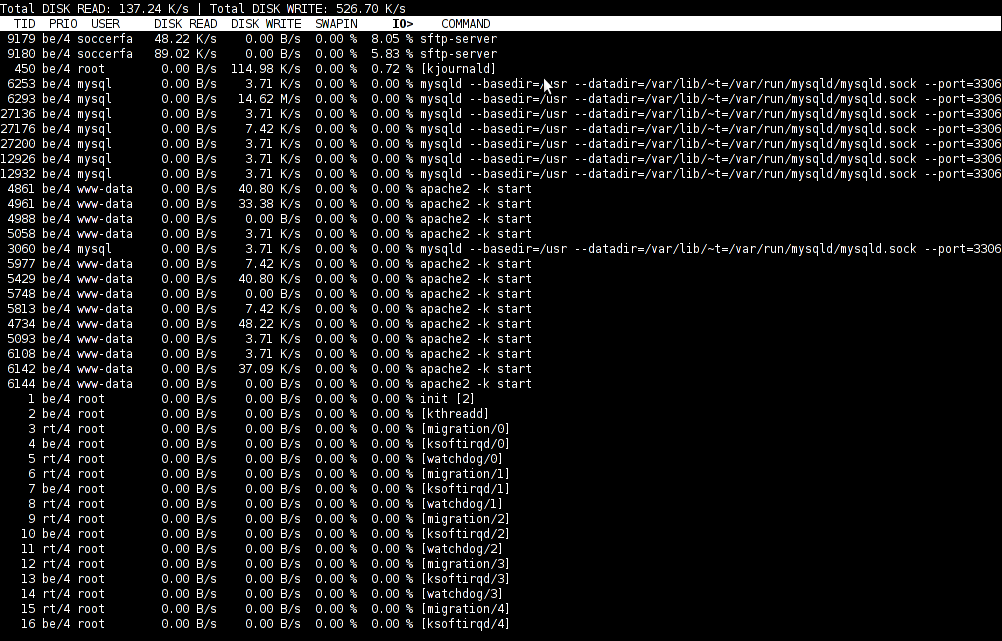
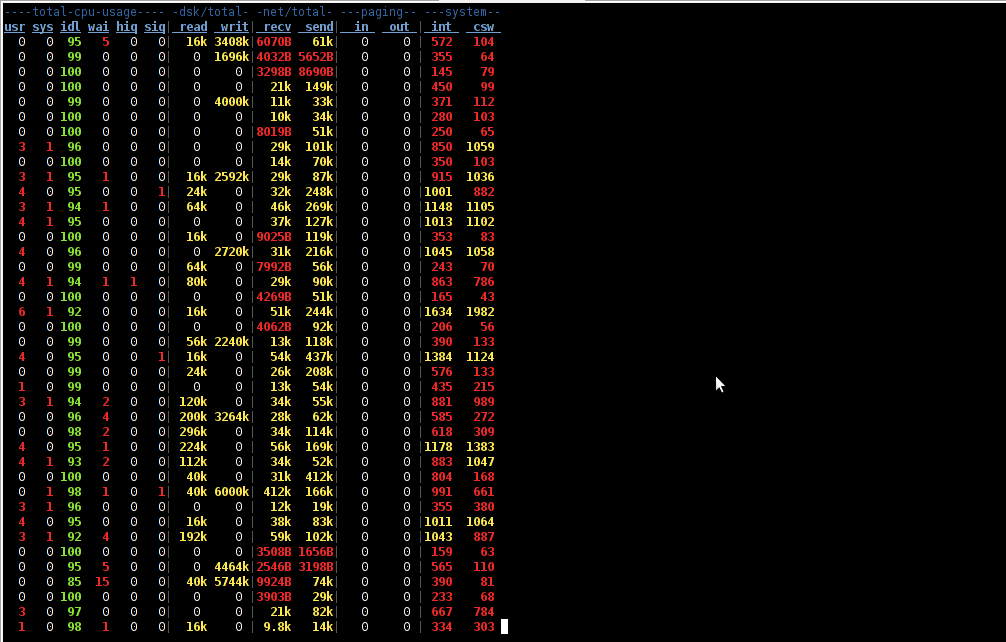
While reading some posts online related to MS-Windows TcpView – network traffic analyzing tool. I've came across very nice tool for tracking connection speed for Linux (Speedometer). If I have to compare it, speedometer is somehow similar to nethogs and iftop bandwidth network measuring utilities .
What differentiates speedometer from iftop / nethogs / iptraf is it is more suitable for visualizing a network file or data transfers.
The graphs speedometer draws are way easier to understand, than iftop graphs.
Even complete newbies can understand it with no need for extraordinary knowledge in networking. This makes Speedometer, a top tool to visually see the amount of traffic flowing through server network interface (eth0) … (eth1) etc.
What speedometer shows is similar to the Midnight Commander's (mc) file transfer status bar, except the statistics are not only for a certain file transfer but can show overall statistics over server passing network traffic amount (though according to its manual it can be used to also track individual file transfers).
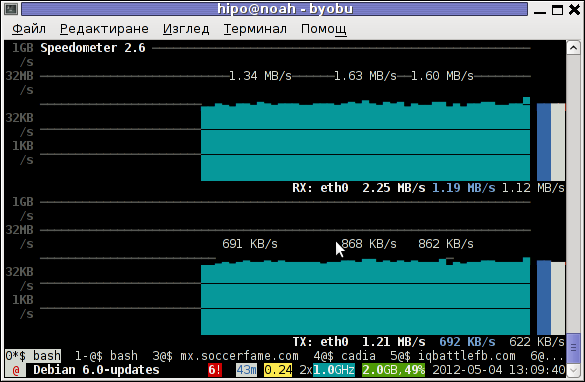
The simplicity for basic use makes speedometer nice tool to track for network congestion issues on Linux. Therefore it is a must have outfit for every server admin. Below you see a screenshot of my terminal running speedometer on a remote server.
1. Installing speedometer on Debian / Ubuntu and Debian derivatives
For Debian and Ubuntu server administrators speedometer is already packaged as a deb so its installation is as simple as:
debian:~# apt-get --yes install speedometer
....
2. Installing speedometer from source for other Linux distributions CentOS, Fedora, SuSE etc.
Speedometer is written in python programming language, so in order to install and use on other OS Linux platforms, it is necessery to have installed (preferably) an up2date python programming language interpreter (python ver. 2.6 or higher)..
Besides that it is necessary to have installed the urwid -( console user interface library for Python) available for download via excess.org/urwid/
Hence to install speedometer on RedHat based Linux distributions one has to follow these steps:
a) Download & Install python urwid library
[root@centos ~]# cd /usr/local/src
[root@centos src]# wget -q http://excess.org/urwid/urwid-1.0.1.tar.gz
[root@centos src]# tar -zxvvf urwid-1.0.1.tar.gz
....
[root@centos src]# cd urwid-1.0.1
[root@centos urwid-1.0.1]# python setup.py install
running install
running build
running build_py
creating build
creating build/lib.linux-i686-2.4
creating build/lib.linux-i686-2.4/urwid
copying urwid/tests.py -> build/lib.linux-i686-2.4/urwid
copying urwid/command_map.py -> build/lib.linux-i686-2.4/urwid
copying urwid/graphics.py -> build/lib.linux-i686-2.4/urwid
copying urwid/vterm_test.py -> build/lib.linux-i686-2.4/urwid
copying urwid/curses_display.py -> build/lib.linux-i686-2.4/urwid
copying urwid/display_common.py -> build/lib.linux-i686-2.4/urwid
....
b) Download and install python-setuptools
python-setuptools is one other requirement of speedometer, happily on CentOS and Fedora the rpm package is already there and installable with yum:
[root@centos ~]# yum -y install python-setuptools
....
c) Download and install Speedometer
[root@centos urwid-1.0.1]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@centos src]# wget -q http://excess.org/speedometer/speedometer-2.8.tar.gz
[root@centos src]# tar -zxvvf speedometer-2.8.tar.gz
.....
[root@centos src]# cd speedometer-2.8
[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# python setup.py install
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "setup.py", line 26, in ?
import speedometer
File "/usr/local/src/speedometer-2.8/speedometer.py", line 112
n = n * granularity + (granularity if r else 0)
^
While running the CentOS 5.6 installation of speedometer-2.8, I hit the
"n = n * granularity + (granularity if r else 0)"
error.
After consultation with some people in #python (irc.freenode.net), I've figured out this error is caused due the outdated version of python interpreter installed by default on CentOS Linux 5.6. On CentOS 5.6 the python version is:
[root@centos ~]# python -V
Python 2.4.3
As I priorly said speedometer 2.8's minimum requirement for a python to be at v. 2.6. Happily there is quick way to update python 2.4 to python 2.6 on CentOS 5.6, as there is an RPM repository maintained by Chris Lea which contains RPM binary of python 2.6.
To update python 2.4 to python 2.6:
[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# rpm -Uvh http://yum.chrislea.com/centos/5/i386/chl-release-5-3.noarch.rpm[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CHL[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# yum install python26
Now the newly installed python 2.6 is executable under the binary name python26, hence to install speedometer:
[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# python26 setup.py install
[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# chown root:root /usr/local/bin/speedometer
[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/speedometer
[root@centos speedometer-2.8]# python26 speedometer -i 1 -tx eth0
The -i will instruct speedometer to refresh the screen graphs once a second.
3. Using speedometer to keep an eye on send / received traffic network congestion
To observe, the amount of only sent traffic via a network interface eth0 with speedometer use:
debian:~# speedometer -tx eth0
To only keep an eye on received traffic through eth0 use:
debian:~# speedometer -rx eth0
To watch over both TX and RX (Transmitted and Received) network traffic:
debian:~# speedometer -tx eth0 -rx eth0
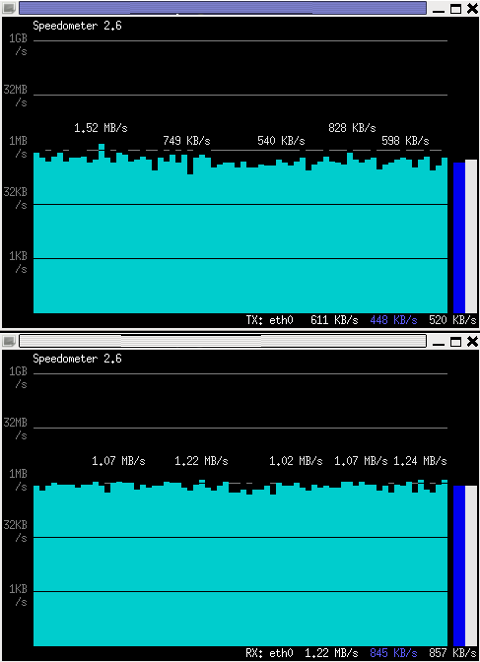
If you want to watch in separate windows TX and RX traffic while running speedometer you can run in separate xterm windows speedometer -tx eth0 and speedometer -rx eth0, like in below screenshot:
4. Using speedometer to test network maximum possible transfer speed between server (host A) and server (host B)
The speedometer manual suggests few examples one of which is:
How fast is this LAN?
host-a$ cat /dev/zero | nc -l -p 12345
host-b$ nc host-a 12345 > /dev/null
host-b$ speedometer -rx eth0
When I red this example in speedometer's manual, it wasn't completely clear to me what the author really meant, but a bit after when I thought over the example I got his point.
The idea behind this example is that a constant stream of zeros taken from /dev/zero will be streamed over via a pipe (|) to nc which will bind a port number 12345, anyone connecting from another host machine, lets say a server with host host-b to port 12345 on machine host-a will start receiving the /dev/zero streamed content.
Then to finally measure the streamed traffic between host-a and host-b machines a speedometer is started to visualize the received traffic on network interface eth0, thus measuring the amount of traffic flowing from host-a to host-b …
I give a try to the exmpls, using for 2 test nodes my home Desktop PC, Linux running arcane version of Ubuntu and my Debian Linux notebook.
First on the Ubuntu PC I issued
hipo@hip0-desktop:~$ cat /dev/zero | nc -l -p 12345
Note that I have previously had installed the netcat, as nc is not installed by default on Ubuntu and Debian. If you, don't have nc installed yet, install it with:
apt-get –yes install netcat
"cat /dev/zero | nc -l -p 12345" will not produce any output, but will display just a blank line.
Then on my notebook I ran the second command example, given in the speedometer manual:
hipo@noah:~$ nc 192.168.0.2 12345 > /dev/null
Here the 192.168.0.2 is actually the local network IP address of my Desktop PC. My Desktop PC is connected via a normal 100Mbit switch to my routing machine and receives its internet via NAT. The second test machine (my laptop), gets its internet through a WI-FI connection received by a Wireless Router connected via a UTP cable to the same switch to which my Desktop PC is connected.
Finally to test / get my network maximum thoroughput I had to use:
hipo@noah:~$ speedometer -rx wlan0
Here, I monitor my wlan0 interface, as this is my (laptop) wireless card interface over which I have connectivity to my local network and via which through the the WI-FI router I get connected to the internet.
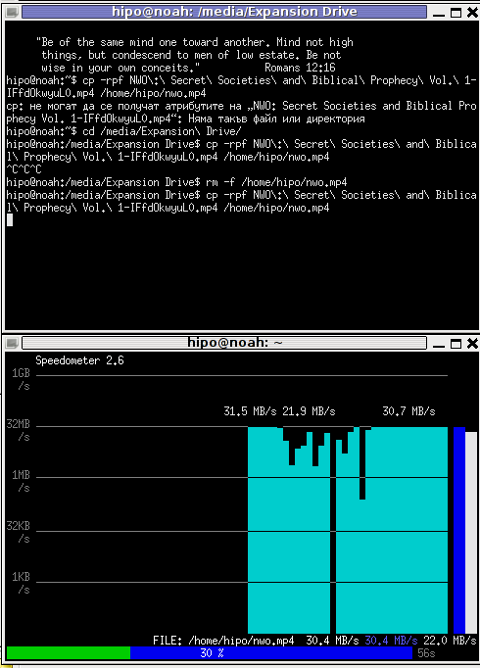
Below is a snapshot captured showing approximately what is the max network thoroughput from:
Desktop PC -> to my Thinkpad R61 laptop
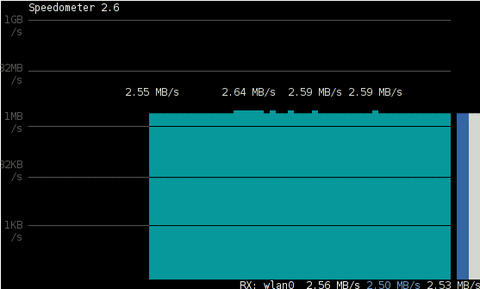
As you can see in the shot approximately the maximum network thoroughput is in between:
2.55MB/s min and 2.59MB/S max, the speed is quite low for a 100 MBit local network, but this is normal as most laptop wireless adapters hardly transfer traffic in more than 10 to 20 MBits per sec.
If the same nework thoroughput test is conducted between two machines both connected to a same 100 M/bit switch, the traffic should be at least a 8 MB/sec.
There is something, else to take in consideration that probably makes the provided example network thoroughput measuring a bit inaccurate. The fact that the /dev/zero content is stremed over is slowing down the zeroes sent over network because of the pipe ( | ) use slows down the stream.
5. Using speedometer to visualize maximum writting speed to a local hard drive on Linux
In the speedometer manual, I've noticed another interesting application of this nifty tool.
speedometer can be used to track and visualize the maximum writing speed a hard disk drive or hard drive partition can support on Linux OS:
A copy paster from the manual text is as follows:
How fast can I write data to my filesystem? (with at least 1GB free)
dd bs=1000000 count=1000 if=/dev/zero of=bigfile &
speedometer bigfile
However, when I tried copy/pasting the example in terminal, to test the maximum writing speed to an external USB hard drive, only dd command was started and speedometer failed to initialize and display graphs of the file creation speed.
I've found a little "hack" that makes the man example work by adding a 3 secs sleep like so:
debian:/media/Expansion Drive# dd bs=1000000 count=1000 if=/dev/zero of=bigfile & sleep 3; speedometer bigfile
Here is a screenshot of the bigfile created by dd and tracked "in real time" by speedometer:
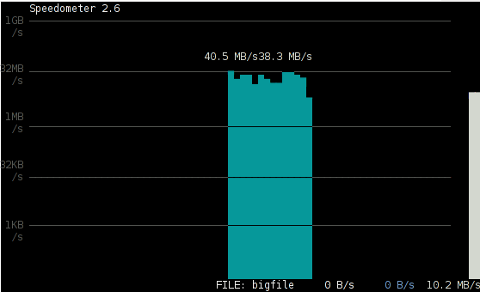
Actually the returned results from this external USB drive are, quite high, the possible reason for that is it is connected to my laptop over an USB protocol verion 3.
6. Using Speedometer to keep an eye on file download in progress
This application of speedometer is mostly useless especially on Linux where it is used as a Desktop.
However in some occasions if files are transferred over ssh or in non interactive FTP / Samba file transfers between Linux servers it can come handy.
To visualize the download and writing speed of lets say FTP transferred .AVI movie (during the actual file transfer) on the download host issue:
# speedometer Download-Folder/What-goes-around-comes-around.avi
7. Estimating approximate time for file transfer
There is another section in the speedometer manual pointing of the program use to calculate the time remaining for a file transfer.
The (man speedometer) provided example text is:
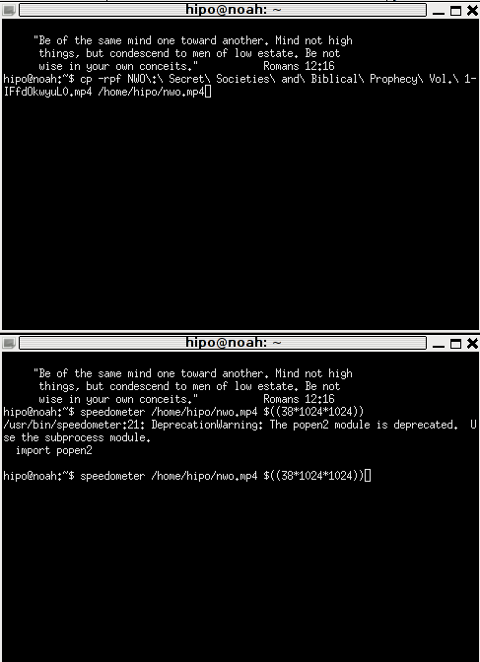
How long it will take for my 38MB transfer to finish?
speedometer favorite_episode.rm $((38*1024*1024))
At first glimpse it hard to understand (like the other manual example). A bit of reasoning and I comprehend what the man author meant by the obscure calculation:
$((38*1024*1024))
This is a formula used in which 38 has to be substituted with the exact file size amount of the transferred file. The author manual used a 38MB file so this is why he put $((38* … in the formula.
I give it a try – (just for the sake to see how it works) with a file with a size of 2500MB, in below two screenshot pictures I show my preparation to copy the file and the actual copying / "real time" transfer tracking with speedometer's status percentage completion bar.