Posts Tagged ‘copy’
Thursday, June 30th, 2011 
Recently has become publicly known for the serious hole found in all Apache webserver versions 1.3.x and 2.0.x and 2.2.x. The info is to be found inside the security CVE-2011-3192 – https://issues.apache.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=51714
Apache remote denial of service is already publicly cirtuculating, since about a week and is probably to be used even more heavily in the 3 months to come. The exploit can be obtained from exploit-db.com a mirror copy of #Apache httpd Remote Denial of Service (memory exhaustion) is for download here
The DoS script is known in the wild under the name killapache.pl
killapache.pl PoC depends on perl ForkManager and thus in order to be properly run on FreeBSD, its necessery to install p5-Parallel-ForkManager bsd port :
freebsd# cd /usr/ports/devel/p5-Parallel-ForkManager
freebsd# make install && make install clean
...
Here is an example of the exploit running against an Apache webserver host.
freebsd# perl httpd_dos.pl www.targethost.com 50
host seems vuln
ATTACKING www.targethost.com [using 50 forks]
:pPpPpppPpPPppPpppPp
ATTACKING www.targethost.com [using 50 forks]
:pPpPpppPpPPppPpppPp
...
In about 30 seconds to 1 minute time the DoS attack with only 50 simultaneous connections is capable of overloading any vulnerable Apache server.
It causes the webserver to consume all the machine memory and memory swap and consequently makes the server to crash in most cases.
During the Denial of Service attack is in action access the websites hosted on the webserver becomes either hell slow or completely absent.
The DoS attack is quite a shock as it is based on an Apache range problem which started in year 2007.
Today, Debian has issued a new versions of Apache deb package for Debian 5 Lenny and Debian 6, the new packages are said to have fixed the issue.
I assume that Ubuntu and most of the rest Debian distrubtions will have the apache's range header DoS patched versions either today or in the coming few days.
Therefore work around the issue on debian based servers can easily be done with the usual apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
On other Linux systems as well as FreeBSD there are work arounds pointed out, which can be implemented to close temporary the Apache DoS hole.
1. Limiting large number of range requests
The first suggested solution is to limit the lenght of range header requests Apache can serve. To implement this work raround its necessery to put at the end of httpd.conf config:
# Drop the Range header when more than 5 ranges.
# CVE-2011-3192
SetEnvIf Range (?:,.*?){5,5} bad-range=1
RequestHeader unset Range env=bad-range
# We always drop Request-Range; as this is a legacy
# dating back to MSIE3 and Netscape 2 and 3.
RequestHeader unset Request-Range
# optional logging.
CustomLog logs/range-CVE-2011-3192.log common env=bad-range
CustomLog logs/range-CVE-2011-3192.log common env=bad-req-range
2. Reject Range requests for more than 5 ranges in Range: header
Once again to implement this work around paste in Apache config file:
This DoS solution is not recommended (in my view), as it uses mod_rewrite to implement th efix and might be additionally another open window for DoS attack as mod_rewrite is generally CPU consuming.
# Reject request when more than 5 ranges in the Range: header.
# CVE-2011-3192
#
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP:range} !(bytes=[^,]+(,[^,]+){0,4}$|^$)
# RewriteCond %{HTTP:request-range} !(bytes=[^,]+(?:,[^,]+){0,4}$|^$)
RewriteRule .* - [F]
# We always drop Request-Range; as this is a legacy
# dating back to MSIE3 and Netscape 2 and 3.
RequestHeader unset Request-Range
3. Limit the size of Range request fields to few hundreds
To do so put in httpd.conf:
LimitRequestFieldSize 200
4. Dis-allow completely Range headers: via mod_headers Apache module
In httpd.conf put:
RequestHeader unset Range
RequestHeader unset Request-Range
This work around could create problems on some websites, which are made in a way that the Request-Range is used.
5. Deploy a tiny Apache module to count the number of Range Requests and drop connections in case of high number of Range: requests
This solution in my view is the best one, I've tested it and I can confirm on FreeBSD works like a charm.
To secure FreeBSD host Apache, against the Range Request: DoS using mod_rangecnt, one can literally follow the methodology explained in mod_rangecnt.c header:
freebsd# wget http://people.apache.org/~dirkx/mod_rangecnt.c
..
# compile the mod_rangecnt modulefreebsd# /usr/local/sbin/apxs -c mod_rangecnt.c
...
# install mod_rangecnt module to Apachefreebsd# /usr/local/sbin/apxs -i -a mod_rangecnt.la
...
Finally to load the newly installed mod_rangecnt, Apache restart is required:
freebsd# /usr/local/etc/rc.d/apache2 restart
...
I've tested the module on i386 FreeBSD install, so I can't confirm this steps works fine on 64 bit FreeBSD install, I would be glad if I can hear from someone if mod_rangecnt is properly compiled and installed fine also on 6 bit BSD arch.
Deploying the mod_rangecnt.c Range: Header to prevent against the Apache DoS on 64 bit x86_amd64 CentOS 5.6 Final is also done without any pitfalls.
[root@centos ~]# uname -a;
Linux centos 2.6.18-194.11.3.el5 #1 SMP Mon Aug 30 16:19:16 EDT 2010 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
[root@centos ~]# /usr/sbin/apxs -c mod_rangecnt.c
...
/usr/lib64/apr-1/build/libtool --silent --mode=link gcc -o mod_rangecnt.la -rpath /usr/lib64/httpd/modules -module -avoid-version mod_rangecnt.lo
[root@centos ~]# /usr/sbin/apxs -i -a mod_rangecnt.la
...
Libraries have been installed in: /usr/lib64/httpd/modules
...
[root@centos ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd configtest
Syntax OK
[root@centos ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart
Stopping httpd: [ OK ]
Starting httpd: [ OK ]
After applying the mod_rangecnt patch if all is fine the memory exhaustion perl DoS script's output should be like so:
freebsd# perl httpd_dos.pl www.patched-apache-host.com 50
Host does not seem vulnerable
All of the above pointed work-arounds are only a temporary solution to these Grave Apache DoS byterange vulnerability , a few days after the original vulnerability emerged and some of the up-pointed work arounds were pointed. There was information, that still, there are ways that the vulnerability can be exploited.
Hopefully in the coming few weeks Apache dev team should be ready with rock solid work around to the severe problem.
In 2 years duration these is the second serious Apache Denial of Service vulnerability after before a one and a half year the so called Slowloris Denial of Service attack was capable to DoS most of the Apache installations on the Net.
Slowloris, has never received the publicity of the Range Header DoS as it was not that critical as the mod_range, however this is a good indicator that the code quality of Apache is slowly decreasing and might need a serious security evaluation.
Tags: apache httpd, apache server, apache webserver, ATTACKING, bugzilla, CentOS, com, config, copy, CustomLog, deb package, denial of service, denial of service attack, dos attack, dos script, download, exploit, freebsd, host, HTTP, info, machine memory, memory exhaustion, minute time, mirror copy, mod, necessery, Netscape, number, perl httpd, poc, pPpPpppPpPPppPpppPp, REJECT, Remote, RewriteCond, script, simultaneous connections, work
Posted in Computer Security, Linux, System Administration | No Comments »
Saturday, March 3rd, 2012 I've recently had to make a copy of one /usr/local/nginx directory under /usr/local/nginx-bak, in order to have a working copy of nginx, just in case if during my nginx update to new version from source mess ups.
I did not check the size of /usr/local/nginx , so just run the usual:
nginx:~# cp -rpf /usr/local/nginx /usr/local/nginx-bak
...
Execution took more than 20 seconds, so I check the size and figured out /usr/local/nginx/logs has grown to 120 gigabytes.
I didn't wanted to extra load the production server with copying thousands of gigabytes so I asked myself if this is possible with normal Linux copy (cp) command?. I checked cp manual e.g. man cp, but there is no argument like –exclude or something.
Even though the cp command exclude feature is not implemented by default there are a couple of ways to copy a directory with exclusion of subdirectories of files on G / Linux.
Here are the 3 major ones:
1. Copy directory recursively and exclude sub-directories or files with GNU tar
Maybe the quickest way to copy and exclude directories is through a littke 'hack' with GNU tar
nginx:~# mkdir /usr/local/nginx-new;
nginx:~# cd /usr/local/nginx#
nginx:/usr/local/nginx# tar cvf - \. --exclude=/usr/local/nginx/logs/* \
| (cd /usr/local/nginx-new; tar -xvf - )
Copying that way however is slow, in my case it fits me perfectly but for copying large chunks of data it is better not to use pipe and instead use regular tar operation + mv
# cd /source_directory
# tar cvf test.tar --exclude=dir_to_exclude/*\--exclude=dir_to_exclude1/* . \
# mv test.tar /destination_directory
# cd /destination# tar xvf test.tar
2. Copy folder recursively excluding some directories with rsync
P>eople who has experience with rsync , already know how invaluable this tool is. Rsync can completely be used as for substitute=de.a# rsync -av –exclude='path1/to/exclude' –exclude='path2/to/exclude' source destination
This example, can also be used as a solution to my copy nginx and exclude logs directory casus like so:
nginx:~# rsync -av --exclude='/usr/local/nginx/logs/' /usr/local/nginx/ /usr/local/nginx-new
As you can see for yourself, this is a way more readable for the tar, however it will not work on servers, where rsync is not installed and it is unusable if you have to do operations as a regular users on such for that case surely the GNU tar hack is more 'portable' across systems.
rsync has also Windows version and therefore, the same methodology should be working on MS Windows and good for batch scripting.
I've not tested it myself, yet as I've never used rsync on Windows, if someone has tried and it works pls drop me a short msg in comments.
3. Copy directory and exclude sub directories and files with find
Find in collaboration with cp can also be used to exclude certain directories while copying. Actually this method is better than the GNU tar hack and surely more efficient. For machines, where rsync is not installed it is just a perfect way to copy files from location to location, while excluding some directories, here is an example use of find and cp, for the above nginx case:
nginx:~# cd /usr/local/nginx
nginx:~# mkdir /usr/local/nginx
nginx:/usr/local/nginx# find . -type d \( ! -name logs \) -print -exec cp -rpf '{}' /usr/local/nginx-bak \;
This will find all directories inside /usr/local/nginx with find command print them on the screen, then execute recursive copy over each found directory and copy to /usr/local/nginx-bak
This example will work fine in the nginx case because /usr/local/nginx does not contain any files but only sub-directories. In other occwhere the directory does contain some files besides sub-directories the files had to also be copied e.g.:
# for i in $(ls -l | egrep -v '^d'); do\
cp -rpf $i /destination/directory
This will copy the files from source directory (for instance /usr/local/nginx/my_file.txt, /usr/local/nginx/my_file1.txt etc.), which doesn't belong to a subdirectory.
The cmd expression:
# ls -l | egrep -v '^d'
Lists only the files while excluding all the directories and in a for loop each of the files is copied to /destination/directory
If someone has better ideas, please share with me 🙂
Tags: argument, Auto, copy, copy cp, copy directory, copy folder, copying, destination directory, directory cd, Draft, eople, exclusion, feature, file, g man, gigabytes, gnu linux, gnu tar, linux linux, littke, location, man cp, mess, mess ups, msg, operation, p eople, production, production server, recursively, rpf, rsync, someone, something, source directory, subdirectories, substitute, tar cvf, tar xvf, test, tool, ups, xvf
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration | 2 Comments »
Tuesday, September 14th, 2010 I’ve recently received a number of images in JPEG format as a feedback on a project plan that was constructed by a team I’m participating at the university where I study.
Somebody from my project group has scanned or taken snapshots of each of the hard copy paper feedback and has sent it to my mail.
I’ve received 13 images so I had to open them one by one to get each of the Project Plan to read the feedback on the page this was really unhandy, so I decided to give it a try on how to generate a common PDF file from all my picture files.
Thanksfully it happened to be very easy and trivial using the good old Image Magick
In order to complete the task of generating one PDF from a number of pictures all I did was.1. Switch to the directory where I have saved all my jpeg images
debian:~# cd /home/hipo/Desktop/my_images_directory/
2. Use the convert binary part of imagemagick package to generate the actual PDF file from the group of images
debian:~# convert *.jpg outputpdffile.pdf
If the images are numbered and contain many scanned pages of course you can always pass by all the images to the /usr/bin/convert binary, like for instance:
debian:~# convert 1.jpg 2.jpg 3.jpg 4.jpg 5.jpg outputpdffile.pdf
Even though in my case I had to convert to PDF from multiple JPEG (JPG) pictures, convertion with convert is not restricted to convert only from JPEG, but you can also convert to PDF by using other graphical file formats.
For instance to convert multiple PNG pictures to a single PDF file the command will be absolutely the same except you change the file extension of the graphic files e.g.:
debian:~# convert 1.PNG 2.PNG 3.PNG 4.PNG 5.PNG OUTPUT-PDF-FILE.PDF
I was quite happy eventually to know Linux is so flexible and such a trivial things are able to be completed in such an easy way.
Tags: cd home, convertion, copy, course, Create PDF file from (jpg) pictures in Linux, Desktop, feedback, file, file extension, file formats, format, gif images, graphic files, hipo, home, Image, image magick, ImageMagick, images directory, instance, JPEG, jpeg images, jpg gif, Linux, Magick, mail, number, order, OUTPUT-PDF-FILE, outputpdffile, package, page, Paper, picture, png, project, project group, snapshots, somebody, switch, team, Thanksfully, trivial things, unhandy, usr, usr bin, way
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, Various | 5 Comments »
Monday, February 20th, 2012

Already on a couple of mail boxes located on one of the qmail powered mail servers I adminiter, there is an over QUOTA reached problem encountered.
Filling up the mailbox quota is not nice as mails starts get bounced back to the sender with a message QUOTA FULL or EXCEEDED MESSAGE, if this is a crucial mail waiting for some important data etc. the data is never received.
Below is a copy of the mail quota waarning notification message:
Delivered-To: email_use@my-mail-domain.net
Date: Wed, 15 Feb 2012 17:40:36 +0000
X-Comment: Rename/Copy this file to ~vpopmail/domains/.quotawarn.msg, and make appropriate changes
X-Comment: See README.quotas for more information
From: Mail Delivery System <Mailer-Daemon@different.bg>
Reply-To: email@www.pc-freak.net
To: Valued Customer:;
Subject: Mail quota warning
Mime-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=iso-8859-1
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit
>
Your mailbox on the server is now more than 90% full. So that you can continue
to receive mail you need to remove some messages from your mailbox.
As you can read from the copy of the mail message above, the message content sent to the mail owner whose quota is getting full is red from /var/vpopmail/domains/.quotawarn.msg
The mail reaching quota problem is very likely to appear in cases like low mailbox quota set, but sometimes also occurs due to bugs in vpopmail quota handling.
Various interesting configuration settings for mail quotas etc. are in /home/vpopmail/etc/vlimits.default file, (assuming vpopmail is installed in /home).
In my specific case, the default vpopmail mailbox quota size was set to only 40 Megabytes.
40MB is too low if compared to todays mailbox size standards which in Gmail and Yahoo mail services are already a couple of gigabytes.
Hence to get around the quota troubles, I removed the quota for the mail.
To remove the quota size in vpopmail set for address (email_user@my-mail-domain.net) used cmd:
qmail-server:~# vmoduser -q NOQUOTA email_user@my-mail-domain.net
To save myself from future quota issues, I decided to apply a permanent fix to all those over quota size VPOPMAIL mailbox problems by removing completely quota restriction for all mailboxes in my vpopmail existent mail domain.
To do so, I wrote a quick simple bash loop one-liner script:
qmail-server:~# cd /home/vpopmail/domains
qmail-server:~/vpopmail/domains# cd my-mail-domain.net
qmail-server:~/vpopmail/domains/my-mail-domain.net# for i in *; do \
vmoduser -q NOQUOTA $(echo $i|grep -v vpasswd)@my-mail-domain.net; \
done
This works only on vpopmail installations which are configured to store the mail messages directly on the filesystem. Therefore this approach will not work for people who during vpopmail install had configured it to store mailboxes in MySQL or in other kind of SQL db engine.
Anyways for Vpopmail installed to use SQL backend, the script can be changed to read directly a list with all the mailboxes obtained from databasae (SQL query) and then, loop over each of the mail addresses apply the vmoduser -q NOQUOTA mail@samplemaildomain.net.
I've written also a few lines shell script (remove_vpopmail_emails_domain_quota.sh), it accepts one argument which is a vpopmail domain to which the admin would like to reset all applied mailbox quotas. The script is useful, if you have to often remove all quotas for vpopmail domainsor have to do quota wipe out simultaneously for multiple email domain names located on different servers.
Tags: Auto, bit, charset, configuration settings, content transfer, copy, Date, Draft, EXCEEDED, file, free mail services, FULL, gigabytes, Gmail, information, ISO, mail boxes, mail delivery system, mail domain, mail message, mail owner, mail quota, mail quotas, mail server, mail servers, mail services, mailbox quota, mailbox size, megabytes, message, message quota, Mime, msg, msgThe, nbs, NOQUOTA, notification message, Qmail, quot, quota problem, README, Rename, script, sender, size, SQL, text, transfer, version, vpopmail
Posted in Qmail, System Administration | No Comments »
Monday, January 9th, 2012 I've recently had to set up a backup system to synchronize backup archive files between two remote servers and as I do usually with this situation I just set up a crontab job to periodically execute rsync to copy data from source server to the destination server . Copying SRC to DEST is the default behaviour rsync uses, however in this case I had to copy from the destination server to the source server host (in other words sync files the reversely.
The usual way to copy with rsync via SSH (from SRC to DEST) is using a cmd line like:
debian:~$ /usr/bin/rsync -avz -e ssh backup-user@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/home/backup-user/my-directory .
Where the xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is my remote server IP with which files are synched.
According to rsync manual, the proposed docs SYNOPSIS is in the format;
Local: rsync [OPTION…] SRC… [DEST
Obviusly the default way to use rsync is to copy source to destination which I used until now, but in this case I had to the other way around and copy files from a destination host to the source server. It was logical that swapping the SRC and DEST would complete my required task. Anyways I consulted with some rsync gurus in irc.freenode.net , just to make sure it is proper to just swap the SRC, DEST arguments.
I was told this is possible, so I swapped args;
debian:~$ /usr/bin/rsync -avz -e ssh . backup-user@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/home/backup-user/my-directory
...
Surprisingly this worked 😉 Anyways I was adviced by by a good guy nick named scheel , that putting -e ssh to command line is generally unnecessery except if there is no some uncommon used SSH port over which the data is transferred. An example case in which -e 'ssh is necessery would be if transferring via lets say SSH port 1234;
rsync -avz -e 'ssh -p1234' /source user@host:/dest
In all other cases omitting '-e ssh' is better as '-e ssh' is rsync default. Therefore my final swapped line I put in cron to copy from a destinatio to source host with rsync looked like so:
05 03 2 * * /usr/bin/ionice -c 3 /usr/bin/rsync -avz my-directory backup-user@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/home/backup-user/ >/dev/null 2>&1
Tags: archive files, Auto, avz, backup system, case, cmd, cmd line, copy, copying, cron, default, default behaviour, destIn, destinatio, destination, destination host, destination server, docs, Draft, example, example case, few words, format, gurus, host, job, nbsp, necessery, nick, option, port 1234, remote server, rsync, scheel, server host, server ip, source host, source server, ssh port, sync files, system, usr bin
Posted in FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration | No Comments »
Monday, November 14th, 2011 
These days more and more people start to forget the g* / Linux old times when we used to copy CDs from console using dd in conjunction with mkisofs .
Therefore to bring some good memories back of the glorious console times I decided to come up with this little post.
To copy a CD or DVD the first thing one should do is to make an image copy of the present inserted CD into the CD-drive with dd :
1. Make copy of the CD/DVD image using dd
# dd if=/dev/cdrom of=/tmp/mycd.iso bs=2048 conv=notrunc
/dev/cdrom is the location of the cdrom device, on many Linuces including (Debian) /dev/cdrom is just a link to the /dev/ which corresponds to the CD drive. Note on FreeBSD the location for the CD Drive is /dev/acd0
/tmp/mycd.iso instructs dd CD image creation to be placed in /tmp/ directory.
bs argument instructs it about the byte size portions by which the content of the CD-Drive inserted CD will be read. bs value of 2048 is actually only 2KB per dd read, increasing this value will decrease the time required for the CD image to be extracted.
2. Prepare CD image file to be ready for burning
After dd completes the image copy operation, next to prepare the extracted image / ISO to be ready for burning mkisofs is used:
# mkisofs -J -L -r -V TITLE -o /tmp/imagefile.iso /tmp/mycd.iso
The -J option makes the CD compatible for Pcs running Microsoft Windows. The -V TITLE option should be changed to whatever title the new CD should have, -r will add up status bar for the mkisofs operation.
-r is passed to create specific file permissions on the newly created CD, -o specifies the location where mkisofs will produce its file based on the CD image /tmp/mycd.iso .
3. Burning the mkisofs image file to a CD/DVD on GNU / Linux
linux:~# cdrecord -scanbus
linux:~# cdrecord dev=1,0,0 /tmp/imagefile.iso
If all wents okay with cdrecord operation, after a while the CD should be ready.
4. Burning the mkisofs image file to CD on FreeBSD
freebsd# burncd -f /dev/acd0 data /tmp/imagefile.iso fixate
Tags: argument, byte, byte size, cd image, CD-drive, cdrom, conv, copy, dd cd, drive, file, file permissions, freeb, gnu linux, Image, image copy, image creation, image file, image iso, imagefile, ISO, isoIf, linux cdrecord, linux linux, location, Microsoft, mkisofs, mycd, new cd, notrunc, operation, option, size, size portions, status, terminal, time, title option, tmp, value
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration, Various | 1 Comment »
Tuesday, August 30th, 2011 
Recently has become publicly known for the serious hole found in all Apache webserver versions 1.3.x and 2.0.x and 2.2.x. The info is to be found inside the security CVE-2011-3192 – https://issues.apache.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=51714
Apache remote denial of service is already publicly cirtuculating, since about a week and is probably to be used even more heavily in the 3 months to come. The exploit can be obtained from exploit-db.com a mirror copy of #Apache httpd Remote Denial of Service (memory exhaustion) is for download here
The DoS script is known in the wild under the name killapache.pl
killapache.pl PoC depends on perl ForkManager and thus in order to be properly run on FreeBSD, its necessery to install p5-Parallel-ForkManager bsd port :
freebsd# cd /usr/ports/devel/p5-Parallel-ForkManager
freebsd# make install && make install clean
...
Here is an example of the exploit running against an Apache webserver host.
freebsd# perl httpd_dos.pl www.targethost.com 50
host seems vuln
ATTACKING www.targethost.com [using 50 forks]
:pPpPpppPpPPppPpppPp
ATTACKING www.targethost.com [using 50 forks]
:pPpPpppPpPPppPpppPp
...
In about 30 seconds to 1 minute time the DoS attack with only 50 simultaneous connections is capable of overloading any vulnerable Apache server.
It causes the webserver to consume all the machine memory and memory swap and consequently makes the server to crash in most cases.
During the Denial of Service attack is in action access the websites hosted on the webserver becomes either hell slow or completely absent.
The DoS attack is quite a shock as it is based on an Apache range problem which started in year 2007.
Today, Debian has issued a new versions of Apache deb package for Debian 5 Lenny and Debian 6, the new packages are said to have fixed the issue.
I assume that Ubuntu and most of the rest Debian distrubtions will have the apache’s range header DoS patched versions either today or in the coming few days.
Therefore work around the issue on debian based servers can easily be done with the usual apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
On other Linux systems as well as FreeBSD there are work arounds pointed out, which can be implemented to close temporary the Apache DoS hole.
1. Limiting large number of range requests
The first suggested solution is to limit the lenght of range header requests Apache can serve. To implement this work raround its necessery to put at the end of httpd.conf config:
# Drop the Range header when more than 5 ranges.
# CVE-2011-3192
SetEnvIf Range (?:,.*?){5,5} bad-range=1
RequestHeader unset Range env=bad-range
# We always drop Request-Range; as this is a legacy
# dating back to MSIE3 and Netscape 2 and 3.
RequestHeader unset Request-Range
# optional logging.
CustomLog logs/range-CVE-2011-3192.log common env=bad-range
CustomLog logs/range-CVE-2011-3192.log common env=bad-req-range
2. Reject Range requests for more than 5 ranges in Range: header
Once again to implement this work around paste in Apache config file:
This DoS solution is not recommended (in my view), as it uses mod_rewrite to implement th efix and might be additionally another open window for DoS attack as mod_rewrite is generally CPU consuming.
# Reject request when more than 5 ranges in the Range: header.
# CVE-2011-3192
#
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP:range} !(bytes=[^,]+(,[^,]+){0,4}$|^$)
# RewriteCond %{HTTP:request-range} !(bytes=[^,]+(?:,[^,]+){0,4}$|^$)
RewriteRule .* - [F]
# We always drop Request-Range; as this is a legacy
# dating back to MSIE3 and Netscape 2 and 3.
RequestHeader unset Request-Range
3. Limit the size of Range request fields to few hundreds
To do so put in httpd.conf:
LimitRequestFieldSize 200
4. Dis-allow completely Range headers: via mod_headers Apache module
In httpd.conf put:
RequestHeader unset Range
RequestHeader unset Request-Range
This work around could create problems on some websites, which are made in a way that the Request-Range is used.
5. Deploy a tiny Apache module to count the number of Range Requests and drop connections in case of high number of Range: requests
This solution in my view is the best one, I’ve tested it and I can confirm on FreeBSD works like a charm.
To secure FreeBSD host Apache, against the Range Request: DoS using mod_rangecnt, one can literally follow the methodology explained in mod_rangecnt.c header:
freebsd# wget http://people.apache.org/~dirkx/mod_rangecnt.c
..
# compile the mod_rangecnt module
freebsd# /usr/local/sbin/apxs -c mod_rangecnt.c
...
# install mod_rangecnt module to Apache
freebsd# /usr/local/sbin/apxs -i -a mod_rangecnt.la
...
Finally to load the newly installed mod_rangecnt, Apache restart is required:
freebsd# /usr/local/etc/rc.d/apache2 restart
...
I’ve tested the module on i386 FreeBSD install, so I can’t confirm this steps works fine on 64 bit FreeBSD install, I would be glad if I can hear from someone if mod_rangecnt is properly compiled and installed fine also on 6 bit BSD arch.
Deploying the mod_rangecnt.c Range: Header to prevent against the Apache DoS on 64 bit x86_amd64 CentOS 5.6 Final is also done without any pitfalls.
[root@centos ~]# uname -a;
Linux centos 2.6.18-194.11.3.el5 #1 SMP Mon Aug 30 16:19:16 EDT 2010 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
[root@centos ~]# /usr/sbin/apxs -c mod_rangecnt.c
...
/usr/lib64/apr-1/build/libtool --silent --mode=link gcc -o mod_rangecnt.la -rpath /usr/lib64/httpd/modules -module -avoid-version mod_rangecnt.lo
[root@centos ~]# /usr/sbin/apxs -i -a mod_rangecnt.la
...
Libraries have been installed in:
/usr/lib64/httpd/modules
...
[root@centos ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd configtest
Syntax OK
[root@centos ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart
Stopping httpd: [ OK ]
Starting httpd: [ OK ]
After applying the mod_rangecnt patch if all is fine the memory exhaustion perl DoS script‘s output should be like so:
freebsd# perl httpd_dos.pl www.patched-apache-host.com 50
Host does not seem vulnerable
All of the above pointed work-arounds are only a temporary solution to these Grave Apache DoS byterange vulnerability , a few days after the original vulnerability emerged and some of the up-pointed work arounds were pointed. There was information, that still, there are ways that the vulnerability can be exploited.
Hopefully in the coming few weeks Apache dev team should be ready with rock solid work around to the severe problem.
In 2 years duration these is the second serious Apache Denial of Service vulnerability after before a one and a half year the so called Slowloris Denial of Service attack was capable to DoS most of the Apache installations on the Net.
Slowloris, has never received the publicity of the Range Header DoS as it was not that critical as the mod_range, however this is a good indicator that the code quality of Apache is slowly decreasing and might need a serious security evaluation.
Tags: apache httpd, apache server, apache webserver, ATTACKING, Auto, bugzilla, com, config, copy, CustomLog, deb package, denial of service, denial of service attack, dos attack, dos script, dos vulnerability, download, Draft, exploit, freebsd, header, host, HTTP, info, machine memory, memory exhaustion, minute time, mirror copy, mod, necessery, Netscape, number, perl httpd, poc, pPpPpppPpPPppPpppPp, REJECT, Remote, RewriteCond, script, simultaneous connections, work
Posted in Computer Security, FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration, Web and CMS | No Comments »
Friday, August 26th, 2011  On many occasions when had to administer on Linux, BSD, SunOS or any other *nix, there is a need to substitute strings inside files or group of files containing a certain string with another one.
On many occasions when had to administer on Linux, BSD, SunOS or any other *nix, there is a need to substitute strings inside files or group of files containing a certain string with another one.
The task is not too complex and many of the senior sysadmins out there would certainly already has faced this requirement and probably had a good idea on files substitution with perl and sed, however I’m quite sure there are dozen of system administrators out there who did not know, how and still haven’t faced a situation where there i a requirement to substitute from a command shell or via a scripting language.
This article tagets exactly these system administrators who are not 100% sys op Gurus 😉
1. Substitute text strings inside files on Linux and BSD with perl
Perl programming language has originally been created to do a lot of text manipulation as well as most of the Linux / Unix based hosts today have installed working copy of perl , therefore using perl as a mean to substitute one string in a file to another one is maybe the best way to completet the task.
Another good thing about perl is that text processing with it is said to be in most cases a bit faster than sed .
However it is still dependent on the string to be substituted I haven’t done benchmark tests to positively say 100% that always perl is quicker, however my common sense suggests perl will be quicker.
Now enough talk here is a very simple way to substitute a reoccuring, text string inside a file with another chosen one is like so:
debian:~# perl -pi -e 's/foo/bar/g' file1 file2
This will substitute the string foo with bar everywhere it’s matched in file1 and file2
However the above code is a bit “dangerous” as it does not preserve a backup copy of the original files, where string is substituted is not made.
Therefore using the above command should only be used where one is 100% sure about the string changes to be made.
Hence a better idea whether conducting the text substitution is to keep also the original file backup under a let’s say .bak extension. To achieve that I use perl as follows:
freebsd# perl -i.bak -p -e 's/syzdarma/magdanoz/g;' file1 file2
This command creates copies of the original files file1 and file2 under the names file1.bak and file2.bak , the files file1 and file2 text occurance of strings syzdarma will get substituted with magdanoz using the option /g which means – (substitute globally).
2. Substitute string in all files inside directory using perl on Linux and BSD
Every now and then the there is a need to do manipulations with large amounts of files, I can’t right now remember a good scenario where I had to change all occuring matching strings to anther one to all files located inside a directory, anyhow I’ve done this on a number of occasions.
A good way to do a mass file string substitution on Linux and BSD hosts equipped with a bash shell is via the commands:
debian:/root/textfiles:# for i in $(echo *.txt); do perl -i.bak -p -e 's/old_string/new_string/g;' $i; done
Where the text files had the default txt file extension .txt
Above bash loop prints each of the files located in /root/textfiles and substitutes everywhere (globally) the old_string with new_string .
Another alternative to the above example to replace multiple occuring text string in all files in multiple directories is possible using a combination of shell commands grep, perl, sort, uniq and xargs .
Let’s say that one wants to match everywhere inside the root directory and all the descendant directories for files with a custom string and substitute it to another one, this can be done with the cmd:
debian:~# grep -R -files-with-matches 'old_string' / | sort | uniq | xargs perl -pi~ -e 's/old_string/new_string/g'
This command will lookup for string old_string in all files in the / – root directory and in case of occurance will substitute with new_string (This command’s idea was borrowed as an idea from http://linuxadmin.org so thx.).
Using the combination of 5 commands, however is not very wise in terms of efficiency.
Therefore to save some system resources, its better in terms of efficiency to take advantage of the find command in combination with xargs , here is how:
debian:~# find / | xargs grep 'old_string' -sl |uniq | xargs perl -pi~ -e 's/old_string/new_string/g'
Once again the find command example will do exactly the same as the substitute method with grep -R …
As enough is said about the way to substitute text strings inside files using perl, I will further explain how text strings can be substituted using sed
The main reason why using sed could be a better choice in some cases is that Unices are not equipped by default with perl interpreter. In general the amount of servers who contains installed sed compared to the ones with perl language interpreter is surely higher.
3. Substitute text strings inside files on Linux and BSD with sed stream editor
In many occasions, wether a website is hosted, one needs to quickly conduct a change in string inside all files located in a directory, to resolve issues with static urls directly encoded in html.
To achieve this task here is a code using two little bash script loops in conjunctions with sed, echo and mv commands:
debian:/var/www/website# for i in $(ls -1); do cat $i |sed -e "s#index.htm#http://www.webdomain.com/#g">$i.new; done
debian:/var/www/website# for i in $(ls *.new); do mv $i $(echo $i |sed -e "s#.new##g"); done
The above command sed -e “s#index.htm#http://www.webdomain.com/#g”, instructs sed to substitute all appearance of the text string index.htm to the new text string http://www.webdomain.com
First for bash loop, creates all the files with substituted string to file1.new, file2.new, file3.new etc.
The second for loop uses mv to overwrite the original input files file1, file2, file3, etc. with the newly created ones file1.new, file2.new, file3.new
There is a a way shorter way to conclude the same text substitutions task using a simpler one liner with only using sed and bash’s eval capabilities, here is how:
debian:/var/www/website# sed -i 's/old_string/new_string/g' *
Above command will change old_string to new_string inside all files in directory /var/www/website
Whether a change has to be made with less than 1024 files using this method might be more efficient, however whether a text substitute has to be done to let’s say 5000+ the above simplistic version will not work. An error of Argument list too long will prevent the sed -i ‘s/old_string/new_string/g’ to complete its task.
The above for loop 2 liner should be also working without problems with FreeBSD and the rest of BSD derivatives, though I have not tested it yet, hence any feedback from FreeBSD guys is mostly welcome.
Consider that in order to have the for loops commands work on FreeBSD or NetBSD, they have to be run under a bash shell.
That’s all folks thanks the Lord for letting me write this nice article, I hope it gives some insights on how multiple files text replace on Unix works .
Cheers 😉
Tags: backup copy, bak, benchmark tests, bit, BSD, code, command shell, common sense, copy, default, file, file1, foo, foo bar, gurus, interpreter, Linux, magdanoz, multiple files, need, nix, perl programming language, processing, root, scripting language, sense, Shell, string changes, substitute text, substitution, sunos, sysadmins, system, system administrators, syzdarma, text, text manipulation, text string, text strings
Posted in FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration, Web and CMS | 1 Comment »
Monday, May 2nd, 2011 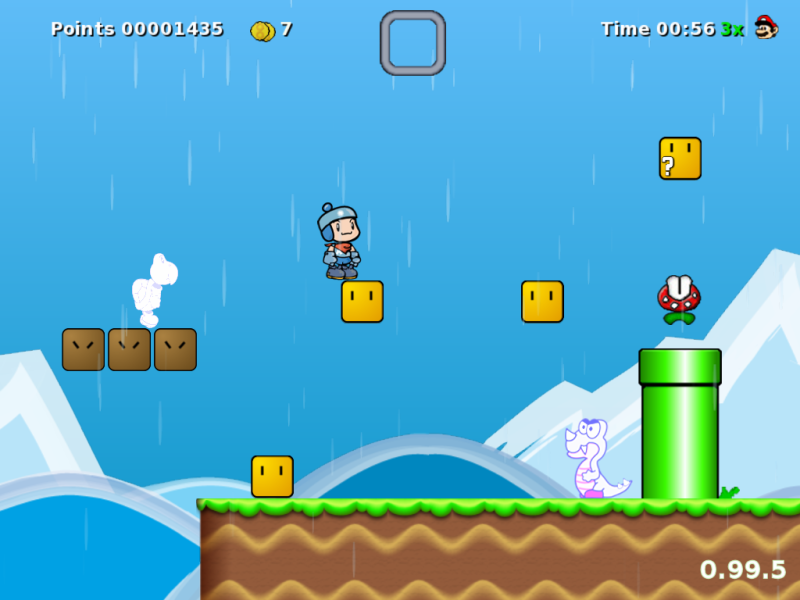
Are you looking for free software version of the old-school absolute Nintendo classic Super Mario Bros. ? 🙂
If you’re an old-school geek gamer like me you definitely do 😉
I was lucky to find Secret Mario Chronicles a Linux version of Super Mario while I was browsing through all the available for installation Linux games in aptitude .
The game is really great and worthy to be played. It’s even a better copy of the classical arcade game than SuperTux (another Mario like Linux clone game)

Both Super Mario Chronicles and Super Mario Bros are available for installation as .deb packages in the repositories of Ubuntu and Debian and most likely the other Debian direvative Linux distrubtion.
To install and play the games out of the box, if you’re a Debian or Ubuntu user, just issue:
linux:~# apt-get install smc supertux
The other good news are that both of the games’s engine, music and graphics are GPLed 🙂
To Launch the games after installation in GNOME I’ve used the menus:
Applications -> Games -> Super Mario Chronicles
andApplications -> Games -> Arcade -> SuperTux
The games can also be launched from terminal with commands:
debian:~$ smc
debian:~$ supertux
The only thing I don’t like about Super Mario Chronicles is that it doesn’t have a good music and only sounds, just to compare SuperTux has an awesome level music.
Along with being an absolute classic I should say that these two games are one of the really good arcade games produced for Linux and if I have to rank them as a gamer among all the other boring arcade games today available for Linux this two ones ranks in the top 10 arcade games prdocuced for Linux
Enjoy and drop me a thanks comment 😉 !
Tags: aptitude, arcade game, arcade games, clone game, copy, deb, deb packages, distrubtion, free software version, Gamer, geek, Gnome, good music, GPLed, gt games, installation, installation linux, issue, level, level music, linux version, music, nintendo super mario bros, play nintendo, repositories, smcorhipo, software, Super, super mario bros, supertux, supertuxThe, terminal, today, two games, Ubuntu, Ubuntu super mario bros, version
Posted in Games Linux, Linux | 5 Comments »



 On many occasions when had to administer on Linux, BSD, SunOS or any other *nix, there is a need to substitute strings inside files or group of files containing a certain string with another one.
On many occasions when had to administer on Linux, BSD, SunOS or any other *nix, there is a need to substitute strings inside files or group of files containing a certain string with another one.





