I've just installed the phpbb forum on a Debian Linux because we needed a goodquick to install communication media in order to improve our internal communication in a student project in Strategic HR we're developing right now in Arnhem Business School.
Here are the exact steps I followed to have a properly it properly instlled:
1. Install the phpbb3 debian package
This was pretty straight forward:
debian:~# apt-get install phpbb3
At this point of installation I've faced a dpkg-reconfigure phpbb deb package configuration issue:
I was prompted to pass in the credentials for my MySQL password right after I've selected the MySQL as my preferred database back engine.
I've feeded my MySQL root password as well as my preferred forum database name, however the database installation failed because, somehow the configuration procedure tried to connect to my MySQL database with the htcheck user.
I guess this has to be a bug in the package itself or something from my previous installation misconfigured the way the debian database backend configuration was operating.
My assumption is that my previously installed htcheck package or something beforehand I've done right after the htcheck and htcheck-php packages installation.
after the package configuration failed still the package had a status of properly installed when I reviewed it with dpkg
I've thought about trying to manually reconfigure it using the dpkg-reconfigure debian command and I gave it a try like that:
debian:~# dpkg-reconfigure phpbb3
This time along with the other fields I've to fill in the ncurses interface I was prompted for a username before the password prompted appeared.
Logically I tried to fill in the root as it's my global privileges MySQL allowed user.
However that didn't helped at all and again the configuration tried to send the credentials with user htcheck to my MySQL database server.
To deal with the situation I had to approach it in the good old manual way.
2. Manually prepare / create the required phpbb forum database
To completet that connected to the MySQL server with the mysql client and created the proper database like so:
debian:~# mysql -u root -p
mysql>
CREATE database phpbb3forum;
3. Use phpmyadmin or the mysql client command line to create a new user for the phpbb forum
Here since adding up the user using the phpmyadmin was a way easier to do I decided to go that route, anyways using the mysql cli is also an option.
From phpmyadmin It's pretty easy to add a new user and grant privileges to a certain database, to do so navigate to the following database:
Privileges -> -> Add a new user ->
Now type your User name: , Host , Password , Re-type password , also for a Host: you have to choose Local from the drop down menu.
Leave the Database for user field empty as we have already previously created our desired database in step 2 of this article
Now press the "Go" button and the user will get created.
Further after choose the Privileges menu right on the bottom of the page once again, select through the checkbox the username you have just created let's say the previously created user is phpbb3
Go to Action (There is a picture with a man and a pencil on the right side of this button
Scroll down to the page part saying Database-specific privileges and in the field Add privileges on the following database: fill in your previosly created database name in our case it's phpbb3forum
and then press the "Go" button once again.
A page will appear where you will have to select the exact privileges you would like to grant on the specific selected database.
For some simplicity just check all the checkbox to grant as many privilegs to your database as you could.
Then again you will have to press the "Go" button and there you go you should have already configured an username and database ready to go with your new phpbb forum.
4. Create a virtualhost if you would like to have the forum as a subdomain or into a separate domain
If you decide to have the forum on a separate sub-domain or domain as I did you will have to add some kind of Virtualhost into either your Apache configuration /etc/apache2/apache2.conf or into where officially the virutualhosts are laid in Debian Linux in /etc/apache2/sites-available
I've personally created a new file like for instance /etc/apache2/sites-available/mysubdomain.mydomain.com
Here is an example content of the new Virtualhost:
<VirtualHost *>
ServerAdmin admin-email@domain.com
ServerName mysubdomain.domain.com
# Indexes + Directory Root.
DirectoryIndex index.php index.php5 index.htm index.html index.pl index.cgi index.phtml index.jsp index.py index.asp
DocumentRoot /usr/share/phpbb3/www/
# Logfiles
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/yourdomain/error.log
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/yourdomain/access.log combined
# CustomLog /dev/null combined
<Directory /usr/share/phpbb3/www/>
Options FollowSymLinks MultiViews -Includes ExecCGI
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
allow from all </Directory>
</VirtualHost>
In above Virtualhost just change the values for ServerAdmin , ServerName , DocumentRoot , ErrorLog , CustomLog and Directory declaration to adjust it to your situation.
5. Restart the Apache webserver for the new Virtualhost to take affect
debian:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Now accessing your http://mysubdomain.domain.com should display the installed phpbb3 forum
The default username and password for your forum you can use straight are:
username: admin
password: admin
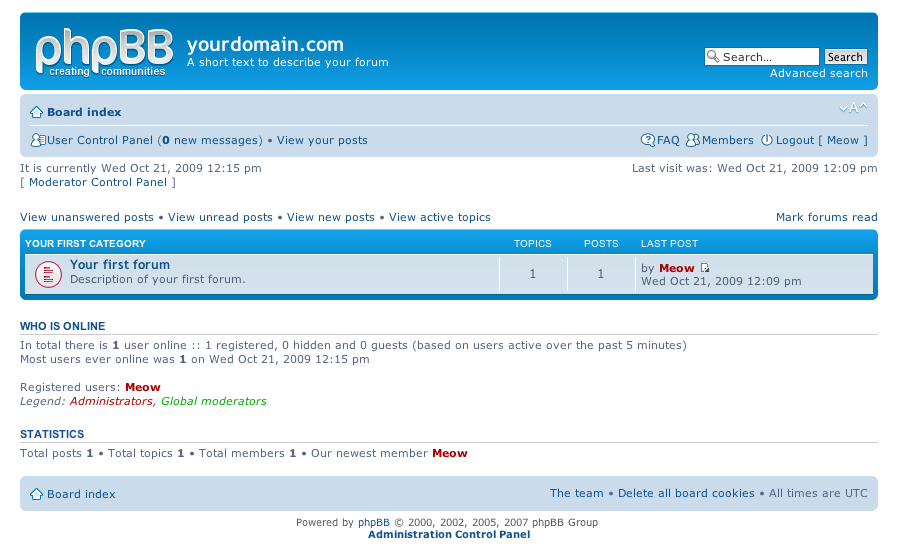
So far so good you by now have the PHPBB3 forum properly installed and running, however if you try to Register a new user in the forum you will notice that it's impossible because of a terrible ugly message reading:
Sorry but this board is currently unavailable.
I've spend few minutes online to scrape through the forums before I can understand what I have to stop that annoying message from appearing and allow new users to register in the phpbb forum
The solution came natural and was a setting that had to be changed with the forum admin account, thus login as admin and look at the bottom of the page, below the text reading Powered by phpBB © 2000, 2002, 2005, 2007 phpBB Group you will notice a link with Administration Control Panel
just press there a whole bunch of menus will appear on the screen allowing you to do numerous things, however what you will have to do is go to
Board Settings -> Disable Board
and change the radio button there to say No
That's all now your forum will be ready to go and your users can freely register and if the server where the forum is installed has an already running mail server, they will receive an emails with a registration data concerning their new registrations in your new phpbb forum.
Cheers and Enjoy your new shiny phpbb Forum 🙂











Linux: Howto Disable logging for all VirtualHosts on Apache and NGINX Webservers one liner
Wednesday, July 1st, 2020Did you happen to administer Apache Webservers or NGINX webservers whose logs start to grow so rapidly that are flooding the disk too quickly?
Well this happens sometimes and it also happens that sometimes you just want to stop logging especially, to offload disk writting.
There is an easy way to disable logging for requests and errors (access_log and error_log usually residing under /var/log/httpd or /var/log/nginx ) for all configured Virtual Domains with a short one liner, here is how.
Before you start Create backup of /etc/apache2/sites-enabled / or /etc/nginx to be able to revert back to original config.
1. Disable Logging for All Virtual Domains configured for Apache Webserver
First lets print what the command will do to make sure we don't mess something
You will get some output like
2. Disable Logging for All configured Virtual Domains for NGINX Webserver
f course above substituations that will comment out with '#' occurances from file configs of only default set access_log and error_log / access.log, error.log
for machines where there is no certain convention on file naming and there are multiple domains in custom produced named log files this won't work.
This one liner was inspired from a friend's daily Martin Petrov. Martin blogged initially about this nice tip for those reading Cyrillic check out mpetrov.net, so. Thanks Marto ! 🙂
Tags: about, access, ALL, and, apache, apache webserver, apache webservers, apache2, are, BACK, blogged, check, command, Comment, config, configured, convention, course, create, custom
Posted in Everyday Life, Nginx, Web and CMS | No Comments »