
If you're a GNU / Linux Desktop user like me and you have to administrate hybrid server environments running mixture of MS Windows with Microsoft IIS webserver running active server pages (.ASP) developed application or UNIX / GNU Linux servers web applications using Mono as a server-side language, often you need to have browser which properly supports Internet Explorer Trident web (layout) renderer (also famous as MSHTML).
Having Internet Explorer on your Linux is very useful for web developers who want to test how their website works under IE.
Of course you can always install Windows in Virtualbox VM and do your testing in the Virtual Machine but this takes time to install and also puts a useless load to a PC ….
IES4 Linux is a Linux free (open source) shell script that lets you run Internet Explorer on your Linux desktop.
ies4linux scripts collection uses emulation with WINE (Wine is Not Emulator) emulator to run the native Windows Internet Explorer thus before use it you have to install Wine.
There are plenty of tutorials online about ies4Linux, problem is as it is not updated and developed most tutorials doesn't work on Debian Wheezy / Ubuntu and rest of deb based linux distros.
This is why I decided to write just another ies4linux tutorial that actually works!
On Debian / Ubuntu / Mint Linux install via apt-get:
apt-get –yes install wine
Then with a non-root user download ies4linux-latest.tar.gz. Just in case ies4linux-latest.tar.gz disappears in future I've created also a ies4linux-latest.tar.gz mirror for download here
and unarchive tar archive:
wget http://www.tatanka.com.br/ies4linux/downloads/ies4linux-latest.tar.gz
tar -zxvf ies4linux-latest.tar.gz
cd ies4linux-*
./ies4linux
You will get:
IEs4Linux 2 is developed to be used with recent Wine versions (0.9.x). It seems that you are using an old version. It's recommended that you update your wine to the latest version (Go to: winehq.com).
You need to install cabextract first!
Download it here: http://www.kyz.uklinux.net/cabextract.php
To fulfill this requirement you will need to also cabetract package which is luckily part of Debian:
apt-get install –yes cabextract
On wine version 1.0 and onwards winprefixcreate has been changed to winecfg binary.
To prevent missing wineprefixcreate, errors during ies4linux installer run its necessery to symlink as a workaround:
ln -sv /usr/bin/winecfg /usr/bin/wineprefixcreate
To continue with Internet Explorer ies4Linux installater run again:
./ies4linux
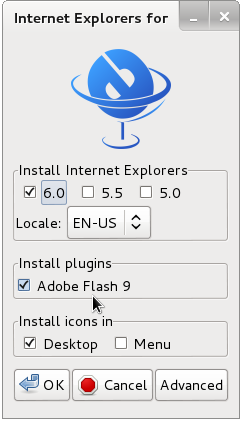
You will get the installer GUI window with selection option which Internet Explorer version you want. Choose between IE 5.0, IE 5.5 and IE 6. It is also possible to install IE 7 which is still considered beta version and is less tested and unstable, will probably lead to crashes. If you want to install also IE 7 check it as an option from Advanced menu.
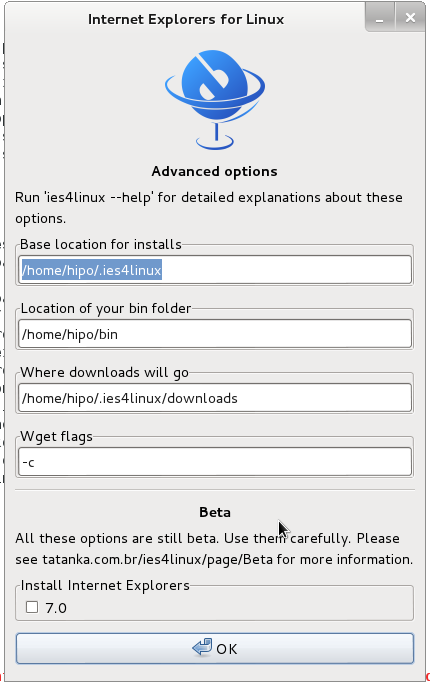
If you get permission errors after running ies4Linux gui installer to solve that chown recursively directory to the user with which you will be running it:
chown -R hipo:hipo ies4linux-2.99.0.1
Internet Explorer for Linux downloader, will connect Microsoft.com website and download DCOM, MCF and various IE required .CAB files.
If you get some ies4linux GUI installer unexpected crashes you can try to download all required IE binaries, surrounding files and flash player using no-gui installer with cmd:
./ies4linux –no-gui –install-corefonts
IEs4Linux 2 is developed to be used with recent Wine versions (0.9.x). It seems that you are using an old version. It's recommended that you update your wine to the latest version (Go to: winehq.com).
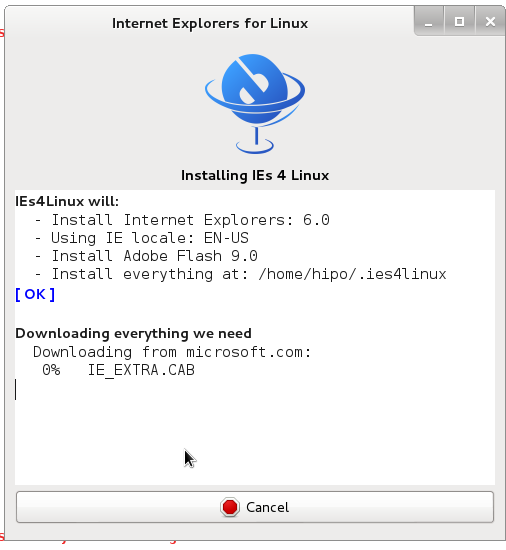
IEs4Linux will:
– Install Internet Explorers: 6.0
– Using IE locale: EN-US
– Install Adobe Flash 9.0
– Install MS Core Fonts
– Install everything at: /home/hipo/.ies4linux
[ OK ]Downloading everything we need
Downloading from microsoft.com:
DCOM98.EXE
mfc42.cab
249973USA8.exe
ADVAUTH.CAB
CRLUPD.CAB
HHUPD.CAB
IEDOM.CAB
IE_EXTRA.CAB
IE_S1.CAB
IE_S2.CAB
IE_S5.CAB
IE_S4.CAB
IE_S3.CAB
IE_S6.CAB
SETUPW95.CAB
FONTCORE.CAB
FONTSUP.CAB
VGX.CAB
SCR56EN.CABDownloading from macromedia.com:
100% swflash.cabDownloading from sourceforge.net
0% webdin32.exe[ OK ]bdin32.exeInstalling IE 6
Initializing
Creating Wine Prefix
Your wine does not have wineprefixcreate installed. Maybe you are running an old Wine version. Try to update it to the latest version.
To fix the error:
Your wine does not have wineprefixcreate installed. Maybe you are running an old Wine version. Try to update it to the latest version.
vim lib/functiions.sh
Go to line 36 (Type :36 in vim)
Line:
wine –version 2>&1 | grep -q "0.9." || warning $MSG_WARNING_OLDWINE
Has to be changed to:
wine –version 2>&1 | egrep -q "0.9.|-1." || warning $MSG_WARNING_OLDWINE
Also you need to substitute wineprefixcreate to wineboot (if you haven't already symlinked wineprefixcreate to winecfg – as pointed earlier in article.
To do so make following substitution in lib/install.sh and in lib/functions.sh
cp -rpf lib/install.sh lib/install.sh.bak; cat lib/install.sh |sed -e 's#wineprefixcreate#wineboot#g' > lib/install_new.sh; mv lib/install_new.sh lib/install.sh
cp -rpf lib/install.sh lib/functions.sh.bak; cat lib/functions.sh |sed -e 's#wineprefixcreate#wineboot#g' > lib/functions_new.sh; mv lib/functions_new.sh lib/functions.sh
Also it is necessery to change default corefonts download url which points to sourceforge but is failing. I've made mirror of corefonts files here
cp -rpf lib/install.sh lib/install.sh.bak; cat lib/install.sh |sed -e 's#http://internap.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/corefonts/#www.pc-freak.net/files/corefonts/#g' > lib/install_new.sh; mv lib/install_new.sh lib/install.sh
Re-run the ies4linux console installer:
./ies4linux –no-gui –install-corefonts
….
Es4Linux installations finished!
On installation success you should get output like this
Hopefully you will see no errors like in my case, if you get the corefonts download error again re-run the installer and it should succesully download the files.
To then run ies4linux:
~/bin/ie6
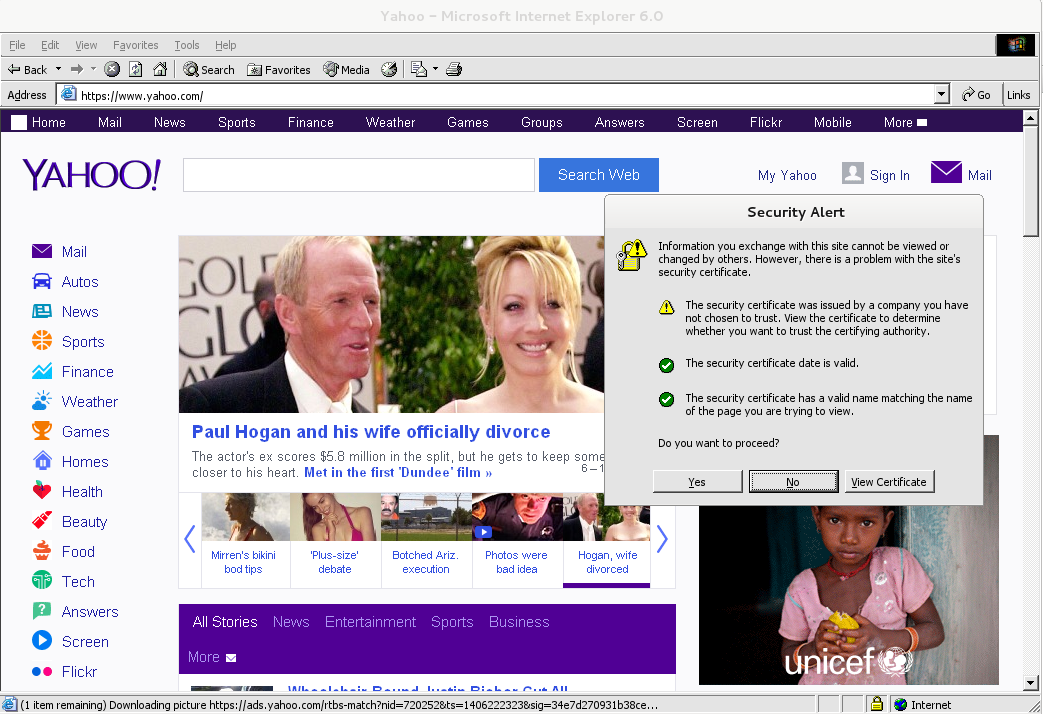
Though Ies 4 Linux is good for basic testing it is not psosible to use the browser for normal browsing because its a bit buggy and slow.
By default Internet Explorer 6 behavior is to prompt security alert on various actions, though this might be useful for debugging it is really annoying so I personally disabled those by decreasing from:
Tools -> Internet Options -> Security -> (Security Level)
I've decreased it from Medium to Medium-Low
ies4Linux was not developed since 2008 and as of time of writting ies4linux official project website seems abandoned.










Manually deleting spam comments from WordPress blogs and websites to free disk space and optimize MySQL
Monday, November 24th, 2014If you're a web-hosting company or a web-development using WordPress to build multitudes of customer blogs or just an independent blogger or sys-admin with a task to optimize a server's MySQL allocated storage / performance on triads of WordPress-es a a good tip that would help is to removing wp_comments marked as spam.
Even though sites might be protected of thousands of spam message daily caught by WP anti-spam plugin Akismet, spam caught messages aer forwarder by Akismet to WP's Spam filter and kept wp_comments table with comments_approved column record 'spam'.
Therefore you will certainly gain of freeing disk space uselessly allocated by spam messages into current MySQL server storage dir (/var/lib/mysql /usr/local/mysql/data – the directory where my.cnf tells the server to keep its binary data .MYI, .MYD, .frm files) as well as save a lot of disk space by excluding the useless spam messages from SQL daily backup archives.
Here is how to remove manually spam comments from a WordPress blog under database (wp_blog1);
The most common and quick way useful for scripting (whether you have to do it for multiple blogs with separate dbs) is to delete all comments being filled as 'Spam'.
To delete all messages which were filled by Akismet's spam filter with high probabily being a spam issue from mysql cli interface:
For Unread (Unapproved) messages the value of comment_approved field are 0 or 1, 0 if the comment is Red and Approved and 1 if still it is to be marked as read (and not spam).
If a wordpress gets heavily hammered with mainly spam and the probability that unapproved message is different from spam is low and you want to delete any message waiting for approvel as not being spam from wordpress use following SQL query:
Another not very common you might want to do is delete only all apprved comments:
For old installed long time unmaintained blogs (with garbish content), it is very likely that 99% of the messages might be spam and in case if there are already >= 100 000 spam messages and you don't have the time to inspect 100 000 spam comments to get only some 1000 legitimate and you want to delete completely all wordpress comments for a blog in one SQL query use:
Another scenario if you know a blog has been maintained until certain date and comments were inspected and then it was left unmaintained for few years without any spam detect and clear plugin like Akismet, its worthy to delete all comments starting from the date wordpress site stopped to be maintained:
Tags: binary data, blogs, command delete coments wordpress, common, disk space, interface, manually delete spam comments, multiple, server, spam messages, SQL, use, Wordpress, wordpress delete comments query, wp
Posted in MySQL, System Administration, Various, Web and CMS, Wordpress | No Comments »