
Having a Proxy server for Load Balancing is a common solutions to assure High Availability of Web Application service behind a proxy.
You can have for example 1 Apache HTTPD webservers serving traffic Actively on one Location (i.e. one city or Country) and 3 configured in the F5 LB or haproxy to silently keep up and wait for incoming connections as an (Active Failure) Backup solution.
Lets say the Webservers usually are set to have local class C IPs as 192.168.0.XXX or 10.10.10.XXX and living in isolated DMZed well firewalled LAN network and Haproxy is configured to receive traffic via a Internet IP 109.104.212.13 address and send the traffic in mode tcp via a NATTed connection (e.g. due to the network address translation the source IP of the incoming connections from Intenet clients appears as the NATTed IP 192.168.1.50.
The result is that all incoming connections from haproxy -> webservers will be logged in Webservers /var/log/apache2/access.log wrongly as incoming from source IP: 192.168.1.50, meaning all the information on the source Internet Real IP gets lost.
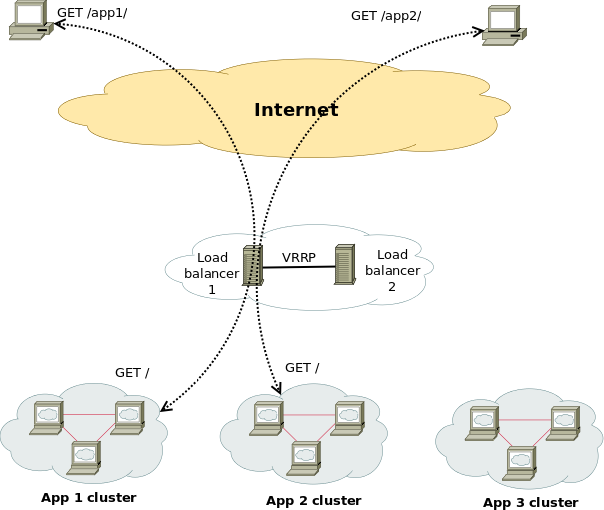
How to pass Real (Internet) Source IPs from Haproxy "mode tcp" to Local LAN Webservers ?
Usually the normal way to work around this with Apache Reverse Proxies configured is to use HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR variable in haproxy when using HTTP traffic application that is proxied (.e.g haproxy.cfg has mode http configured), you have to add to listen listener_name directive or frontend Frontend_of_proxy
option forwardfor
option http-server-close
However unfortunately, IP Header preservation with X_FORWADED_FOR HTTP-Header is not possible when haproxy is configured to forward traffic using mode tcp.
Thus when you're forced to use mode tcp to completely pass any traffic incoming to Haproxy from itself to End side, the solution is to
- Use mod_remoteip infamous module that is part of standard Apache installs both on apache2 installed from (.deb) package or httpd rpm (on redhats / centos).
1. Configure Haproxies to send received connects as send-proxy traffic
The idea is very simple all the received requests from outside clients to Haproxy are to be send via the haproxy to the webserver in a PROXY protocol string, this is done via send-proxy
send-proxy – send a PROXY protocol string
Rawly my current /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg looks like this:
global
log /dev/log local0
log /dev/log local1 notice
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
maxconn 99999
nbproc 1
nbthread 2
cpu-map 1 0
cpu-map 2 1
defaults
log global
mode tcp
timeout connect 5000
timeout connect 30s
timeout server 10stimeout queue 5s
timeout tunnel 2m
timeout client-fin 1s
timeout server-fin 1soption forwardfor
retries 15
frontend http-in
mode tcpoption tcplog
log globaloption logasap
option forwardfor
bind 109.104.212.130:80
fullconn 20000
default_backend http-websrv
backend http-websrv
balance source
maxconn 3000stick match src
stick-table type ip size 200k expire 30m
stick on src
server ha1server-1 192.168.0.205:80 check send-proxy weight 254 backup
server ha1server-2 192.168.1.15:80 check send-proxy weight 255
server ha1server-3 192.168.2.30:80 check send-proxy weight 252 backup
server ha1server-4 192.168.1.198:80 check send-proxy weight 253 backup
server ha1server-5 192.168.0.1:80 maxconn 3000 check send-proxy weight 251 backup
frontend https-in
mode tcpoption tcplog
log globaloption logasap
option forwardfor
maxconn 99999
bind 109.104.212.130:443
default_backend https-websrv
backend https-websrv
balance source
maxconn 3000
stick on src
stick-table type ip size 200k expire 30m
server ha1server-1 192.168.0.205:443 maxconn 8000 check send-proxy weight 254 backup
server ha1server-2 192.168.1.15:443 maxconn 10000 check send-proxy weight 255
server ha1server-3 192.168.2.30:443 maxconn 8000 check send-proxy weight 252 backup
server ha1server-4 192.168.1.198:443 maxconn 10000 check send-proxy weight 253 backup
server ha1server-5 192.168.0.1:443 maxconn 3000 check send-proxy weight 251 backuplisten stats
mode http
option httplog
option http-server-close
maxconn 10
stats enable
stats show-legends
stats refresh 5s
stats realm Haproxy\ Statistics
stats admin if TRUE
After preparing your haproxy.cfg and reloading haproxy in /var/log/haproxy.log you should have the Real Source IPs logged in:
root@webserver:~# tail -n 10 /var/log/haproxy.log
Apr 15 22:47:34 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 159.223.65.16:58735 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:34.586] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 7/7/7/7/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:34 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 20.113.133.8:56405 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:34.744] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 7/7/7/7/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:35 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 54.36.148.248:15653 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:35.057] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 7/7/7/7/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:35 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 185.191.171.35:26564 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:35.071] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 8/8/8/8/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:35 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 213.183.53.58:42984 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:35.669] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 6/6/6/6/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:35 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 159.223.65.16:54006 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:35.703] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 7/7/7/7/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:36 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 192.241.113.203:30877 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:36.651] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 4/4/4/4/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:36 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 185.191.171.9:6776 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:36.683] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 5/5/5/5/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:36 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 159.223.65.16:64310 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:36.797] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/0/+0 +0 — 6/6/6/6/0 0/0
Apr 15 22:47:36 pcfr_hware_local_ip haproxy[2914]: 185.191.171.3:23364 [15/Apr/2022:22:47:36.834] https-in https-websrv/ha1server-2 1/1/+1 +0 — 7/7/7/7/0 0/0
2. Enable remoteip proxy protocol on Webservers
Login to each Apache HTTPD and to enable remoteip module run:
# a2enmod remoteip
On Debians, the command should produce a right symlink to mods-enabled/ directory
# ls -al /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/*remote*
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 31 Mar 30 2021 /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/remoteip.load -> ../mods-available/remoteip.load
3. Modify remoteip.conf file and allow IPs of haproxies or F5s
Configure RemoteIPTrustedProxy for every Source IP of haproxy to allow it to send X-Forwarded-For header to Apache,
Here are few examples, from my apache working config on Debian 11.2 (Bullseye):
webserver:~# cat remoteip.conf
RemoteIPHeader X-Forwarded-For
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.0.1
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.0.205
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.1.15
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.0.198
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.2.33
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.2.30
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.0.215
#RemoteIPTrustedProxy 51.89.232.41
On RedHat / Fedora other RPM based Linux distrubutions, you can do the same by including inside httpd.conf or virtualhost configuration something like:
<IfModule remoteip_module>
RemoteIPHeader X-Forwarded-For
RemoteIPInternalProxy 192.168.0.0/16
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 192.168.0.215/32
</IfModule>
4. Enable RemoteIP Proxy Protocol in apache2.conf / httpd.conf or Virtualhost custom config
Modify both haproxy / haproxies config as well as enable the RemoteIP module on Apache webservers (VirtualHosts if such used) and either in <VirtualHost> block or in main http config include:
RemoteIPProxyProtocol On
5. Change default configured Apache LogFormat
In Domain Vhost or apache2.conf / httpd.conf
Default logging Format will be something like:
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
or
LogFormat "%v:%p %h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
Once you find it in /etc/apache2/apache2.conf / httpd.conf or Vhost, you have to comment out this by adding shebang infont of sentence make it look as follows:
LogFormat "%v:%p %a %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" vhost_combined
LogFormat "%a %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%a %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O" common
LogFormat "%{Referer}i -> %U" referer
LogFormat "%{User-agent}i" agent
The Changed LogFormat instructs Apache to log the client IP as recorded by mod_remoteip (%a) rather than hostname (%h). For a full explanation of all the options check the official HTTP Server documentation page apache_mod_config on Custom Log Formats.
and reload each Apache server.
on Debian:
# apache2ctl -k reload
On CentOS
# systemctl restart httpd
6. Check proxy protocol is properly enabled on Apaches
remoteip module will enable Apache to expect a proxy connect header passed to it otherwise it will respond with Bad Request, because it will detect a plain HTML request instead of Proxy Protocol CONNECT, here is the usual telnet test to fetch the index.htm page.
root@webserver:~# telnet localhost 80
Trying 127.0.0.1…
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
GET / HTTP/1.1HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Date: Fri, 15 Apr 2022 19:04:51 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.51 (Debian)
Content-Length: 312
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>400 Bad Request</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Bad Request</h1>
<p>Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand.<br />
</p>
<hr>
<address>Apache/2.4.51 (Debian) Server at grafana.pc-freak.net Port 80</address>
</body></html>
Connection closed by foreign host.
root@webserver:~# telnet localhost 80
Trying 127.0.0.1…
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
HEAD / HTTP/1.1HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Date: Fri, 15 Apr 2022 19:05:07 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.51 (Debian)
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1Connection closed by foreign host.
To test it with telnet you can follow the Proxy CONNECT syntax and simulate you're connecting from a proxy server, like that:
root@webserver:~# telnet localhost 80
Trying 127.0.0.1…
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
CONNECT localhost:80 HTTP/1.0HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Date: Fri, 15 Apr 2022 19:13:38 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.51 (Debian)
Location: https://zabbix.pc-freak.net
Cache-Control: max-age=900
Expires: Fri, 15 Apr 2022 19:28:38 GMT
Content-Length: 310
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>301 Moved Permanently</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Moved Permanently</h1>
<p>The document has moved <a href="https://zabbix.pc-freak.net">here</a>.</p>
<hr>
<address>Apache/2.4.51 (Debian) Server at localhost Port 80</address>
</body></html>
Connection closed by foreign host.
You can test with curl simulating the proxy protocol CONNECT with:
root@webserver:~# curl –insecure –haproxy-protocol https://192.168.2.30
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta name="generator" content="pc-freak.net tidy">
<script src="https://ssl.google-analytics.com/urchin.js" type="text/javascript">
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
_uacct = "UA-2102595-3";
urchinTracker();
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var gaJsHost = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ? "https://ssl." : "http://");
document.write(unescape("%3Cscript src='" + gaJsHost + "google-analytics.com/ga.js' type='text/javascript'%3E%3C/script%3E"));
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
try {
var pageTracker = _gat._getTracker("UA-2102595-6");
pageTracker._trackPageview();
} catch(err) {}
</script>
–haproxy-protocol
(HTTP) Send a HAProxy PROXY protocol v1 header at the beginning of the connection. This is used by some load balancers and reverse proxies
to indicate the client's true IP address and port.This option is primarily useful when sending test requests to a service that expects this header.
Added in 7.60.0.
7. Check apache log if remote Real Internet Source IPs are properly logged
root@webserver:~# tail -n 10 /var/log/apache2/access.log
213.183.53.58 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:18:59 +0300] "GET /proxy/browse.php?u=https%3A%2F%2Fsteamcommunity.com%2Fmarket%2Fitemordershistogram%3Fcountry HTTP/1.1" 200 12701 "https://www.pc-freak.net" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:98.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/98.0"
88.198.48.184 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:18:58 +0300] "GET /blog/iq-world-rank-country-smartest-nations/?cid=1330192 HTTP/1.1" 200 29574 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; DataForSeoBot/1.0; +https://dataforseo.com/dataforseo-bot)"
213.183.53.58 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:00 +0300] "GET /proxy/browse.php?u=https%3A%2F%2Fsteamcommunity.com%2Fmarket%2Fitemordershistogram%3Fcountry
HTTP/1.1" 200 9080 "https://www.pc-freak.net" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:98.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/98.0"
159.223.65.16 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:01 +0300] "POST //blog//xmlrpc.php HTTP/1.1" 200 5477 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/89.0.4389.114 Safari/537.36"
159.223.65.16 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:02 +0300] "POST //blog//xmlrpc.php HTTP/1.1" 200 5477 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/89.0.4389.114 Safari/537.36"
213.91.190.233 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:02 +0300] "POST /blog/wp-admin/admin-ajax.php HTTP/1.1" 200 1243 "https://www.pc-freak.net/blog/wp-admin/post.php?post=16754&action=edit" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:89.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/89.0"
46.10.215.119 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:02 +0300] "GET /images/saint-Paul-and-Peter-holy-icon.jpg HTTP/1.1" 200 134501 "https://www.google.com/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/100.0.4896.75 Safari/537.36 Edg/100.0.1185.39"
185.191.171.42 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:03 +0300] "GET /index.html.latest/tutorials/tutorials/penguins/vestnik/penguins/faith/vestnik/ HTTP/1.1" 200 11684 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; SemrushBot/7~bl; +http://www.semrush.com/bot.html)"116.179.37.243 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:50 +0300] "GET /blog/wp-content/cookieconsent.min.js HTTP/1.1" 200 7625 "https://www.pc-freak.net/blog/how-to-disable-nginx-static-requests-access-log-logging/" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Baiduspider-render/2.0; +http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.html)"
116.179.37.237 – – [15/Apr/2022:22:19:50 +0300] "GET /blog/wp-content/plugins/google-analytics-dashboard-for-wp/assets/js/frontend-gtag.min.js?ver=7.5.0 HTTP/1.1" 200 8898 "https://www.pc-freak.net/blog/how-to-disable-nginx-static-requests-access-log-logging/" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Baiduspider-render/2.0; +http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.html)"
You see from above output remote Source IPs in green are properly logged, so haproxy Cluster is correctly forwarding connections passing on in the Haproxy generated Initial header the Real IP of its remote connect IPs.
Sum it up, What was done?
HTTP_X_FORWARD_FOR is impossible to set, when haproxy is used on mode tcp and all traffic is sent as received from TCP IPv4 / IPv6 Network stack, e.g. modifying any HTTP sent traffic inside the headers is not possible as this might break up the data.
Thus Haproxy was configured to send all its received data by sending initial proxy header with the X_FORWARDED usual Source IP data, then remoteip Apache module was used to make Apache receive and understand haproxy sent Header which contains the original Source IP via the send-proxy functionality and example was given on how to test the remoteip on Webserver is working correctly.
Finally you've seen how to check configured haproxy and webserver are able to send and receive the End Client data with the originator real source IP correctly and those Internet IP is properly logged inside both haproxy and apaches.












Linux: Howto Disable logging for all VirtualHosts on Apache and NGINX Webservers one liner
Wednesday, July 1st, 2020Did you happen to administer Apache Webservers or NGINX webservers whose logs start to grow so rapidly that are flooding the disk too quickly?
Well this happens sometimes and it also happens that sometimes you just want to stop logging especially, to offload disk writting.
There is an easy way to disable logging for requests and errors (access_log and error_log usually residing under /var/log/httpd or /var/log/nginx ) for all configured Virtual Domains with a short one liner, here is how.
Before you start Create backup of /etc/apache2/sites-enabled / or /etc/nginx to be able to revert back to original config.
1. Disable Logging for All Virtual Domains configured for Apache Webserver
First lets print what the command will do to make sure we don't mess something
You will get some output like
2. Disable Logging for All configured Virtual Domains for NGINX Webserver
f course above substituations that will comment out with '#' occurances from file configs of only default set access_log and error_log / access.log, error.log
for machines where there is no certain convention on file naming and there are multiple domains in custom produced named log files this won't work.
This one liner was inspired from a friend's daily Martin Petrov. Martin blogged initially about this nice tip for those reading Cyrillic check out mpetrov.net, so. Thanks Marto ! 🙂
Tags: about, access, ALL, and, apache, apache webserver, apache webservers, apache2, are, BACK, blogged, check, command, Comment, config, configured, convention, course, create, custom
Posted in Everyday Life, Nginx, Web and CMS | No Comments »