In my last article Debugging and routing network issues on Linux (common approaches), I've given some step by step methology on how to debug a network routing or unreachability issues between network hosts. As the article was mostly targetting a command line tools that can help debugging the network without much interactivity. I've decided to blog of a few other tools that might help the system administrator to debug network issues by using few a bit more interactive tools. Throughout the years of managing multitude of Linux based laptops and servers, as well as being involved in security testing and penetration in the past, these tools has always played an important role and are worthy to be well known and used by any self respecting sys admin or network security expert that has to deal with Linux and *Unix operating systems.
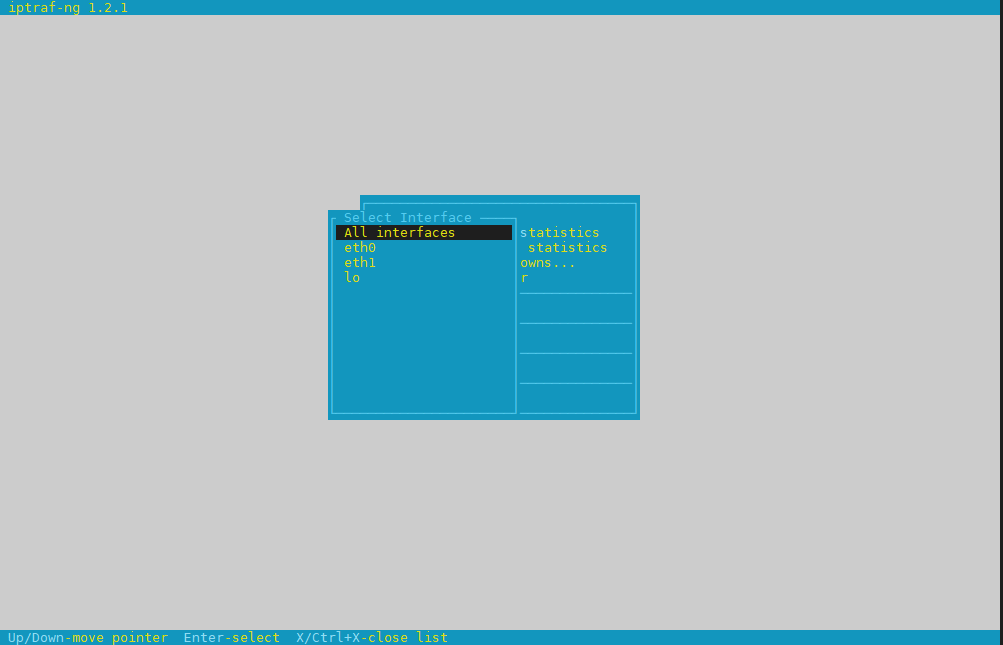
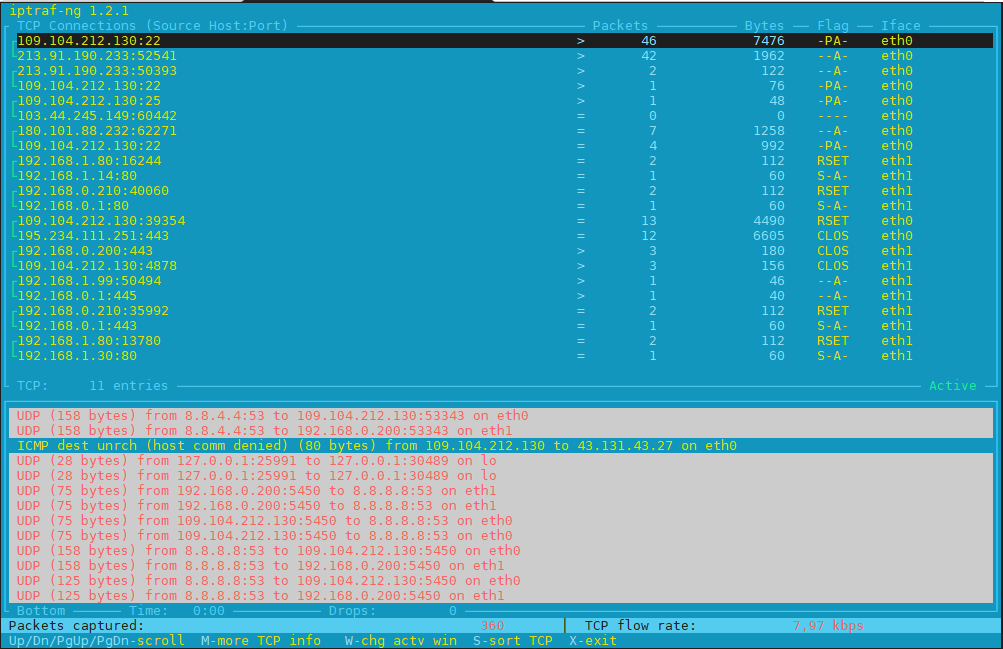
1. Debugging what is going on on a network level interactively with iptraf-ng
Historically iptraf and today's iptraf is also a great tool one can use to further aid the arsenal debug a network issue or Protocol problem, failure of packets or network interaction issues SYN -> ACK etc. proto interactions and check for Flag states and packets flow.
To use iptraf-ng which is a ncurses based tool just install it and launch it and select the interface you would like to debug trafic on.
To install On Debians distros
# apt install iptraf-ng –yes
# iptraf-ng
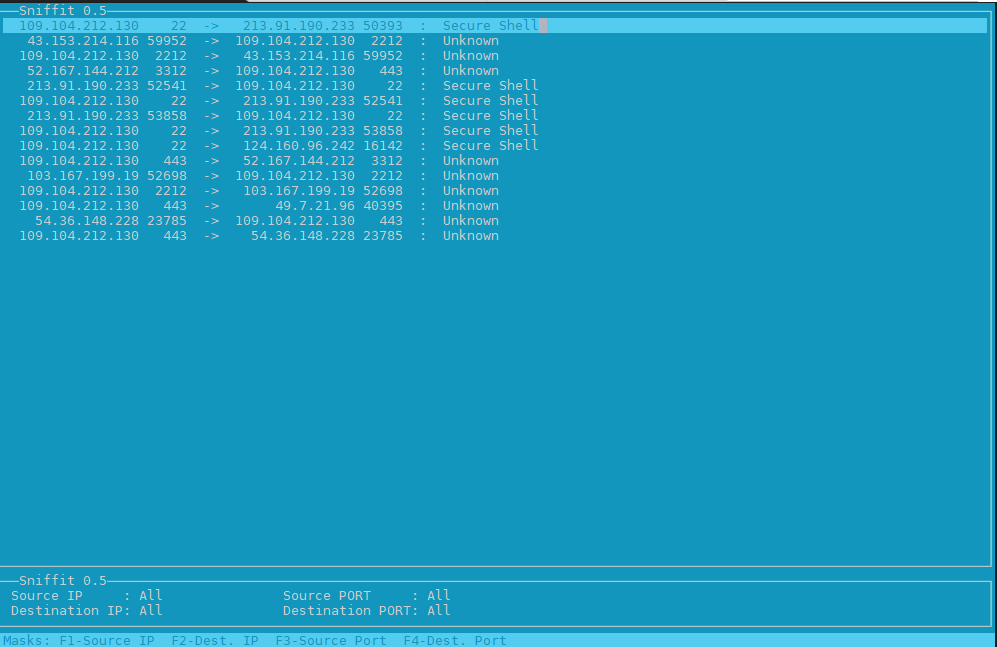
2. Use hackers old tool sniffit to monitor current ongoing traffic and read plain text messages
Those older who remember the rise of Linux to the masses, should remember sniffit was a great tool to snoop for traffic on the network.
root@pcfreak:~# apt-cache show sniffit|grep -i description -A 10 -B10
Package: sniffit
Version: 0.5-1
Installed-Size: 139
Maintainer: Joao Eriberto Mota Filho <eriberto@debian.org>
Architecture: amd64
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.14), libncurses6 (>= 6), libpcap0.8 (>= 0.9.8), libtinfo6 (>= 6)
Description-en: packet sniffer and monitoring tool
Sniffit is a packet sniffer for TCP/UDP/ICMP packets over IPv4. It is able
to give you a very detailed technical info on these packets, as SEQ, ACK,
TTL, Window, etc. The packet contents also can be viewed, in different
formats (hex or plain text, etc.).
.
Sniffit is based in libpcap and is useful when learning about computer
networks and their security.
Description-md5: 973beeeaadf4c31bef683350f1346ee9
Homepage: https://github.com/resurrecting-open-source-projects/sniffit
Tag: interface::text-mode, mail::notification, role::program, scope::utility,
uitoolkit::ncurses, use::monitor, use::scanning, works-with::mail,
works-with::network-traffic
Section: net
Priority: optional
Filename: pool/main/s/sniffit/sniffit_0.5-1_amd64.deb
Size: 61796
MD5sum: ea4cc0bc73f9e94d5a3c1ceeaa485ee1
SHA256: 7ec76b62ab508ec55c2ef0ecea952b7d1c55120b37b28fb8bc7c86645a43c485
Sniffit is not installed by default on deb distros, so to give it a try install it
# apt install sniffit –yes
# sniffit
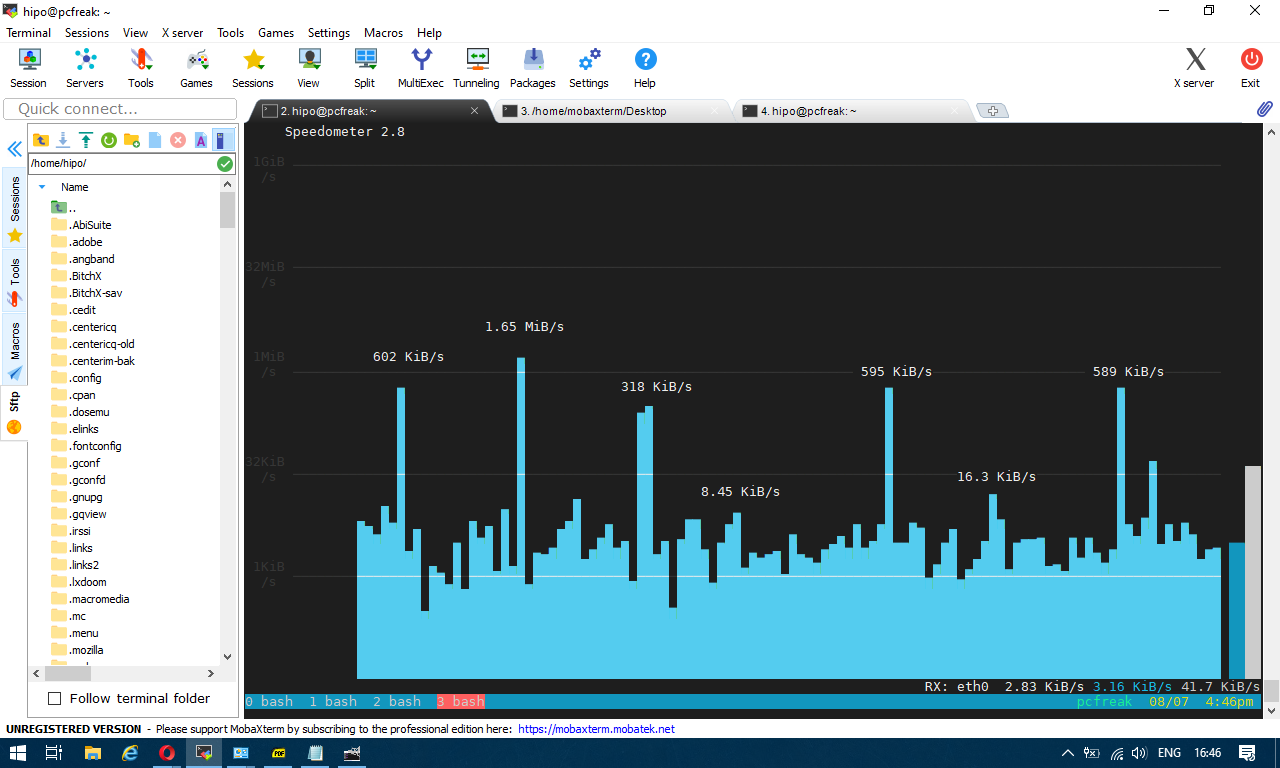
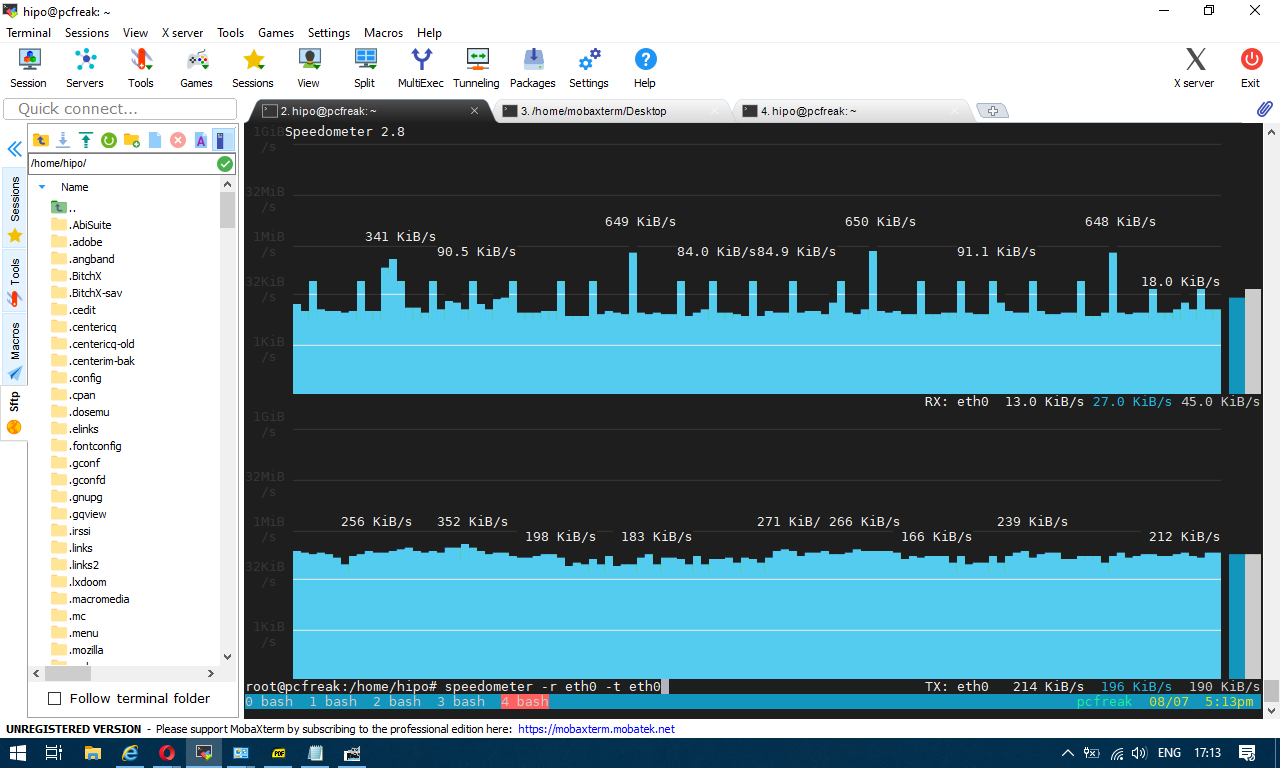
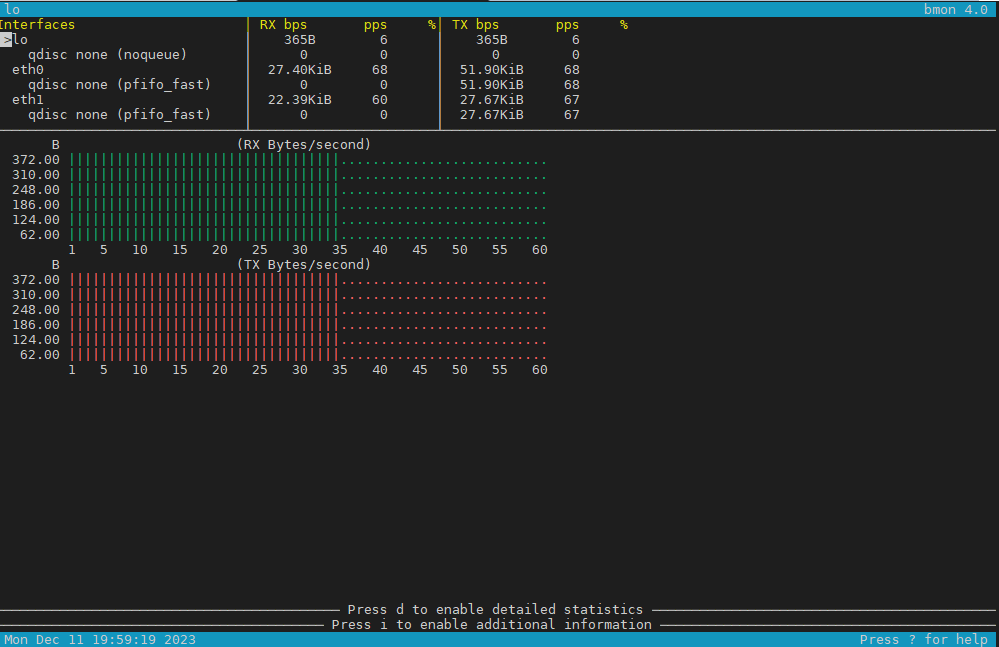
3. Use bmon to monitor bandwidth and any potential traffic losses and check qdisc pfifo
Linux network stack queues
root@pcfreak:~# apt-cache show bmon |grep -i description
Description-en: portable bandwidth monitor and rate estimator
Description-md5: 3288eb0a673978e478042369c7927d3f
root@pcfreak:~# apt-cache show bmon |grep -i description -A 10 -B10
Package: bmon
Version: 1:4.0-7
Installed-Size: 146
Maintainer: Patrick Matthäi <pmatthaei@debian.org>
Architecture: amd64
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.17), libconfuse2 (>= 3.2.1~), libncursesw6 (>= 6), libnl-3-200 (>= 3.2.7), libnl-route-3-200 (>= 3.2.7), libtinfo6 (>= 6)
Description-en: portable bandwidth monitor and rate estimator
bmon is a commandline bandwidth monitor which supports various output
methods including an interactive curses interface, lightweight HTML output but
also simple ASCII output.
.
Statistics may be distributed over a network using multicast or unicast and
collected at some point to generate a summary of statistics for a set of
nodes.
Description-md5: 3288eb0a673978e478042369c7927d3f
Homepage: http://www.infradead.org/~tgr/bmon/
Tag: implemented-in::c, interface::text-mode, network::scanner,
role::program, scope::utility, uitoolkit::ncurses, use::monitor,
works-with::network-traffic
Section: net
Priority: optional
Filename: pool/main/b/bmon/bmon_4.0-7_amd64.deb
Size: 47348
MD5sum: c210f8317eafa22d9e3a8fb8316e0901
SHA256: 21730fc62241aee827f523dd33c458f4a5a7d4a8cf0a6e9266a3e00122d80645
root@pcfreak:~# apt install bmon –yes
root@pcfreak:~# bmon
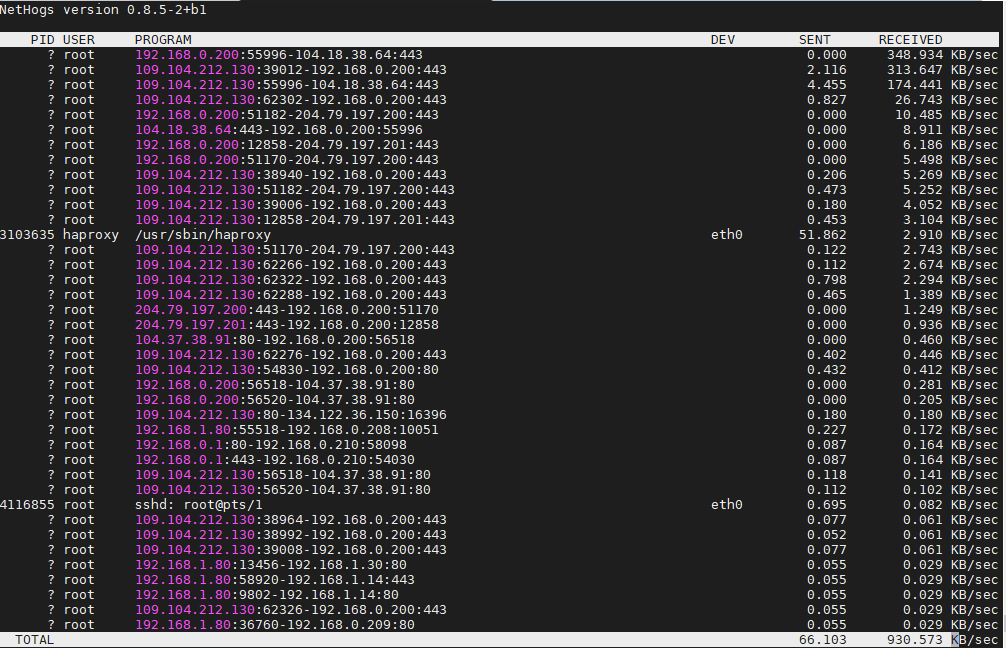
4. Use nethogs net diagnosis text interactive tool
NetHogs is a small 'net top' tool.
Instead of breaking the traffic down per protocol or per subnet, like most tools do, it groups bandwidth by process.
root@pcfreak:~# apt-cache show nethogs|grep -i description -A10 -B10
Package: nethogs
Source: nethogs (0.8.5-2)
Version: 0.8.5-2+b1
Installed-Size: 79
Maintainer: Paulo Roberto Alves de Oliveira (aka kretcheu) <kretcheu@gmail.com>
Architecture: amd64
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.15), libgcc1 (>= 1:3.0), libncurses6 (>= 6), libpcap0.8 (>= 0.9.8), libstdc++6 (>= 5.2), libtinfo6 (>= 6)
Description-en: Net top tool grouping bandwidth per process
NetHogs is a small 'net top' tool. Instead of breaking the traffic down per
protocol or per subnet, like most tools do, it groups bandwidth by process.
NetHogs does not rely on a special kernel module to be loaded.
Description-md5: 04c153c901ad7ca75e53e2ae32565ccd
Homepage: https://github.com/raboof/nethogs
Tag: admin::monitoring, implemented-in::c++, role::program,
uitoolkit::ncurses, use::monitor, works-with::network-traffic
Section: net
Priority: optional
Filename: pool/main/n/nethogs/nethogs_0.8.5-2+b1_amd64.deb
Size: 30936
MD5sum: 500047d154a1fcde5f6eacaee45148e7
SHA256: 8bc69509f6a8c689bf53925ff35a5df78cf8ad76fff176add4f1530e66eba9dc
root@pcfreak:~# apt install nethogs –yes
# nethogs
5;.Use iftop – to display network interface usage
root@pcfreak:~# apt-cache show iftop |grep -i description -A10 -B10
Package: iftop
Version: 1.0~pre4-7
Installed-Size: 97
Maintainer: Markus Koschany <apo@debian.org>
Architecture: amd64
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.29), libncurses6 (>= 6), libpcap0.8 (>= 0.9.8), libtinfo6 (>= 6)
Description-en: displays bandwidth usage information on an network interface
iftop does for network usage what top(1) does for CPU usage. It listens to
network traffic on a named interface and displays a table of current bandwidth
usage by pairs of hosts. Handy for answering the question "Why is my Internet
link so slow?".
Description-md5: f7e93593aba6acc7b5a331b49f97466f
Homepage: http://www.ex-parrot.com/~pdw/iftop/
Tag: admin::monitoring, implemented-in::c, interface::text-mode,
role::program, scope::utility, uitoolkit::ncurses, use::monitor,
works-with::network-traffic
Section: net
Priority: optional
Filename: pool/main/i/iftop/iftop_1.0~pre4-7_amd64.deb
Size: 42044
MD5sum: c9bb9c591b70753880e455f8dc416e0a
SHA256: 0366a4e54f3c65b2bbed6739ae70216b0017e2b7421b416d7c1888e1f1cb98b7
root@pcfreak:~# apt install –yes iftop
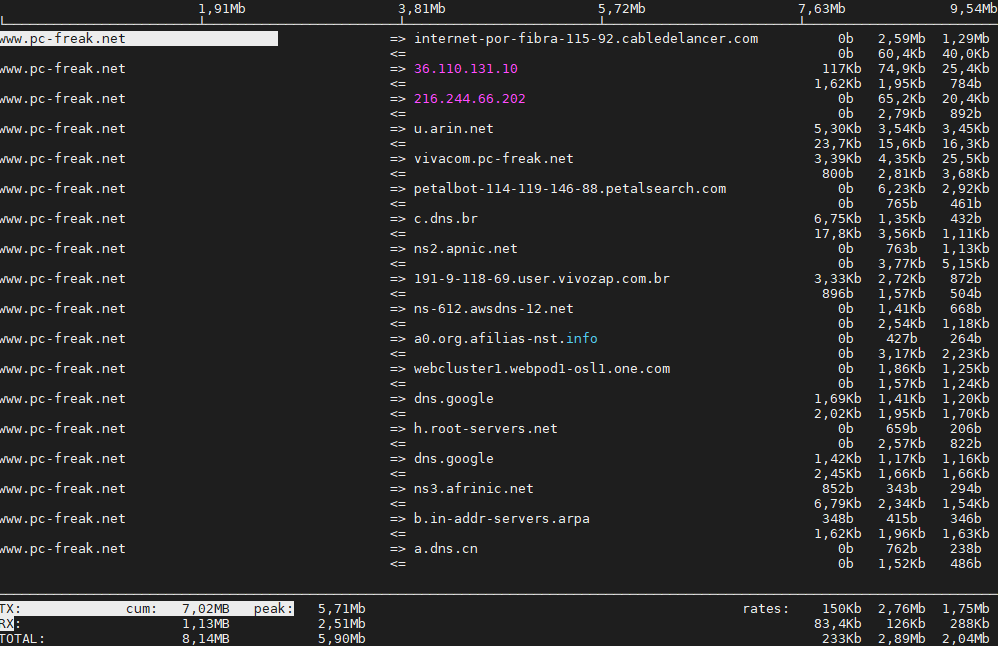
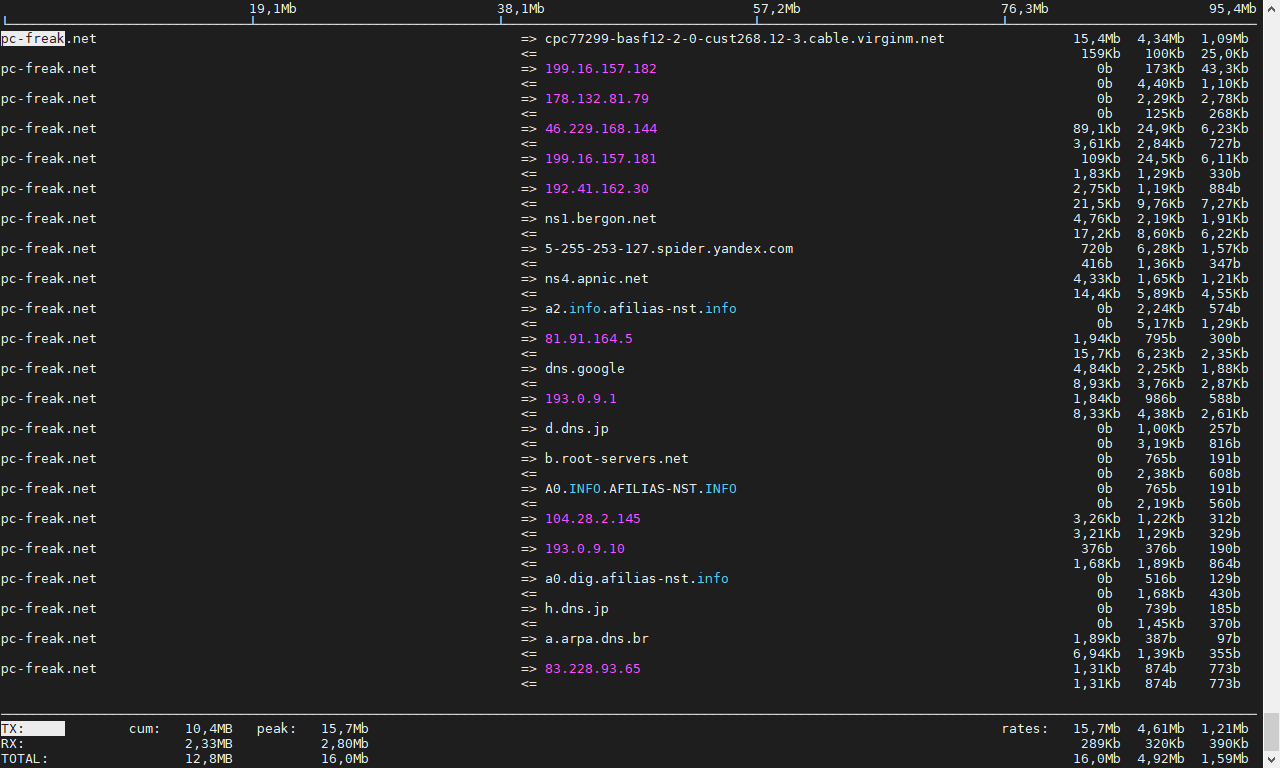
6. Ettercap (tool) to active and passive dissect network protocols for in depth network and host analysis
root@pcfreak:/var/www/images# apt-cache show ettercap-common|grep -i description -A10 -B10
Package: ettercap-common
Source: ettercap
Version: 1:0.8.3.1-3
Installed-Size: 2518
Maintainer: Debian Security Tools <team+pkg-security@tracker.debian.org>
Architecture: amd64
Depends: ethtool, geoip-database, libbsd0 (>= 0.0), libc6 (>= 2.14), libcurl4 (>= 7.16.2), libgeoip1 (>= 1.6.12), libluajit-5.1-2 (>= 2.0.4+dfsg), libnet1 (>= 1.1.6), libpcap0.8 (>= 0.9.8), libpcre3, libssl1.1 (>= 1.1.1), zlib1g (>= 1:1.1.4)
Recommends: ettercap-graphical | ettercap-text-only
Description-en: Multipurpose sniffer/interceptor/logger for switched LAN
Ettercap supports active and passive dissection of many protocols
(even encrypted ones) and includes many feature for network and host
analysis.
.
Data injection in an established connection and filtering (substitute
or drop a packet) on the fly is also possible, keeping the connection
synchronized.
.
Many sniffing modes are implemented, for a powerful and complete
sniffing suite. It is possible to sniff in four modes: IP Based, MAC Based,
ARP Based (full-duplex) and PublicARP Based (half-duplex).
.
Ettercap also has the ability to detect a switched LAN, and to use OS
fingerprints (active or passive) to find the geometry of the LAN.
.
This package contains the Common support files, configuration files,
plugins, and documentation. You must also install either
ettercap-graphical or ettercap-text-only for the actual GUI-enabled
or text-only ettercap executable, respectively.
Description-md5: f1d894b138f387661d0f40a8940fb185
Homepage: https://ettercap.github.io/ettercap/
Tag: interface::text-mode, network::scanner, role::app-data, role::program,
uitoolkit::ncurses, use::scanning
Section: net
Priority: optional
Filename: pool/main/e/ettercap/ettercap-common_0.8.3.1-3_amd64.deb
Size: 734972
MD5sum: 403d87841f8cdd278abf20bce83cb95e
SHA256: 500aee2f07e0fae82489321097aee8a97f9f1970f6e4f8978140550db87e4ba9
root@pcfreak:/ # apt install ettercap-text-only –yesroot@pcfreak:/ # ettercap -C
7. iperf and netperf to measure connecitivity speed on Network LAN and between Linux server hosts
iperf and netperf are two very handy tools to measure the speed of a network and various aspects of the bandwidth. It is mostly useful when designing network infrastructure or building networks from scratch.
If you never used netperf in the past here is a description from man netperf
NAME
netperf – a network performance benchmark
SYNOPSIS
netperf [global options] — [test specific options]
DESCRIPTION
Netperf is a benchmark that can be used to measure various aspects of
networking performance. Currently, its focus is on bulk data transfer
and request/response performance using either TCP or UDP, and the
Berkeley Sockets interface. In addition, tests for DLPI, and Unix Do‐
main Sockets, tests for IPv6 may be conditionally compiled-in.
root@freak:~# netperf
MIGRATED TCP STREAM TEST from 0.0.0.0 (0.0.0.0) port 0 AF_INET to localhost () port 0 AF_INET : demo
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec87380 65536 65536 10.00 17669.96
Testing UDP network throughput using NetPerf
Change the test name from TCP_STREAM to UDP_STREAM. Let’s use 1024 (1MB) as the message size to be sent by the client.
If you receive the following error send_data: data send error: Network is unreachable (errno 101) netperf: send_omni:
send_data failed: Network is unreachable, add option -R 1 to remove the iptable rule that prohibits NetPerf UDP flow.
$ netperf -H 172.31.56.48 -t UDP_STREAM -l 300 — -R 1 -m 1024
MIGRATED UDP STREAM TEST from 0.0.0.0 (0.0.0.0) port 0 AF_INET to 172.31.56.48 () port 0 AF_INET
Socket Message Elapsed Messages
Size Size Time Okay Errors Throughput
bytes bytes secs # # 10^6bits/sec212992 1024 300.00 9193386 0 251.04
212992 300.00 9131380 249.35
UDP Throughput in a WAN
$ netperf -H HOST -t UDP_STREAM -l 300 — -R 1 -m 1024
MIGRATED UDP STREAM TEST from (null) (0.0.0.0) port 0 AF_INET to (null) () port 0 AF_INET : histogram : spin interval
Socket Message Elapsed Messages
Size Size Time Okay Errors Throughput
bytes bytes secs # # 10^6bits/sec9216 1024 300.01 35627791 0 972.83
212992 300.01 253099 6.91
Testing TCP throughput using iPerf
Here is a short description of iperf
NAME
iperf – perform network throughput tests
SYNOPSIS
iperf -s [options]
iperf -c server [options]
iperf -u -s [options]
iperf -u -c server [options]
DESCRIPTION
iperf 2 is a tool for performing network throughput and latency mea‐
surements. It can test using either TCP or UDP protocols. It supports
both unidirectional and bidirectional traffic. Multiple simultaneous
traffic streams are also supported. Metrics are displayed to help iso‐
late the causes which impact performance. Setting the enhanced (-e) op‐
tion provides all available metrics.
The user must establish both a both a server (to discard traffic) and a
client (to generate traffic) for a test to occur. The client and server
typically are on different hosts or computers but need not be.
Run iPerf3 as server on the server:
$ iperf3 –server –interval 30
———————————————————–
Server listening on 5201
———————————————————–
Test TCP Throughput in Local LAN
$ iperf3 –client 172.31.56.48 –time 300 –interval 30
Connecting to host 172.31.56.48, port 5201
[ 4] local 172.31.100.5 port 44728 connected to 172.31.56.48 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr Cwnd
[ 4] 0.00-30.00 sec 1.70 GBytes 488 Mbits/sec 138 533 KBytes
[ 4] 30.00-60.00 sec 260 MBytes 72.6 Mbits/sec 19 489 KBytes
[ 4] 60.00-90.00 sec 227 MBytes 63.5 Mbits/sec 15 542 KBytes
[ 4] 90.00-120.00 sec 227 MBytes 63.3 Mbits/sec 13 559 KBytes
[ 4] 120.00-150.00 sec 228 MBytes 63.7 Mbits/sec 16 463 KBytes
[ 4] 150.00-180.00 sec 227 MBytes 63.4 Mbits/sec 13 524 KBytes
[ 4] 180.00-210.00 sec 227 MBytes 63.5 Mbits/sec 14 559 KBytes
[ 4] 210.00-240.00 sec 227 MBytes 63.5 Mbits/sec 14 437 KBytes
[ 4] 240.00-270.00 sec 228 MBytes 63.7 Mbits/sec 14 516 KBytes
[ 4] 270.00-300.00 sec 227 MBytes 63.5 Mbits/sec 14 524 KBytes
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr
[ 4] 0.00-300.00 sec 3.73 GBytes 107 Mbits/sec 270 sender
[ 4] 0.00-300.00 sec 3.73 GBytes 107 Mbits/sec receiver
Test TCP Throughput in a WAN Network
$ iperf3 –client HOST –time 300 –interval 30
Connecting to host HOST, port 5201
[ 5] local 192.168.1.73 port 56756 connected to HOST port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate
[ 5] 0.00-30.00 sec 21.2 MBytes 5.93 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 30.00-60.00 sec 27.0 MBytes 7.55 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 60.00-90.00 sec 28.6 MBytes 7.99 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 90.00-120.00 sec 28.7 MBytes 8.02 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 120.00-150.00 sec 28.5 MBytes 7.97 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 150.00-180.00 sec 28.6 MBytes 7.99 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 180.00-210.00 sec 28.4 MBytes 7.94 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 210.00-240.00 sec 28.5 MBytes 7.97 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 240.00-270.00 sec 28.6 MBytes 8.00 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 270.00-300.00 sec 27.9 MBytes 7.81 Mbits/sec
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate
[ 5] 0.00-300.00 sec 276 MBytes 7.72 Mbits/sec sender
[ 5] 0.00-300.00 sec 276 MBytes 7.71 Mbits/sec receiver
$ iperf3 –client 172.31.56.48 –interval 30 -u -b 100MB
Accepted connection from 172.31.100.5, port 39444
[ 5] local 172.31.56.48 port 5201 connected to 172.31.100.5 port 36436
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 5] 0.00-30.00 sec 354 MBytes 98.9 Mbits/sec 0.052 ms 330/41774 (0.79%)
[ 5] 30.00-60.00 sec 355 MBytes 99.2 Mbits/sec 0.047 ms 355/41903 (0.85%)
[ 5] 60.00-90.00 sec 354 MBytes 98.9 Mbits/sec 0.048 ms 446/41905 (1.1%)
[ 5] 90.00-120.00 sec 355 MBytes 99.4 Mbits/sec 0.045 ms 261/41902 (0.62%)
[ 5] 120.00-150.00 sec 354 MBytes 99.1 Mbits/sec 0.048 ms 401/41908 (0.96%)
[ 5] 150.00-180.00 sec 353 MBytes 98.7 Mbits/sec 0.047 ms 530/41902 (1.3%)
[ 5] 180.00-210.00 sec 353 MBytes 98.8 Mbits/sec 0.059 ms 496/41904 (1.2%)
[ 5] 210.00-240.00 sec 354 MBytes 99.0 Mbits/sec 0.052 ms 407/41904 (0.97%)
[ 5] 240.00-270.00 sec 351 MBytes 98.3 Mbits/sec 0.059 ms 725/41903 (1.7%)
[ 5] 270.00-300.00 sec 354 MBytes 99.1 Mbits/sec 0.043 ms 393/41908 (0.94%)
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 5] 0.00-300.04 sec 3.45 GBytes 98.94 Mbits/sec 0.043 ms 4344/418913 (1%)
UDP Throughput in a WAN
$ iperf3 –client HOST –time 300 -u -b 7.7MB
Accepted connection from 45.29.190.145, port 60634
[ 5] local 172.31.56.48 port 5201 connected to 45.29.190.145 port 52586
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 5] 0.00-30.00 sec 27.4 MBytes 7.67 Mbits/sec 0.438 ms 64/19902 (0.32%)
[ 5] 30.00-60.00 sec 27.5 MBytes 7.69 Mbits/sec 0.446 ms 35/19940 (0.18%)
[ 5] 60.00-90.00 sec 27.5 MBytes 7.68 Mbits/sec 0.384 ms 39/19925 (0.2%)
[ 5] 90.00-120.00 sec 27.5 MBytes 7.68 Mbits/sec 0.528 ms 70/19950 (0.35%)
[ 5] 120.00-150.00 sec 27.4 MBytes 7.67 Mbits/sec 0.460 ms 51/19924 (0.26%)
[ 5] 150.00-180.00 sec 27.5 MBytes 7.69 Mbits/sec 0.485 ms 37/19948 (0.19%)
[ 5] 180.00-210.00 sec 27.5 MBytes 7.68 Mbits/sec 0.572 ms 49/19941 (0.25%)
[ 5] 210.00-240.00 sec 26.8 MBytes 7.50 Mbits/sec 0.800 ms 443/19856 (2.2%)
[ 5] 240.00-270.00 sec 27.4 MBytes 7.66 Mbits/sec 0.570 ms 172/20009 (0.86%)
[ 5] 270.00-300.00 sec 25.3 MBytes 7.07 Mbits/sec 0.423 ms 1562/19867 (7.9%)
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 5] 0.00-300.00 sec 272 MBytes 7.60 Mbits/sec 0.423 ms 2522/199284 (1.3%)
[SUM] 0.0-300.2 sec 31 datagrams received out-of-order
Sum it up what learned
Debugging network issues and snooping on a Local LAN (DMZ) network on a server or home LAN is useful to debug for various network issues and more importantly track and know abou tsecurity threads such as plain text passowd communication via insecure protocols a failure of proper communication between Linux network nodes at times, or simply to get a better idea on what kind of network is your new purchased dedicated server living in .It can help you also strenghten your security and close up any possible security holes, or even help you start thinking like a security intruder (cracker / hacker) would do. In this article we went through few of my favourite tools I use for many years quite often. These tools are just part of the tons of useful *Unix free tools available to do a network debug. Tools mentioned up are worthy to install on every server you have to administratrate or even your home desktop PCs, these are iptraf, sniffit, iftop, bmon, nethogs, nmon, ettercap, iperf and netperf.
If you have some other useful tools used on Linux sys admin tasks please share, I'll be glad to know it and put them in my arsenal of used tools.
Enjoy ! 🙂