I've upgraded recently all my machines from Debian Buster Linux 10 to Debian 11 Bullseye (if you wonder what Bullseye is) this is one of the heroes of Disneys Toy Stories which are used for a naming of General Debian Distributions.
After the upgrade most of the things worked expected, expect from some stuff like MariaDB (MySQL) and other weirdly behaving services. After some time of investigation being unable to find out what was causing the random issues observed on the machines. I finally got the strange daemon improper functioning and crashing was caused by AppArmor.
AppArmor ("Application Armor") is a Linux kernel security module that allows the system administrator to restrict programs' capabilities with per-program profiles. Profiles can allow capabilities like network access, raw socket access, and the permission to read, write, or execute files on matching paths. AppArmor supplements the traditional Unix discretionary access control (DAC) model by providing mandatory access control (MAC). It has been partially included in the mainline Linux kernel since version 2.6.36 and its development has been supported by Canonical since 2009.
The general idea of apparmor is wonderful as it could really strengthen system security, however it should be setup on install time and not setup on update time. For one more time I got convinced myself that upgrading from version to version to keep up to date with security is a hard task and often the results are too much unexpected and a better way to upgrade from General version to version any modern Linux / Unix distribution (and their forked mobile equivalents Android etc.) is to just make a copy of the most important configuration, setup the services on a freshly new installed machine be it virtual or a physical Server and rebuild the whole system from scratch, test and then run the system in production, substituting the old server general version with the new machine.
The rest is leading to so much odd issues like this time with AppArmors causing distractions on the servers hosted applications.
But enough rent if you're unlucky and unwise enough to try to Upgrade Debian / Ubuntu 20, 21 / Mint 18, 19 etc. or whatever Deb distro from older general release to a newer One. Perhaps the best first thing to do onwards is stop and remove AppArmor (those who are hardcore enthusiasts could try to enable the failing services due to apparmor), by disabling the respective apparmor hardening profile but i did not have time to waste on stupid stuff and experiment so I preferred to completely stop it.
To identify the upgrade oddities has to deal with apparmors service enabled security protections you should be able to find respective records inside /var/log/messages as well as in /var/log/audit/audit.log
# dmesg
[ 64.210463] audit: type=1400 audit(1548120161.662:21): apparmor="DENIED" operation="sendmsg" info="Failed name lookup – disconnected path" error=-13 profile="/usr/sbin/mysqld" name="run/systemd/notify" pid=2527 comm="mysqld" requested_mask="w" denied_mask="w" fsuid=113 ouid=0
[ 144.364055] audit: type=1400 audit(1548120241.595:22): apparmor="DENIED" operation="sendmsg" info="Failed name lookup – disconnected path" error=-13 profile="/usr/sbin/mysqld" name="run/systemd/notify" pid=2527 comm="mysqld" requested_mask="w" denied_mask="w" fsuid=113 ouid=0
[ 144.465883] audit: type=1400 audit(1548120241.699:23): apparmor="DENIED" operation="sendmsg" info="Failed name lookup – disconnected path" error=-13 profile="/usr/sbin/mysqld" name="run/systemd/notify" pid=2527 comm="mysqld" requested_mask="w" denied_mask="w" fsuid=113 ouid=0
[ 144.566363] audit: type=1400 audit(1548120241.799:24): apparmor="DENIED" operation="sendmsg" info="Failed name lookup – disconnected path" error=-13 profile="/usr/sbin/mysqld" name="run/systemd/notify" pid=2527 comm="mysqld" requested_mask="w" denied_mask="w" fsuid=113 ouid=0
[ 144.666722] audit: type=1400 audit(1548120241.899:25): apparmor="DENIED" operation="sendmsg" info="Failed name lookup – disconnected path" error=-13 profile="/usr/sbin/mysqld" name="run/systemd/notify" pid=2527 comm="mysqld" requested_mask="w" denied_mask="w" fsuid=113 ouid=0
[ 144.767069] audit: type=1400 audit(1548120241.999:26): apparmor="DENIED" operation="sendmsg" info="Failed name lookup – disconnected path" error=-13 profile="/usr/sbin/mysqld" name="run/systemd/notify" pid=2527 comm="mysqld" requested_mask="w" denied_mask="w" fsuid=113 ouid=0
[ 144.867432] audit: type=1400 audit(1548120242.099:27): apparmor="DENIED" operation="sendmsg" info="Failed name lookup – disconnected path" error=-13 profile="/usr/sbin/mysqld" name="run/systemd/notify" pid=2527 comm="mysqld" requested_mask="w" denied_mask="w" fsuid=113 ouid=0
1. How to check if AppArmor is running on the system
If you have a system with enabled apparmor you should get some output like:
root@haproxy2:~# apparmor_status
apparmor module is loaded.
5 profiles are loaded.
5 profiles are in enforce mode.
/usr/sbin/ntpd
lsb_release
nvidia_modprobe
nvidia_modprobe//kmod
tcpdump
0 profiles are in complain mode.
1 processes have profiles defined.
1 processes are in enforce mode.
/usr/sbin/ntpd (387)
0 processes are in complain mode.
0 processes are unconfined but have a profile defined.
Also if you check the service you will find out that Debian's Major Release upgrade from 10 Buster to 11 BullsEye with.
# apt update -y && apt upgrade -y && apt dist-update -y
…
automatically installed apparmor and started the service, e.g.:
# systemctl status apparmor
● apparmor.service – Load AppArmor profiles
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apparmor.service; enabled; vendor pres>
Active: active (exited) since Sat 2022-01-22 23:04:58 EET; 5 days ago
Docs: man:apparmor(7)
https://gitlab.com/apparmor/apparmor/wikis/home/
Process: 205 ExecStart=/lib/apparmor/apparmor.systemd reload (code=exited, >
Main PID: 205 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CPU: 43msяну 22 23:04:58 haproxy2 apparmor.systemd[205]: Restarting AppArmor
яну 22 23:04:58 haproxy2 apparmor.systemd[205]: Reloading AppArmor profiles
яну 22 23:04:58 haproxy2 systemd[1]: Starting Load AppArmor profiles…
яну 22 23:04:58 haproxy2 systemd[1]: Finished Load AppArmor profiles.
# dpkg -l |grep -i apparmor
ii apparmor 2.13.6-10 amd64 user-space parser utility for AppArmor
ii libapparmor1:amd64 2.13.6-10 amd64 changehat AppArmor library
ii libapparmor-perl:amd64 2.13.6-10
In case AppArmor is disabled, you will get something like:
root@pcfrxenweb:~# aa-status
apparmor module is loaded.
0 profiles are loaded.
0 profiles are in enforce mode.
0 profiles are in complain mode.
0 processes have profiles defined.
0 processes are in enforce mode.
0 processes are in complain mode.
0 processes are unconfined but have a profile defined.
2. How to disable AppArmor for particular running services processes
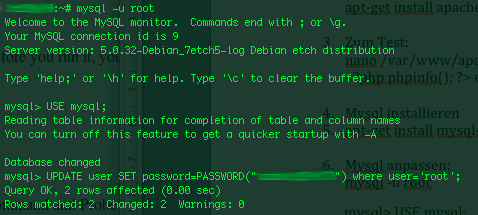
In my case after the upgrade of a system running a MySQL Server suddenly out of nothing after reboot the Database couldn't load up properly and if I try to restart it with the usual
root@pcfrxen: /# systemctl restart mariadb
I started getting errors like:
DBI connect failed : Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket '/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock' (2)
To get an idea of what kind of profile definitions, could be enabled disabled on apparmor enabled system do:
root@pcfrxen:/var/log# ls -1 /etc/apparmor.d/
abstractions/
force-complain/
local/
lxc/
lxc-containers
samba/
system_tor
tunables/
usr.bin.freshclam
usr.bin.lxc-start
usr.bin.man
usr.bin.tcpdump
usr.lib.telepathy
usr.sbin.clamd
usr.sbin.cups-browsed
usr.sbin.cupsd
usr.sbin.ejabberdctl
usr.sbin.mariadbd
usr.sbin.mysqld
usr.sbin.named
usr.sbin.ntpd
usr.sbin.privoxy
usr.sbin.squid
Lets say you want to disable any protection AppArmor profile for MySQL you can do it with:
root@pcfrxen:/ # ln -s /etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqld /etc/apparmor.d/disable/
root@pcfrxen:/ # apparmor_parser -R /etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqld
To make the system know you have disabled a profile you should restart apparmor service:
root@pcfrxen:/ # systemctl restart apparmor.service
3. Disable completely AppArmor to save your time weird system behavior and hang bangs
In my opinion the best thing to do anyways, especially if you don't run Containerized applications, that runs only one single application / service at at time is to completely disable apparmor, otherwise you would have to manually check each of the running applications before the upgrade and make sure that apparmor did not bring havoc to some of it.
Hence my way was to simple get rid of apparmor by disable and remove the related package completely out of the system to do so:
root@pcfrxen:/ # systemctl stop apparmor
root@pcfrxen:/ # systemctl disable apparmor
root@pcfrxen:/ # apt-get remove -y apparmor
Once disabled to make the system completely load out anything loaded related to apparmor loaded into system memory, you should do machine reboot.
root@pcfrxen:/ # shutdown -r now
Hopefully if you run into same issue after removal of apparmor most of the things should be working fine after the upgrade. Anyways I had to go through each and every app everywhere and make sure it is working as expected. The major release upgrade has also automatically enabled me some of the already disable services, thus if you have upgraded like me I would advice you do a close check on every enabled / running service everywhere:
root@pcfrxen:/# systemctl list-unit-files|grep -i enabled
Beware of AppArmor !!! 🙂