I need to make my laptop automatically sleep on LID Screen close but it doesn't why?
If have used your laptop for long years with Windows or any Windows user is used to the default beavrior of Windows to automatically sleep the computer on PC close. This default behavior of automatically sleep on LID Close has been Windows standard for many years
and the reason behind that usually laptop is used for mobility and working on a discharging battery so a LID screen close puts the laptop in (SLEEP) BATTERY SUSPEND MODE aiming to make the charged battery last longer. However often for Desktop use in the Office LID close
trigger of laptop sleep mode is annoying and undesired I've blogged earlier on that issue and how to make laptop not to sleep on LID close on M$ Windows 10 here.
This bahavior was copied and was working in many of the Linux distributions for years however in Debian GNU / Linux and Ubuntu 16.X this feature is often not properly working due to a systemd bug. Of course closing the notebook LID screen without putting
the PC in sleep mode is not a bug but a very useful feature for those who use their laptop as a Desktop machine that is non-stop running, however for most ppl default behavior to auto-suspend the computer on Laptop Monitor close is desired.
Here is how to force the close of the laptop lid to go to suspend/sleep mode and when open the lid, it wake it up.
1. First requirement is to make sure the laptop has installed the package pm-utils, if it is not there install it with:
# apt-get install –yes pm-utils
2. Next we need to edit logind.conf and append 3 variables
# vim /etc/systemd/logind.conf
Normally the file should have a bit of commented informative lines as well as a commented variables that could be enabled like so:
[Login]
#NAutoVTs=6
#ReserveVT=6
#KillUserProcesses=no
#KillOnlyUsers=
#KillExcludeUsers=root
#InhibitDelayMaxSec=5
#HandlePowerKey=poweroff
#HandleSuspendKey=suspend
#HandleHibernateKey=hibernate
#HandleLidSwitch=suspend
#HandleLidSwitchExternalPower=suspend
#HandleLidSwitchDocked=ignore
#PowerKeyIgnoreInhibited=no
#SuspendKeyIgnoreInhibited=no
#HibernateKeyIgnoreInhibited=no
#LidSwitchIgnoreInhibited=yes
#HoldoffTimeoutSec=30s
#IdleAction=ignore
#IdleActionSec=30min
#RuntimeDirectorySize=10%
#RemoveIPC=yes
#InhibitorsMax=8192
#SessionsMax=8192
These entries are usually the files that are used by default as a systemd settings.
Before starting make a copy just you happen to mess systemd.conf, e.g.:
cp -rpf /etc/systemd/logind.conf /etc/systemd/logind.conf_bak
To make the PC LID close active append in the end of file below 3 lines:
HandleSuspendKey=suspend
HandleLidSwitch=suspend
HandleLidSwitchDocked=suspend
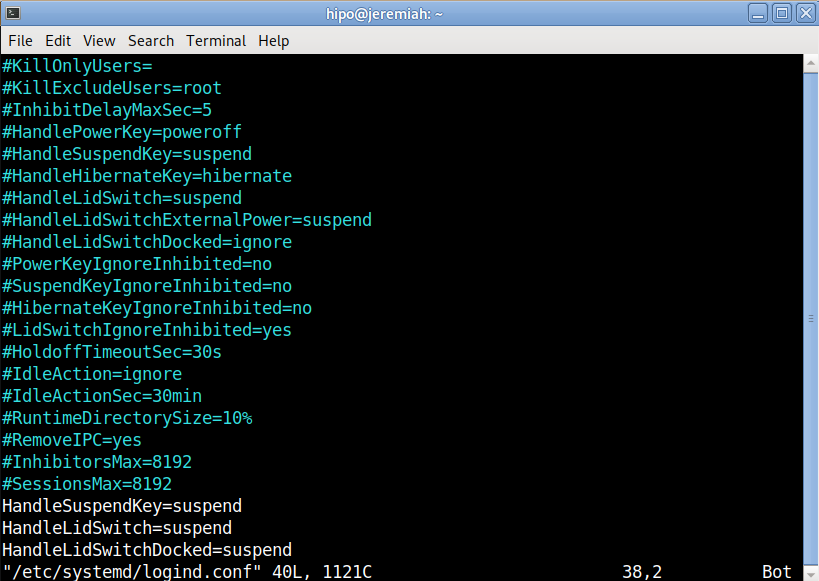
Save the file and to make systemd daemon reload restart the PC, even though theoretically systemd can be reloaded to digest its new /etc/systemd/logind.conf with:
# systemctl daemon-reexec
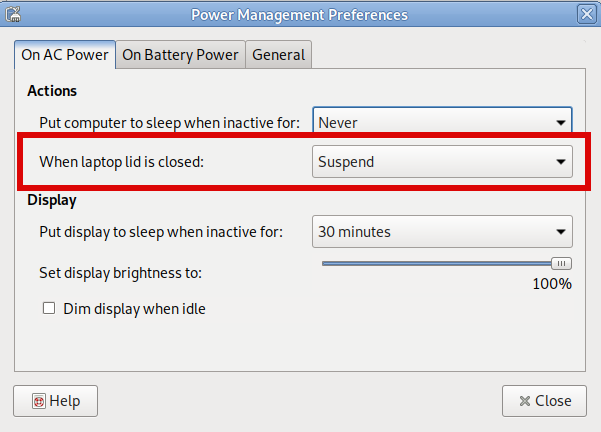
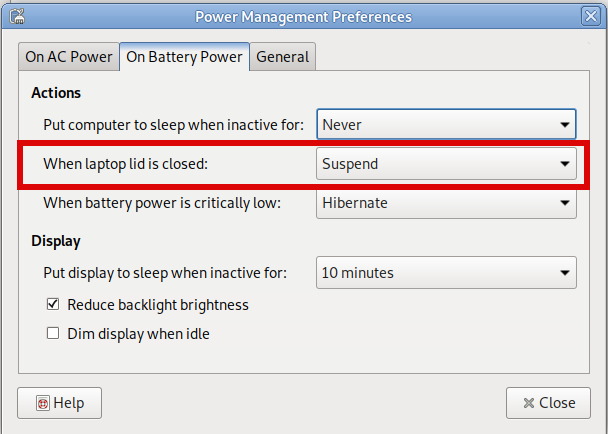
3. Assure yourself the Power Management LID setting of the Desktop Graphical User Interface are set to SUSPEND on close
I use MATE Desktop environment as it is simplistic and quite stable fork of GNOME 2.0, anyway depending on the GUI used on the Linux powered laptop e.g. GNOME / KDE Plasma / XFce etc. make sure the respective
Control Panel -> Power Management
settings are set to Force the Laptop Screen LID SUSPEND on Close.
Below is how this is done on MATE:
That's all folks, now close your Laptop and enjoy it going to sleep, open it up and get it awaked 🙂 Cheers !



 GANTTProject Chart
GANTTProject Chart  Planner GANTT Chone Chart
Planner GANTT Chone Chart  Task Juggler
Task Juggler