Why would anyone disable ACPI support on a server machine??
Well ACPI support kernel loaded code is just another piece of code constantly being present in the memory, that makes the probability for a fatal memory mess up leading to a fatal bug resulting in system crash (kernel panic) more likely.
Many computers ship with buggy or out of specifications ACPI firmware which can cause a severe oddities on a brand new bought piece of comp equipment.
One such oddity related to ACPI motherboard support problems is if you notice your machine randomly powering off or failing to boot with a brand new Linux installed on it.
Another reason to switch off ACPI code will would to be prevent the CPU FAN rotation from being kernel controlled.
If the kernel controls the CPU fan on high CPU heat up it will instruct the fan to rotate quickly and on low system loads it will bring back the fan to loose speed.
This frequent switch of FAN from high speed to low speed increases the probability for a short fan damage due to frequent changes of fan speed. Such a fan damage leads often to system outage due to fan failure to rotate properly.
Therefore in my view it is better ACPI support is switched off completely on servers. On some servers ACPI is useful as it can be used to track CPU temperature with embedded motherboard sensors with lm_sensors or any piece of hardwre vendor specific software provided. On many machines, however lm_sensors will not properly recognize the integrated CPU temperature sensors and hence ACPI is mostly useless.
There are 3 ways to disable fully or partially ACPI support.
- One is to disable it straight for BIOS (best way IMHO)
- Disable via GRUB or LILO passing a kernel parameter
- Partial ACPI off-ing - /disabling the software that controls the CPU fan/
1. Disable ACPI in BIOS level
Press DEL, F1, F2, F10 or whatever the enter bios key combination is go through all the different menus (depending on the vios BENDOR) and make sure every occurance of ACPI is set to off / disable whatever it is called.
Below is a screenshot of menus with ACPI stuff on a motherboard equipped with Phoenix AwardBIOS:
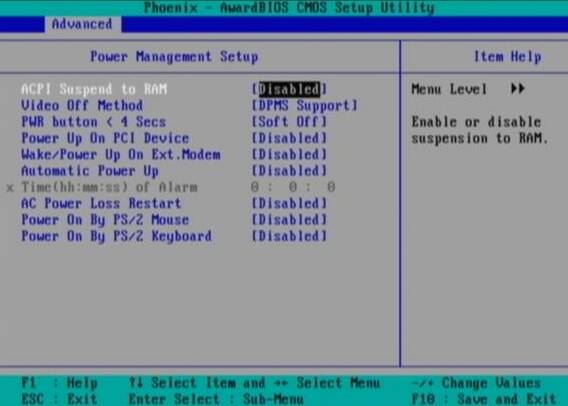
This is the in my opinon best and safest way to disable ACPI power saving, Unfortunately some newer PCs lack the functionality to disable ACPI; (probably due to the crazy "green" policy the whole world is nowdays mad of).
If that's the case with you, thanksfully there is a "software way" to disable ACPI via passing kernel options via GRUB and LILO boot loaders.
2. Disabling ACPI support on kernel boot level through GRUB boot loader config
There is a tiny difference in command to pass in order to disable ACPI depending on the Linux installed GRUB ver. 1.x or GRUB 2.x.
a) In GRUB 0.99 (GRUB version 1)
Edit file /etc/grub/menu.lst or /etc/grub/grub.conf (location differs across Linux distribution). Therein append:
acpi=off
to the end of kernel command line.
Here is an example of a kernel command line with ACPI not disabled (example taken from CentOS server grub.conf):
[root@centos ~]# grep -i title -A 4 /etc/grub/grub.conf
title Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server (2.6.18-36.el5)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-36.el5 ro root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 console=ttyS0,115200n8
initrd /initrd-2.6.18-36.el5.img
The edited version of the file with acpi=off included should look like so:
title Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server (2.6.18-36.el5)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-36.el5 ro root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 console=ttyS0,115200n8 acpi=off
initrd /initrd-2.6.18-36.el5.img
The kernel option root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 means the the server is configured to use LVM (Logical Volume Manager).
b) Disabling ACPI on GRUB version 1.99 +
This version is by default installed on newer Ubuntu and Debian Linux-es.
In grub 1.99 on latest Debian Squeeze, the file to edit is located in /boot/grub/grub.cfg. The file is more messy than with its predecessor menu.lst (grub 0.99).
Thanks God there is no need to directly edit the file (though this is possible), but on newer Linuces (as of time of writting the post), there is another simplied grub config file /etc/grub/config
Hence to add the acpi=off to 1.99 open /etc/grub/config find the line reading:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet"
and append the "acpi=off" option, e.g. the line has to change to:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet acpi=off"
On some servers it might be better to also disable APIC along with ACPI:
Just in case you don't know what is the difference between ACPI and APIC, here is a short explanation:
ACPI = Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
APIC = Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers
ACPI is the system that controls your dynamic speed fans, the power button behavior, sleep states, etc.
APIC is the replacement for the old PIC chip that used to come imbedded on motherboards that allowed you to setup interrupts for your soundcard, ide controllers, etc.
Hence on some machines experiencing still problems with even ACPI switched off, it is helpful to disable the APIC support too, by using:
acpi=off noapic noacpi
Anyways, while doing the changes, be very very cautious or you might end up with un-boot-able server. Don't blame me if this happens :); be sure you have a backup option if server doesn't boot.
To assure faultless kernel boot, GRUB has ability to be configured to automatically load up a second kernel if 1st one fails to boot, if you need that read the grub documentation on that.
To load up the kernel with the new setting, give it a restart:
[root@centos ~]# shutdown -r now
....
3. Disable ACPI support on kernel boot time on Slackware or other Linuxes still booting kernel with LILO
Still, some Linux distros like Slackware, decided to keep the old way and use LILO (LInux LOader) as a default boot loader.
Disabling ACPI support in LILO is done through /etc/lilo.conf
By default in /etc/lilo.conf, there is a line:
append= acpi=on
it should be changed to:
append= acpi=off
Next to load up the new acpi disabled setting, lilo has to be reloaded:
slackware:~# /sbin/lilo -c /etc/lilo.conf
....
Finally a reboot is required:
slackware:~# reboot
....
(If you don't have a physical access or someone near the server you better not 🙂 )
4. Disable ACPI fan control support on a running Linux server without restart
This is the most secure work-around, to disabling the ACPI control over the machine CPU fan, however it has a downside that still the ACPI code will be loaded in the kernel and could cause kernel issues possibly in the long run – lets say the machine has uptime of more than 2 years…
The acpi support on a user level is controlled by acpid or haldaemon (depending on the Linux distro), hence to disable the fan control on servers this services has to be switched off:
a) disabling ACPI on Debian and deb based Linux-es
As of time of writting on Debian Linux servers acpid (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface event daemon) is there to control how power management will be handled. To disable it stop it as a service (if running):
debian:~# /etc/init.d/acpid stop
To permanently remove acpid from boot up on system boot disable it with update-rc.d:
debian:~# update-rc.d acpid disable 2 3 4 5
update-rc.d: using dependency based boot sequencing
insserv: Script iptables is broken: incomplete LSB comment.
insserv: missing `Required-Start:' entry: please add even if empty.
insserv: warning: current start runlevel(s) (empty) of script `acpid' overwrites defaults (2 3 4 5).
insserv: warning: current stop runlevel(s) (2 3 4 5) of script `acpid' overwrites defaults (empty).
insserv: missing `Required-Start:' entry: please add even if empty.
b) disabling ACPI on RHEL, Fedora and other Redhat-s (also known as RedHacks 🙂 )
I'm not sure if this is safe,as many newer rpm based server system services, might not work properly with haldaemon disabled.
Anyways you can give it a try if when it is stopped there are issues just bring it up again.
[root@rhel ~]# /etc/init.d/haldaemon stop
If all is fine with the haldaemon switched off (hope so), you can completely disable it to load on start up with:
[root@centos ~]# /sbin/chkconfig --level 2 3 4 5 haldaemon off
Disabling ACPI could increase a bit your server bills, but same time decrease losses from downtimes, so I guess it worths its costs 🙂