Torrentflux is web based, feature-rich BitTorrent download manager.
Torrentflux is a must have installed server software for anyone who does regular torrent downloads and want to access the downloads from anywhere on the internet.
TorrentFlux is a PHP based BitTorrent controller that runs on a web
server. It can manage all of your BitTorrent downloads from anywhere
through a convenient and easy-to-use web interface.
.
TorrentFlux uses a MySQL database to manage the downloads.
TorrentFlux enables you to run BitTorrent downloads unattended on a monitor-less or remote server 24 hours a day, while still maintaining complete control from any web browser. Now you can control your downloading on your firewall, or keep up with downloads while on vacation. It uses the BitTornado client to download files, and also requires a web server with PHP.
Some of the Torrentflux features:
* Upload Torrents via URL or File Upload
* Start, Stop, and Delete Torrents with ease
* Advanced Torrent start options (ports, speeds, etc.)
* Multi-user interface
* RSS Feeds, download Torrents files with a click
* Run several torrents at once
* View Download Progress of all torrents at a glance
* View drive space at a glance
* View Torrent file meta information
* Built-in User management and Security
* Private Messaging
* Themes (selectable per user)
* Upload History
Before installing Bittorrent you will need to have a running version of Debian, Ubuntu or any other debian derivative (though it can easily be run on any Linux distro). To install AMP (Apache MySQL Server, PHP) you can follow first part of my previous article Installing Usual PHP Apache MySQL for new Debian GNU / Linux installs.
So what for is TorrentFlux Useful?
Torrenflux is precious and must have if you have to access filtered torrent from outside of your homecountry and you have a running server already in your home country in that I was using TorrentFlux to access Bulgarian Zamunda.Net Torrent Tracker from Holland and was downloading first movies from the Bulgarian Torrent Tracker to my Fluxbox installed on my Dobrich home router and then used FTP to transfer movies to the Netherlands. Talking about many people choose to also install VSFTP and use it together with Torrentflux …
1. Install TorrentFlux and its dependencies (BitTornado, Bittorrent, Zip, Unzip, Bzip etc.) the "Debian Way"
On my Debian 7 Wheezy home machine I run
apt-get install –yes bzip2 php5-gd php5-cli unrar-free grep python net-tools mawk wget unzip cksfv vlc-nox uudeview python-crypto libxml-simple-perl libxml-dom-perl libdbd-mysql-perl bittorrent bittornado
a) Install TorrentFlux the Debian Way
apt-get install –yes torrentflux
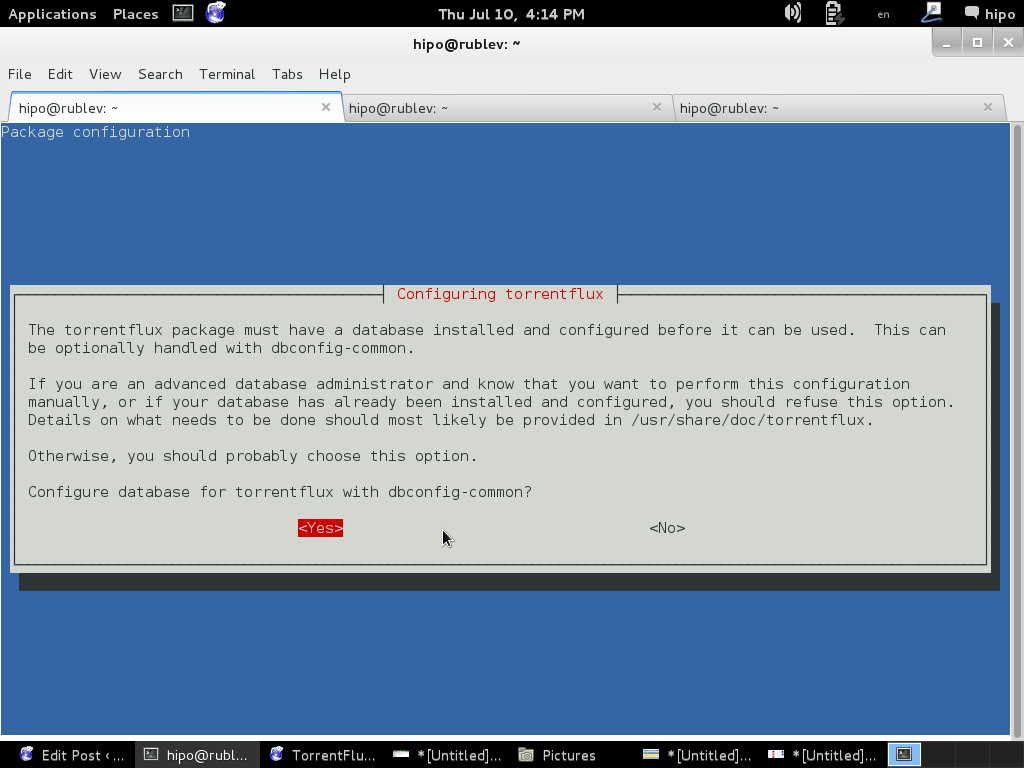
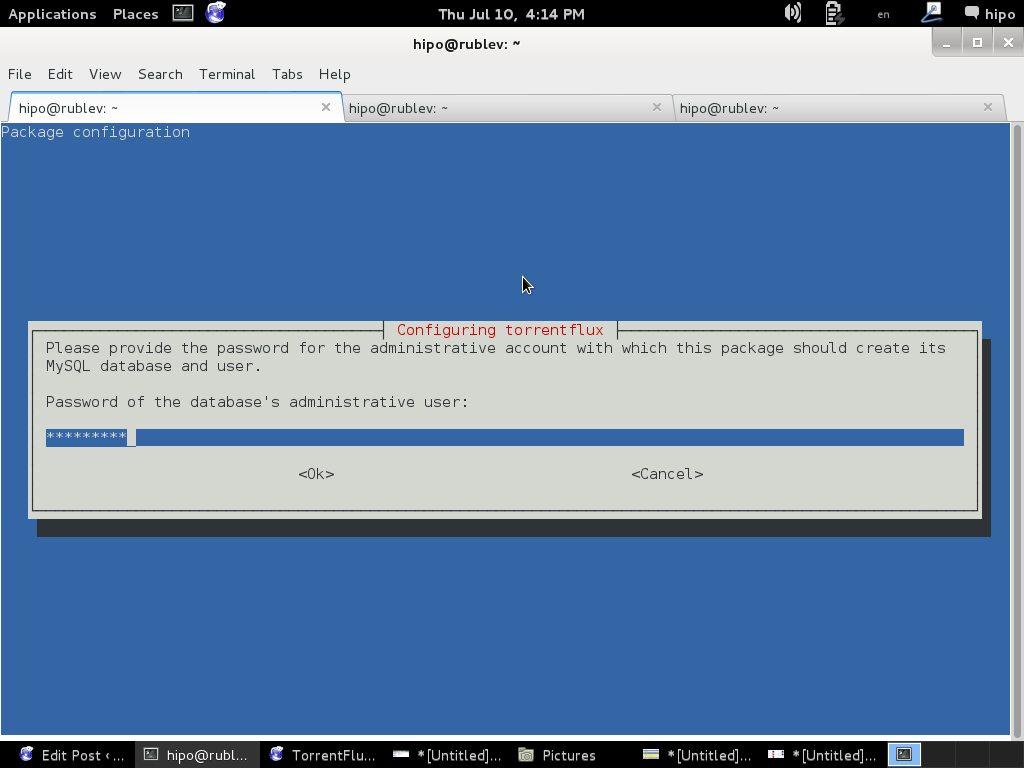
You will be prompted with a coule of screens, to set a new MySQL database user and password and SQL database, as well as offered to restart Apache to make Torrentflux accessible like as on below screenshots.
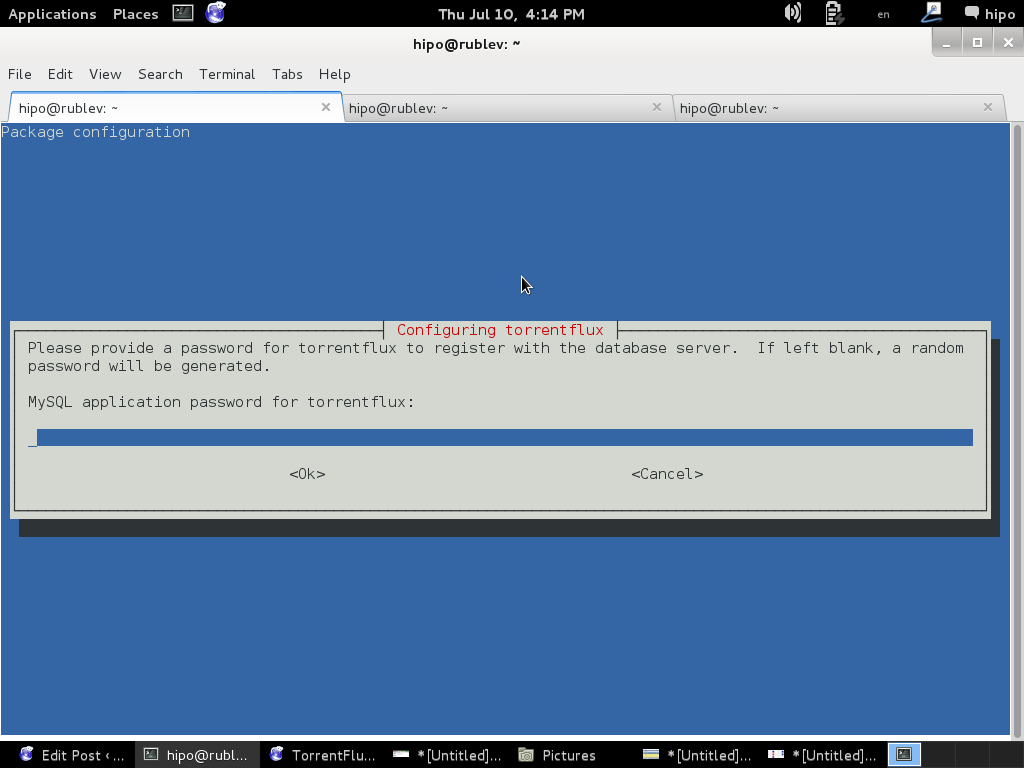
To make new installed torrentflux accessible from web you will either have to configure it via some new Apache VirtualHost or make a symbolic link to /usr/share/torrentflux/www :
cd /var/www/
ln -sf /usr/share/torrentflux/www/ torrentflux
That's all you're all done to access torrentflux either access it via your default configured webserver domain name or via localhost if you're logged in to same pc where installing.
http://www.your-domain.com/torrentflux
or
http://127.0.0.1/torrentflux
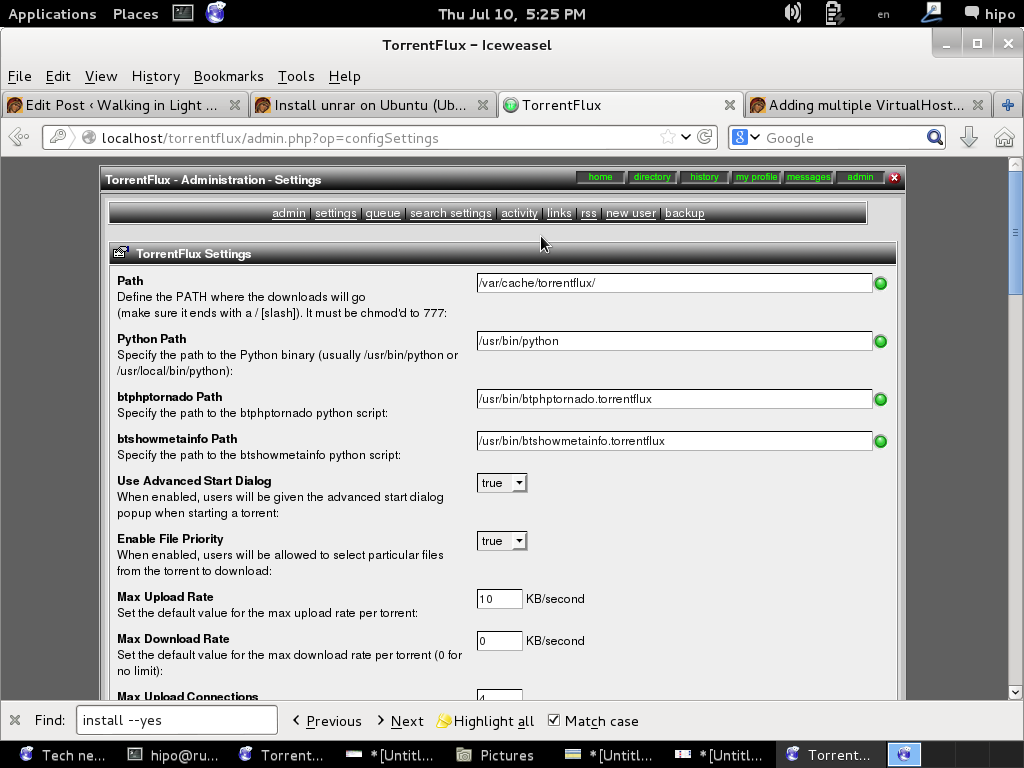
2. Install latest Torrentflux version from source
Alternatively if you want to have the latest version (because the Debian version is part of the stable distribution is a little bit outdated you will have to fetch Torrentflux-b4rt and unarchive it:
cd /tmp/
wget http://download.berlios.de/tf-b4rt/torrentflux-b4rt_1.0-beta2.tar.bz2
tar -xjf torrentflux-b4rt_1.0-beta2.tar.bz2
mv torrentflux-b4rt_1.0-beta2 /opt/torrentflux
Then to make torrentflux visible from web server I had to create a symbolic link to installation directory:
ln -sf /opt/torrentflux/html /var/www/torrentflux
For further initial configuration its necessery to make Torrentflux config writtable by www-data (the user with which Apache is running on Debian).
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/torrentflux/inc/config/
Next it its required to create somewhere download folder where TorrentFlux will keep downloaded Torrents
mkdir /var/lib/torrentflux
Apache HTTP server will have to have write ther:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/lib/torrentflux
If you already haven't restarted Apache earlier in installing TorrentFlux pre-requirements, you will have to do it now:
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
As TorrentFlux depends on its MySQL backend, we need to also create manually TorrentFlux database username and a password
export SQL_DB='torrentflux';
TFLUXSQL_USERNAME='torrentflux';
TFLUX_SQL_PWD='any-secret-password';
echo "CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS $SQL_DB DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci"
| mysql –user=root –password
echo "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON $SQL_DB.*
TO $TFLUXSQL_USERNAME@localhost
IDENTIFIED BY $TFLUX_SQL_PWD;" | mysql –user=root –password
Substitute with your Database, Username and Password above shell variables – $SQL_DB, $TFLUX_USERNAME, $TFLUX_SQL_PWD
To configure TorrentFlux access it in browser:
http://your-domain.com/torrentflux
By accessing it for a first time, you will redirected to setup.php, in case something goes wrong and yuo're not redirected (probably some mod_rewrite issues add setup.php to url – e.g., acess –
http://your-domain.com/torrentflux/setup.php
I will not enter details, about Web config, because everything there is pretty clear.
Just in short – you will have to now choose:
Choose Database
Choose Database Information of database (put in the exact name of TorrentFlux databse previously created)
Uncheck the box for "Create new database"
Choose as a download location upper created directory – /var/lib/torrentflux
If you get an error on software dependencies screen for missing unrar – just install it
VLC may show an error as well, that's not a problem because VLC is probably not to be used.
Finally after completion of all, you will get an error that setup.php cannot be deleted.
To prevent, someone to re-configure it through http://your-domain/torrentflux/setup.php URL remove setup.php
rm /var/www/torrentflux/setup.php
To prevent someone rewrite anything in config file from web we have to revert back config/ folder not to be writable by Apache
chown -R root:root /var/www/torrentflux/inc/config/
Now in browser to access torrentflux type:
http://ipofyourbox/torrentflux
/torrentflux should redirect you to login.php if for some reason it doesn't type it manually in URL.
First account you will login is the super user account, you can allow multiple users to use it by adding multiple accounts.
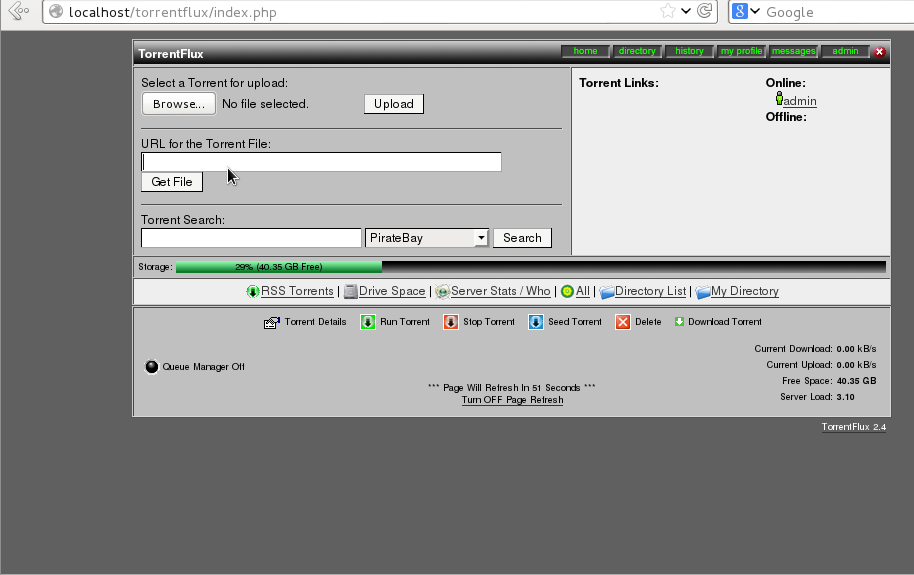
As you will see there is plety of configuration options to play with.
You will definitely want to look in Server Page, some very important page to look is the Transfer Page – from there you can adjust the bandwidth of your connection on 100Mbit network this would be 12500 – to use the maximum possible connection provided by your ISP set the max bandwidth to 0. You have the option to also set a default bittorrent client, by default this will be bittornado.
If you have troubles downloading from TorrentTrackers make sure your router is configured to forward port 49160 to 49300
Now if you have a lot of storage create accounts also for your friends and enjoy torrentflux 🙂