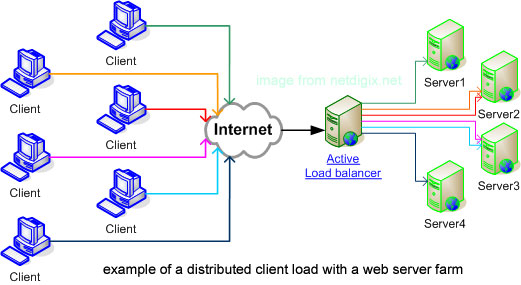
In this small article I will try to clear it up the general types of Web Server Load Balancers available. Whether one choose a Load Balancer he has the option to use a software LB or a hardware LB one there are plenty of software load balancer scripts out there. In this pos t I will mention just what choice is available in hardware load balancer interface BigIP LTM F5 standard. Generally BigIP LTM Load Balancers can be grouped in Static, Dynamic and Additional. One or more Load Balancers can be configured in front of group or farm of appplication servers. When more than one load balancer is used in front of application Load Balancer could be Active Load Balancer and Passive Load Balancer.
Below information will hopefully be useful to Web and Middleware working sys admins and anybody involved in frequent and large web systems integration.
Static Load Balancing
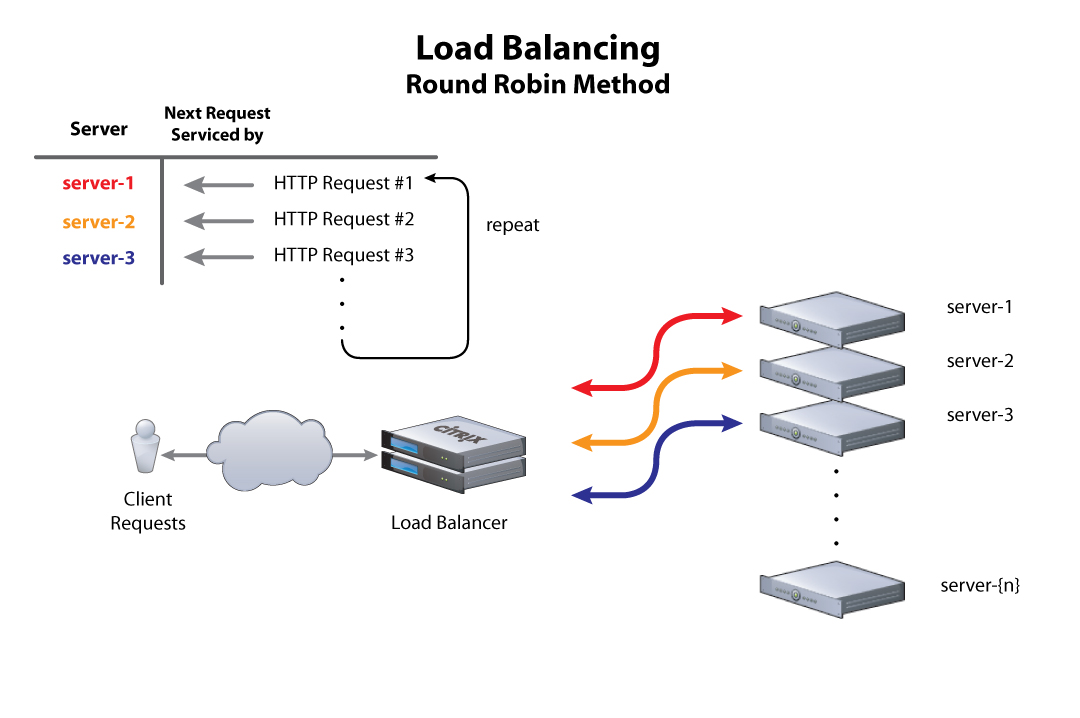
Round Robin Load Balancing
This is the default load balancing method. Round Robin mode passes each new connection request to the next server in line, eventually distributing connections evenly across the array of machines being load balanced.
Round Robin mode works well in most configurations, especially if the equipment that you are load balancing is roughly equal in processing speed and memory.
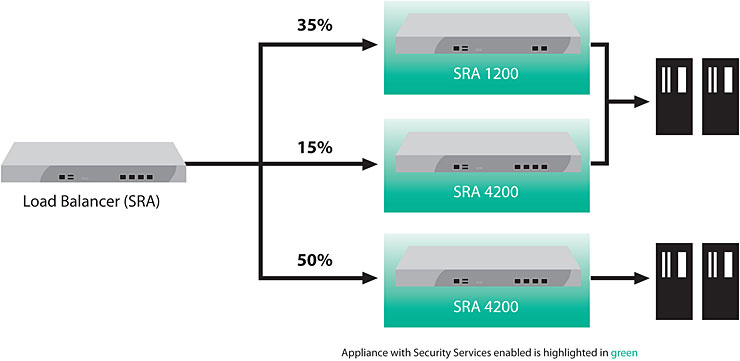
Ratio (member) / Ratio (node) Load Balancer
The Ratio (member) system distributes connections among pool members or nodes in a static rotation according to ratio weights that you define. In this case, the number of connections that each system receives over time is proportionate to the ratio weight you defined for each pool member or node. You set a ratio weight when you create each pool member or node.
These are static load balancing methods, basing distribution on user-specified ratio weights that are proportional to the capacity of the servers.
Dynamic Load Balancers
Dynamic Ratio (member) Dynamic Ratio (node) LB
The Dynamic Ratio load balancing select a server based on various aspects of real-time server performance analysis. These methods are similar to the Ratio methods, except that with Dynamic Ratio methods, the ratio weights are system-generated, and the values of the ratio weights are not static. These methods are based on continuous monitoring of the servers, and the ratio weights are therefore continually changing.
The Dynamic Ratio LBs are used specifically for load balancing traffic to RealNetworks® RealSystem® Server platforms, Windows® platforms equipped with Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), or any server equipped with an SNMP agent such as the UC Davis SNMP agent or Windows 2000 Server SNMP agent.
Fastest (node) /Fastest (application) LB
The Fastest methods select a server based on the least number of current sessions. The following rules apply to the Fastest load balancing methods:
These LB require that you assign both a Layer 7 and a TCP type of profile to the virtual server interface where LB IP is binded.
If a Layer 7 profile is not configured, the virtual server falls back to Least Connections load balancing mode.
Note: If the OneConnect feature is enabled, the Least Connections methods do not include idle connections in the calculations when selecting a pool member or node. The Least Connections balancing use only active connections in their calculations.
Fastest node load balancing is useful in environments where nodes are distributed across separate logical networks.
Least Connections (member) / Least Connections (node) LB
The Least Connections method are relatively simple in that the system passes a new connection to the pool member or node that has the least number of active connections.
Note: If the OneConnect feature is enabled, the Least Connections methods do not include idle connections in the calculations when selecting a pool member or node. The Least Connections methods use only active connections in their calculations.
The Least Connections balancing function best in environments where the servers have similar capabilities. Otherwise, some amount of latency can occur.
For example, consider the case where a pool has two servers of differing capacities, A and B. Server A has 95 active connections with a connection limit of 100, while server B has 96 active connections with a much larger connection limit of 500. In this case, the Least Connections method selects server A, the server with the lowest number of active connections, even though the server is close to reaching capacity.
If you have servers with varying capacities, consider using the Weighted Least Connections load balancing instead.
Weighted Least Connections (member) / Weighted Least Connections (node)
Like Least Connections, these load balancing methods select pool members or nodes based on the number of active connections. However, the Weighted Least Connections methods also base their selections on server capacity.
The Weighted Least Connections (member) method specifies that the system uses the value you specify in Connection Limit to establish a proportional algorithm for each pool member. The system bases the load balancing decision on that proportion and the number of current connections to that pool member. Example is member_a has 40 connections and its connection limit is 200, so it is at 20% of capacity. Similarly, member_b has 40 connections and its connection limit is 400, so it is at 10% of capacity. In this case, the system select selects member_b. This algorithm requires all pool members to have a non-zero connection limit specified.
The Weighted Least Connections (node) method specifies that the system uses the value you specify in the node's Connection Limit setting and the number of current connections to a node to establish a proportional algorithm. This algorithm requires all nodes used by pool members to have a non-zero connection limit specified.
If all servers have equal capacity, these load balancing behave in the same way as the Least Connections methods.
Note: If the OneConnect feature is enabled, the Weighted Least Connections methods do not include idle connections in the calculations when selecting a pool member or node. The Weighted Least Connections use only active connections in their calculations.
Weighted Least Connections methods work best in environments where the servers have differing capacities.
For example, if two servers have the same number of active connections but one server has more capacity than the other, the BIG-IP system calculates the percentage of capacity being used on each server and uses that percentage in its calculations.
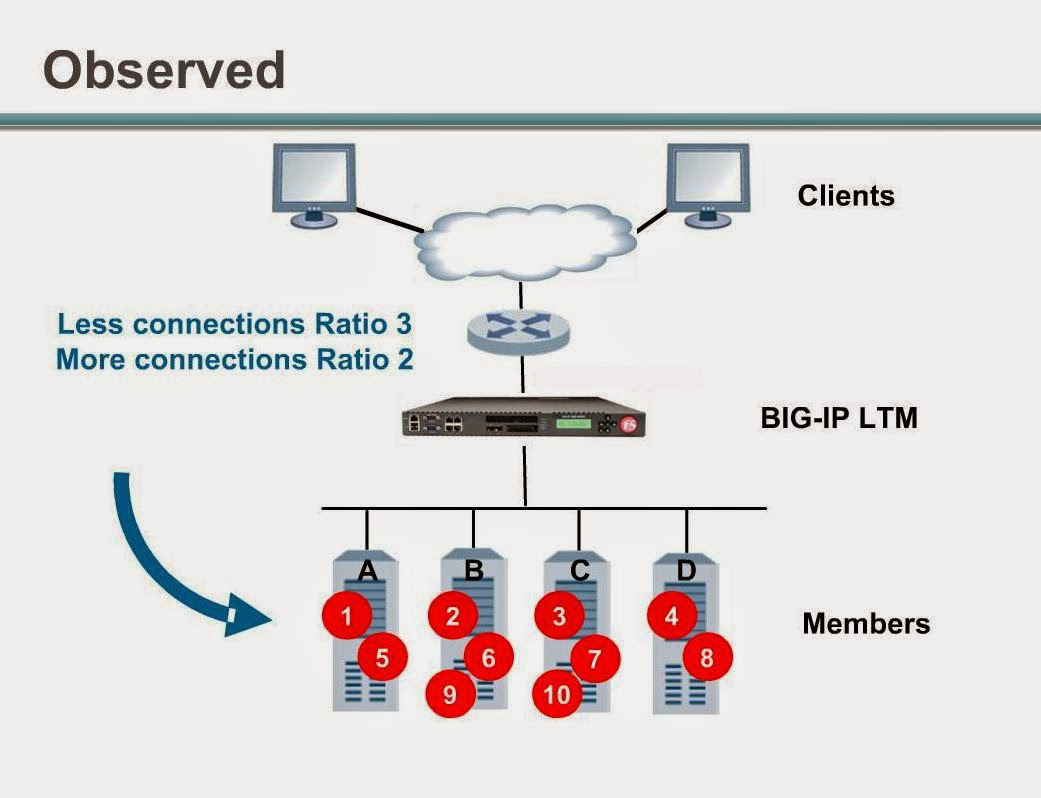
Observed (member) / Observed (node)
With the Observed methods, nodes are ranked based on the number of connections. The Observed methods track the number of Layer 4 connections to each node over time and creates a ratio for load balancing.
The need for the Observered methods is rare, and they are not recommended for large pools.
Predictive (member) / Predictive (node)
The Predictive methods use the ranking methods used by the Observed methods, where servers are rated according to the number of current connections. However, with the Predictive methods, the BIG-IP system analyzes the trend of the ranking over time, determining whether a nodes performance is currently improving or declining. The servers with performance rankings that are currently improving, rather than declining, receive a higher proportion of the connections.
The need for the Predictive methods is rare, and they are not recommend for large pools.
Least Sessions LB type
The Least Sessions method selects the server that currently has the least number of entries in the persistence table. Use of this load balancing method requires that the virtual server reference a type of profile that tracks persistence connections, such as the Source Address Affinity or Universal profile type.
Note: The Least Sessions methods are incompatible with cookie persistence.
The Least Sessions method works best in environments where the servers or other equipment that you are load balancing have similar capabilities.
L3 Address
L3 Address is same LB type as Least Connections methods.