I use VIM as an editor of choice for many years already.
Yet it's until recently I use it for a PHP ZF (Zend Framework) web development.
Few days ago I've blogged How to configure vimrc for a php syntax highlightning (A Nicely pre-configured vimrc to imrpove the daily text editing experience
This enhancements significantly improves the overall PHP code editing with VIM. However I felt something is yet missing because I didn't have the power and functunality of a complete IDE like for instance The Eclipse IDE
I was pretty sure that VIM has to have a way to be used in a similar fashion to a fully functional IDE and looked around the net to find for any VIM plugins that will add vim an IDE like coding interface.
I then come accross a vim plugin called VIM Prokject : Organize/Navigate projects of files (like IDE/buffer explorer)
The latest VIM Project as of time of writting is 1.4.1 and I've mirrored it here
The installation of the VIM Project VIM extension is pretty straight forward to install it and start using it on your PC issue commands:
1. Install the project VIM add-on
debian:~$ wget https://www.pc-freak.net/files/project-1.4.1.tar.gz
debian:~$ mv project-1.4.1.tar.gz ~/.vim/
debian:~$ cd ~/.vim/
debian:~$ tar -zxvvf project-1.4.1.tar.gz
2. Load the plugin
Launch your vim editor and type : Project(without the space between : and P)
You will further see a screen like:
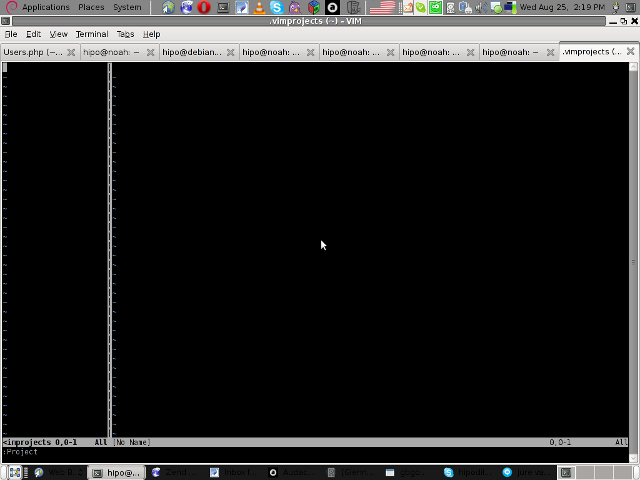
3. You will have to press C within the Project window to load a new project
Then you will have to type a directory to use to load a project sources files from:
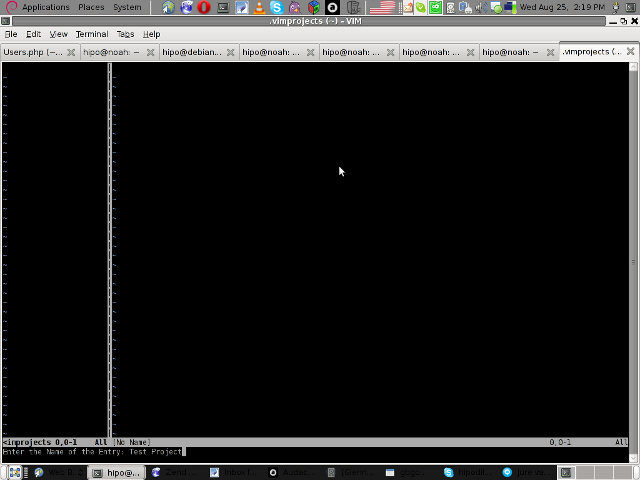
You will be prompted with to type a project name like in the screenshot below:
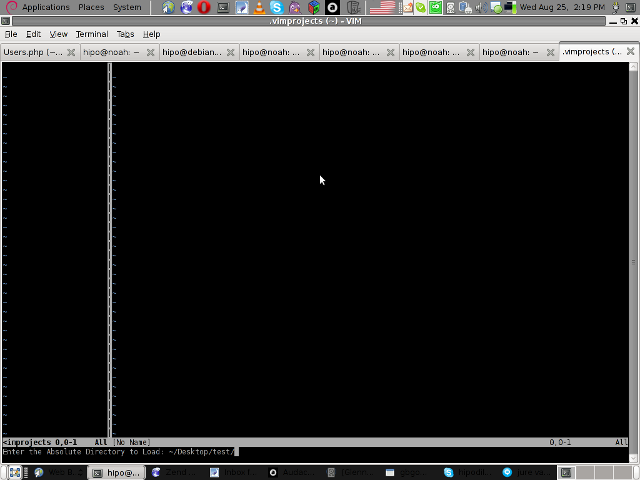
4. Next you will have to type a CD (Current Dir) parameter
To see more about the CD parameter consult vim project documentation by typing in main vim pane :help project
The appearing screen will be something like:
5. Thereafter you will have to type a file filter
File filter is necessary and will instruct the vim project plugin to load all files with the specified extension within vim project pane window
You will experience a screen like:
vim project plugin file filter screen
Following will be a short interval in which all specified files by the filter type will get loaded in VIM project pane and your Zend Framework, PHP or any other source files will be listed in a directory tree structure like in the picture shown below:
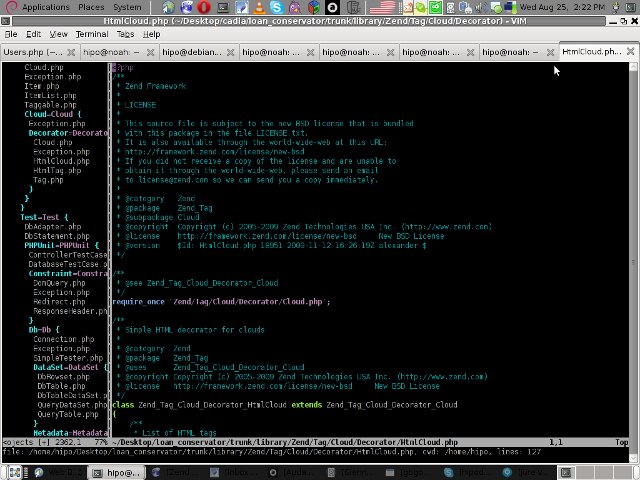
6. Saving loaded project hierarchy state
In order to save a state of a loaded project within the VIM project window pane you will have to type in vim, let's say:
:saveas .projects/someproject
Later on to load back the saved project state you will have to type in vim :r .projects/someproject
You will now have almost fully functional development IDE on top of your simple vim text editor.
You can navigate within the Project files loaded with the Project extension pane easily and select a file you would like to open up, whenever a source file is opened and you work on it to switch in between the Project file listing pane and the opened source code file you will have to type twice CTRL+w or in vim language C-w
To even further sophisticate your web development in PHP with vim you can add within your ~/.vimrc file the following two lines:
" run file with PHP CLI (CTRL-M)
:autocmd FileType php noremap <C-M> :w!<CR>:!/usr/bin/php %<CR>
" PHP parser check (CTRL-L)
:autocmd FileType php noremap <C-L> :!/usr/bin/php -l %>CR>
In the above vim configuration directovies the " character is a comment line and the autocmd is actually vim declarations.
The first :autocmd … declaration will instruct vim to execute your current opened php source file with the php cli interpreter whenever a key press of CTRL+M (C-m) occurs.
The second :autocmd … will add to your vim a shortcut, so whenever a CTRL+L (C-l) key combination is pressed VIM editor will check your current edited source file for syntax errors.
Therefore this will enable you to very easily periodically check if your file syntax is correct.
Well this things were really helpful to me, so I hope they will be profitable for you as well.
Cheers 🙂