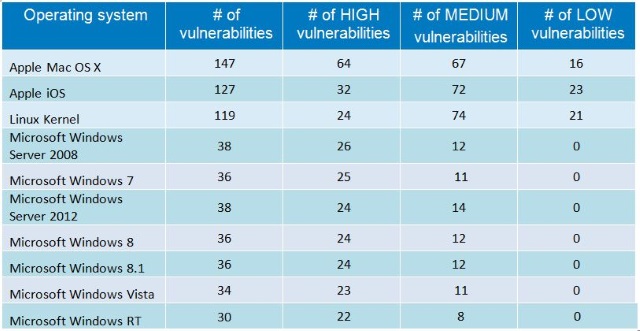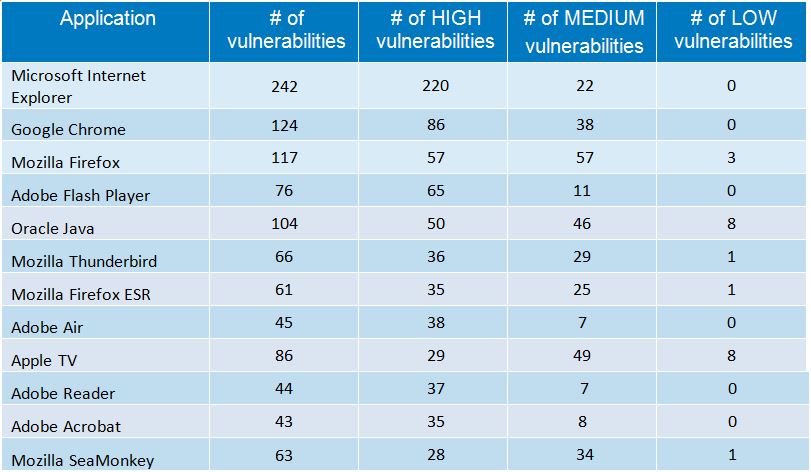
I've been given a HUAWEI Mobile Broadband E173 USB 3g model. The USB modem contains a flash USB Storage segment storing a little install program dedicated to make the modem work fine on Microsoft Windows XP / Vista / 7 and probably other M$ OSes. I'm a long time DebianGNU / Linux user and as a free software enthusiast I ofcourse wanted to be able to use Vivacom's 3G USB Modem on my Linux powered notebook.
Thanksfully as I've red on Vivacom's website the modem supports Linux OS 🙂
For those unaware in Bulgaria there are currently 3 major GSM network providers providing 3G internet this are;;;
- VIVACOM – The ex Government ran national company BTC (Bulgarian Telecommunication Company)
- M-Tel – The first GSM network provider that entered Bulgaria around year 1995
- GLOBUL – The 3rd and last GSM mobile and net provider entered last and not so much used by Bulgarians today
Until today I had no experience in running any 3G modems on Linux, neither I had used the 3 networks 3G internet to determine which one is best, however I've been given for temporal use a VIVACOM 3G internet modem today so I proceeded to try installing it on my Debian host.
My Linux system is a bit strangely configured as I use wicd network connection manager -( wicd-gtk ) to manage wireless and LAN connections instead of the standard installed GNOME network manager – available through package ( network-manager-gnome ).
The reason I use wicd is not that it is so much better than GNOME network manger but rather for historical reasons because few years past I had impression it works better in connecting me to wireless networks. Another reason why I choosed wicd back then was the nice looking stats …
I tried plugging in the Vivacom USB 3G modem stick and checked in wicd to see if I can see a possibility to connect to the mobile opeartor 3G network but unfortunately nothing appeared.
Though the 3G adsl modem was unavailable straing in wicd, checking about it in the list of attached USB devices I could see it detected, e.g.:
noah:~# lsusb |grep -i huawei
Bus 001 Device 007: ID 12d1:1c05 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
This was at least a good sign pointing me to the thoughts that the modem is probably gonna work.
I did a quick Google search to see if other people succeded running the device on a Linux host and came across a few blog posts in Bulgarian explaining a "success story" on Ubuntu Linux through using a tweakened shell script – sakis3g. For more on how the script works and script download check out Sakis3g
Here is a quote from sakis3g's website describing the script:
It automagically setups your USB or Bluetooth™ modem, and may even detect operator settings.
You should try it when anything else fails!
Sakis3g has different versions designed for for plenty of spacific hware architectures i.e. for (i386, amd64, armv4t, armv5t).
There is also a version of the script which by the way contains a combination of bash shell scripting instruction and some binary exec data.
To run sakis3g on my laptop I did:
1. Download sakis3g
My notebook architecture is 64 bit so I download and used the amd64 version of the script;;;
hipo@noah:~$ mkdir sakis3g
hipo@noah:~$ cd sakis3g
hipo@noah:~/sakis3g$ wget http://www.sakis3g.org/versions/latest/amd64/sakis3g.gz
I've made also a mirror of sakis3g i386, 64 bit and all architecture the mirrors just in case it disappears in future. The mirror versions of sakis3g are here:
a. sakis3g i386 b. sakis3g amd64 c. sakis3g all architectures source
2. Unarchive and make it executable
After downloading it as it is in gzip I had to do the usual de-gzipping and making the file executable;;;
hipo@noah:~/sakis3g$ /bin/gzip -d sakis3g.gz
hipo@noah:~/sakis3g$ chmod +x sakis3g
The script is then ready to run by either clicking twice on it or (as I prefer for debugging reasons to run it in terminal):
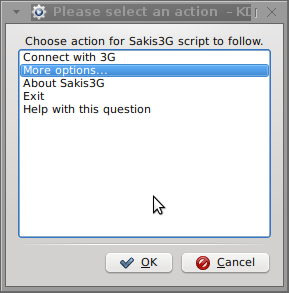
hipo@noah:~$ ./sakis3g
Something that I have wondered a bit was the dialog where I had to fill in some data of some variable APN abbreviation for – (Access Point Name)
The APN host for VIVACOM mobile internet is;;;
APN: internet.vivacom.bg
I've used the Windows configuration progrma to gather also the following data that I thought might be important for configuring the 3G adsl modem on the Linux host;;;
Auth: *99#
User: VIVACOM
pass: VIVACOM
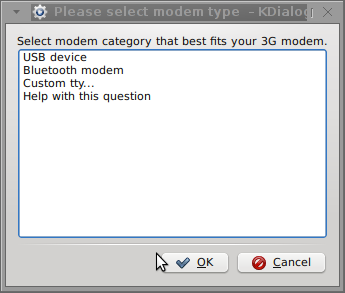
Here are all the configuration screenshots I've taken from sakis3g and all the data that I filled in.
Next the following tiny window appeared on screen:

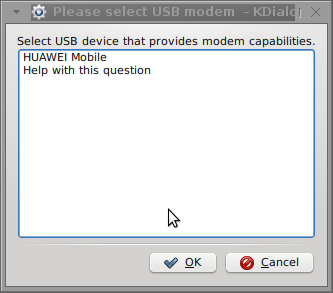
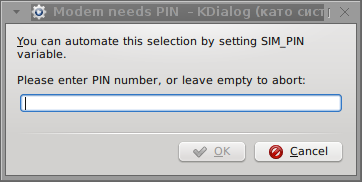
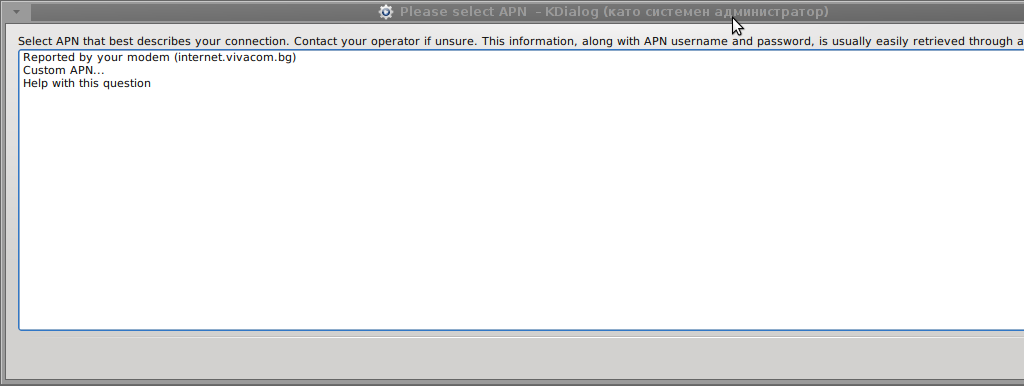
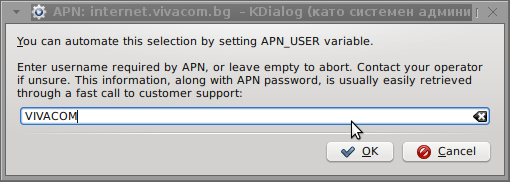
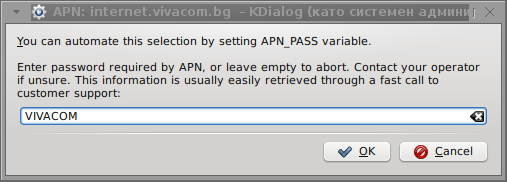
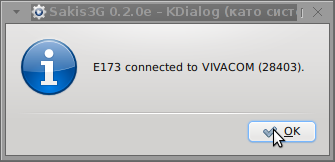
Well that's all folks, now sakis3g succesfully connected to the I_net via an (PPP) VPN connection tunnel here is data from ifconfig command showing the succesful 3G connection to VIVACOM;;;
noah:~# /sbin/ifconfig ppp0
ppp0 Link encap:Point-to-Point Protocol
inet addr:10.58.146.232 P-t-P:10.64.64.64 Mask:255.255.255.255
UP POINTOPOINT RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:2066 errors:1 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1609 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:3
RX bytes:2232058 (2.1 MiB) TX bytes:341693 (333.6 KiB)
The internet via the 3G connection is not blazing fast but good enough to check your mail or read some webpages. VIVACOM currently has different (traffic limited packages) for their 3G internet, I'm not sure which package exactly is the 3G USB stick modem but probably the "quick" internet connection that is now would slow down once the traffic limit is reached …
Hope this post helps someone to configure 3G internet on VIVACOM in Debian and Ubuntu Linux. Though I've tested sakis3g on Debian it should work with no hassles on any other GNU Linux distribution that has bash installed.