A very common problem that happens on both Linux installed servers and Desktop Linux is a starting to fill / (root partition). This problem could happen due to several reasons just to point few of them out of my experience low disk space (ending free space) could be due to:
– Improper initial partitioning / bad space planning / or OS install made in a hurry (due to time constrains)
– Linux installed on old laptop machine with low Hard Disk Drive capacity (e.g. 80 Giga / 160 GB)
– Custom user partitioning on install time aiming for a small root partition originally and changing space requirements in time
– Due to increasing space taken by Linux updates / user stored files etc / distribution OS Level upgrades dist-upgrades.
– Improperly assigned install time partitions cause of lack of knowledge to understand how partitioning is managed.
– Due to install being made in a hurry
– Linux OS installed on a Cloud based VPN (e.g. running) in a Cloud Instance that is hosted in Amazon EC2, Linode, Digital Ocean, Hostgator etc.
So here is a real time situation that happened me many times, you're launching an apt-get upgrade / apt-get dist-upgrade or yum upgrade the packages are about to start downloading or downloaded and suddenly you get a message of not enough disk space to apply OS package updates …
That's nasty stuff mostly irritating and here there are few approaches to take.
a. perhaps easiest you can ofcourse extend the partition (with a free spaced other Primary or Extended partition) with something like:
parted (the disk partitioning manipulator for Linux), gparted (in case if Desktop with GUI / XOrg server running)
b. if not enough space on the Hard Disk Drive or SSD (Solid State Drive) and you have a budget to buy and free laptop / PC slot to place another physical HDD to clone it to a larger sized HDD and use some kind of partition clone tool, such as:
- dd
- clonezilla
- rsync
- Mondo GPL Rescue Disaster recovery
- Fog – Free Open Source network computer cloning tool
or any of the other multiple clone tools available in Linux.
But what if you don't have the option for some reason to extend the paritiotn, how can you apply the Critical Security Errata Updates issued to patch security vulnerabilities reported by well known CVEs?
Well you can start with the obvious easy you can start removing unnecessery stuff from the system (if home is also stored on the / – root partiiton) to delete something from there, even delete the /usr/local/man pages if you don't plan to read it free some logs by archiving purging logs from /var/log/* …
But if this is not possible, a better approach is simply try to remove / purge any .deb / .rpm whatever distro package manager packages that are not necessery used and just hanging around, that is often the case especially on Linux installed on Notebooks for a personal home use, where with years you have installed a growing number of packages which you don't actively use but installed just to take a look, while hunting for Cool Linux games and you wanted to give a try to Battle of Wesnoth / FreeCIV / AlienArena / SuperTux Kart / TuxRacer etc. or some GUI heavy programs like Krita / Inskape / Audacity etc.
To select which package might be not needed and just takes space hence you need to to list all installed packages on the system ordered by their size this is different in Debian based Linuces e.g. – Debian GNU / Linux / Ubuntu / Mint etc. and RPM based ones Fedora / CentOS / OpenSuSE
1. List all RPM installed packages by Size on CentOS / SuSE
Finding how much space each of the installed rpm packages take on the HDD and displaying them in a sorted order is done with:
rpm -qa –queryformat '%10{size} – %-25{name} \t %{version}\n' | sort -n
From the command above, the '%10{size}' option aligns the size of the package to the right with a padding of 10 characters. The '%-25{name} aligns the name of the package to the left, padded to 25 characters. The '%{version} indicates the version and 'sort -n' flag sorts the packages according to size from the smallest to the largest in bytes.
2. List all installed RPM packages sorted by size on Fedora
Fedora has introduced the dnf package manager instead of yum, to get how much size individual rpm package occupies on system:
dnf info samba
Available Packages
Name : samba
Arch : x86_64
Epoch : 2
Version : 4.1.20
Release : 1.fc21
Size : 558 k
Repo : updates
Summary : Server and Client software to interoperate with Windows machines
URL : http://www.samba.org/
License : GPLv3+ and LGPLv3+
Description : Samba is the standard Windows interoperability suite of programs
: for Linux and Unix.
To get a list of all packages on system with their size
dnf info * | grep -i "Installed size" |sort -n
3. List all installed DEB packages on Debian / Ubuntu / Mint etc. with dpkg / aptitude / apt-get and wajig
The most simple way to get a list of largest packages is through dpkg
# dpkg-query -Wf '${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -n
brscan4
6 default-jre
6 libpython-all-dev
6 libtinfo-dev
6 python-all
6 python-all-dev
6 task-cinnamon-desktop
6 task-cyrillic
6 task-desktop
6 task-english
6 task-gnome-desktop
6 task-laptop
6 task-lxde-desktop
6 task-mate-desktop
6 task-print-server
6 task-ssh-server
6 task-xfce-desktop
8 mysql-client
8 printer-driver-all
…
…
207766 libwine
215625 google-chrome-stable
221908 libwine
249401 frogatto-data
260717 linux-image-4.19.0-5-amd64
262512 linux-image-4.19.0-6-amd64
264899 mame
270589 fonts-noto-extra
278903 skypeforlinux
480126 metasploit-framework
above cmd displays packages in size order, largest package last, but the output will include also size of packages, that used to exist,
have been removed but was not purged. Thus if you find a package that is shown as very large by size but further dpkg -l |grep -i package-name shows package as purged e.g. package state is not 'ii' but 'rc', the quickest work around is to purge all removed packages, that are still not purged and have some configuration remains and other chunks of data that just take space for nothing with:
# dpkg –list |grep "^rc" | cut -d " " -f 3 | xargs sudo dpkg –purge
Be cautious when you execute above command, because if for some reason you uninstalled a package with the idea to keep old configuration files only and in case if you decide to use it some time in future to reuse already custom made configs but do run above purge commands all such package saved kept configs will disappear.
For people who don't want to mess up with, uninstalled but present packages use this to filter out ready to be purged state packages.
# dpkg-query -Wf '${db:Status-Status} ${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sed -ne 's/^installed //p'|sort -n
aptitude – (high level ncurses interface like to package management) can also be easily used to list largest size packages eating up your hard drive in both interactive or cli mode, like so:
# aptitude search –sort '~installsize' –display-format '%p %I' '~i' | head
metasploit-framework 492 MB
skypeforlinux 286 MB
fonts-noto-extra 277 MB
mame 271 MB
linux-image-4.19.0-6-amd64 269 MB
linux-image-4.19.0-5-amd64 267 MB
frogatto-data 255 MB
libwine 227 MB
google-chrome-stable 221 MB
libwine:i386 213 MB
- –sort is package sort order, and ~installsize specifies a package sort policy.
- installsize means 'sort on (estimated) installed size', and the preceding ~ means sort descending (since default for all sort policies is ascending).
- –display-format changes the <you guessed :->. The format string '%p %I' tells aptitude to output package name, then installed size.
- '~i' tells aptitude to search only installed packages.
How much a certain .deb package removal will free up on the disk can be seen with apt-get as well to do so for the famous 3D acceleration Graphic Card (enabled) or not test game extremetuxracer:
# apt-get –assume-no –purge remove "texlive*" | grep "be freed" |
awk '{print $4, $5}'
Perhaps, the easiest to remember and more human readable output biggest packages occupied space on disk is to install and use a little proggie called wajig to do so
# apt install –yes wajig
Here is how to pick up 10 biggest size packages.
root@jeremiah:/home/hipo# wajig large|tail -n 10
fonts-noto-cjk-extra 204,486 installed
google-chrome-stable 215,625 installed
libwine 221,908 installed
frogatto-data 249,401 installed
linux-image-4.19.0-5-amd64 260,717 installed
linux-image-4.19.0-6-amd64 262,512 installed
mame 264,899 installed
fonts-noto-extra 270,589 installed
skypeforlinux 278,903 installed
metasploit-framework 480,126 installed
As above example lists a short package name and no description for those who want get more in depth knowledge on what exactly is the package bundle used for use:
# aptitude search –sort '~installsize' –display-format '%30p %I %r %60d' '~i' |head
%30p %I %r %60d display more information in your format string, or change field widths, enhanced format string
Meaning of parameters is:
- %30p : package name in field width=30 char
- %I : estimated install size
- %r : 'reverse depends count': approximate number of other installed packages which depend upon this package
- %60d : package's short description in field width=60 char
wajig is capable is a python written and idea is to easify Debian console package management (so you don't have to all time remember when and with which arguments to use apt-get / apt-cache etc.), below is list of commands it accepts.
root@jeremiah:/home/hipo## wajig commands
addcdrom Add a Debian CD/DVD to APT's list of available sources
addrepo Add a Launchpad PPA (Personal Package Archive) repository
aptlog Display APT log file
autoalts Mark the Alternative to be auto-set (using set priorities)
autoclean Remove no-longer-downloadable .deb files from the download cache
autodownload Do an update followed by a download of all updated packages
autoremove Remove unused dependency packages
build Get source packages, unpack them, and build binary packages from them.
builddeps Install build-dependencies for given packages
changelog Display Debian changelog of a package
clean Remove all deb files from the download cache
contents List the contents of a package file (.deb)
dailyupgrade Perform an update then a dist-upgrade
dependents Display packages which have some form of dependency on the given package
describe Display one-line descriptions for the given packages
describenew Display one-line descriptions of newly-available packages
distupgrade Comprehensive system upgrade
download Download one or more packages without installing them
editsources Edit list of Debian repository locations for packages
extract Extract the files from a package file to a directory
fixconfigure Fix an interrupted install
fixinstall Fix an install interrupted by broken dependencies
fixmissing Fix and install even though there are missing dependencies
force Install packages and ignore file overwrites and depends
hold Place packages on hold (so they will not be upgraded)
info List the information contained in a package file
init Initialise or reset wajig archive files
install Package installer
installsuggested Install a package and its Suggests dependencies
integrity Check the integrity of installed packages (through checksums)
large List size of all large (>10MB) installed packages
lastupdate Identify when an update was last performed
listall List one line descriptions for all packages
listalternatives List the objects that can have alternatives configured
listcache List the contents of the download cache
listcommands Display all wajig commands
listdaemons List the daemons that wajig can start, stop, restart, or reload
listfiles List the files that are supplied by the named package
listhold List packages that are on hold (i.e. those that won't be upgraded)
listinstalled List installed packages
listlog Display wajig log file
listnames List all known packages; optionally filter the list with a pattern
listpackages List the status, version, and description of installed packages
listscripts List the control scripts of the package of deb file
listsection List packages that belong to a specific section
listsections List all available sections
liststatus Same as list but only prints first two columns, not truncated
localupgrade Upgrade using only packages that are already downloaded
madison Runs the madison command of apt-cache
move Move packages in the download cache to a local Debian mirror
new Display newly-available packages
newdetail Display detailed descriptions of newly-available packages
news Display the NEWS file of a given package
nonfree List packages that don't meet the Debian Free Software Guidelines
orphans List libraries not required by any installed package
policy From preferences file show priorities/policy (available)
purge Remove one or more packages and their configuration files
purgeorphans Purge orphaned libraries (not required by installed packages)
purgeremoved Purge all packages marked as deinstall
rbuilddeps Display the packages which build-depend on the given package
readme Display the README file(s) of a given package
recdownload Download a package and all its dependencies
recommended Display packages installed as Recommends and have no dependents
reconfigure Reconfigure package
reinstall Reinstall the given packages
reload Reload system daemons (see LIST-DAEMONS for available daemons)
remove Remove packages (see also PURGE command)
removeorphans Remove orphaned libraries
repackage Generate a .deb file from an installed package
reportbug Report a bug in a package using Debian BTS (Bug Tracking System)
restart Restart system daemons (see LIST-DAEMONS for available daemons)
rpm2deb Convert an .rpm file to a Debian .deb file
rpminstall Install an .rpm package file
search Search for package names containing the given pattern
searchapt Find nearby Debian package repositories
show Provide a detailed description of package
sizes Display installed sizes of given packages
snapshot Generates a list of package=version for all installed packages
source Retrieve and unpack sources for the named packages
start Start system daemons (see LIST-DAEMONS for available daemons)
status Show the version and available versions of packages
statusmatch Show the version and available versions of matching packages
stop Stop system daemons (see LISTDAEMONS for available daemons)
tasksel Run the task selector to install groups of packages
todo Display the TODO file of a given package
toupgrade List versions of upgradable packages
tutorial Display wajig tutorial
unhold Remove listed packages from hold so they are again upgradeable
unofficial Search for an unofficial Debian package at apt-get.org
update Update the list of new and updated packages
updatealternatives Update default alternative for things like x-window-manager
updatepciids Updates the local list of PCI ids from the internet master list
updateusbids Updates the local list of USB ids from the internet master list
upgrade Conservative system upgrade
upgradesecurity Do a security upgrade
verify Check package's md5sum
versions List version and distribution of given packages
whichpackage Search for files matching a given pattern within packages
4. List installed packages order by size in Arch Linux
ArchLinux is using the funny named package manager – pacman (a nice prank for the good old arcade game).
What is distinctive of pacman uses libalpm (Arch Linux Package Management (ALPM) library) as a back-end to perform all the actions.
# pacman -Qi | awk '/^Name/{name=$3} /^Installed Size/{print $4$5, name}' | sort -hr | head -25
296.64MiB linux-firmware
144.20MiB python
105.43MiB gcc-libs
72.90MiB python2
66.91MiB linux
57.47MiB perl
45.49MiB glibc
35.33MiB icu
34.68MiB git
30.96MiB binutils
29.95MiB grub
18.96MiB systemd
13.94MiB glib2
13.79MiB coreutils
13.41MiB python2-boto
10.65MiB util-linux
9.50MiB gnupg
8.09MiB groff
8.05MiB gettext
7.99MiB texinfo
7.93MiB sqlite
7.15MiB bash
6.50MiB lvm2
6.43MiB openssl
6.33MiB db
There is another mean to list packages by size using a ArchLinux tool called pacgraph
# pacgraph -c | head -25
Autodetected Arch.
Loading package info
Total size: 1221MB
367MB linux
144MB pacgraph
98MB cloud-init
37MB grub
35MB icu
34MB git
31698kB binutils
19337kB pacman
11029kB man-db
8186kB texinfo
8073kB lvm2
7632kB nano
7131kB openssh
5735kB man-pages
3815kB xfsprogs
3110kB sudo
3022kB wget
2676kB tar
2626kB netctl
1924kB parted
1300kB procps-ng
1248kB diffutils
4. Debian Goodies
Most debian users perhaps never hear of debian-goodies package, but I thought it is worthy to mention it as sooner or later as a sysadmin or .deb based Desktop user it might help you somewhere.
Debian-goodies is sall toolbox-style utilities for Debian systems
These programs are designed to integrate with standard shell tools,
extending them to operate on the Debian packaging system.
.
dglob – Generate a list of package names which match a pattern
[dctrl-tools, apt*, apt-file*, perl*]
dgrep – Search all files in specified packages for a regex
[dctrl-tools, apt-file (both via dglob)]
.
These are also included, because they are useful and don't justify
their own packages:
.
check-enhancements
– find packages which enhance installed packages [apt,
dctrl-tools]
checkrestart
– Help to find and restart processes which are using old versions
of upgraded files (such as libraries) [python3, procps, lsof*]
debget – Fetch a .deb for a package in APT's database [apt]
debman – Easily view man pages from a binary .deb without extracting
[man, apt* (via debget)]
debmany – Select manpages of installed or uninstalled packages [man |
sensible-utils, whiptail | dialog | zenity, apt*, konqueror*,
libgnome2-bin*, xdg-utils*]
dhomepage – Open homepage of a package in a web browser [dctrl-tools,
sensible-utils*, www-browser* | x-www-browser*]
dman – Fetch manpages from online manpages.debian.org service [curl,
man, lsb-release*]
dpigs – Show which installed packages occupy the most space
[dctrl-tools]
find-dbgsym-packages
– Get list of dbgsym packages from core dump or PID [dctrl-tools,
elfutils, libfile-which-perl, libipc-system-simple-perl]
popbugs – Display a customized release-critical bug list based on
packages you use (using popularity-contest data) [python3,
popularity-contest]
which-pkg-broke
– find which package might have broken another [python3, apt]
which-pkg-broke-build
– find which package might have broken the build of another
[python3 (via which-pkg-broke), apt]
Even simpler by that is to use dpigs shell script part of the debian-goodies package which will automatically print out the largest packages.
dpigs command output is exactly the same as 'dpkg-query -Wf '${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -nr | head', but is useful cause you don't have to remember that complex syntax.
5. Checking where your space is gone in a Spacesniffer like GUI manner with Baobab
In my prior article Must have software on a new installed Windows 2 of the of the precious tools to set are Spacesniffer and WinDirStat.
Windows users will be highly delighted to know that SpaceSniffer equivallent is already present on Linux – say hello baobab.
Baobab is simple but useful Graphic disk usage overview program for those who don't want to mess to much with the console / terminal to find out which might be the possible directory candidate for removal. It is very simplistic but it does well what it is aimed for, to install it on a Debian or .deb based OS.
# apt install –yes baobab
baobab Linux Hard Disk Usage Analyzer for GNOME. – It can easily scan either the whole filesystem or a specific user-requested branch (Iocal or remote)
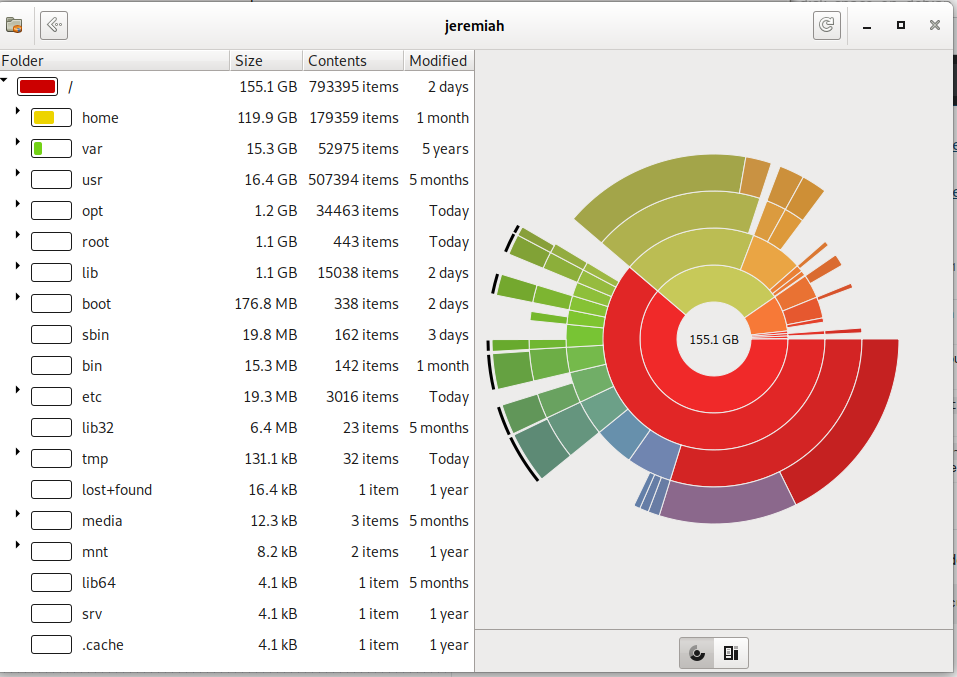
Baobab / (root) directory statistics Rings Chart pie
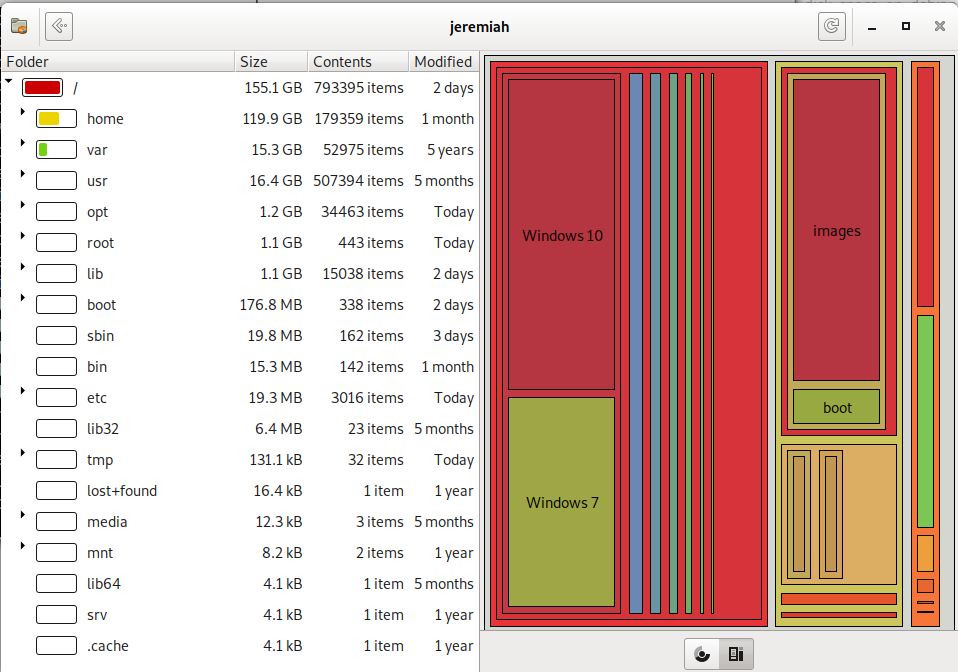
baobab – Treemap Chart for directory usage sorted by size on disk
!!! Note that before removing any files found as taking up too much space with baobab – make sure this files are not essential parts of a .deb package first, otherwise you might break up your system !!!
KDE (Plasma) QT library users could use Qdirstat instead of baobab
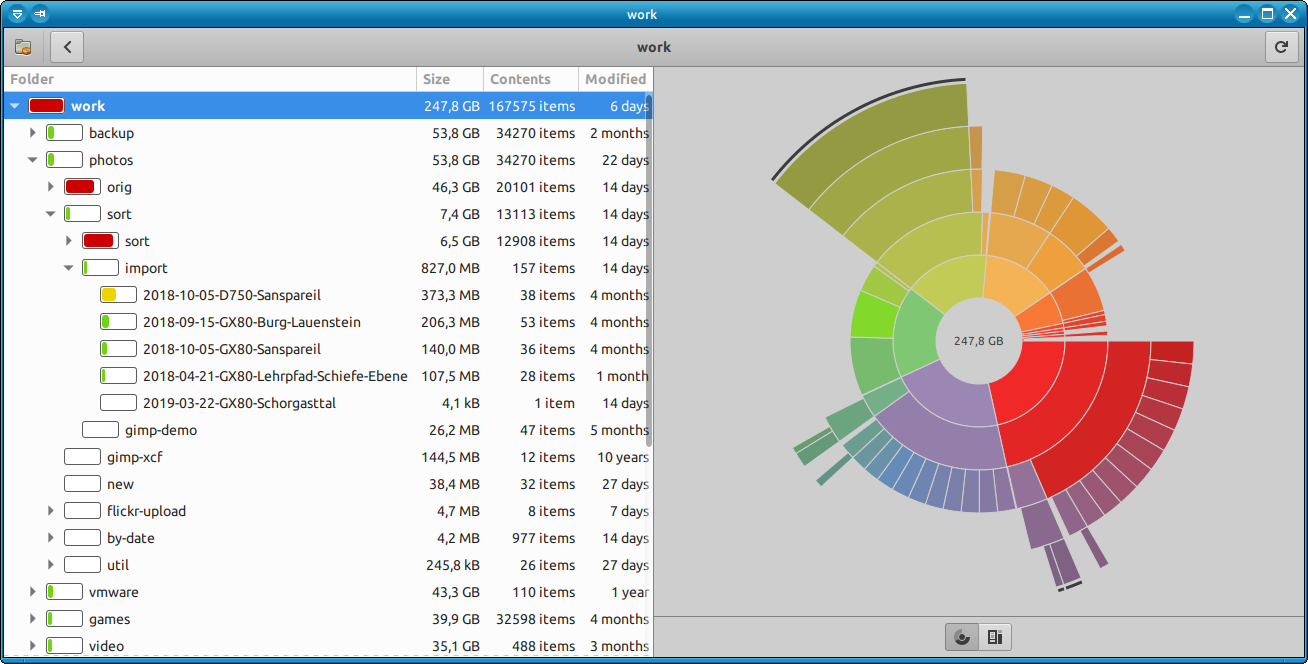
6. Use ncdu or duper perl script tool to generate directory disk usage in ASCII chart bar
ncdu and duper are basicly the same except one is using ncurses and is interactive in a very simplistic interface with midnight commander.
# apt install –yes ncdu
# ncdu /root
# apt-get install –yes durep
# durep -td 1 /usr
[ /usr 14.4G (0 files, 11 dirs) ]
6.6G [############# ] 45.54% lib/
5.5G [########### ] 38.23% share/
1.1G [## ] 7.94% bin/
552.0M [# ] 3.74% local/
269.2M [ ] 1.83% games/
210.4M [ ] 1.43% src/
88.9M [ ] 0.60% libexec/
51.3M [ ] 0.35% sbin/
41.2M [ ] 0.28% include/
8.3M [ ] 0.06% lib32/
193.8K [ ] 0.00% lib64/
Conclusion
In this article, I've shortly explained the few approach you can take to handle low disk space preventing you to update a regular security updates on Linux.
The easiest one is to clone your drive to a bigger (larger) sized SATA HDD or SDD Drive or using a free space left on a hard drive to exnted the current filling up the root partition.
Further, I looked through the common reasons for endind with a disk being low spaced and a quick work around to free disk space through listing and purging larges sized package, this is made differently in different Linux distributions, because different Linux has different package managers. As I'm primary using Debian, I explained thoroughfully on how this is achieved with apt-get / dpkg-query / dpkg / aptitude and the little known debian-goodies .deb package manager helper pack. For GUI Desktop users there is baobab / qdirstat. ASCII lovers could enjoy durep and ncdu.
That's all folks hope you enjoyed and learned something new. If you know of other cool tools or things this article is missing please share.