Some long time ago I’ve written an article Optimizing Linux tcp/ip networking
In the article I’ve examined a number of Linux kernel sysctl variables, which significantly improve the way TCP/IP networking is handled by a non router Linux based servers.
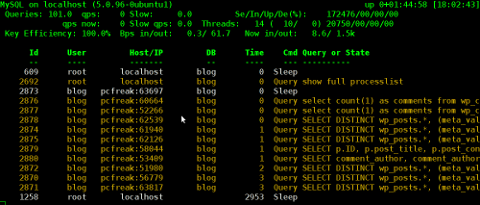
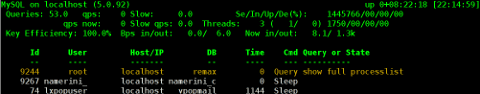
As the time progresses I’ve been continuing to read materials on blogs and internet sites on various tips and anti Denial of Service rules which one could apply on newly installed hosting (Apache/MySql/Qmail/Proxy) server to improve webserver responce times and tighten the overall security level.
In my quest for sysctl 😉 I found a few more handy sysctl variables apart from the old ones I incorporate on every Linux server I adminstrate.
The sysctl variables improves the overall network handling efficiency and protects about common SYN/ACK Denial of service attacks.
Here are the extra sysctl variables I started incorporating just recently:
############ IPv4 Sysctl Settings ################
#Enable ExecShield protection (randomize virtual assigned space to protect against many exploits)
kernel.randomize_va_space = 1
#Increase the number of PIDs processes could assign this is very needed especially on more powerful servers
kernel.pid_max = 65536
# Prevent against the common 'syn flood attack'
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
# Controls the use of TCP syncookies two is generally a better idea, though you might experiment
#net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2
##################################################
#
############## IPv6 Sysctl Settings ################
# Number of Router Solicitations to send until assuming no routers are present.
net.ipv6.conf.default.router_solicitations = 0
# Accept Router Preference in RA? Again not necessery if the server is not a router
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_rtr_pref = 0
# Learn Prefix Information in Router Advertisement (Unnecessery) for non-routers
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_pinfo = 0
# disable accept of hop limit settings from other routers (could be used for DoS)
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_defrtr = 0
# disable ipv6 global unicasts server assignments
net.ipv6.conf.default.autoconf = 0
# neighbor solicitations to send out per address (better if disabled)
net.ipv6.conf.default.dad_transmits = 0
# disable assigning more than 1 address per network interface
net.ipv6.conf.default.max_addresses = 1
#####################################################
To use this settings paste the above sysctl variables in /etc/sysctl.conf and ask sysctl command to read and apply the newly added conf settings:
server:~# sysctl -p
...
Hopefully you should not get errors while applying the sysctl settings, if you get some errors, it’s possible some of the variable is differently named (depending on the Linux kernel version) or the Linux distribution on which sysctl’s are implemented.
For some convenience I’ve created unified sysctl variables /etc/sysct.conf containing the newly variables I started implementing to servers with the ones I already exlpained in my previous post Optimizing Linux TCP/IP Networking
Here is the optimized / hardened sysctl.conf file for download
I use this exact sysctl.conf these days on both Linux hosting / VPS / Mail servers etc. as well as on my personal notebook 😉
Here is also the the complete content of above’s sysctl.conf file, just in case if somebody wants to directly copy/paste it in his /etc/sysctl.conf
# Sysctl kernel variables to improve network performance and protect against common Denial of Service attacks
# It's possible that not all of the variables are working on all Linux distributions, test to make sure
# Some of the variables might need a slight modification to match server hardware, however in most cases it should be fine
# variables list compiled by hip0
### https://www.pc-freak.net
#### date 08.07.2011
############ IPv4 Sysctl Kernel Settings ################
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0
# ( Turn off IP Forwarding )
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1
# ( Control Source route verification )
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0
# ( Disable ICMP redirects )
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
# ( same as above )
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0
# ( Disable IP source routing )
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0
# ( - || - )net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 40
# ( Decrease FIN timeout ) - Useful on busy/high load server
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 4000
# ( keepalive tcp timeout )
net.core.rmem_default = 786426
# Receive memory stack size ( a good idea to increase it if your server receives big files )
##net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = "4096 87380 4194304"
net.core.wmem_default = 8388608
#( Reserved Memory per connection )
net.core.wmem_max = 8388608
net.core.optmem_max = 40960
# ( maximum amount of option memory buffers )
# tcp reordering, increase max buckets, increase the amount of backlost
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 360000
net.ipv4.tcp_reordering = 5
##net.core.hot_list_length = 256
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 1024
#Enable ExecShield protection (randomize virtual assigned space to protect against many exploits)
kernel.randomize_va_space = 1
#Increase the number of PIDs processes could assign this is very needed especially on more powerful servers
kernel.pid_max = 65536
# Prevent against the common 'syn flood attack'net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
# Controls the use of TCP syncookies two is generally a better idea, though you might experiment
#net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2
###################################################
############## IPv6 Sysctl Settings ################
# Number of Router Solicitations to send until assuming no routers are present.
net.ipv6.conf.default.router_solicitations = 0
# Accept Router Preference in RA? Again not necessery if the server is not a router
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_rtr_pref = 0
# Learn Prefix Information in Router Advertisement (Unnecessery) for non-routersnet.
ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_pinfo = 0
# disable accept of hop limit settings from other routers (could be used for DoS)
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra_defrtr = 0
# disable ipv6 global unicasts server assignmentsnet.
ipv6.conf.default.autoconf = 0
# neighbor solicitations to send out per address (better if disabled)
net.ipv6.conf.default.dad_transmits = 0
# disable assigning more than 1 address per network interfacenet.
ipv6.conf.default.max_addresses = 1
#####################################################
# Reboot if kernel panic
kernel.panic = 20
These sysctl settings will tweaken the Linux kernel default network settings performance and you will notice the improvements in website responsiveness immediately in some cases implementing this kernel level goodies will make the server perform better and the system load might decrease even 😉
This optimizations on a kernel level are not only handy for servers, their implementation on Linux Desktop should also have a positive influence on the way the network behaves and could improve significantly the responce times of opening pages in Firefox/Opera/Epiphany Torrent downloads etc.
Hope this kernel tweakenings are helpful to someone.
Cheers 😉