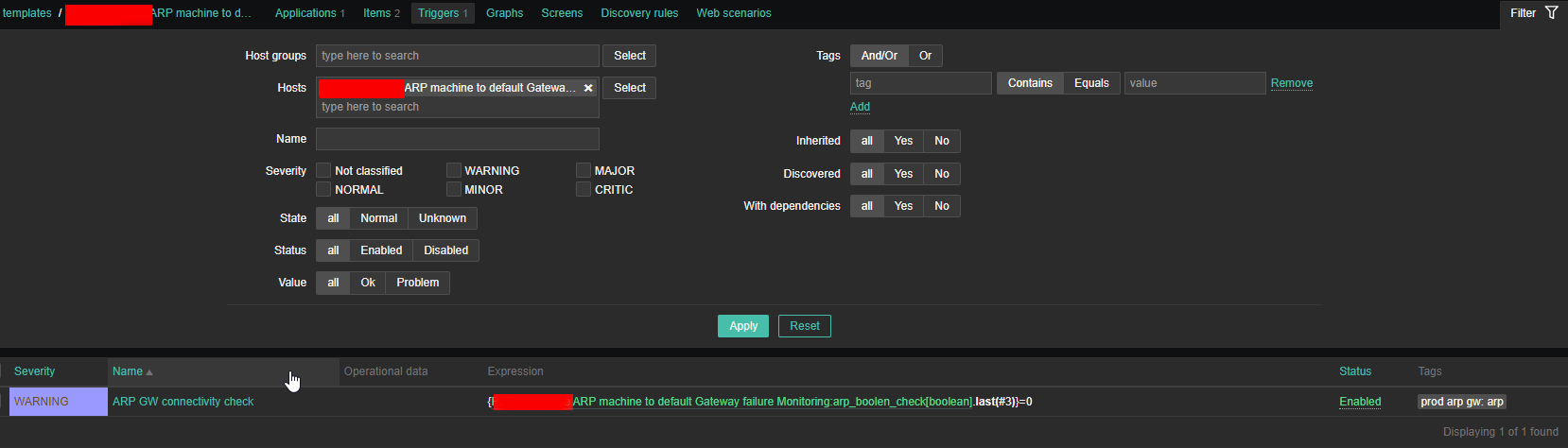
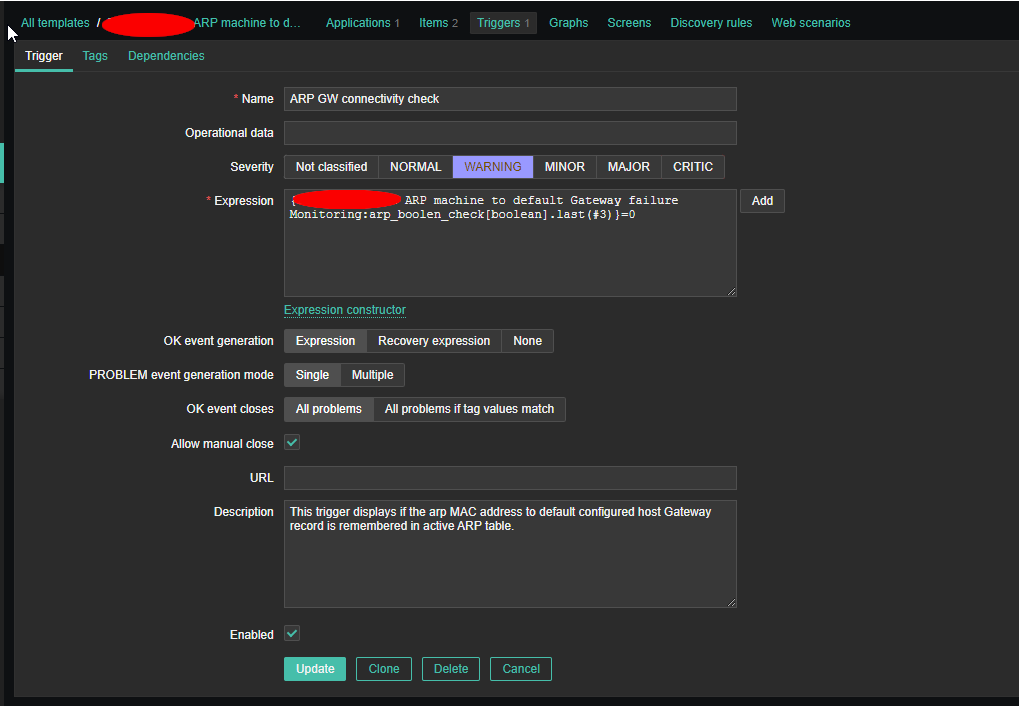
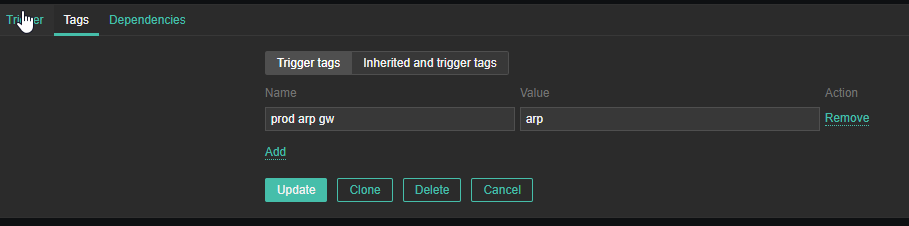
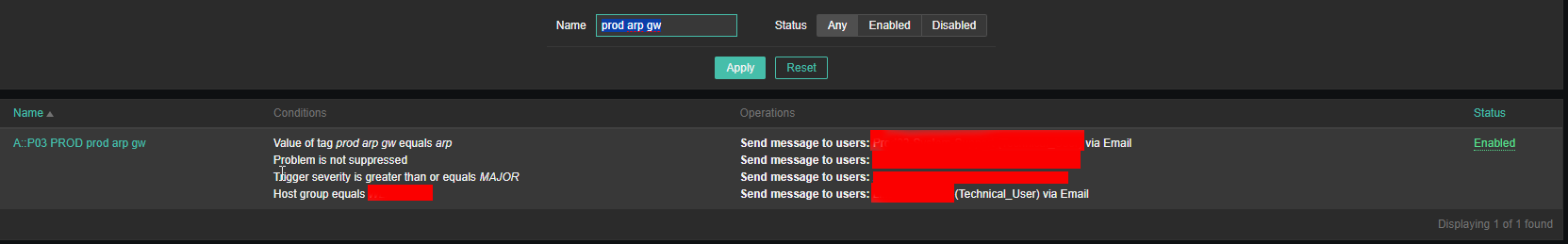
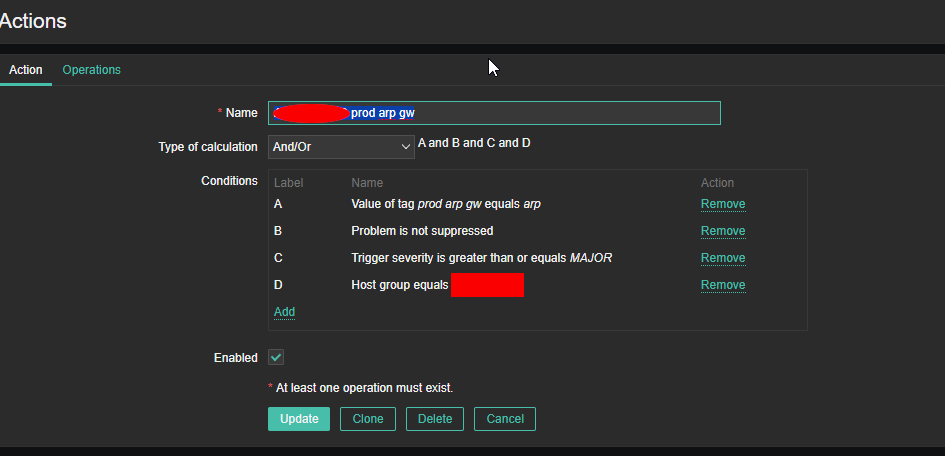

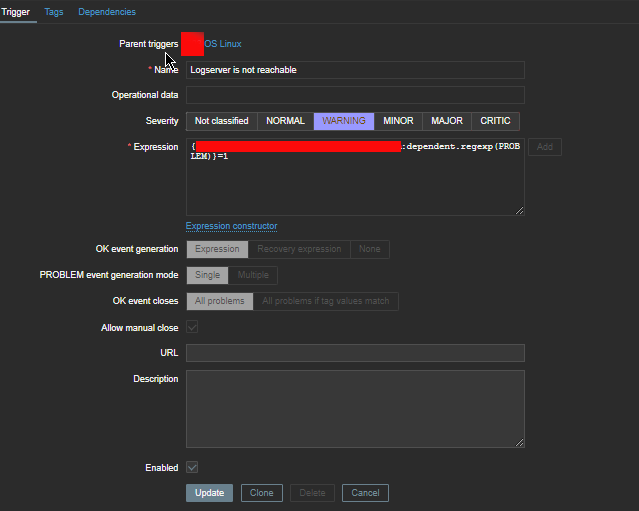
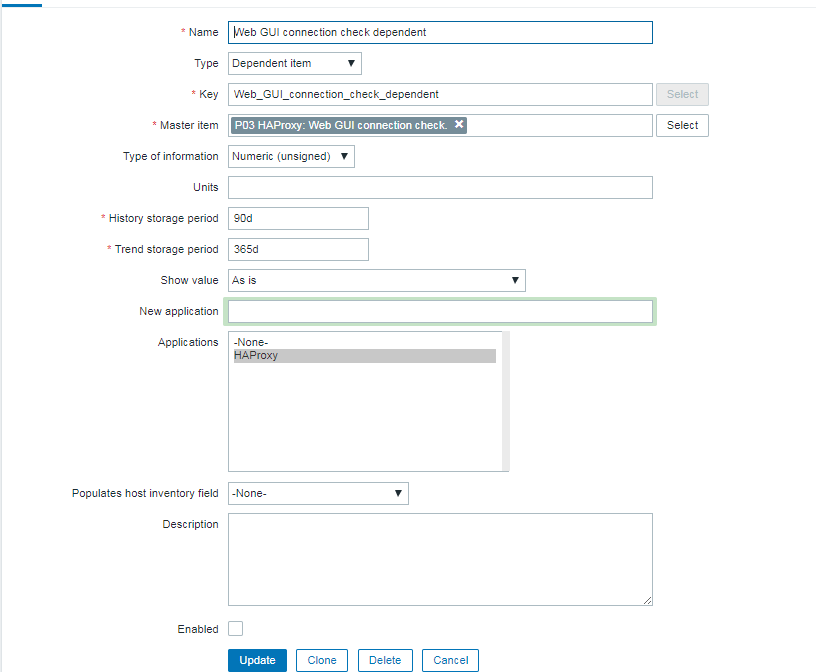
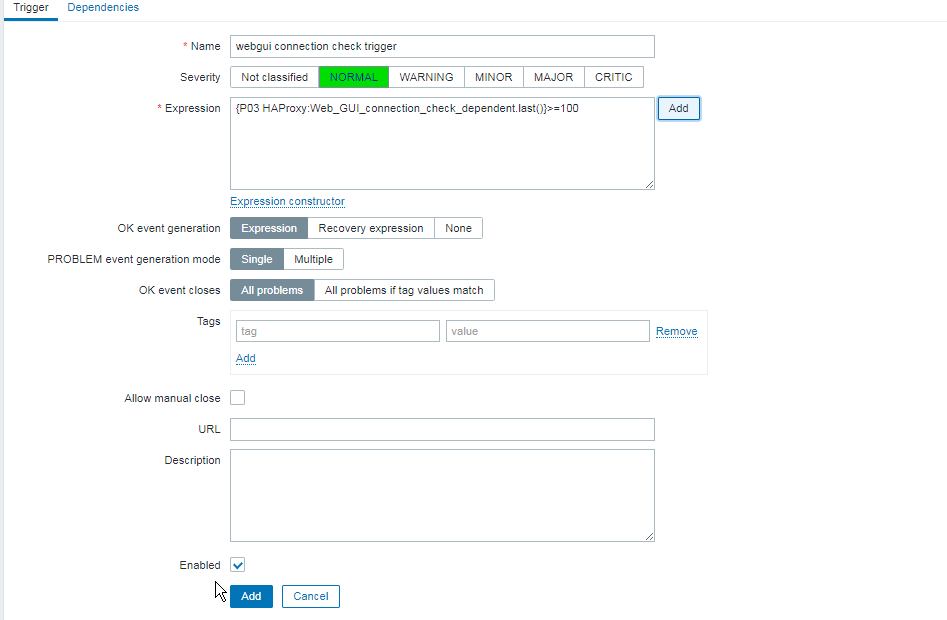
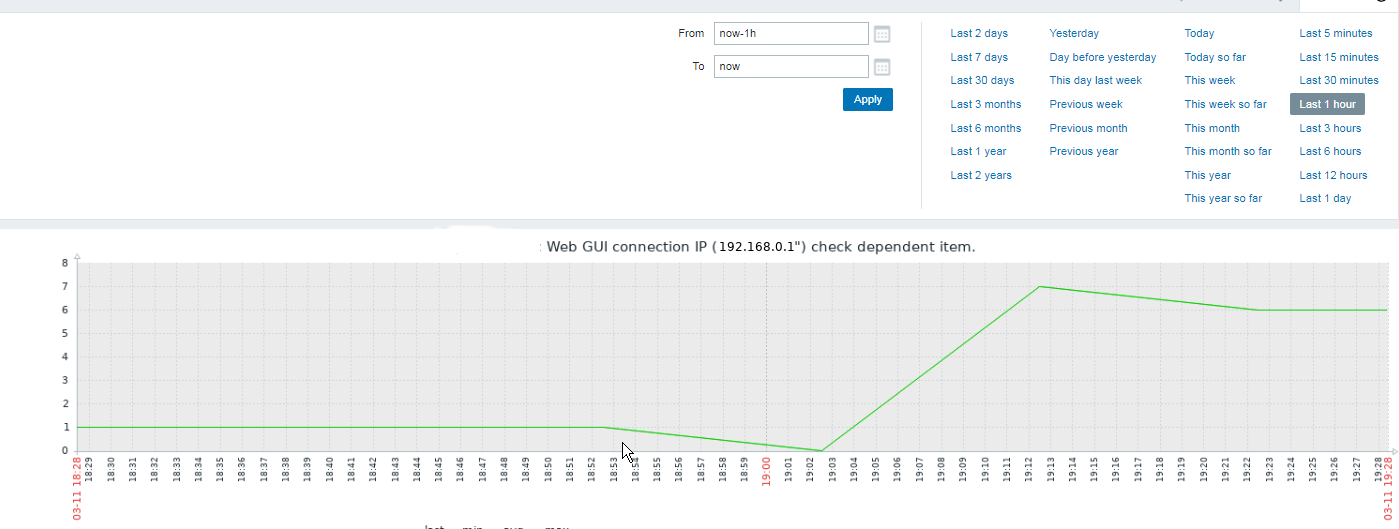
 4. Create a Zabbix trigger
4. Create a Zabbix trigger