
Nmap (Network Mapper) is one of the most essential tools for checking server security. As a penetration testing instrument it is both used by SysAdmins / Crackers and Security Specialists. Its perfect too to make periodic port audits and determine how good is configured server firewall or even in time of building one. Often with time Firewall rules grow bigger and bigger and as a consequence there is a risk of loopholes in FW rules, nmap routine host checks (i.e. run as a cronjob and logging port status on server is IMHO a good preventive measure).
I first get introduced to Nmap in the early days of my careers as IT Geek and System Administrator around year 2000. Back then Computer Security and hacking culture was a common thing across IT geeks and ppl hanging in IRC 😉 This article will not say much of news for those accustomed to Nmap, but hope interesting for people newly introduced to Computer Security it will be of use.
1. Checking host status with Nmap (Is remote scanned host up).
There is plenty of ways to check, whether remote host is reachable, ping is classics, but not always relevant as many network admins decide to filter ping for security reasons. Of course one can do manual try outs with telnet on common Services Ports (Apache, Mail, Squid, MySQL etc. / 80,25,8080, 3306), or even write on own prog to do so but its worthless as Nmap is already there with options for this and its report in about 90% of cases is relevant:
To check whether host is up with Nmap:
pcfreak:~# nmap -sP google.com
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 11:58 EEST
Nmap scan report for google.com (173.194.39.227)
Host is up (0.013s latency).
Other addresses for google.com (not scanned): 173.194.39.238 173.194.39.231 173.194.39.226 173.194.39.232 173.194.39.230 173.194.39.233 173.194.39.228 173.194.39.225 173.194.39.229 173.194.39.224
rDNS record for 173.194.39.227: sof01s02-in-f3.1e100.net
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.74 seconds
2. Port map with Quick remote host (connect) scan
Most classical way of scanning, since the early days of computing is to attempt connecting to remote host ports opening connection via creating new TCP or UDP protocol socket with C's connect(); function. Hence nmap's "default" way of scanning is like so. Anyways it doesn't scan all possible 65534 ports, when run with no extra arguments, but instead scans only those more popular widespread used.
noah:~# nmap -sT www.pc-freak.net
Starting Nmap 5.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 15:05 EEST
Stats: 0:00:01 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 2.00% done; ETC: 15:07 (0:01:38 remaining)
Stats: 0:00:02 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 24.40% done; ETC: 15:05 (0:00:09 remaining)
Stats: 0:00:03 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 77.25% done; ETC: 15:05 (0:00:01 remaining)
Interesting ports on www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76):
Not shown: 985 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open smtps
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
8022/tcp open unknown
9001/tcp open tor-orport
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 4.69 seconds
During scan, pressing Enter, prints on screen statistics on how many percentage of scan is completed. In older Nmap, releases this was not so, it is very convenient stuff, as some host scans (with specific firewalls), can have anti port scan rules making the scan time ultra luggish. If this is the case nmap can be run in different scan mode, I'm gonna say few words on that later.
3. Nmap – Scanning only selected ports of interest and port range
a) Scanning only desired ports
Whether scanning a complete range of IPs from C or B class network, it is handy to only scan only ports of interests for example (Apache, SMTP, POP3, IMAP etc.).
Here is how to scan those 4;
noah:~# nmap -sT www.pc-freak.net -p 80,25,110,143
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 15:49 EEST
Stats: 0:00:00 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (0 up), 1 undergoing Ping Scan
Ping Scan Timing: About 100.00% done; ETC: 15:49 (0:00:00 remaining)
Stats: 0:00:00 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 100.00% done; ETC: 15:49 (0:00:00 remaining)
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.20s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
25/tcp open smtp
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.00 seconds
List of all common network services with port number is located in /etc/services
b) Scanning a port range
By default nmap does not scan all the ports in the low ports range 1-1024. This port range according to RFC standards are reserved for standard more often and high priority network services. Default's nmap scan does not scan all of the 1-1024 ports and sometimes, some people prefer to run services in non-standard port numbers on some obscure ports in those port range. It is common that some "hacked (cracked is proper word here)", have secretly install Connect Shell or Connect back shell services running in those port range. Thus scanning those port range on administrated servers (especially whether there is suspicion for intrusion).
noah:~# nmap -sT www.pc-freak.net -p 1-1024
Starting Nmap 5.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 15:47 EEST
Stats: 0:00:04 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 77.44% done; ETC: 15:47 (0:00:01 remaining)
Stats: 0:00:04 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 84.86% done; ETC: 15:47 (0:00:01 remaining)
Interesting ports on www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76):
Not shown: 1011 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open smtps
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
4. Scanning all possible ports to make complete node port audit
As I said prior, if no extra port arguments nmap scans only number of pre-selected high use ports. However it is always nice to run complete port scan. Doing complete port scan on host, can reveal unusual open ports for cracker backdoors or ports or whether on Windows (ports open by Viruses and Trojans). As the complete number of possible remote ports to attempt to connect to is (65536), such a scan is much slower and sometimes can take literally "ages". To scan all ports on my home router in a local 100 M/Bit network with my notebook it takes about 23 minutes. On remote hosts it can take from 30 / 40 minutes to many hours – depending on firewall type on remote scanned host. Also by scanning all ports, there is risk remote host add you to its FW reject rules, whether its running some kind of automated software for Intrusion Detection (IDS) like Snort or AIDE.
To run complete port scan with nmap;
noah:~# nmap -sT www.pc-freak.net -p 0-65535
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 22:28 EEST
Stats: 0:00:01 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 0.03% done
Stats: 0:00:01 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 0.05% done
Stats: 0:06:35 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 31.23% done; ETC: 22:50 (0:14:28 remaining)
Stats: 0:06:35 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 31.24% done; ETC: 22:50 (0:14:27 remaining)
Stats: 0:08:21 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 37.41% done; ETC: 22:51 (0:13:57 remaining)
Stats: 0:08:21 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 37.43% done; ETC: 22:51 (0:13:56 remaining)
Stats: 0:08:21 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 37.46% done; ETC: 22:51 (0:13:56 remaining)
Stats: 0:08:22 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 37.50% done; ETC: 22:51 (0:13:55 remaining)
Stats: 0:08:22 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 37.53% done; ETC: 22:51 (0:13:56 remaining)
Stats: 0:08:28 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 37.96% done; ETC: 22:51 (0:13:50 remaining)
Stats: 0:11:55 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 53.22% done; ETC: 22:51 (0:10:28 remaining)
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.0023s latency).
Not shown: 65518 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open smtps
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
2060/tcp open unknown
2070/tcp open ah-esp-encap
2207/tcp closed unknown
8022/tcp open oa-system
9001/tcp open tor-orport
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1367.73 seconds
5. Scanning a network range of IPs with NMAP
It is common thing to scan a network range in C class network, especially as usually we admins have to administrate a number of hosts running in a local network:
noah:~# nmap -sP '192.168.0.*'
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 22:29 EEST
Stats: 0:00:01 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (0 up), 256 undergoing Ping Scan
Ping Scan Timing: About 0.98% done
Stats: 0:00:09 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (0 up), 256 undergoing Ping Scan
Parallel DNS resolution of 256 hosts. Timing: About 0.00% done
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.16
Host is up (0.00029s latency).
Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 9.87 seconds
You can also scan class C network with:
>noah:~# nmap -sP 192.168.1.0/24
6. Obtaining network services version numbers
Nmap is capable digging version numbers of remote running application binding to port:. Option to try to guess obtain version number is -sV (Show Version).
noah:~# nmap -sV www.pc-freak.net
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 22:35 EEST
Stats: 0:00:05 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Service scan Timing: About 90.91% done; ETC: 22:37 (0:00:09 remaining)
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.0083s latency).
Not shown: 985 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp ProFTPD 1.3.3a
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 5.5p1 Debian 6+squeeze3 (protocol 2.0)
25/tcp open smtp qmail smtpd
53/tcp open domain?
80/tcp open http Apache httpd
110/tcp open pop3 qmail pop3d
143/tcp open imap Courier Imapd (released 2005)
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open ssl/smtp qmail smtpd
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open tcpwrapped
995/tcp closed pop3s
8022/tcp open http ShellInABox httpd
9001/tcp open ssl/tor-orport?
Service Info: Host: mail.www.pc-freak.net; OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at http://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 126.37 seconds
7. Checking remote server OS version
noah:~# nmap -O www.pc-freak.net
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 22:42 EEST
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.0017s latency).
Not shown: 985 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open smtps
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
8022/tcp open oa-system
9001/tcp open tor-orport
Device type: general purpose|broadband router|WAP|media device
Running (JUST GUESSING): Linux 2.6.X|2.4.X|3.X (94%), Gemtek embedded (89%), Siemens embedded (89%), Netgear embedded (88%), Western Digital embedded (88%), Comtrend embedded (88%)
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:kernel:2.6 cpe:/o:linux:kernel:2.4.20 cpe:/o:linux:kernel:3 cpe:/o:linux:kernel:2.4
Aggressive OS guesses: Linux 2.6.32 – 2.6.35 (94%), Vyatta 4.1.4 (Linux 2.6.24) (94%), Linux 2.6.32 (93%), Linux 2.6.17 – 2.6.36 (93%), Linux 2.6.19 – 2.6.35 (93%), Linux 2.6.30 (92%), Linux 2.6.35 (92%), Linux 2.4.20 (Red Hat 7.2) (92%), Linux 2.6.22 (91%), Gemtek P360 WAP or Siemens Gigaset SE515dsl wireless broadband router (89%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
OS detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at http://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 8.76 seconds
As you can see from above output OS version guess is far from adequate, as my home router is running a Debian Squeeze. However in some older Linux releases, where services return OS version nr., it reports proper.
8. Scanning silently with Nmap SYN (Stealth Scan)
As many servers run some kind of IDS logging attempts to connect to multiple ports on the host and add scanning IP to filtering CHAIN. It is generally good idea to always scan with SYN Scan. SYN scan is not a guarantee that scanning attempt will not be captured by well configured IDS, or admin snorting on network with tcpdump,trafshow or iptraf. Stealth scan is useful to prevent IDS from raising red lamps.
noah:~# nmap -sS www.pc-freak.net
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-08 22:57 EEST
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.0075s latency).
Not shown: 985 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open smtps
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
8022/tcp open oa-system
9001/tcp open tor-orport
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 7.73 seconds
9. Nmap Scan Types (Paranoid | sneaky | polite | normal | insane)
Nmap has 6 modes of scanning. Whether no Type of scan is passed on with (-T) arg. , it scans in normal mode. Paranoid and sneaky are the slowest but lest aggressive and less likely to be captured by automated firewall filtering rules soft or IDS.
Insane mode is for people, who want to scan as quickly as possible not caring about consequences. Usually whether scanning your own hosts Insane is nice as it saves you time.
Paranoid scan is ultra, slow so in general, such scan is helpful if you're going to sleep and you want to scan your concurrent company servers, without being identified. Paraonid scan, takes hours and depending on where remote scanned host is located can sometimes take maybe 12 to 24 hours.
noah:~# nmap -T0 www.pc-freak.net
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-09 00:23 EEST
Stats: 0:15:00 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing SYN Stealth Scan
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 0.05% done
Almost always -T3 or T4 is reasonable.
10. Scanning hosts in verbose mode
pcfreak:~# nmap -vv localhost
Starting Nmap 5.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-09 01:14 EEST
NSE: Loaded 0 scripts for scanning.
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 01:14
Scanning localhost (127.0.0.1) [1000 ports]
Discovered open port 21/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 111/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 53/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 993/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 143/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 110/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 3306/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 25/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 783/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 8022/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 9001/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Discovered open port 465/tcp on 127.0.0.1
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 01:14, 0.09s elapsed (1000 total ports)
Host localhost (127.0.0.1) is up (0.0000070s latency).
Scanned at 2013-06-09 01:14:27 EEST for 1s
Interesting ports on localhost (127.0.0.1):
Not shown: 986 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
111/tcp open rpcbind
143/tcp open imap
465/tcp open smtps
783/tcp open spamassassin
993/tcp open imaps
3306/tcp open mysql
8022/tcp open unknown
9001/tcp open tor-orport
Read data files from: /usr/share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.21 seconds
Raw packets sent: 1000 (44.000KB) | Rcvd: 2014 (84.616KB)
11. Nmap typical scan arguments combinations
noah:~# nmap -sS -P0 -sV www.pc-freak.net
Stats: 0:01:46 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Service Scan
Service scan Timing: About 90.91% done; ETC: 01:22 (0:00:10 remaining)
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.0063s latency).
Not shown: 985 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp ProFTPD 1.3.3a
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 5.5p1 Debian 6+squeeze3 (protocol 2.0)
25/tcp open smtp qmail smtpd
53/tcp open domain?
80/tcp open http Apache httpd
110/tcp open pop3 qmail pop3d
143/tcp open imap Courier Imapd (released 2005)
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open ssl/smtp qmail smtpd
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open tcpwrapped
995/tcp closed pop3s
8022/tcp open http ShellInABox httpd
9001/tcp open ssl/tor-orport?
Service Info: Host: mail.www.pc-freak.net; OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at http://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 106.23 seconds
12. Logging nmap output
Nmap can output logs in Plain Text (TXT) / GNMAP and XML. I prefer logging to TXT, as plain text is always better:
noah:~# nmap www.pc-freak.net -o nmap-log.txt
Starting Nmap 6.00 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2013-06-09 01:32 EEST
Stats: 0:00:01 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan
Connect Scan Timing: About 4.60% done; ETC: 01:32 (0:00:21 remaining)
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.013s latency).
Not shown: 985 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open smtps
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
3306/tcp closed mysql
8022/tcp open oa-system
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 5.23 seconds
Below is also a paste from nmap man page (Example section)
nmap -Pn -p80 -oX logs/pb-port80scan.xml -oG logs/pb-port80scan.gnmap 216.163.128.20/20
This scans 4096 IPs for any web servers (without pinging them) and saves the output in grepable and XML formats.
13. Other good Nmap scanning examples and arguments
One very useful Nmap option is;
-A – Enables OS detection and Version detection, Script scanning and Traceroute
Whether you have a list of all IPs administrated by you and you would like to scan all of them;
noah:~# nmap -iL /root/scan_ip_addresses.txt
Other useful option is -sA (This does TCP ACK Scan), it is useful way to determine if remote host is running some kind of stateful firewall. Instead of connecting to ports to check whether opened, ACKs are send.
– Fast port Scan
noah:~# nmap -F www.pc-freak.net
...
-D argument (Decoy scanning
Nmap has option for simulating port scan from multiple IPs, the so called Decoyed scanning. Using Decoys, one can hide real IP address from which Nmap scan is initiated
# nmap -n -D192.168.1.5,10.5.1.2,172.1.2.4,3.4.2.1 192.168.1.5
– Scan firewall for security weaknesses
(TCP Null Scan to full firewall to generate responce)
# nmap -sN 10.10.10.1
(TCP Fin scan to check firewall)
# nmap -sF 10.10.10.1
(TCP Xmas scan to check firewall)
# nmap -sX 10.10.10.1
– Scan UDP ports
# nmap -sU hostname
– Scan remote host using IP (ping) Protocol
noah:~# nmap -P0 www.pc-freak.net
Connect Scan Timing: About 96.20% done; ETC: 23:16 (0:00:00 remaining)
Nmap scan report for www.pc-freak.net (83.228.93.76)
Host is up (0.0099s latency).
Not shown: 985 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
20/tcp closed ftp-data
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
110/tcp open pop3
143/tcp open imap
443/tcp closed https
465/tcp open smtps
631/tcp closed ipp
993/tcp open imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
8022/tcp open oa-system
9001/tcp open tor-orport
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 4.97 seconds

















A must have collection of WordPress plugins that enpowers your blog and improves SEO
Tuesday, April 5th, 2011Since I’m using wordpress as a blogging platform for about two years now and I’m constantly experimenting with valueable wordpress plugins.
I’ve decided to publish a compilation of wordpress plugins that empowers my blog
The plugins included in the compilation are quite various, some of the plugins aims at easy post sharing via the general social networks and main websites used by users today, others significantly helps in increasing the blog ranking in major search engines, there are some that adds like button to the blog.
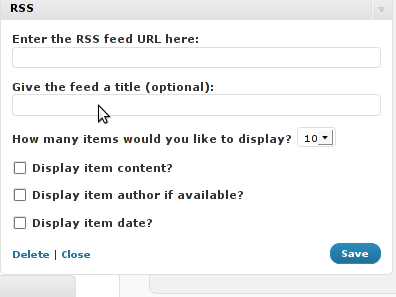
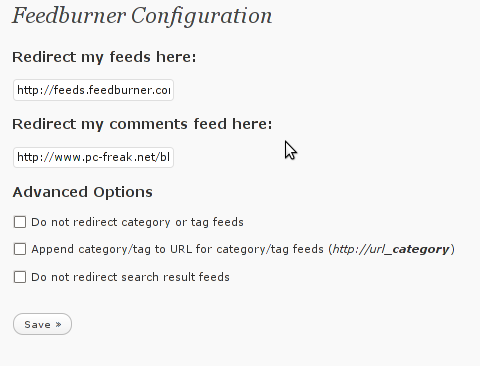
These plugins also strenghthen the easy blog RSS file sharing, some post straight to twitter all your blog posts, generate tags automatically, puts a better features to the default wordpress commenting mechanism, prevent from spam comments, add features for easily adding Google adsense to the wordpress installation to help you advertise on your blog.
There are also plugins which delete duplicate posts (if you have such), puts better wordpress blog search bar, generates a sitemap to the blog, add an option to include php codes straight into your posts, adds wordpress an option to easily put mod rewrite rules straight from the wordpress interface, boost wordpress speed by adding static html generation cache, boost performance etc. etc.
Here is the complete list of wordpress plugins which I have currently installed on my wordpress blog:
ad-squares-widgetadd-to-any-subscribe
advertising-manager
ajax-comments
akismet
all-in-one-adsense-and-ypn
all-in-one-seo-pack
askapache-google-404
auto-tag
bm-custom-login
commentluv
comments-statistics
cyr2lat-slugs
delete-duplicate-posts
easy-adsenser
extended-search-plugin
facebook-share-new
favourite-bible-verse
feedburner-plugin
feedburner-widget
feedburner_feedsmith_plugin_2.3
feedlist
force-publish-schedule
google-analytics-for-wordpress
google-sitemap-generator
headspace2
my-link-order
php-code-widget
platinum-seo-pack
post-plugin-library
post-to-twitter
profile-pic
profile-pics
redirection
rss-atom-avatar
seo-automatic-links
seo-slugs
share-on-facebook
share-this
similar-posts
simple-tags
subscribe-to-comments-reloaded
subscribe-to-comments
subscribe2
text-control
tidy-up
tinymce-advanced
what-would-seth-godin-do
wordbook
wordpress-23-related-posts-plugin
wordpress-mobile-edition
wordpress-thread-comment
wp-codebox
wp-keiths-easy-rss
wp-likes
wp-o-matic
wp-postviews
wp-super-cache
wp-syntax
yourls-wordpress-to-twitter
I do have enabled most of the plugins, though some are disabled but still might be helpful somewhere in the close-future thus I still keep them installed.
I would skip the time to describe one by one what each of the above list of plugins will do for your wordpress, since the list is quite long.
However I defnitely think this is a list of plugins you might want to have installed in a newly established wordpress blog for sure.
Note that the versions of the plugins which are included in this must have wordpress plugins collection might not be the latest as the included ones are the ones I do have installed at the time of writting of this article.
Also be aware that some of the plugins might create some issues with newer versions of wordpress (your blog might beak up!), however most of the plugins should work out of the box by just enabling each one of them from the wordpress interface via the menus:
Settings -> Plugins -> InactiveTo straight install my bundled package of plugins you have to issue the commands:
linux:~# cd /var/www/blog/wp-content/pluginslinux:/var/www/blog/wp-content/plugins# wget https://www.pc-freak.net/files/a_must_have_wordpress_plugins_collection.tar.gz
linux:/var/www/blog/wp-content/plugins# tar -zxvf a_must_have_wordpress_plugins_collection.tar.gz
...
linux:/var/www/blog/wp-content/plugins# unzip *.zip
Now as they should be installed under the plugins directory go and enable the plugins.
Further on many of the plugins will require configuration from the menus:
Settingsor in the menu
Tools
After being setup up your new wordpress installation will look significantly better, you will notice a tons of useful features which you might have previously missing and desperately needed 😉
Most of the bundled package of wordpress plugins works fine with wordpress version 3.1, if you’re trying to install enable and configure the plugins on some other versions of wordpress, there might be problems!
If you experience problems by trying out my bunch of wordpress plugins please drop me a comment.
I hope you enjoyed this improvised article, if these bunch of plugins are useful to you please give me a thanks 🙂
Thanks!
Tags: adsense, advertising manager, aims, ajax, analytics, auto tag, bible, bible verse, blog, boost, Button, collection, commentluv, compilation, complete list, configure, custom login, cyr, drop, extended search, generation, google, google sitemap generator, html generation, Inactive, installation, interface, major search engines, mechanism, mod, option, package, php, platform, plugin, post, Search, search bar, search plugin, SEO, Settingsor, Slugs, social networks, squares, time, twitter, wget, widget, wordbook, Wordpress, wordpress blog, wordpress plugins, ypn
Posted in SEO, Web and CMS, Wordpress | 8 Comments »