Posts Tagged ‘location’
Tuesday, January 31st, 2012 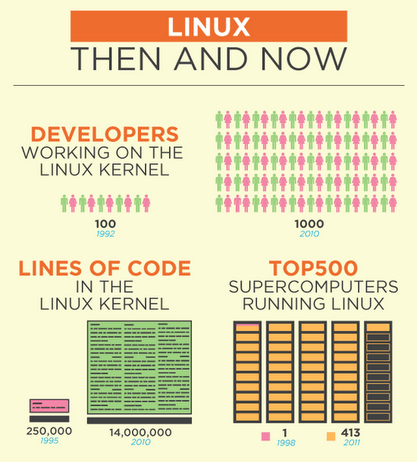
In above graphics you see development of GNU/Linux through the years startingfrom 1992 to 2010. You see for the past 18 years the number of kernel developers has rasised from 100 to 1000 (10 times). The number of super computers based on GNU / Linux operating system was only 1, while in 2011 they were already 413. Just for information Top 10 Super computers in terms of CPU power are running on top of some Linux + GNU environment based operating system.
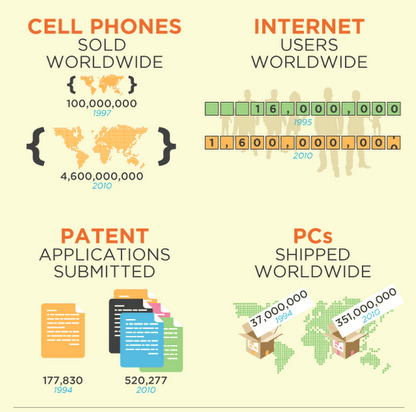
You see the number of Patented software increased approximate 3 times for 16 years … PC shipped with Linux all oer the world increased almost 10 times.
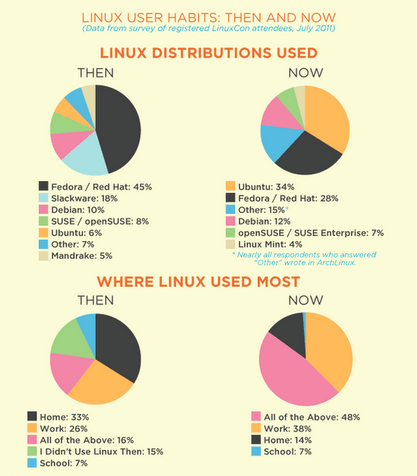
A survey was run among the biggest Linux convention LinuxCon aiming to find out the share difference between users using different distros, as well as a survey to answer the question where is Linux mostly used. Obviously even though the Ubuntu desktop boom this years Linux is still mostly used in work location, home desktop / notebook users are almost 3 times less.
The survey show the sad results, the Linux in school and academic communities is less used than for professional purposes. On the desktop things has slightly changed, for the last 5-7 years. From the position of being a Linux Desktop leading OS, Fedora went into the shadows in favour of the "less free" (in terms of Freedom) Ubuntu.

All system administrators knows well Linux is a very common choice for building small or middle enterprise business information systems. Hugest platforms which are the web backbone today like Google, Facebook, Twitter, Stock Exchanges, Mail services, various technical equipment etc. runs on top of Linux. Even though the huge number of adoption Linux and free software is though to not be legally assured this is well known among free software and open source evangelist under the term FUD.
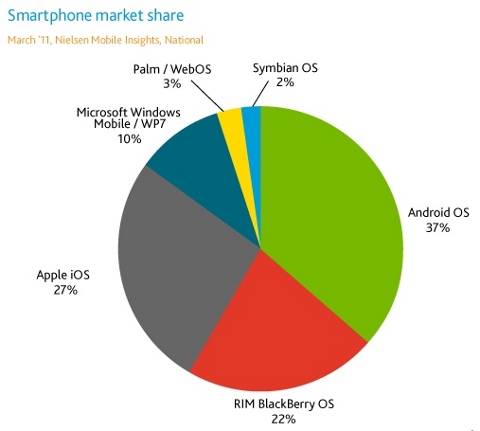
Android found its way also in Samsung Galaxy and a number of tablet devices running Linux based kernel OS was shipped in 2011.
With the raise of Android which (base is mostly Linux kernel and less GNU tools based). The spread of Linux has seen a huge raise on the mobile (smart phones) market as well. You see in above chart as of 2011 Android sells had the highest market share with 37%.
The year 2011 was not among the best Linux users anywas, as Unity does turned away many users to become Linux converts. The big GNOME 3 mess, which was called by Linus Toravlds a "holy mess" , along with the kernel.org's security break in does also contributed that year 2011 ended up as a bad one for free software.
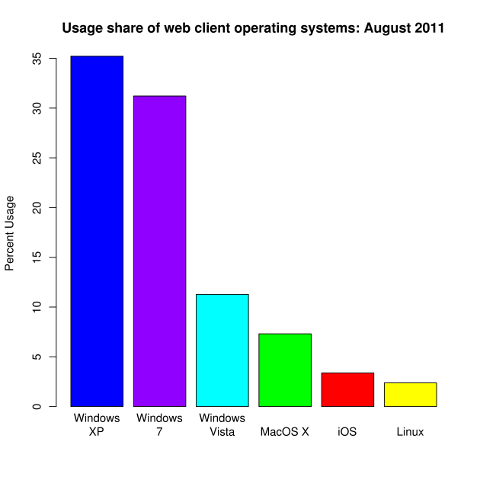
As of August 2011, the global Linux market approximate market share is about 3% of all the installed OSes currently existing in the world. And compared to 5 years ago there is a little decline in the share. I believe the 2012 will be a better year for both development and adoption of free software and Linux.
Tags: Auto, business information systems, convention, cpu power, Desktop, distros, Draft, enterprise, equipment, facebook, gnu linux, google, home desktop, information, kernel developers, Linux, linux desktop, linux gnu, linux operating system, location, mail services, mess, nbsp, notebook users, number, oer, power, professional purposes, quot, sad results, show, software, Stock, stock exchanges, survey, term fud, Ubuntu, work, work location, year
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, Linux Audio & Video, Various | No Comments »
Tuesday, November 22nd, 2011 In order to debug some PHP session problems on Debian, I needed to check the count of existing session files.
When PHP is compiled from source usually, by default sessions are stored in /tmp directory, however this is not the case on Debian.
Debian’s PHP session directory is different, there the sessions are stored in the directory:
/var/lib/php5
I’ve discovered the session directory location by reading Debian’s cron shell script, which delete session files on every 30 minutes.
Here is the file content:
debian~# cat /etc/cron.d/php5
# /etc/cron.d/php5: crontab fragment for php5
# This purges session files older than X, where X is defined in seconds
# as the largest value of session.gc_maxlifetime from all your php.ini
# files, or 24 minutes if not defined. See /usr/lib/php5/maxlifetime
# Look for and purge old sessions every 30 minutes
09,39 * * * * root [ -x /usr/lib/php5/maxlifetime ] &&
[ -d /var/lib/php5 ] && find /var/lib/php5/ -type f -cmin +$(/usr/lib/php5/maxlifetime) -delete
To check the amount of existing PHP opened session files:
debian:~# ls -1 /var/lib/php5|wc -l
14049
Tags: amount, amp, apache, cat, check, count, cron, crontab, Debian, debian gnu, DEBUG, directory location, file, fragment, gnu linux, ini files, lib, Linux, linux apache, location, maxlifetime, order, php session, purges, root, session directory, session files, sessions, Shell, shell script, tmp, type, usr, value, var
Posted in Linux, System Administration, Various | No Comments »
Monday, November 14th, 2011 
These days more and more people start to forget the g* / Linux old times when we used to copy CDs from console using dd in conjunction with mkisofs .
Therefore to bring some good memories back of the glorious console times I decided to come up with this little post.
To copy a CD or DVD the first thing one should do is to make an image copy of the present inserted CD into the CD-drive with dd :
1. Make copy of the CD/DVD image using dd
# dd if=/dev/cdrom of=/tmp/mycd.iso bs=2048 conv=notrunc
/dev/cdrom is the location of the cdrom device, on many Linuces including (Debian) /dev/cdrom is just a link to the /dev/ which corresponds to the CD drive. Note on FreeBSD the location for the CD Drive is /dev/acd0
/tmp/mycd.iso instructs dd CD image creation to be placed in /tmp/ directory.
bs argument instructs it about the byte size portions by which the content of the CD-Drive inserted CD will be read. bs value of 2048 is actually only 2KB per dd read, increasing this value will decrease the time required for the CD image to be extracted.
2. Prepare CD image file to be ready for burning
After dd completes the image copy operation, next to prepare the extracted image / ISO to be ready for burning mkisofs is used:
# mkisofs -J -L -r -V TITLE -o /tmp/imagefile.iso /tmp/mycd.iso
The -J option makes the CD compatible for Pcs running Microsoft Windows. The -V TITLE option should be changed to whatever title the new CD should have, -r will add up status bar for the mkisofs operation.
-r is passed to create specific file permissions on the newly created CD, -o specifies the location where mkisofs will produce its file based on the CD image /tmp/mycd.iso .
3. Burning the mkisofs image file to a CD/DVD on GNU / Linux
linux:~# cdrecord -scanbus
linux:~# cdrecord dev=1,0,0 /tmp/imagefile.iso
If all wents okay with cdrecord operation, after a while the CD should be ready.
4. Burning the mkisofs image file to CD on FreeBSD
freebsd# burncd -f /dev/acd0 data /tmp/imagefile.iso fixate
Tags: argument, byte, byte size, cd image, CD-drive, cdrom, conv, copy, dd cd, drive, file, file permissions, freeb, gnu linux, Image, image copy, image creation, image file, image iso, imagefile, ISO, isoIf, linux cdrecord, linux linux, location, Microsoft, mkisofs, mycd, new cd, notrunc, operation, option, size, size portions, status, terminal, time, title option, tmp, value
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration, Various | 1 Comment »
Monday, November 7th, 2011 After upgrading my sis’s notebook from Ubuntu 11.04 to Ubuntu 11.10 on her Acer Aspire 5736Z the default gnome wireless network manager started behaving oddly.
The Network Manager did not show any networks, even though the network drivers showed that are loaded properly on the Linux host and using the normal commands like iwlist or iwconfig I could list and see the networks and even connect to a network.
As my sister is not a console geek like me it was necessery of course to have an easy way to connect herself to the Internet with nice GUI application. I personally love WICD Network Manager and as the default gnome manager was misbehaving I immediately installed her wicd.
With wicd , the wireless networks were properly listed and there was no connection issues to the wireless networks, however the wicd system tray was missing and hence everytime she wanted to connect to a wireless network, she had to keep wicd-client running active in the Dock or run it manually every time on connect, when she had to change her physical location and connect to another wireless network.
This of course is quite unhandy and gives her a bad image of Linux and I definitely want to make her love free software and GNU / Linux. Thus I want to give her a GNU / Linux she will be easy to use.
To make her more satisfied with her Ubuntu I googled around to see what causes the wicd systray to be missing after some research online I found out, its probably due to either wicd bug or some kind of interface changes in unity newer versions of Ubuntu. Some people online suggested a fix via changing values in gconf-editor but this work around by changing the values in gconf-editor:
'desktop' -> 'unity' -> 'panel'
I tried this suggested fix which was reported to work on Ubuntu 11.04 but the gconf registry suggested pathway was missing at all so this solution did not worked.
I further read some other suggested solution using wicd-client by invoking it with two args like so:
stanimira@ubuntu:~$ wicd-client -n &
...stanimira@ubuntu:~$ wicd-client -a &
This proposed solution did not worked either, then I found in one of the Ubuntu bugs reports, a little shell script (add-wicd-to-whitelist.sh) that changes some values in gconf so I proceeded downloaded and give it a try:
stanimira@ubuntu:~$ wget https://www.pc-freak.net/files/add-wicd-to-whitelist.sh
...
stanimira@ubuntu:~$ sh add-wicd-to-whitelist.sh
...
For my surprise running the script doesn’t immediately changed nothing and wicd wireless connectivity indicator was still missing from the tray.
I thought it might need to reload gnome so I give it a restart and HOORAY! after the restart the WICD connected wireless strength show up, like you can see in the screenshot below 😉

Now hope this fix will, help out there experiencing the same issues to work around his wireless network connectivity issues 😉 Cheers.
Tags: acer, connection, course, Desktop, doesn, everytime, free software, gconf, geek, Gnome, gnu linux, gui application, host, Image, interface changes, Linux, linux host, location, love, manager, necessery, network drivers, notebook, physical location, script, Shell, software, system tray, systray, time, Ubuntu, unity, wget, wicd, wireless networks, work
Posted in Everyday Life, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, System Administration, Various | 11 Comments »
Monday, September 26th, 2011 
A friend of mine gave me a VCD with some coptic Orthodox Christian exorcism, where there pope was chasing some evil spirits from possessed muslims who came to the Coptic Orthodox Church in egypt. The video was made to be in VCD and as you can expect this did not worked out of the box with Totem and VLC out of the box.
Putting in the VCD video inside my cdrom poped up an error like the one in the header of the post.
In order to make the video play I had to use the old school and now a bit obsolete mplayer.
Hence in order to play the VCD on Debian Linux I had to install mplayer and w32codecs packages first e.g.:
debian:~# apt-get update && apt-get install mplayer w32codecs
Second to play the video from gnome-terminal, I had to switch to the mounted cdrom location /media/cdrom0 and launch the video with mplayer cmd like so:
debian:~$ cd /media/cdrom0/vcd
debian:/media/cdrom0/vcd$ mplayer vcd://2
...
In some cases it might be necessery to play the video with mplayer command like:
debian:/media/cdrom0/vdd$ mplayer vcd://2 vcd://3
Watching it with mplayer from console has some downsides as I couldn’t make the fast rewind work, but still it’s way better than nothing.
Too bad in Debian Squeeze 6 gmplayer is no longer installable. The gmplayer can probably be installed if mplayer is compiled from source, but I’m too lazy to try it out.
I’ve red also in some forums online that gxine is capable of playing the VCD play nice, but I couldn’t install it from my existing Debian repositories so I did not give it a go.
Tags: cd media, cmd, codecsSecond, command, coptic orthodox christian, coptic orthodox church, Debian, debian cd, debian linux, debian repositories, ERROR, evil spirits, exorcism, fast rewind, gmplayer, Gnome, gxine, location, mine, mplayer, muslims, necessery, old school, online, order, poped, post, rewind, squeeze, totem, update, VCD, vdd, video, video play, VLC, way, work
Posted in Entertainment, Everyday Life, Linux Audio & Video, Various | 1 Comment »
Monday, April 19th, 2010 1. First it’s necessery to have the mrtg debian package installed.
If it’s not installed then we have to install it:
debian-server:~# apt-get install mrtg
2. Second download the qmailmrtg source binary
To download the latest current source release of qmailmrtg execute:
debian-server:~# wget http://www.inter7.com/qmailmrtg7/qmailmrtg7-4.2.tar.gz
It’s a pity qmailmrtg is not available for download via debian repositories.
3. Third download the qmail.mrtg.cfg configuration file
debian-server~# wget https://www.pc-freak.net/files/qmail.mrtg.cfg
Now you have to put the file somewhere, usually it’s best to put it in the /etc/ directory.
Make sure the file is existing in /etc/qmail.mrtg.cfg
4. Untar compile and install qmailmrtg binary
debian-server:~# tar -xzvvf qmailmrtg7-4.2.tar.gz
...
debian-server:~# make && make install
strip qmailmrtg7
cp qmailmrtg7 /usr/local/bin
rm -rf *.o qmailmrtg7 checkq core
cc checkq.c -o checkq
./checkq
cc -s -O qmailmrtg7.c -o qmailmrtg7
qmailmrtg7.c: In function ‘main’:
qmailmrtg7.c:69: warning: incompatible implicit declaration of
built-in function ‘exit’
qmailmrtg7.c:93: warning: incompatible implicit declaration of
built-in function ‘exit’
qmailmrtg7.c:131: warning: incompatible implicit declaration of
built-in function ‘exit’
qmailmrtg7.c:137: warning: incompatible implicit declaration of
built-in function ‘exit’
5. Set proper file permissions according to the user you indent to execute qmailmrtg as
I personally execute it as root user, if you intend to do so as well set a permissions to
/etc/qmail.mrtg.cfg of 700.
In order to do that issue the command:
debian-server:~# chmod 700 /etc/qmail.mrtg.cfg
6. You will now need to modify the qmail.mrtg.cfg according to your needs
There you have to set a proper location where the qmailmrtg shall generate it’s html data files.
I use the /var/www/qmailmrtg qmailmrtg log file location. If you will do so as wellyou have to create the directory.
7. Create qmailmrtg html log files directory
debian-server:~# mkdir /var/log/qmailmrtg
8. Now all left is to set a proper cron line to periodically invoke qmailmrtg in order to generate qmail activity statistics.
Before we add the desired root’s crontab instructions we have to open the crontab for edit, using the command.
debian-server:~# crontab -u root -e
I personally use and recommend the following line as a line to be added to root’s crontab.
0-55/5 * * * * env LANG=C /usr/bin/mrtg /etc/qmail.mrtg.cfg > /dev/null
9. Copy index.html from qmailmrtg source directory to /var/log/qmailmrtg
debian-server:/usr/local/src/qmailmrtg7-4.2# cp -rpf index.html /var/log/qmailmrtg
10. Last step is to make sure Apache’s configuration contains lines that will enable you to access the qmail activity statistics.
The quickest way to do that in Debian running Apache 2.2 is to edit /etc/apache2/apache2.conf and add a directory Alias as follows
Alias /qmailmrtg/ "/var/www/qmailmrtg/"
Now after Apache restart
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
You should be now able to access the qmail mrtg qmail log statistics through your Apache’s default configured host.
For instance, assuming your default configured Apache host is domain.com. You’ll be able to reach the qmailmrtg statistics through an url like:
http://domain.com/qmailmrtg/
After I verified and ensured myself qmail mrtg is working correctly after all the above explained steps partook I wasn’t happy with some headlines in the index.html and the html tile of qmailmrtg,
so as a last step I manually edited the /var/www/qmailmrtg/index.html to attune it to my likings.
Here is a screenshot of the qmailmrtg web statistics in action.
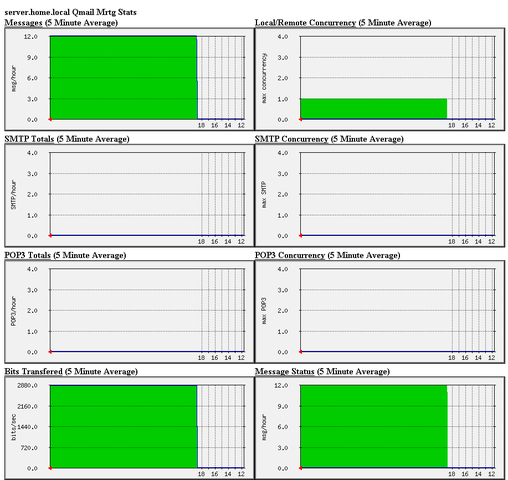
Tags: amp, checkq, configuration file, cron, current source, debian package, debian repositories, declaration, default, download, exit, file, file permissions, freak, function, graph, host, html data, implicit declaration, indent, index, Installing qmailmrtg (qmail graph statistics on qmail activity) on Debian Lenny, loc, location, log, mrtg, necessery, package, proper location, rf, root, root user, Set, source release, statistics, strip, untar, wget
Posted in System Administration | 6 Comments »
Wednesday, August 3rd, 2011 During the install of a new Debian GNU/Linux server I was in a real hurry, so I mistakenly choose a wrong timezone of US/Pacific
As a consequence the server date and time was incorrect and I had to fix that to adjust to the proper server location which of this case was:Europe/London
Here is the quick fix:
debian:~# dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
Next I choose my timezone from the ncurses interface navigating with arrow keys and used ntpdate to synchronize the time for the server like so:
debian:~# ntpdate time.nist.gov
3 Aug 16:02:26 ntpdate[26658]: adjust time server 192.43.244.18 offset 0.000802 sec
Done 😉
Tags: arrow, arrow keys, Aug, consequence, Date, Debian, debian gnu, europe, fix, GNU, gnu linux, hurry, interface, Linux, location, LondonHere, ncurses interface, nist, ntpdate, PacificAs, proper server, secDone, server, server location, time, time server, timezone, tzdataNext, Ubuntu
Posted in Linux, System Administration | 2 Comments »
Friday, May 27th, 2011 As an administrator of few company email delivery servers, I always had to debug problems related to emails unable to drop in Yahoo’s Mail and Gmail default mail Inbox
In that reason I always need to take a close look on Email headers to try to isolate email issues.
Most often the problems with messages unable to deliver in default in Inbox are with the 3 most popular mail services:
Thus I decided to explain shortly here how one can check full email headers in Gmail and Yahoo public mail services in order to be able to later derive conclusions on what is wrong with his mail server outgoing messages.
1. How to view full email headers in Gmail
It’s pretty easy, though for some reason Google decided to place the button which shows the complete email message headers in a I would say not too user friendly location.
To view email headers, login to Gmail, click over some random email in Inbox or some of the other mail folders.
Once you can read the email and you see the Reply button located on the right,next to the Reply button there is the down triangle which while pressed will display a menu.
To view the full email headers one has to press over the Show original button presented in the menu. Below you see a sample screenshot on the menu with the Show Original button.
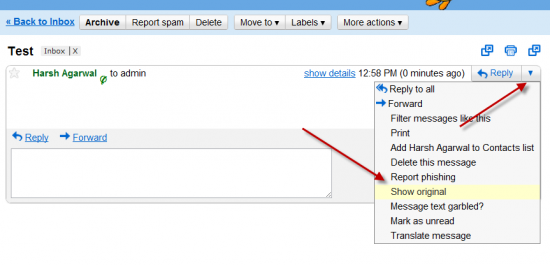
Show complete e-mail message headers and content in Gmail
2. How to view full email headers in Yahoo Mail Classic
I use Yahoo Mail Classic, as I like old stuff, Checking the full email headers there is a bit more intuitive than with Gmail.
To check email headers, just login to Yahoo mail, click over inbox, select an email message you would like to review as text.
Further on after the end of the email, you will see the Delete, Reply, Forward, Spam and Move buttons, right below this field of buttons there is the Full Headers blue text link with very small letters.
Here is a screenshot I’ve made of a sample opened mail. On the screenshot in right bottom you see the blue Full Headers button.
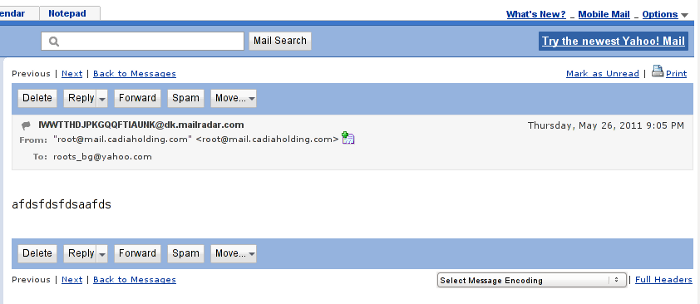
Yahoo Mail Cassic View Email Full Header
3. How to view full mail headers in Hotmail
In Hotmail checking the email, headers’s button position is very similar to Gmail’s, the only difference is the exact button which shows the Full Email header is named View Message source
In order to check Email headers in Hotmail, one has to click over a desired message, click once again on the down triangle near the Reply button and press over View Message source
Here is a screenshot showing the View Message source menu
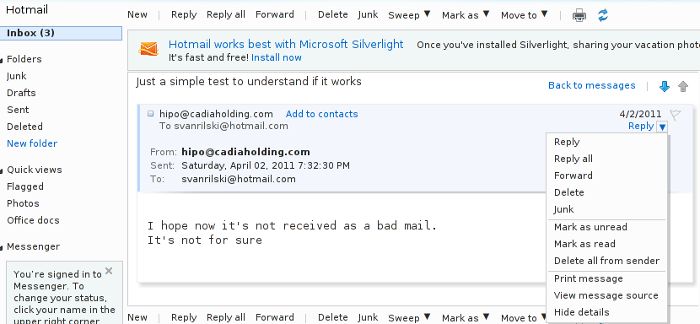
Hotmail View Full email Headers
One small note to make here is that the View source headers buttons is currently not working on Epiphany browser running on Linux.
As always Microsoft are making stuff incompatible, if it’s not used with a Microsoft product ..
Tags: bit, Button, Cassic, content, default, default mail, Delete, delivery servers, difference, e mail, email, Forward, forward spam, Gmail, google, hotmail, location, login, mail folders, mail headers, mail inbox, mail message, mail server, mail services, menu, message headers, Microsoft, move buttons, old stuff, outgoing messages, public mail, reason, reply button, right, screenshot, show, stuff, text, yahoo mail
Posted in System Administration, Various | 3 Comments »
Wednesday, April 27th, 2011 I just completed a fresh Ubuntu 10.10 Maverick-Merkaat install.
Following the installation I used a small script to install a bunch of packages I used on the same notebook before the Ubuntu re-installation.
Now after the number of packages are installed on the newly installed Ubuntu, everytime I login with any GNOME user account I get mail notification settings window to automatically start-up
Closing on every gnome login session the mail settings is not a pleasent experience, therefore I took a bit of seconds to find out what launches the New Mail pop-up window
Here is how the annoying window looks like everytime I login on my ubuntu:
Some of the text on the above screenshot is in Bulgarian as the default configured locale for this Ubuntu install is set to Bulgarian but I hope this doesn’t matter as other people who have the same popup can still recognize the window.
Now to find out the process which spawned the mail notification popup I issued:
root@ubuntu:~# ps ax |grep -i mail 2651 pts/1 Sl+ 0:01 mail-notification --sm-disable
Further on I checked what is the original location of mail notification command :
root@ubuntu:~# which mail-notification
/usr/bin/mail-notification
To be absolutely sure mail-notification does spawn the mail settings window I used pkill -9 mail-notification
As the window suddenly died now I was absolutely sure that mail-notification is spawning the unwanted pop-up window which appeared right after me logging in.
I used dpkg -S to check which package does the mail-notification program belong to as I thought that the solution to get rid of this annoying popup will come to removing the whole package, here is what I did:
root@ubuntu:~# dpkg -S /usr/bin/mail-notification
mail-notification: /usr/bin/mail-notification
root@ubuntu:~#
Now knowing the package I simply wiped it off:
root@ubuntu:~# apt-get remove --yes mail-notification
...
root@ubuntu:~# dpkg --purge mail-notification
...
After that I guarantee you you won’t see the irritating new mail settings pop-up window again.
Farewell mail-notification annoyance, hope to never see you again!!! 🙂
Tags: annoyance, annoying popup, annoying window, command, dpkg, experience, Farewell, Gnome, gnome user, grep, installation, locale, location, login, mail notification program, mail pop, mail settings, maverick, new mail, notebook, notification, notification settings, ome, package, pkill, pleasent experience, pop up window, popup, purge, root, screenshot, settings window, solution, Ubuntu, usr, usr bin
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop | No Comments »
Monday, April 11th, 2011 
If you’re experiencing problems with maximising flash (let’s say youtube) videos on your Debian or Ubuntu or any other debian derivative.
You’re not the only one! I myself has often experienced the same annoying issue.
The flash fullscreen failures or slownesses are caused by flash player’s attempts to use directly your machine hardware, as Linux kernel is rather different than Windows and the guys from Macromedia are creating always a way more buggy port of flash for unix than it’s windows versions, it’s quite normal that the flash player is unable to properly address the computer hardware on Linux.
As i’m not programmer and I couldn’t exactly explain the cause for the fullscreen flash player mishaps, I’ll skip this and right give you the two command lines solution:
debian:~# mkdir /etc/adobe
debian:~# echo "OverrideGPUValidation = 1" >> /etc/adobe/mms.cfg
This should fix it for, you now just restart your Icedove (Firefox), Epiphany Opera or whatever browser you’re used to and launch some random video in youtube to test the solution, hopefully it should be okay 😉 But you never know with flash let’s just hope that very soon the open flash alternative gnash will be production ready and at last we the free software users will be freed from the evil “slavery” of adobe’s non-free flash player!
Though this tip is tested on Debian based Linux distributions it should most likely work same in all kind of other Linuxes.
The tip should also probably have effect in FreeBSD, though the location of the adobe directory and mms.cfg should probably be /usr/local/etc/adobe, I’ll be glad to hear from some FreeBSD user if including the OverrideGPUValidation = 1 flash option to mms.cfg like below:
# mkdir /usr/local/etc/adobe
# echo "OverrideGPUValidation = 1" >> /usr/local/etc/adobe/mms.cfg
would have an impact on any flash player fullscreen issues on FreeBSD and other BSD direvative OSes that run the linux-flash port.
Tags: Adobe, adobe flash, adobedebian, browser, BSD, buggy, cause, cfg, command, Computer, computer hardware, derivative, Flash, flash fullscreen, flash issues, flash option, free flash player, free software users, freebsd user, fullscreen flash, gnash, hardware, Icedove, impact, issue, kernel, linux distributions, linux flash, linuxes, location, machine hardware, macromedia, mms, option, oses, player, port, production, programmer, Resolving, right, slavery, software, solution, sudo, tip, Ubuntu, video, way, windows versions, work, youtube, youtube videos
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, Linux Audio & Video | No Comments »



















