In this post I'm about to explain how to configure Apache Web server for Two Way SSL Authentication alone and how to configure Two Way SSL Authentication for a Certain Domain URL Locations and the mixture of both One Way standar SSL authentication and Two Way Handshake Authentication .
Generally before starting I have to say most Web sites does not require a Mutual SSL Authentication (the so called Two-Way SSL).
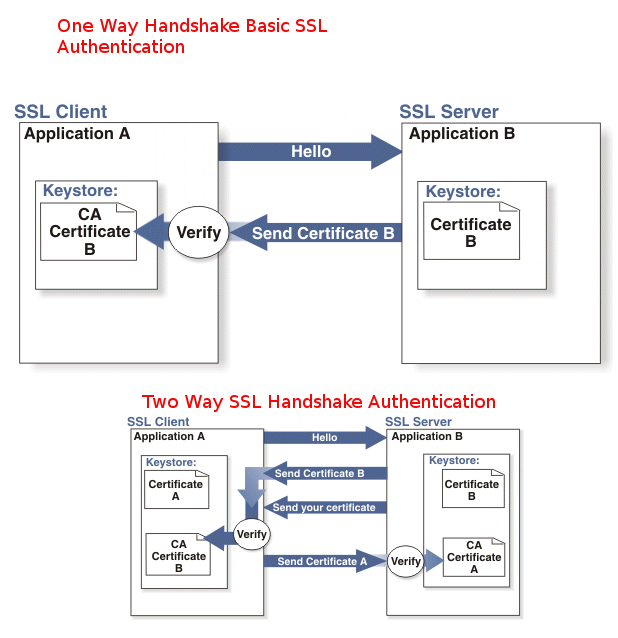
In most configurations Apache Web server is configured for One Way Basic authentication where The Web server authenticates to the Client usuall that's Browser program such as Mozilla Firefox / Chrome / IE / Epiphany whatever presenting certificate signed by Trustable Certificate Authority such as VeriSign.
The authority then autneticates to the browser that the Installed certificate on the Apache Web Server is trustable and the website is not a fraudulant, that is especially important for websites where sensitive data is being transferred, lets say Banks (Doing Money Transfers online), Hospitals (Transfelling your Medical results data) or purchasing something from Amazon.com, Ebay.Com, PayPal etc.
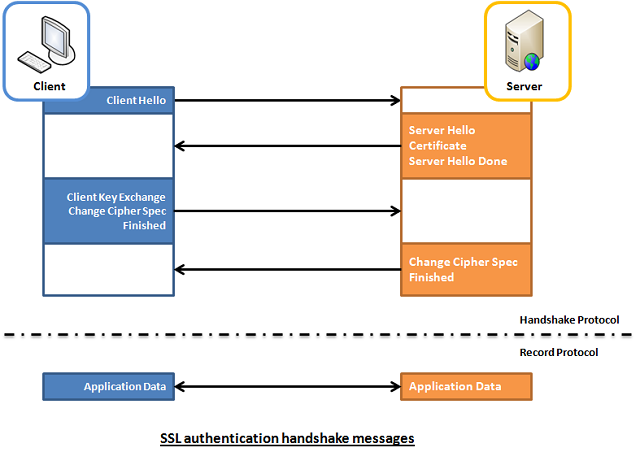
Once client validates the certificate the communication line gets encrypted based on Public Key, below diagram illustrates this.
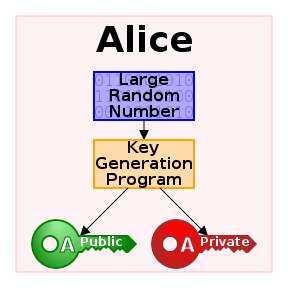
However in some casis where an additional Security Hardening is required, the Web Server might be configured to require additional certificate so the authentication between Client -> Server doesn't work by certificating with just a Server provided certificate but to work Two Ways, e.g. the Client might be setup to also have a Trusted Authority Certificate and to present it to server and send back this certificate to the Server as well for a mutual authentication and only once the certificate handshake between;
client -> server and server -> client
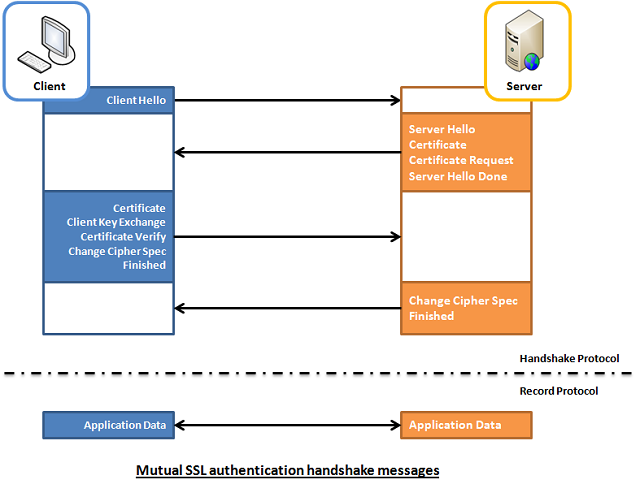
is confirmed as successful the two could establish a trustable encypted SSL channel over which they can talk securely this is called
Two way SSL Authentication.
1. Configure Two Way SSL Authentication on Apache HTTPD
To be able to configure Two Way SSL Authentication handshake on Apache HTTPD just like with One way standard one, the mod_ssl Apache module have to enabled.
Enabling two-way SSL is usually not done on normal clients but is done with another server acting as client that is using some kind of REST API to connect to the server
The Apache directive used for Mutual Authentication is SSLVerifyClient directive (this is provided by mod_ssl)
the options that SSLVerifyClient receives are:
none: instructs no client Certificate is required
optional: the client is allowed to present a valid certificate but optionally
require: the client is always required to present a valid Certificate for mutual Authenticaton
optional_no_ca: the client is asked to present a valid Certificate however it has to be successfully verified.
In most of Apache configuratoins the 2 ones that are used are either none or require
because optional is reported to not behave properly with some of the web browsers and
optional_no_ca is not restrictive and is usually used just for establishing basic SSL test pages.
At some cases when configuring Apache HTTPD it is required to have a mixture of both One Way and Two Way Authentication, if that is your case the SSLVerifyClient none is to be used inside the virtual host configuration and then include SSLVerifyClient require to each directory (URL) location that requires a client certificate with mutual auth.
Below is an example VirtualHost configuration as a sample:
The SSLVerifyClient directive from mod_ssl dictates whether a client certificate is required for a given location:
<VirtualHost *:443>
…
SSLVerifyClient none
<Location /whatever_extra_secured_location/dir>
…
SSLVerifyClient require
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
Because earlier in configuration the SSLVerifyClient none is provided, the client will not be doing a Two Way Mutual Authentication for the whole domain but just the selected Location the client certificate will be not requested by the server for a 2 way mutual auth, but only when the client requests the Location setupped resouce a renegotiation will be done and client will be asked to provide certificate for the two way handshake authentication.
Keep in mind that on a busy servers with multitudes of connections this renegotiation might put an extra load on the server and this even can turn into server scaling issue on a high latency networks, because of the multiple client connects. Every new SSL renegotiation is about to assign new session ID and that could have a negative impact on overall performance and could eat you a lot of server memory.
To avoid this often it i suseful to use SSLRenegBufferSize directive which by default is set in Apache 2.2.X to 128 Kilobytes and for multiple connects it might be wise to raise this.
A mutual authentication that is done on a Public Server that is connected to the Internet without any DMZ might be quite dangerous thing as due to to the multiple renegotiations the server might end up easily a victim of Denial of Service (DOS) attack, by multiple connects to the server trying to consume all its memory …
Of course the security is not dependent on how you have done the initial solution design but also on how the Client software that is doing the mutual authentication is written to make the connections to the Web Server.
2. Configure a Mixture of One Way Standard (Basic) SSL Authentication together with Two Way Client Server Handshake SSL Authentication
Below example configuring is instructing Apache Webserver to listen for a mixture of One Way standard Client to browser authentication and once the client browser establishes the session it asks for renegotiation for every location under Main Root / to be be authenticated with a Mutual Two Way Handshake Authentication, then the received connection is proxied by the Reverse Proxy to the end host which is another proxy server listening on the same host on (127.0.0.1 or localhost) on port 8080.
<VirtualHost *:8001>
ServerAdmin name@your-server.com
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/server-cert.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/server-key.pemSSLVerifyClient require
SSLVerifyDepth 10
SSLCACertificateFile /home/etc/ssl/cacert.pem
<location />
Order allow,deny
allow from all
SSLRequire (%{SSL_CLIENT_S_DN_CN} eq "clientcn")
</location>
ProxyPass / http://127.0.0.1:8080/
ProxyPassReverse / http://127.0.0.1:8080/
</VirtualHost>
3. So what other useful options do we have?
Keep Connections Alive
This is a good option but it may consume significant amount of memory. If Apache is using the prefork MPM (as many Webservers still do instead of Apache Threading), keeping all connections alive means multiple live processes. For example, if Apache has to support 1000 concurrent connections, each process consuming 2.7MB, an additional 2700MB should be considered. This may be of lesser significance when using other MPMs. This option will mitigate the problem but will still require SSL renegotiation when the SSL sessions will time out.
Another better approach in terms of security to the mixture of requirement for both One Side Basic SSL Authentication to a Webserver and Mutual Handshake SSL Auth is just to set different Virtualhosts one or more configuration to serve the One Way SSL authentication and others that are configured just to do the Mutual Two Way Handshake SSL to specified Locations.
4. So what if you need to set-up multiple Virtualhosts with SSL authentication on the Same IP address Apache (SNI) ?
For those who did not hear still since some time Apache Web Server has been rewritten to support SNI (Server Name Indication), SNI is really great feature as it can give to the webserver the ability to serve multiple one and two way handshake authentications on the same IP address. For those older people you might remember earlier before SNI was introduced, in order to support a VirtualHost with SSL encryption authentication the administrator had to configure a separate IP address for each SSL certificate on each different domian name.
SNI feature can also be used here with both One Way standard Apache SSL auth or Two Way one the only downside of course is SNI could be a performance bottleneck if improperly scaled. Besides that some older browsers are not supporting SNI at all, so possibly for public services SNI is less recommended but it is better to keep-up to the good old way to have a separate IP address for each :443 set upped VirtualHost.
One more note to make here is SNI works by checking the Host Header send by the Client (browser) request
SSL with Virtual Hosts Using SNI.
SNI (Server Name Indication) is a cool feature. Basically it allows multiple virtual hosts with different configurations to listen to the same port. Each virtual host should specify a unique server name identification using the SeverName directive. When accepting connections, Apache will select a virtual host based on the host header that is part of the request (must be set on both HTTP and SSL levels). You can also set one of the virtual hosts as a default to serve clients that don’t support SNI. You should bear in mind that SNI has different support levels in Java. Java 1.7 was the first version to support SNI and therefore it should be a minimum requirement for Java clients.
5. Overall list of useful Options for Mutual Two Way And Basic SSL authentication
Once again the few SSL options for Apache Mutual Handhake Authentication
SSLVerifyClient -> to enable the two-way SSL authentication
SSLVerifyDepth -> to specify the depth of the check if the certificate has an approved CA
SSLCACertificateFile -> the public key that will be used to decrypt the data recieved
SSLRequire -> Allows only requests that satisfy the expression
Below is another real time example for a VirtualHost Apache configuration configured for a Two Way Handshake Mutual Authentication
For the standard One way Authentication you need the following Apache directives
SSLEngine on -> to enable the single way SSL authentication
SSLCertificateFile -> to specify the public certificate that the WebServer will show to the users
SSLCertificateKeyFIle -> to specify the private key that will be used to encrypt the data sent
6. Configuring Mutual Handshake SSL Authentication on Apache 2.4.x
Below guide is focusing on Apache HTTPD 2.2.x nomatter that it can easily be adopted to work on Apache HTTPD 2.4.x branch, if you're planning to do a 2 way handshake auth on 2.4.x I recommend you check SSL / TLS Apache 2.4.x Strong Encryption howto official Apache documentation page.
In meantime here is one working configuration for SSL Mutual Auth handshake for Apache 2.4.x:
<Directory /some-directory/location/html>
RedirectMatch permanent ^/$ /auth/login.php
Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks# Anything which matches a Require rule will let us in
# Make server ask for client certificate, but not insist on it
SSLVerifyClient optional
SSLVerifyDepth 2
SSLOptions +FakeBasicAuth +StrictRequire# Client with appropriate client certificate is OK
<RequireAll>
Require ssl-verify-client
Require expr %{SSL_CLIENT_I_DN_O} eq "Company_O"
</RequireAll># Set up basic (username/password) authentication
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Password credentials"
AuthBasicProvider file
AuthUserFile /etc/apache2/htaccess/my.passwd# User which is acceptable to basic authentication is OK
Require valid-user# Access from these addresses is OK
Require ip 10.20.0.0/255.255.0.0
Require ip 10.144.100
</Directory>
Finally to make the new configurations working depending you need to restart Apache Webserver depending on your GNU / Linux / BSD or Windows distro use the respective script to do it.
Enjoy!


 .
.